8: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
1
New cards
Describe three types of RNA
mRNA: messenger RNA; carries protein information in the form of codons to the ribosome to be translated.
tRNA: transfer RNA; key functional component of protein synthesis, translates DNA code into protein code
rRNA: ribosomal RNA; site of protein synthesis
tRNA: transfer RNA; key functional component of protein synthesis, translates DNA code into protein code
rRNA: ribosomal RNA; site of protein synthesis
2
New cards
What are four functions of nucleotides/nucleic acids?
1) encoding information (DNA)
2) chemical messaging (mRNA)
3) cofactors/metabolic intermediates
4) energy currency (ATP)
2) chemical messaging (mRNA)
3) cofactors/metabolic intermediates
4) energy currency (ATP)
3
New cards
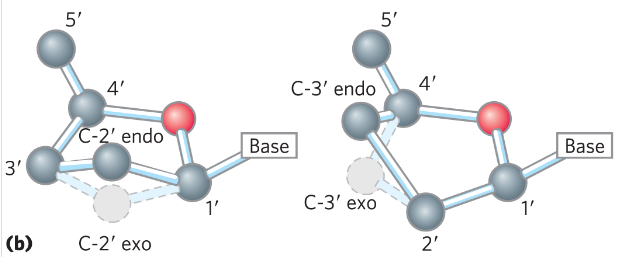
What is the term for a pentose sugar in its closed-ring conformation?
This closed-ring ____ (is/isn't) planar.
This closed-ring ____ (is/isn't) planar.
β-furanose
It is not planar, it is puckered.
It is not planar, it is puckered.
4
New cards
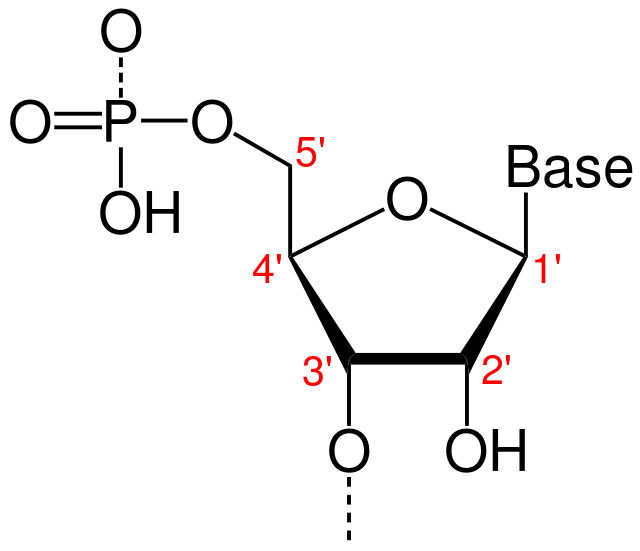
What are the components of a nucleotide?
1) Pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose)
2) Nucleotide base
3) 1 or more phosphate groups
2) Nucleotide base
3) 1 or more phosphate groups
5
New cards
What are the components of a nucleoside?
1) Pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose)
2) Nucleotide base
2) Nucleotide base
6
New cards
What type of bond joins a sugar to a nucleotide base?
At what positions on the sugar and base do this bond occur?
At what positions on the sugar and base do this bond occur?
N-β glycosidic bond
The bond is positioned at the 1' position of the sugar.
On the nucleotide base, the bond occurs at the 5-membered ring's NH group.
The bond is positioned at the 1' position of the sugar.
On the nucleotide base, the bond occurs at the 5-membered ring's NH group.
7
New cards
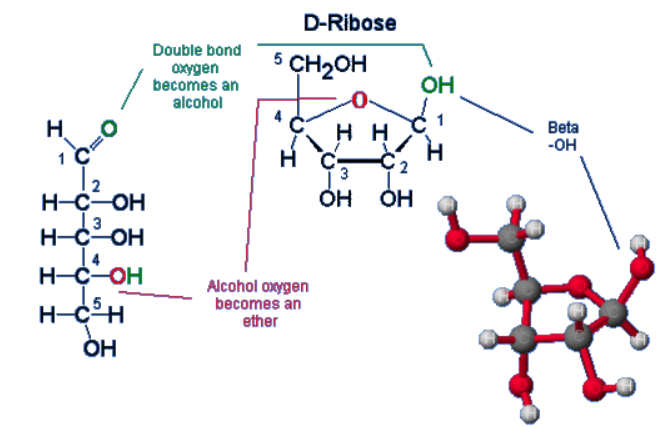
How are the carbons numbered within a nucleotide?
1' carbon does NOT denote the carbon to which the base is attached (Holmstrom REALLY wants us not to think about it like that.)
1' carbon follows the 1' carbon of a Fischer projection sugar, containing an aldehyde group. The =O is converted to an -OH group, and hemiacetal synthesis causes ring closure, to which the 1' carbon has an attached OH as well as an ester bond.
Carbon labelling just follows around the ring clockwise.
1' carbon follows the 1' carbon of a Fischer projection sugar, containing an aldehyde group. The =O is converted to an -OH group, and hemiacetal synthesis causes ring closure, to which the 1' carbon has an attached OH as well as an ester bond.
