Biology Exam 2 Ch 8-11
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Activation Energy (Ea)
the ammount of energy needed to reach the transition state
Transition State
The unstable state at which the reaction transitions from activation energy to the release in the reaction
Catylists
lower activation energy and raise the probability that two things within the cell will react
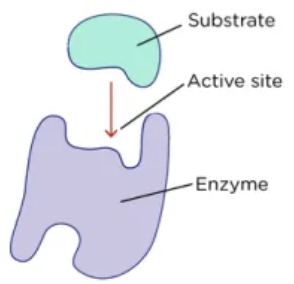
Active Sites
An area where a substrate can bond on an enzyme that allows for reactants to meet
Substrate
The reactants that bind to the active sites
Disassociation Constant (Kd)
Measures the affinity for a substrate to bind to a receptor
Oriented Correctly
In order to bind to the active site the molecules they have to be what? (Citric synthase)
Physical Strain
Breaking chemical bonds by changing the shape of the molecule. bending/breaking (lysosome)
Energy
The Capacity to do work
Metabolism
the NET of all chemical reactions in a system
Potential Energy
Stored or available energy. Ex: Concentration and charge gradients, chemical bonds
Kenetic Energy
the energy of movement
First Law of Thermodynamics
The total amount of energy before a transformation is the same as the amount of energy as after the reaction
Annabolic reaction (annabolism)
Building up of simple reactants to form complex molecules
Catabolic Reaction (catabolism)
Breaking down of molecules from complex to simple products releasing energy
Reaction Coupling
Getting energy for an endergonic reaction from an exergonic reaction
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Although the transformation does not change the total amount of energy not all of it can be used
Entrophy (s)
disordered/unusable energy
Exergonic reaction
a chemical reaction that releases energy.
Endergonic reaction
a chemical reaction that requires an input of energy in order to proceed.
Enthalpy (H)
total amount of energy usable and unusable
Free Energy (G)
Energy available to do work
DELTA (G)
Change in Free energy
(-G) Negative DELTA G
Free energy that is released
(+G) Positive DELTA G
Free energy that is required for the reaction to occur
ATP
Energy currency
Chemical charge
the need of reactants having the proper charge to bind to the Active site (chymotrypsin)
Enzyme Saturation
When there are only so many active sites and the the reaction rate flatlines when all of the reating points are being used
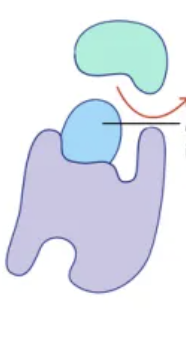
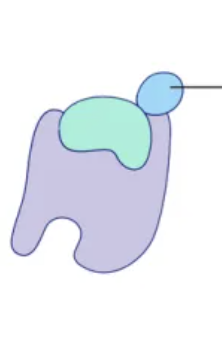
Inhibition
the process of suppressing or restraining enzyme function
Normal Enzyme binding
Competative Inhibition
Uncompetative Inhibition
Noncompetative Inhibition
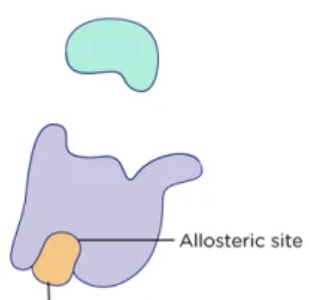
Allosteric Regulation
Changing the shape of the enzyme
Photosynthesis/Glucose
Where does Chemica Energy come from
Heterotrophs
Things that are herbivores that do not get energy via sunlight
Energy Transformation
Oxidation Reduction
the complete transfer of electrons in a redox reaction.
