Economics
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
scarcity
needs and wants are unlimited but resources are limited (this is the basic economic problem)
2
New cards
trade-off
having to make a decision because of scarcity
3
New cards
opportunity cost
what is NOT chosen in a decision
4
New cards
4 factors of production
land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurs
5
New cards
land
resources found on the earth
6
New cards
labor
Human effort directed toward producing goods and services
7
New cards
physical capital
all human-made goods that are used to produce other goods and services; tools and buildings
8
New cards
human capital
the skills and knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience
9
New cards
entrepreneurs
people who decide how to combine the other factors of production to create new goods and services
10
New cards
productivity
degree to which resources are used efficiently
11
New cards
underutilization
the condition in which economic resources are not being used to their full potential
12
New cards
law of diminishing return
at a point, adding more resources will decrease production
13
New cards
incentive
reward offered to persuade people to make certain economic decisions
14
New cards
fixed cost
do not change (ex. rent, mortgage, loan payment)
15
New cards
variable cost
changes based on production (ex. electric bills, wages, materials)
16
New cards
total costs
fixed + variable
17
New cards
cost-benefit analysis
economic model that compares the marginal costs and marginal benefits of a decision
18
New cards
specialization
A focus on a particular activity or area of study
19
New cards
division of labor
dividing up the production process between multiple workers
20
New cards
technological advances
The introduction of new techniques or methods that increase output per unit of input
21
New cards
traditional economy
economy where things are done the same as they have always been done based on agriculture (farming) and barter (trade)
22
New cards
command economy
An economic system in which the government controls a country's economy.
23
New cards
market economy
a system based on private ownership, free trade, and competition
24
New cards
mixed economy
an economic system combining private and public enterprise.
25
New cards
natural resources
resources (actual and potential) supplied by nature
26
New cards
3 Basic Economic Questiosn
What to produce, how to produce it, for whom to produce
27
New cards
free enterprise
a type of economy in which people are free to buy, sell, and produce whatever they want
28
New cards
invisible hand
a term coined by Adam Smith to describe the self-regulating nature of the marketplace
29
New cards
supply and demand
relationship between the amount of product and the desire for the product
30
New cards
equilibrium price
the price that balances quantity supplied and quantity demanded
31
New cards
shortage
a situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied
32
New cards
surplus
A situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
33
New cards
competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
34
New cards
productivity
the value of a particular product compared to the amount of labor needed to make it
35
New cards
labor union
association of workers organized to improve wages and working conditions
36
New cards
business cycle
Alternating periods of economic expansion and economic recession
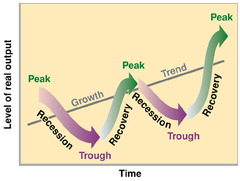
37
New cards
Gross domestic product (GDP)
the total value of all final goods and services produced in a country during one year.
38
New cards
Trade deficit
An imbalance in international trade in which the value of imports exceeds the value of exports.
39
New cards
Economic interdependence
situation in which countries rely on each other to provide goods and services
40
New cards
Trade surplus
when a country exports more than it imports
41
New cards
Fiscal policy
Government policy that attempts to manage the economy by controlling taxing and spending.
42
New cards
Substitute
A good that can be used in place of another good
43
New cards
Shift in the demand curve
Caused by change in external factors (Right = increase & Left = decrease)
44
New cards
disequilibrium
any price or quantity not at equilibrium
45
New cards
law of supply and demand
When demand goes up, supply goes down; when supply goes up, demand goes down.