Carbon labelling just follows around the ring clockwise.
8
New cards
Describe key positions of a nucleotide where key components attach.
Nucleotide bases bind to 1' carbon through a dehydration synthesis reaction; the sugar has an OH group on the 1' position and the base has an H that are both abstracted to form the n-β glycosidic bond.
The phosphate group(s) are typically found bound to the 5' carbon (remember, the 5' carbon is not directly part of the ring) and the 3' carbon. This is what makes up the classic phosphodiester bonds of a nucleotide backbone.
The phosphate group(s) are typically found bound to the 5' carbon (remember, the 5' carbon is not directly part of the ring) and the 3' carbon. This is what makes up the classic phosphodiester bonds of a nucleotide backbone.
9
New cards
Draw the phosphate backbone of linked nucleotides. Label key carbon positions on the sugar.
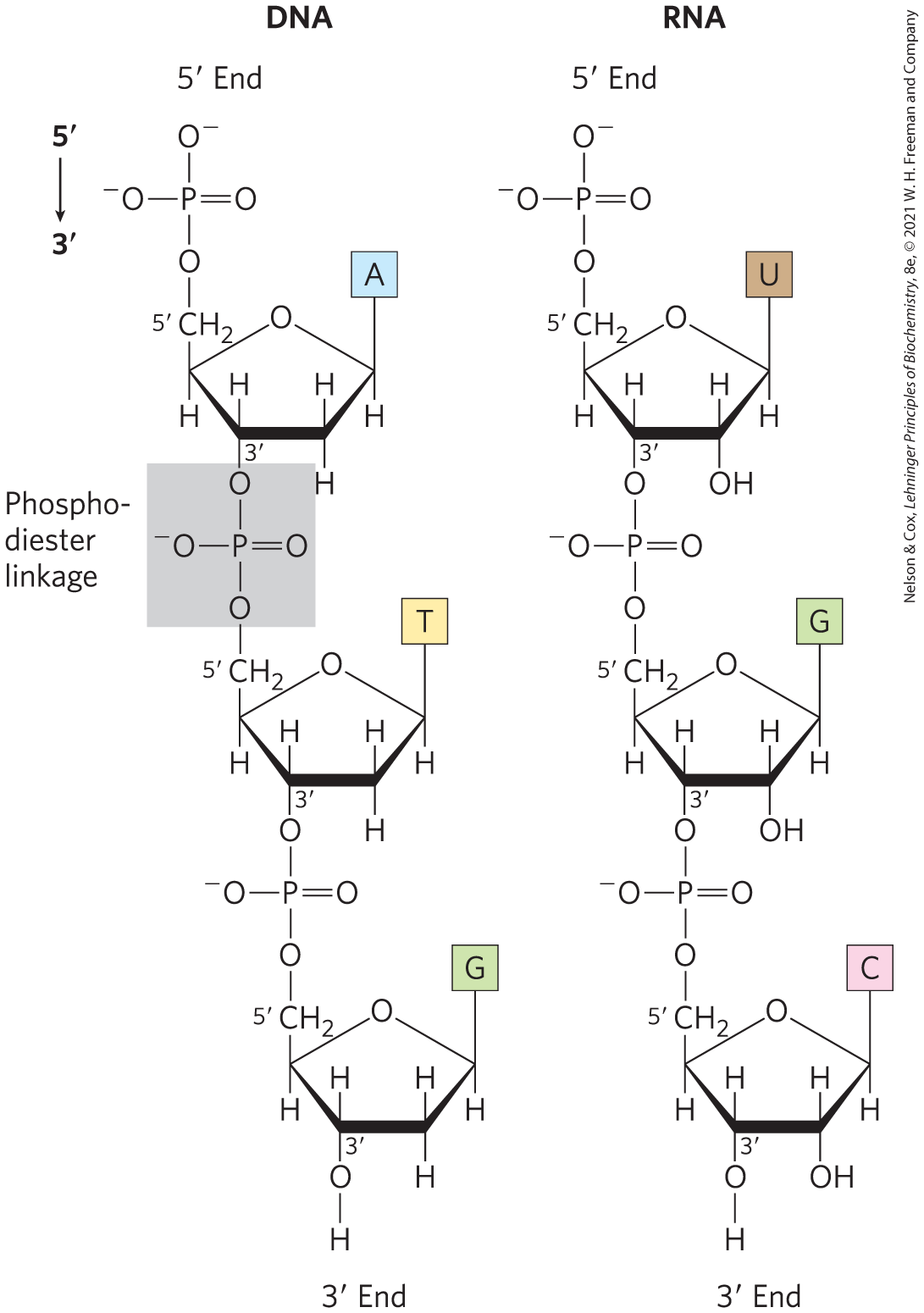
10
New cards
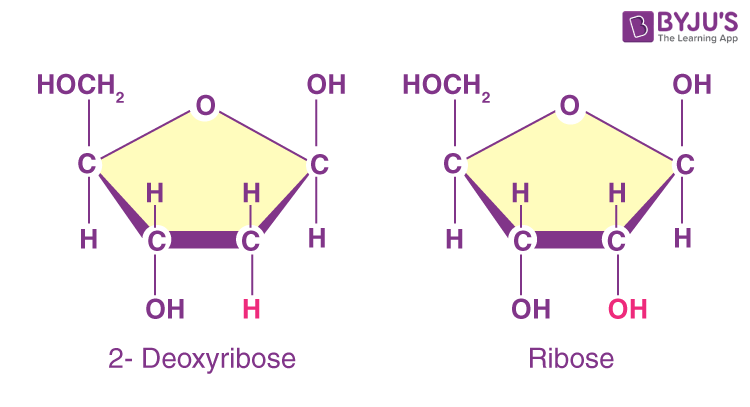
What is the difference between the sugars ribose and deoxyribose?
