Final Exam Review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/125
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:51 AM on 8/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
1
New cards
Which of the following will speed up a reaction?
Increased temperature
2
New cards
Which of the following statements is true?
NOT None of these
3
New cards
The minimum amount of energy needed for a reaction to take place is called the _____________.
Activation energy
4
New cards
During a reaction with solids generally the _______ the size of each piece, the larger the total surface area. This means _______ collisions and a greater chance of reaction.
Smaller, more
5
New cards
In the graph below, why does the graph stop increasing after 30 seconds?
No more hydrogen can be produced because all of the reactants have become products at this point
6
New cards
Which of the following data tables correctly shows how temperature affects the reaction between sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid?
Reaction rate and temperature 1 (hover over picture)
7
New cards
Which of the following is not a catalyst?
Phosphorus
8
New cards
When magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid, hydrogen gas is produced. The amount of gas produced is dependent upon the concentration of hydrochloric acid. Below is the data for a reaction with 1 molar hydrochloric acid. Determine which of the choices shows possible data for a reaction with 2 molar hydrochloric acid.
NOT Conc over time 4 (hover over picture)
9
New cards
Which of the following would have the greatest amount of surface area?
1 cubic foot of loose sand
10
New cards
A reaction is moving most slowly when its reactant/product mix is:
90% product, 10% reactant
11
New cards
Why does an increased temperature cause a reaction to occur slower?
NOT The increased temperature makes the molecules more resistant to successful collision, they bounce off of each other more often
12
New cards
You are experimenting on the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and potassium iodide (KI). When the reaction is completed at 400K there are approximately 250,000 collisions per mole of reactant. You run the experiment again at 150K. Which of the following would you expect to be the number of collisions recorded at 150K
15,000
13
New cards
You are driving to a snowboarding trip in the mountains. It is significantly colder there and you must be careful not to get dizzy because the air pressure is lower and there is less oxygen. After snowboarding all day you go back to your car only to discover that it will not turn on. The battery seems to be dead. What has likely happened?
The cold temperature has slowed the reaction that produced electricity and it cannot generate enough current to start the car
14
New cards
During a reaction involving gases, the pressure is increased. Would this increase or decrease the speed of the reaction. Why?
Increase because the particles are closer together and more likely to collide
15
New cards
Which of the following would have the greatest reaction speed?
A reaction with solids at high temperatures and high surface area
16
New cards
A reaction happens quickest during:
The beginning of the reaction
17
New cards
Which of the following factors will only affect the reaction rate of a solid?
Surface area
18
New cards
Why does an increased temperature cause a reaction to occur faster?
The increased kinetic energy causes the particles to move faster, causing more collisions.
19
New cards
Why does a lower concentration of dissolved particles decrease the reaction rate?
When there are less dissolved particles, less collisions take place.
20
New cards
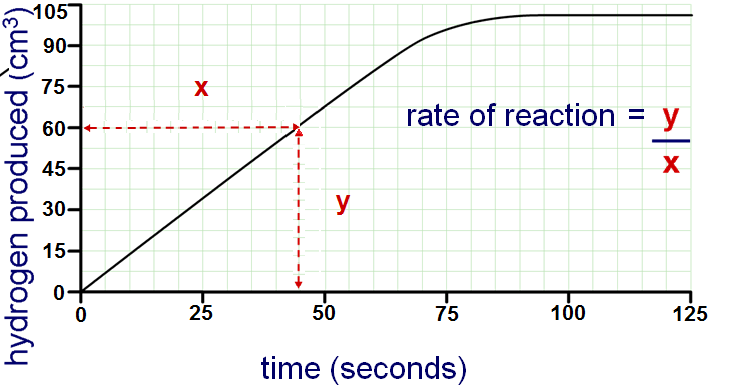
Determine the rate of reaction based on the data below:
1\.33 cm3/s
21
New cards
Where do reactions in a solid generally take place?
On the surface of the solid
22
New cards
Oxidation can be described as:
The loss of electrons
23
New cards
Which of the following ions is in the lowest oxidation state?