More Oxidation
Lower free Energy -DELTA G
Electron Carriers
they pass H+ and their associated e-
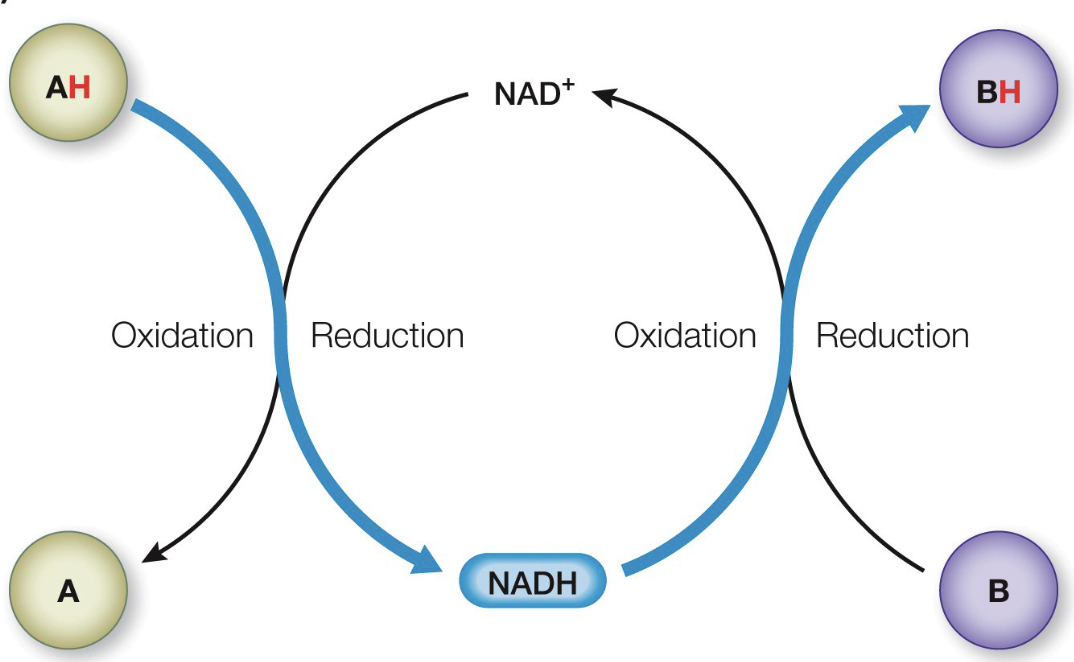
NAD+
Oxidized version of Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
NADH
Reduced version of Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
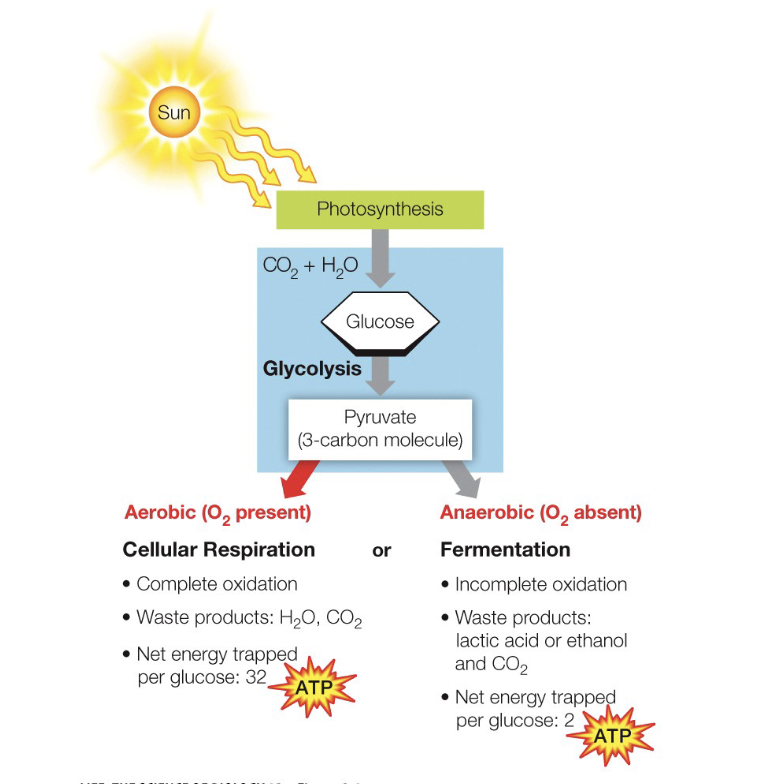
Glycolysis + Cellular Respiration
What does the diagram depict
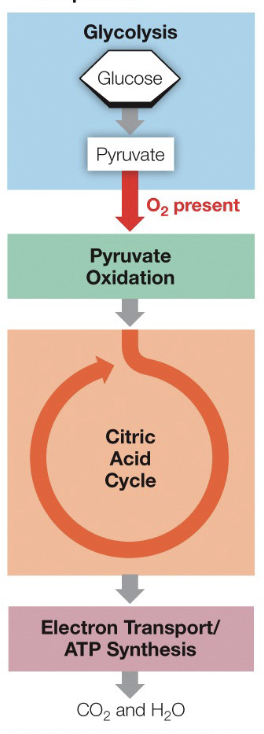
Glycolysis + Fermentation
What does the diagram depict
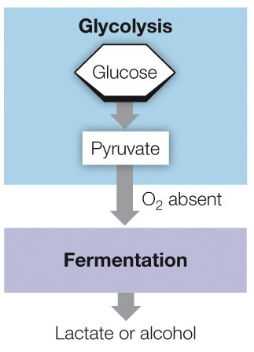
Glycolysis and Fermentation
What occurs in the Cytoplasm of a eukaryote
Citric Acid Cycle and Pyruvate Oxidation
What occurs inside of the mitochondrial matrix
Respitory Chain
What occurs inside of the inner mitochondrial membrane
Glycolysis, Fermentation, and Citric Acid Cycle
What occurs in the cytoplasm of a prokaryote
Pyruvate Oxidation and Repitory chain
What occurs on the cell membrane of a prokaryote
Pyruvate
a three-carbon acid that is naturally formed during glycolysis
Glycolysis
the process in which the body breaks down sugar
+2ATP, +2NADH, +2Pyruvate
The net amount of product produced in Glycolysis
+2NADH, +2CO2, +2Acetyl Acid
Pyruvate Oxidation NET production
+2ATP(GTP), +6NADH, +2FADH2, +4CO2
Citric Acid Cycle(Aerobic Respiration) NET production
Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron Transport)
Cellular proscess that harnesses the reduction oxygen to generarte high energy phosphate bonds in the form of atp
Respitory Chain
The first four enzyme complexes comprise the mitochondrial __________ , which facilitates electron transfer from reducing equivalents to molecular oxygen coupled to the generation of a proton gradient across the inner membrane that will be used by the ATP synthase to drive ATP synthesis
Photosynthesis
What is depicted
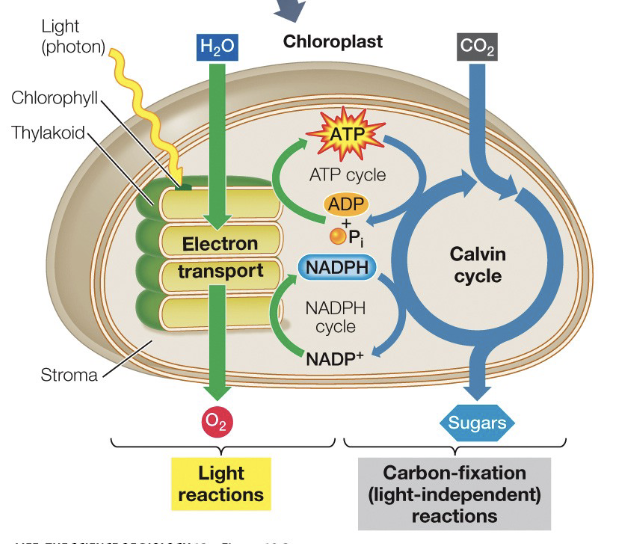
Calvin Cycle
Part of photosynthesis that produces the sugar. does not need light
32 ATP
How much ATP does Glycolysis and Cellular respiration produce together
Fermentation
If the by-product is CO2
Autotrophs
Self-feeders ,they produce their own energy
heterotrophs
Other-feeders, prey on other living organisms
Photon