Ribose has hydroxyl groups at both the 2' and 3' positions.
Deoxyribose does not have a hydroxyl group at the 2' position.
Deoxyribose does not have a hydroxyl group at the 2' position.
11
New cards
DNA is ______ (more/less) susceptible to degradation than RNA
MUCH less.
The lack of a 2' hydroxyl makes DNA more stable and nonreactive than RNA. Further, DNA is typically found in double-stranded form with many repair mechanisms.
The lack of a 2' hydroxyl makes DNA more stable and nonreactive than RNA. Further, DNA is typically found in double-stranded form with many repair mechanisms.
12
New cards
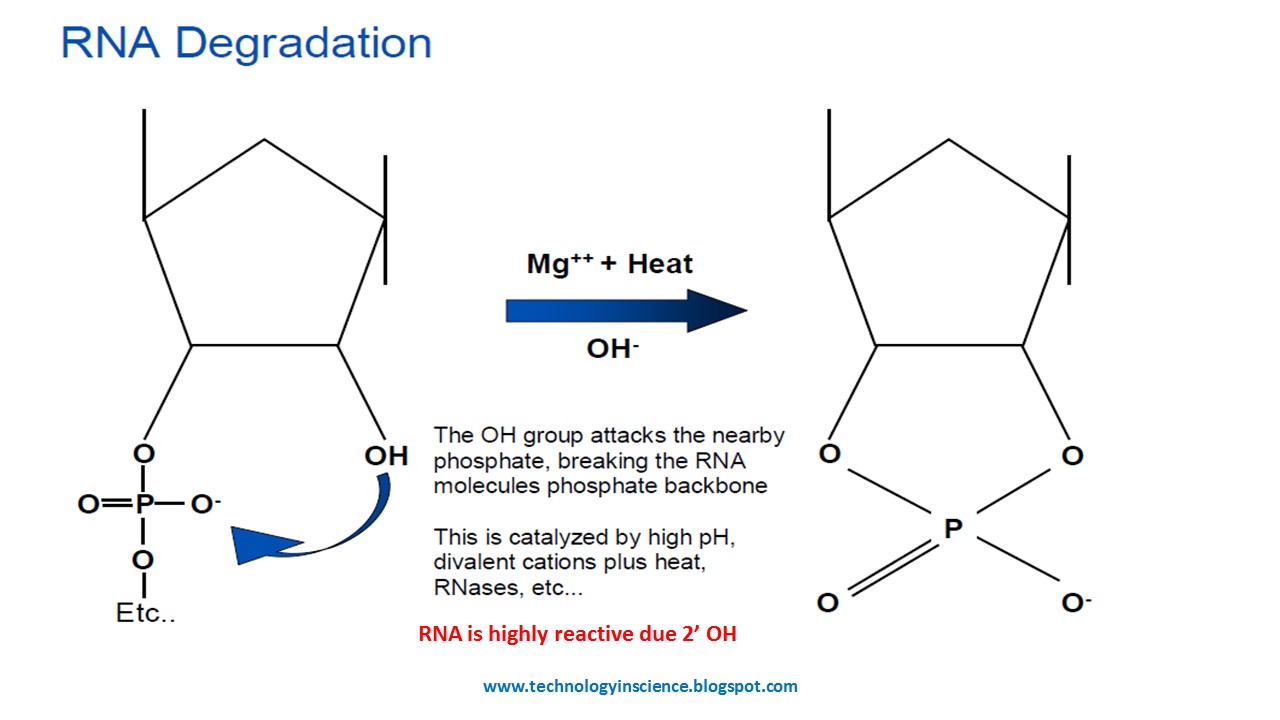
How does RNA degradation occur?
RNA's 2' hydroxyl group acts as a nucleophile.
There is a phosphate group at the 3' position, a strong electrophile.
This causes nucleophilic attack that breaks its phosphodiester backbone.
There is a phosphate group at the 3' position, a strong electrophile.
This causes nucleophilic attack that breaks its phosphodiester backbone.