S in S2O3 2-
24
New cards
What is the oxidation number of sulfur in H2SO4?
\+6
25
New cards
What is the change in electrons for manganese in the following reaction? \n \n 2 MnO 4 - ( *aq* ) + H 2 O 2 ( *aq* ) + 6 H + ( *aq* ) -> 2 Mn 2+ ( *aq* ) + 3 O 2 ( *g* ) + 4 H 2 O( *l* )
NOT Lose 2 electrons
26
New cards
Which of the following ions is in a higher oxidation state than their normal ion?
F-
27
New cards
How many electrons does a single oxygen gain or lose in the following reaction?
H 2 + O 2 → H 2 O
H 2 + O 2 → H 2 O
\+2
28
New cards
What is the oxidation number of H2?
0
29
New cards
Use the following equation to determine the charge on iron when it dissociates from oxygen and determine whether it is being oxidized or reduced:
Fe2O3 + 3CO -> 2Fe + 3CO2
Fe2O3 + 3CO -> 2Fe + 3CO2
It starts with a charge of +3 and is reduced
30
New cards
What are the correct half reactions for the following reaction:
Cu2+ + Mg -> Cu + Mg2+
Cu2+ + Mg -> Cu + Mg2+
NOT Mg+2e−→Mg2+Cu2+→Cu+2e−
31
New cards
What are the correct half reactions for the following reaction:
Zn + 2 HCl -> H 2 + ZnCl 2
Zn + 2 HCl -> H 2 + ZnCl 2
Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻, 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → H₂.
32
New cards
A pure element unbound or in a diatomic state, such as Cl2, always has an oxidation number of ________.
0
33
New cards
What is the change in electrons for nitrogen in the following reaction? \n \n S + NO3 - -> SO2 + NO
Gain 3 electrons
34
New cards
What is the oxidation number of carbon in CO2
\+4
35
New cards
Which of the following ions is in the lowest oxidation state?
Fe in Fe2O3
36
New cards
In which of the following compounds does iron have the lowest oxidation number?
FeOH
37
New cards
Which of the following is a half-reaction?
2Cl− −> Cl2+2e−
38
New cards
A voltaic cell has a zinc anode and a copper cathode. They are connected by a wire but no salt bridge. What can you predict will happen?
NOT The electrons will flow to the zinc anode where a negative charge will build up and eventually halt the reaction
39
New cards
A(n) _________ is a substance used during electrolysis that splits apart and is attracted to an oppositely charged electrode.
Electrolyte
40
New cards
In the following reaction, what element is losing mass? \n \n Mg(s) + CuSO4(aq) -> MgSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
NOT Cu
41
New cards
A battery is an example of a(n) _________.
Voltaic cell
42
New cards
A voltaic cell consists of a sodium anode and an iron cathode. How will the electrons move?
NOT Electrons will move across the salt bridge from the anode to the cathode
43
New cards
Determine the correct order of the steps to processing aluminum from bauxite. \n \n I. Al3+ ions undergo reduction, O2- ions undergo oxidation. \n II. Al3+ ions are attracted to the negative electrode on the bottom, O2- ions are attracted to the positive electrode on the top. \n III. Electric current is added \n IV. Oxygen and carbon from graphite form carbon dioxide, pure aluminum on the bottom is collected. \n V. Bauxite is added to molten cryolite in a tank with graphite electrodes.
V, III, II, I, IV
44
New cards
In the following reaction, what element is gaining mass? \n \n Mg(s) + CuSO4(aq) -> MgSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Cu
45
New cards
You perform an electrolysis reaction using FeCl, iron (I) chloride. Which of the following will happen?
Iron will move to the negative electrode and become reduced
46
New cards
If cobalt is emitting radiation but there is no change in its atomic number, what type of radiation is being emitted?
Gamma
47
New cards
Determine the half-life of carbon-14 if a 1218.70 gram sample diminishes to 152.34 grams in 17,190 years.
5730
48
New cards
You are a paleontology professor working at a dig site looking for fossils. You come across a deposit that is emitting radiation. Upon further testing you find that the sample is changing from carbon (atomic number 6) into nitrogen (atomic number 7) as radiation is emitted. What type of radiation is it?