A particle of light is equivilent to
high energy
Short wave lengths equal what
low energy
long wavelengths equal
two
how many types of photosystems are there
Photosystem II
Absorbs Photons of light, Photopigment absorbs light, consumes H2O
Photosystem I
Absorbs photons of light, passes e- ions, NAD+ → NADH via reductase enzyme
Calvin Cycle
Starts with Rubisco(RUBP), and ends with Rubisco(RUBP)
Carbon Fixation
Fix the C from CO2 into sugar step one of Calvin Cycle
reduction & sugar production
consume atp
consume NADPH → NAD+
Make sugar’
step 2 in calvin
Regenerate Rubisco
final step in calvin cycle
Chemiosmosis
The way ATP is generated from a concentration gradient
Proton-Motive Force
the way chemicals move protons to produce ATP
H → Proton
cancer
Unregulated cell growth and division
Chromosomes
Tightly coiled DNA within the nucleus during cell division
chromatid
one half of a duplicated chromosome. It contains identical DNA sequences and is joined together by a centromere
Centromere
the connecting point of a chromosome
Sister Chromatids
two identical copies of a single chromosome that are joined together at the centromere.
Prokaryote
Single Circular Chromosome
Eukaryotic
Many, Linear Chromosomes
Binary Fission
Prokaryotic Cell division
Mitosis
Eukaryotic Cell division
ORI (origin of replication)
begining point for DNA replication
TER (terminus)
ending point for DNA replication
G1
Preparing to replicate DNA
S
DNA replication/synthesis
G2
preparation for mitosis
M (mitosis)
Cell replication for body/somatic cells
M (meiosis)
Cell replication for reproductive cells
DNA Damage
G1 phase checkpoint checks for ____________ .
Incomplete replication / DNA Damage
S phase checkpoint checks for
DNA damage in both sets of DNA
G2 phase checkpoint checks for
Chromosome that is not attached to the spindle
M phase checkpoint checks for
Prophase
Condensation of chromosomes; spindle assembly
Prometaphase
Nuclear envelope breaks down, chromosomes attachment to the spindle
metaphase
Alignment of Chromosomes at the ________ plate
Anaphase
separation of Chromatids; migration to poles
Telophase
chromosomes decondense; nuclear envelope reforms
Cytokenesis
cell separation; cell membrane and wall function