13
New cards
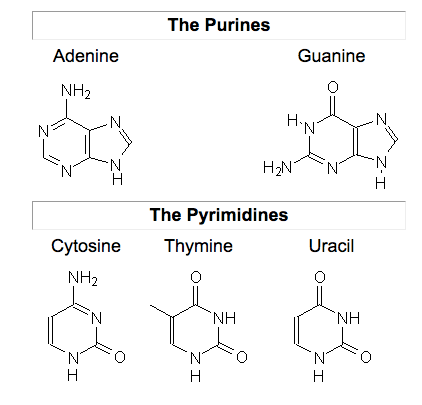
What is the difference between a purine and pyrimidine? Which nucleotide bases are which?
A purine is a 2-ringed structure comprised of 6 member and 5 member nitrogenous rings.
A pyrimidine can be though of as just the 6 membered portion of a purine.
Purines: adenine and guanine
Pyrimidines: thymine, cytosine, uracil.
A pyrimidine can be though of as just the 6 membered portion of a purine.
Purines: adenine and guanine
Pyrimidines: thymine, cytosine, uracil.
14
New cards
The purine and pyrimidine bases are ________ (hydrophobic/hydrophilic) at the near-neutral pH of the cell. At acidic or alkaline pH, the bases become _______ (charged/uncharged) and their solubility in water _________ (increases/decreases).
hydrophobic, charged, increases
Think about the sugar phosphate backbone. It's the backbone of DNA because it's the exterior; that is, the charged sugar phosphates have the closest proximity to cellular water. The nucleotide bases are hiding inside because they hate water.
Think about the sugar phosphate backbone. It's the backbone of DNA because it's the exterior; that is, the charged sugar phosphates have the closest proximity to cellular water. The nucleotide bases are hiding inside because they hate water.
15
New cards
What interactions are involved with base-stacking?
van der Waals interactions, dipole-dipole interactions, hydrophobic effect
Hydrogen bonding isn't really considered ~part~ of base stacking, but it is what contributes to base ~pairing~ in double stranded forms of nucleic acids.
Base pairing = opposite/complementary bases joining via H-bonding
Base stacking = adjacent/same-strand base interactions.
Hydrogen bonding isn't really considered ~part~ of base stacking, but it is what contributes to base ~pairing~ in double stranded forms of nucleic acids.
Base pairing = opposite/complementary bases joining via H-bonding
Base stacking = adjacent/same-strand base interactions.
16
New cards
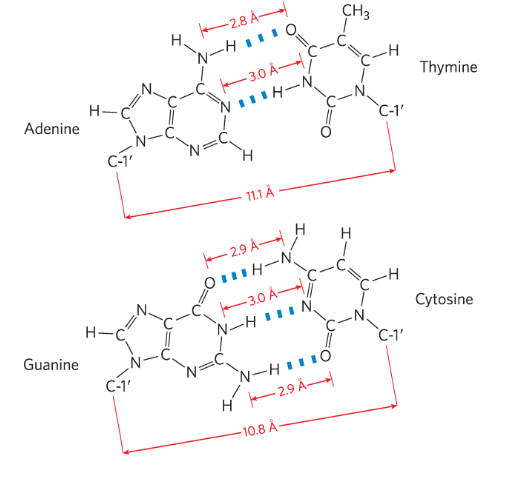
Within base pairing, How many hydrogen bonds between G and C?
How many hydrogen bonds between A and T?
How many hydrogen bonds between A and T?
G≡C
A=T
A=T
17
New cards
What does primary nucleic acid structure refer to?
Its covalent sequential structure; sequence of nucleotides.
E.g. 5'-GAATCGATCGATTCGACGTA-3'
E.g. 5'-GAATCGATCGATTCGACGTA-3'
18
New cards
What does secondary nucleic acid structure refer to?
Any regular, stable structure that nucleotides in a given segment of DNA take.
E.g. represented by a double stranded illustration depicting key features such as hairpins, cruciforms, loops, etc.
E.g. represented by a double stranded illustration depicting key features such as hairpins, cruciforms, loops, etc.
19
New cards
What does tertiary nucleic acid structure refer to?
The complex folding patterns of large chromosomes (like in eukaryotic chromatin or tRNA/rRNA)
E.g. helices
E.g. helices
20
New cards
DNA's double helix is ______ (left/right) handed. It is very _____ (flexible/rigid).
Right handed helix.
Very flexible structure; rotation is possible about the n-β glycosidyl bond, about each ester bond within the phosphate backbond, as well as slight rotation between 3' and 4' carbon of the sugar.
Very flexible structure; rotation is possible about the n-β glycosidyl bond, about each ester bond within the phosphate backbond, as well as slight rotation between 3' and 4' carbon of the sugar.
21
New cards
What factors contribute to the different 3D structures of DNA? (In other words, why is DNA so flexible?)
1) Different conformations of the deoxyribose sugar (endo/exo)
2) Rotation of phosphodeoxyribose bonds (both of the 5' carbon bonds are flexible)
3) Rotation about phosphodiester bonds between attached phosphate groups.
4) Free rotation about the n-β glycosidic bond.
2) Rotation of phosphodeoxyribose bonds (both of the 5' carbon bonds are flexible)
3) Rotation about phosphodiester bonds between attached phosphate groups.