Beta
49
New cards
If Iridium (element 77) emits radiation and becomes platinum (element 78) what type of radiation is emitted?
\
\
Beta
50
New cards
You are an astrophysicist studying different phenomena in space. You notice that a particular asteroid is emitting radiation. When you use a spectroscope to test it further you determine that the entire asteroid is composed of nickel and that it is not forming any new elements. What type of radiation is being emitted?
Gamma
51
New cards
If plutonium (element 94) decays into uranium (element 92), what type of radiation is released?
Alpha
52
New cards
What is a half-life?
The time it takes half of the atoms in a sample to decay
53
New cards
Why does radiation decrease over time?
NOT Radiation is derived from the concentration of radioactive atoms and the concentration decreased as radioactive particles are emitted
54
New cards
PD-99 has a half-life of 22.3 hours. How many grams of a 89.8 gram sample would have decayed after exactly three half-lives
11\.23
55
New cards
Atoms in a radioactive material:
Decay randomly
56
New cards
You are working in an astrophysics lab studying newly discovered asteroids. You determine that one of the asteroids is emitting radiation but you are not sure what kind. You use a spectroscope and determine that the asteroid has large deposits of two very heavy, dense elements with one element being slightly lighter than the other. You determine that the heavier element is decaying into the lighter element. What type of radiation is it most likely emitting?
Alpha
57
New cards
OS-182 has a half-life of 3.6 days. If a sample started at 175 grams, how much would be left after 18 days?
5\.47
58
New cards
Which type of radiation involves the conversion of a neutron into a proton?
Beta
59
New cards
_________ radiation is the release of a particle composed of 2 protons and 2 neutrons.
Alpha
60
New cards
You are working in a lab when radiation alarms go off. You are only wearing a lab coat. Preliminary reports show that the radiation was weakly deflected by a magnetic field and had a positive charge. Were you safe?
NOT Yes, it was beta radiation and the lab coat was enough to block it
61
New cards
Why would an atom emit particles or waves from its nucleus?
To create a more stable nucleus
62
New cards
Xenon-133 has a half life of 5.2 days. A 237 gram sample of Xenon is collected and stored. It is later measured to be 29.625 grams. How long has it been in storage?
15\.6 days
63
New cards
Which of the following types of radiation consists of a high energy electron?
Beta
64
New cards
What occurs during beta decay?
A neutron decays into a proton and an electron
65
New cards
Which of the following best describes radiation?
Particles or waves emitted from an atom
66
New cards
You are working in a lab on your magnetic levitation experiment. You are standing directly in front of two magnets. Another scientist near you has a malfunction with their equipment and beta radiation is emitted directly at you, passing through the magnets first. You are wearing a lab coat and goggles. Are you safe?
Yes, beta radiation is strongly deflected by magnets so it would have missed you
67
New cards
You are working in a lab when radiation alarms go off. You are able to hide inside a steel cabinet, whose sides are about 1.5 inches thick, until the alarm goes off. Preliminary reports show that the radiation was weakly ionizing and negatively charged. Were you safe in the cabinet?
Yes, it was beta radiation and the steel was enough to block it
68
New cards
The conversion of mass into huge amounts of energy is the basis of __________.
All of these
69
New cards
What shape is the JET experimental fusion reactor?
Doughnut shape
70
New cards
Splitting nuclei is called __________ and joining nuclei is called _________.
Nuclear fission, nuclear fusion
71
New cards
What occurs when a neutron strikes a stable isotope and causes it to become unstable?
Nuclear fission
72
New cards
Who predicted that a small amount of mass could be converted into a large amount of energy?
Einstein
73
New cards
What nuclear reaction takes place inside stars?
Nuclear fusion
74
New cards
Why has nuclear fusion been difficult to develop?
It is hard to recreate the extremely high temperatures and pressures found inside stars
75
New cards
What is pair production
The creation of an electron and a positron from a gamma photon.
76
New cards
How does a fusion reactor contain the super heated plasma it creates?
