Bio Unit 1
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
emergent properties
reproduction, growth and development, order and structure, metabolism, respiration, response to environmental stimuli, adaptation and evolution, and autonomous movement
Disulfide (-S-S-) bond between two cysteines
covalent bond
Even though H-bonding occurs in ammonia and ethanol, they cannot be used to replace water in living cells because
of water’s solvent and reactant properties
1 mL equals __ gram(s)
1
what type of molecule is this? C₁₄H₃₀O₂
fatty acid
Decreasing pH will decrease enzyme activity because of the disruption of
secondary and tertiary structure
the 5’ ends of RNA polymers have ____ groups attached to the number 5 carbons of ribose
phosphate
what property of water is most essential to support life
water’s medium and reactant properties for biochem reactions
mRNA
messenger RNA; carries info from DNA to translate to protein
rRNA
ribosol; major part of ribosomes for protein synthesis
tRNA
transfer; transfers amino acids during protein synthesis
You are given a polysaccharide consisting of 67 glucose molecules. Hydrolysis of this polysaccharide would result in the production of
67 glucose molecules
eukarya kingdoms
protista, fungi, plantae, animalia
protista
mostly unicellular eukaryotes; heterotrophic; phototrophic; some multicellular
fungi
mostly multicellular but some unicellular; heterotrophic
plantae
all higher plants including flowering (angiosperm) and non-flowering (gymnosperm); flowering plants include monocot and dicot; all autotrophs
animalia
all animals; multicellular and heterotrophic
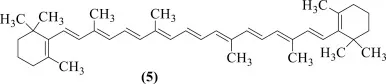
what molecule is this
carotenoid
what is a model system
representative organism or a cell type used for conducting simple to complex biological experiments
example of prokaryotic model system
e. coli
example of plant model systems
corn, rice, and arabidopsis
example of fungi model system
yeast
examples of animal model systems
fruit fly, nematode, mouse, zebra fish, human cells
mass number
amount of protons + neutrons
molecular weight is
is atomic mass but in amu
what is this
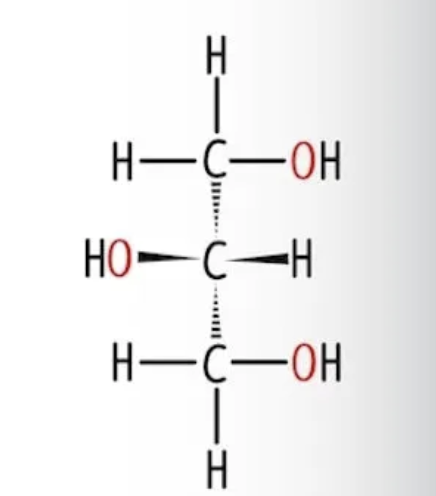
glycerol
holism
studying whole organisms
reductionism
studying multicellular organisms at tissue or cell or molecular level
covalent bonding
~ 50 - 170 kcal/mol
ionic and h-bond
~3-7 kcal/mol
van der waals
abt 1 kcal/mol
examples of monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
examples of disaccharides
sucrose, lactose, maltose
examples of storage polysaccharides
starch (plants) and glycogen (animals
examples of structural polysaccharides
cellulose (plant walls), callose (plant wound sites), chitin (fungal walls)
in vivo studies
living conditions
in vitro studies
non living conditions
in situ studies
determine the presence of certain molecules
in sillico studies
computer analysis of data to draw conclusions or identify patterns in genome or gene expression studies
inductive
specific observations make general statement
deductive
general observations make specific statement
Kw
[H+] X [OH-]