4) Free rotation about the n-β glycosidic bond.
22
New cards
With respect to deoxyribose,
-What conformation(s) are purines able to assume?
-What conformation(s) are pyrimidines able to assume?
-What conformation(s) are purines able to assume?
-What conformation(s) are pyrimidines able to assume?
Purines can be found either SYN or ANTI to its sugar.
Pyrimidines will be found only ANTI to its sugar; this is due to steric interference by the sugar's C-2 carbonyl oxygen.
Pyrimidines will be found only ANTI to its sugar; this is due to steric interference by the sugar's C-2 carbonyl oxygen.
23
New cards
Deoxyribose sugars typically take the _____ (endo/exo) conformation
Endo
24
New cards
In general, what are the major/minor grooves in DNA?
DNA helices have two surfaces; the grooves represent the varying distances between the backbones within the helix, due to folding patterns. Changing folding patterns can alter the sizes of the major and minor grooves.
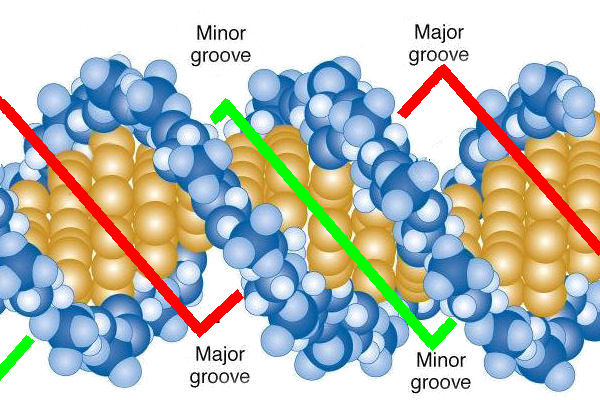
25
New cards
At biological conditions, one helical turn of DNA is how many angstroms long? How many base pairs per turn?
One helical turn is 36 Å. 10.5bp per turn.
26
New cards
How many angstroms apart are nucleotides found in a helix?
Nucleotides are found 3.4Å apart within a DNA helix.
27
New cards
Describe B-form DNA
Right handed helix. The most stable physiological form of DNA. It is the standard reference point that the other forms deviate from.
28
New cards
Describe A-form DNA; helical handedness, general shape, grooviness
Right handed helix. Has a wider helix than B-form, and more base pairs per turn. Essentially, it's like squished/compressed B-form DNA.
It is found in low-water environments. Upon crystallization of DNA, A-form becomes dominant.
Deeper major groove, shallower minor groove.
It is found in low-water environments. Upon crystallization of DNA, A-form becomes dominant.
Deeper major groove, shallower minor groove.
29
New cards
Describe Z-form DNA; helical handedness, general shape, grooviness
Z is for zig-zag. LEFT-HANDED helix. Essentially, it's like stretched-out B-form DNA.
The glycosyl bond between purines is syn, while for pyrimidines it's anti; this is what causes its left-handedness.
Major groove is barely apparent, minor groove is narrow and deep.
The glycosyl bond between purines is syn, while for pyrimidines it's anti; this is what causes its left-handedness.
Major groove is barely apparent, minor groove is narrow and deep.
30
New cards
What form does double-stranded RNA typically assume?
What forms is it able and unable to assume?
What forms is it able and unable to assume?
double stranded RNA typically is found in A-form, however it has been created/observed in Z form.
B-form dsRNA has never been observed.
B-form dsRNA has never been observed.
31
New cards
Order the strengths of the following base-stacking interactions:
Purine-purine
Pyrimidine-pyrimidine
Purine-pyrimidine
Purine-purine
Pyrimidine-pyrimidine
Purine-pyrimidine
In order of strongest to weakest,
purine-purine >> pyrimidine-purine > pyrimidine-pyrimidine
purine-purine >> pyrimidine-purine > pyrimidine-pyrimidine
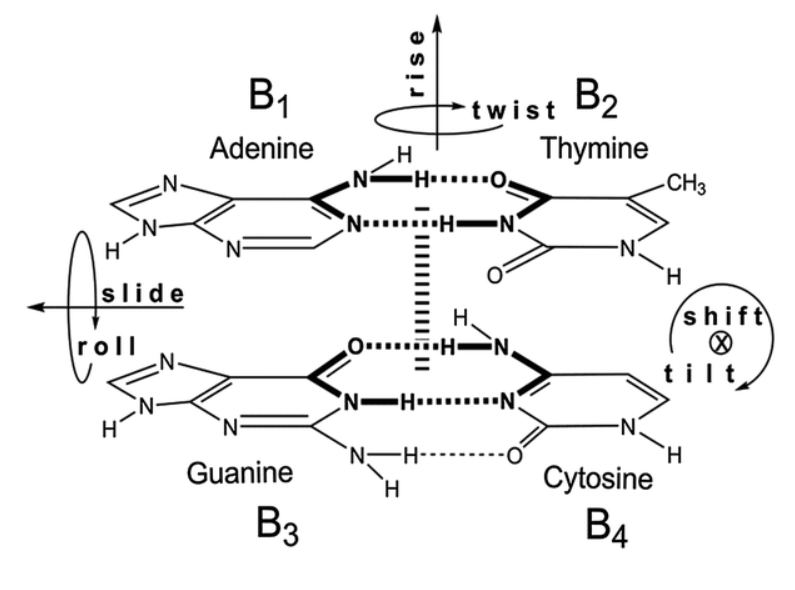
32
New cards
What contributes more strength to base-stacking, A=T or G≡C?