Magnetic fields
77
New cards
How did elements with more than 2 protons, such as the carbon in our cells, form?
NOT They are formed when lighter elements are pulled together by gravity to form a planet
NOT They formed from hydrogen and helium slamming into each other in the first few minutes after the big bang.
NOT They formed from hydrogen and helium slamming into each other in the first few minutes after the big bang.
78
New cards
In 1933, work by Irène and Frédéric Joliot-Curie proved Einstein’s prediction. They produced:
produced a photograph that showed the creation of two particles when a particle of light was destroyed.
79
New cards
If the speed of light is 3.0 × 108 m/s2, then how much energy would be released if a 23.7 gram object is converted to pure energy?
NOT 2.133 x 10^18 J
80
New cards
What force holds the nucleus of an atom together?
Strong nuclear force
81
New cards
How will a fusion reactor produce electricity?
Hydrogen plasma will be ‘squeezed’ to produce helium and high energy neutrons. The energy of the neutrons will then be transferred by a water cooling loop to a heat exchanger to make steam which spins a turbine.
82
New cards
How did elements with more than 2 protons, such as the carbon in our cells, form?
Any unusable isotopes are recovered and unusable isotopes are sealed in cement inside steel drums and buried
83
New cards
Which of the following is true:
Gamma radiation is frequently used on food to kill bacteria
84
New cards
Which of the following are gamma rays NOT used for?\`
None of these
85
New cards
Which of the following statements is true?
Alpha radiation is very dangerous if the source is inside the body
86
New cards
The emission of light due to increased temperature is ___________.
Incandescence
87
New cards
The International Commission of Radiological Protection has set the limit for yearly radiation exposure at 1000 uSv. What is the risk associated with this dose?
NOT 1/2400 chance of cancer over a 40 year period
88
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a safety precaution for handling radioactive material?
Remove all metal before entering the containment room
89
New cards
How are archaeological finds dated?
Carbon dating
90
New cards
You are an archaeologist who uncovers a new site of early human activity. Currently, there is evidence of humans living in this area from 8000 to 22,500 years ago. A few bones are found at the site including a human skull. A current skull contains a carbon-14 count of 10,000. The fossil skull contains a carbon-14 count of 312.5. How does your find affect knowledge of early humans?
This find shows that humans arrived there 6,000 years earlier than previously thought
91
New cards
Which of the following is a safety precaution for handling radioactive material?
Store radioactive material in a shielded container
92
New cards
Why does an increased temperature cause a reaction to occur faster?
The increased kinetic energy causes the particles to move faster, causing more collisions
93
New cards
Which of the following is an example of a mixture?
CO2 + H2 + O2
94
New cards
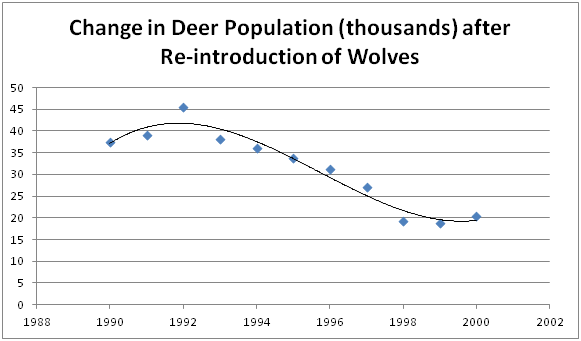
Determine which of the following data points is an outlier, on the graph below:
1992, 45.4 thousand
95
New cards
Which of the following are properties of metalloids?
All of these
96
New cards
A candle on a platform is surrounded by water in a dish. The candle is lit and a bell jar is placed over it. After a minute, what happens?
All of these
97
New cards
How many moles of sulfur are in 80 grams of sulfur?
2\.5 Moles
98
New cards
Each orbital can contain no more than 2 electrons. This is:
The Pauli exclusion principle
99
New cards
What are emission spectra?
The photons emitted when an electron drops down an energy level
100
New cards
What type of bond would occur between carbon (C) and nitrogen (N)?
Covalent bond