G≡C
33
New cards
Describe the difference between palindromic and mirror repeat sequences.
Palindromic DNA sequences have ~inverted~ repeats; that is, the palindrome center is where it switches strands.
Eg: 5' - T T A G C G C T A A - 3'
3' - A A T C G C G A T T - 5'
Mirror repeats are palindromic sequences on just one strand.
Eg: 5' - T T A G C C G A T T - 3'
3' - A A T C G G C T A A - 5'
Eg: 5' - T T A G C G C T A A - 3'
3' - A A T C G C G A T T - 5'
Mirror repeats are palindromic sequences on just one strand.
Eg: 5' - T T A G C C G A T T - 3'
3' - A A T C G G C T A A - 5'
34
New cards
What conformations may palindromic and mirror repeat sequences form?
Palindromic sequences may form hairpins/cruciforms.
Mirror repeats cannot form these.
Mirror repeats cannot form these.
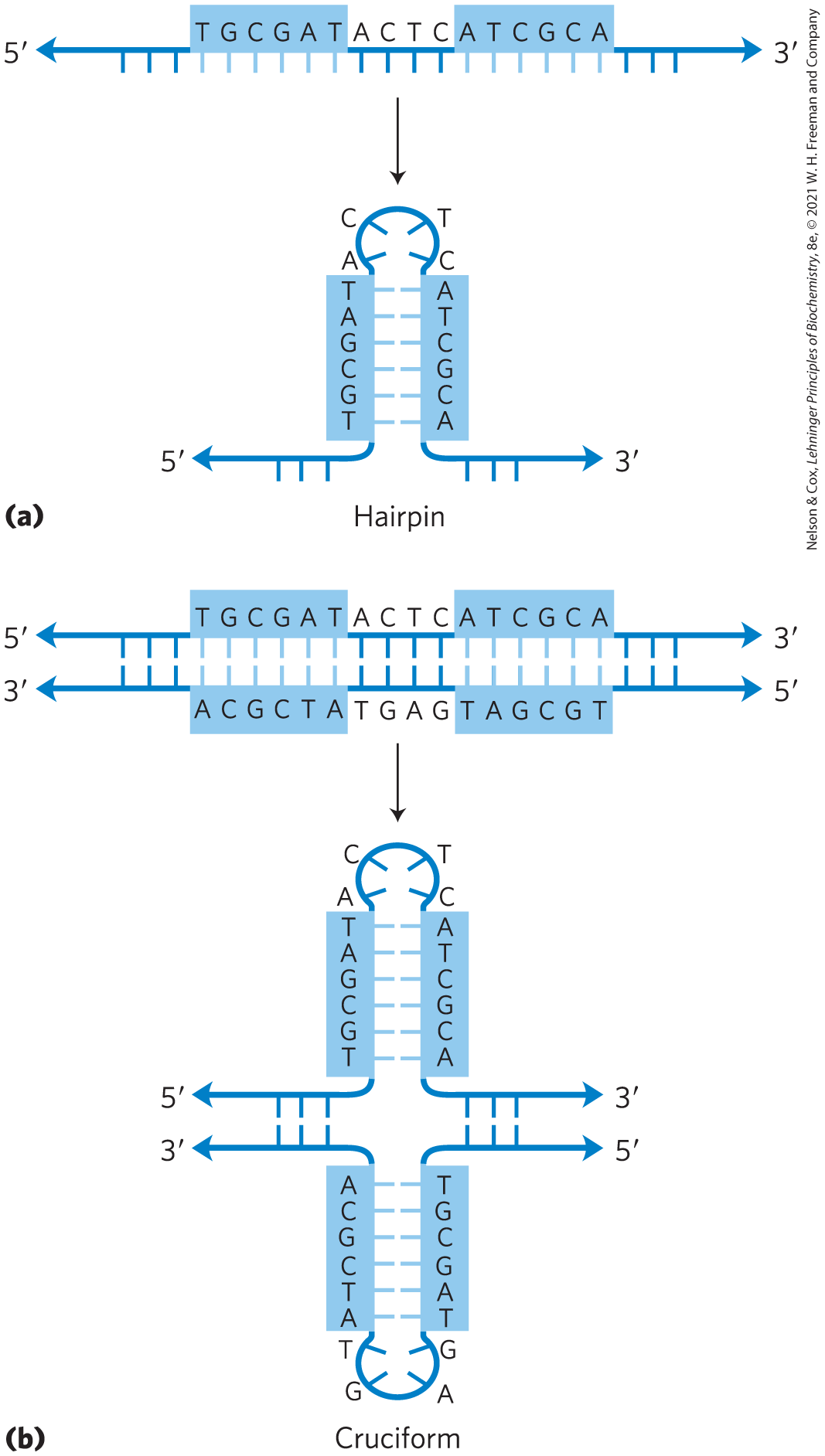
35
New cards
How may a DNA double helix form a triplex?
Watson-Crick (standard) base pairs may pair with a third residue, especially on the major groove. This is known as Hogsteen triplex forming base pairs.
36
New cards
Hogsteen base pairing is most stable at ___ (low/high) pH. Why?
Low pH. It requires the third base to be protonated in order to form a triplex.
37
New cards
How may a DNA double helix form a tetraplex? Is it stable?
If 4 DNA strands have high proportions of guanosine residues, they may form a guanosine tetraplex. It is very stable.
38
New cards
Describe monocystrionic RNA vs polycistrionic RNA.
Monocistrionic RNA codes (has a gene) for one peptide only.
Polycistrionic RNA codes (has a gene) for many peptides.
In eukaryotes, most RNA is polycistrionic. Think about introns, noncoding regions, and alternative splicing.
Polycistrionic RNA codes (has a gene) for many peptides.
In eukaryotes, most RNA is polycistrionic. Think about introns, noncoding regions, and alternative splicing.
39
New cards
The product of DNA transcription is always:
A right-handed, helical, single-stranded RNA.
40
New cards
What factors denature DNA? How do these factors affect interactions holding DNA together?
Extremes of heat and/or pH cause disruption to hydrogen bonds that contribute to base-stacking and base-pairing. While no covalent bonds are broken, the DNA unwinds into two strands.
41
New cards
What happens after reversing heat or pH extremes back to biological conditions?
Spontaneous annealing (for partially degraded sequences)
Two step-annealing (for fully degraded strands)
Two step-annealing involves the first, slow process of random collisions and base pairing, then rapid zipping up of the helix.
Two step-annealing (for fully degraded strands)
Two step-annealing involves the first, slow process of random collisions and base pairing, then rapid zipping up of the helix.
42
New cards
What is the hypochromic effect?
What is the hyperchromic effect?
What is the hyperchromic effect?
Hypochromic effect: UV absorption of a DNA sequences DECREASES as base-pairing INCREASES.
In other words, as strands pair, UV absorption decreases.
Hyperchromic effect: UV absorption of DNA sequences INCREASES as base-pairing DECREASES.
In other words, as DNA is degraded, UV absorption increases.
In other words, as strands pair, UV absorption decreases.
Hyperchromic effect: UV absorption of DNA sequences INCREASES as base-pairing DECREASES.
In other words, as DNA is degraded, UV absorption increases.
43
New cards
UV absorption at what wavelength is monitored to determine degradation status of a DNA sequence?
260nm, or 2.60 x 10^-9 m
44
New cards
Why does every unique DNA strand have a unique temperature of degradation (melting point)?
The higher G≡C content, the higher its melting point, because G≡C pairs contribute greatly to holding the strand together under extreme conditions.
45
New cards
During DNA replication and transcription, what sequences are more often seen as the site of unzipping/unravelling (start of replication/transcription)?
Regions with a high proportion of A=T base pairs; because they don't hold onto each other as strong as G≡C.
46
New cards
Rank the following in order of increasing resistance to thermal degradation:
RNA-RNA duplexes
DNA-DNA duplexes
RNA-DNA duplexes
RNA-RNA duplexes
DNA-DNA duplexes
RNA-DNA duplexes
DNA-DNA < RNA-DNA < RNA-RNA
It is unknown why RNA has higher thermal resistance, but it is found to degrade at about 20 C higher temps than DNA.
It is unknown why RNA has higher thermal resistance, but it is found to degrade at about 20 C higher temps than DNA.
47
New cards
Why does DNA contain thymine instead of uracil?
Cytosine is deaminated spontaneously into uracil; if DNA normally contained uracil, then it would not be able to recognize mutated U nucleotides from native U nucleotides.
Having thymine acts as a guard that helps DNA repair mechanisms work; all uracil bases are recognized as degradations and thereby repaired.
Having thymine acts as a guard that helps DNA repair mechanisms work; all uracil bases are recognized as degradations and thereby repaired.
48
New cards
What are 3 methods of non-enzymatic alterations of DNA?
What do each of these entail?
What do each of these entail?
Deamination, hydrolysis of n-β glycosyl bond (bond between sugar and base)
Deamination: a base loses its exocyclic amino group.
Hydrolysis: Creating of an abasic site (the sugar loses its base)
Radiation: Ring creation and ring opening, breaking of DNA's covalent backbone.
Deamination: a base loses its exocyclic amino group.
Hydrolysis: Creating of an abasic site (the sugar loses its base)
Radiation: Ring creation and ring opening, breaking of DNA's covalent backbone.
49
New cards
In DNA, hydrolysis of n-β glycosyl bond occurs more frequently in ______ (purines/pyrimidines)
Purines.
50
New cards
What factors accelerate hydrolysis of n-β glycosyl bonds in DNA?
Addition of dilute acid.
51
New cards
What three types of factors contribute to accelerating DNA damage?
1) deaminating agents (nitrous acids/nitrites) cause loss of a base's exocyclic amino group
2) alkylating agents cause modification of bases that disrupt base pairing and base stacking interactions
3)***Oxidative damage: oxidation of deoxyribose/caused by reactive oxygen species: hydroxyl radicals are the most prevalent effectors.
2) alkylating agents cause modification of bases that disrupt base pairing and base stacking interactions
3)***Oxidative damage: oxidation of deoxyribose/caused by reactive oxygen species: hydroxyl radicals are the most prevalent effectors.
52
New cards
Name two functions of DNA methylation within E. coli
1) Defense: E. coli methylates its own genome to distinguish against foreign DNA
2) Distinction between old/new DNA: the longer DNA exists, the more methylated it becomes. This allows E. coli to recognize younger vs. older DNA within its genome.
2) Distinction between old/new DNA: the longer DNA exists, the more methylated it becomes. This allows E. coli to recognize younger vs. older DNA within its genome.
53
New cards
Adenine and cytosine are _____ (more often/less often) methylated than guanine and thymine.
Adenine and cytosine are MORE OFTEN methylated than guanine and thymine.
54
New cards
What is the purpose of PCR?
To replicate and amplify a given DNA sequence.
55
New cards
What chemical components are required for PCR? What do each of them do?
DNA Polymerase: Catalyzes the synthesis of DNA
dNTPs: nucleotide bases that are used for DNA synthesis
Template DNA: the strand that is replicated by DNA polymerase
Two primers flanking the target sequence: allow targeted replication
dNTPs: nucleotide bases that are used for DNA synthesis
Template DNA: the strand that is replicated by DNA polymerase
Two primers flanking the target sequence: allow targeted replication
56
New cards
What are the steps of PCR?
1) Add all components to DNA soup
2) Heat reaction to denature and separate target DNA strands
3) Cool reaction to allow primers to bind to DNA template
4) Using available dNTPs, Taq (DNA) polymerase catalyzes synthesis of target sequence
5) Repeat until desired amplification is achieved.
2) Heat reaction to denature and separate target DNA strands
3) Cool reaction to allow primers to bind to DNA template
4) Using available dNTPs, Taq (DNA) polymerase catalyzes synthesis of target sequence
5) Repeat until desired amplification is achieved.
57
New cards
What is the goal of Sanger-sequencing?
To determine the sequence of an unknown segment of DNA via the usage of unlabeled dNTPs in conjunction with fluorescently labeled ddNTPs.
58
New cards
What chemical components does Sanger-sequencing require?
Similar to PCR, Sanger-sequencing requires:
DNA-Polymerase
DNA primers
Excess, unlabeled dNTPS
Fluorescently labeled ddNTPs.
DNA-Polymerase
DNA primers
Excess, unlabeled dNTPS
Fluorescently labeled ddNTPs.
59
New cards
What is the role of ddNTPs in Sanger-sequencing?
ddNTPs (dideoxynucleotide phosphates) are randomly selected along with dNTPs during the process of strand elongation, by the DNA polymerase responsible for synthesis.
However, because ddNTPs lack a 3' hydroxyl, the strand to which it was added is unable to elongate further.
ddNTPs halt chain elongation, and because they are fluorescently labelled for each nucleotide, it can be determined what nucleotide is present at a given position in a DNA strand.
However, because ddNTPs lack a 3' hydroxyl, the strand to which it was added is unable to elongate further.
ddNTPs halt chain elongation, and because they are fluorescently labelled for each nucleotide, it can be determined what nucleotide is present at a given position in a DNA strand.
60
New cards
Describe reversible-terminator sequencing.
RT-sequencing uses lasers to excite fluorescently labelled nucleotides. The nucleotides are added one by one, and contain blocking groups that, when added to a sequence via DNA polymerase, only allow one nucleotide to be added to a strand. This allows locations of each nucleotide to be determined in a given sequence.
61
New cards
Describe single-molecule real-time sequencing.
SMRT sequencing utilizes special cells with pores smaller than the wavelength of visible light. A single DNA polymerase is fixed to each pore. Genomic DNA is sheared, and oligonucleotide hairpin sequences within it are ligated to each end of the DNA fragments, generating a circular loop.
Polymerase is added to the end of the single strand of DNA via the usage of primers, initiating synthesis.
Using pulses of light generated by the addition of fluorescently tagged nucleotides, a detector can record the sequence that is synthesized within the circular loop of DNA.
Polymerase is added to the end of the single strand of DNA via the usage of primers, initiating synthesis.
Using pulses of light generated by the addition of fluorescently tagged nucleotides, a detector can record the sequence that is synthesized within the circular loop of DNA.
62
New cards
Describe the error rate of SMRT-sequencing and how it is mitigated.
SMRT-sequencing has a high error rate; however, because synthesis occurs around a circular portion of DNA, the elongation (and thus reading/sequencing) process can essentially happen multiple times, so the detector software can account for possible errors and correct them over time as it becomes more certain.