PM371 Encoding Part 1 & Language Cortical Areas - Lecture 3
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards on association cortices, neuroanatomy, and aphasias.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Which sensory modality bypasses the thalamus?
Olfaction
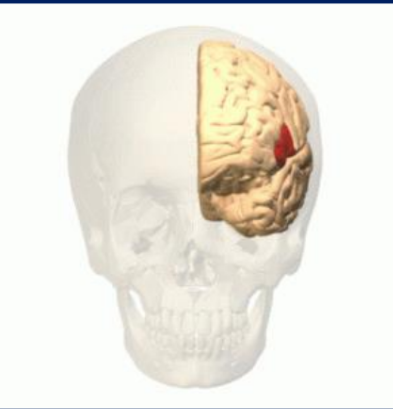
whata area of the brain is this?…
brocas area
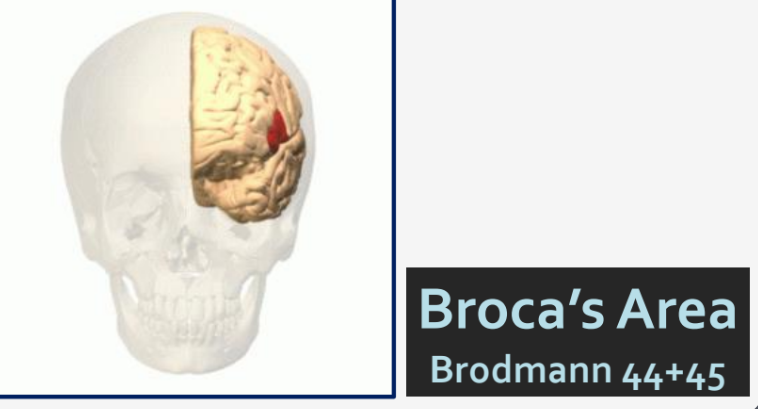
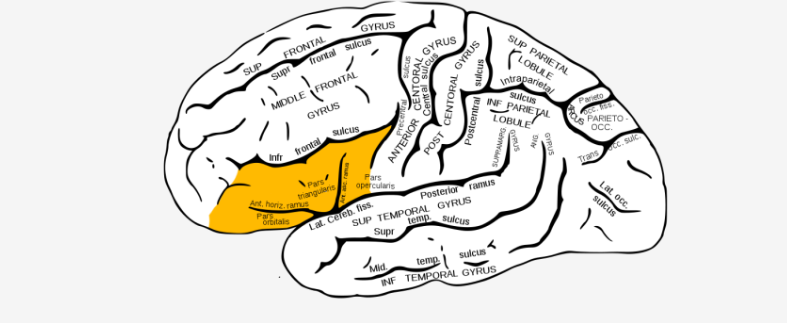
where in the brain is the highlighted area?…
Inferior Frontal Gyrus
This region is involved in processing language and executive functions.
Example of a commissural tract…
is the corpus callosum, which connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
give an example of an association tract
Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus is an example of an association tract
connects the frontal lobes with the occipital lobes in the brain.
what are association fibres?…
Association fibers are bundles of axons that connect different areas within the same hemisphere of the brain, facilitating communication between regions.
In what pathologies is executive function important?…
Addiction
• Personality Disorders
• • Dementia
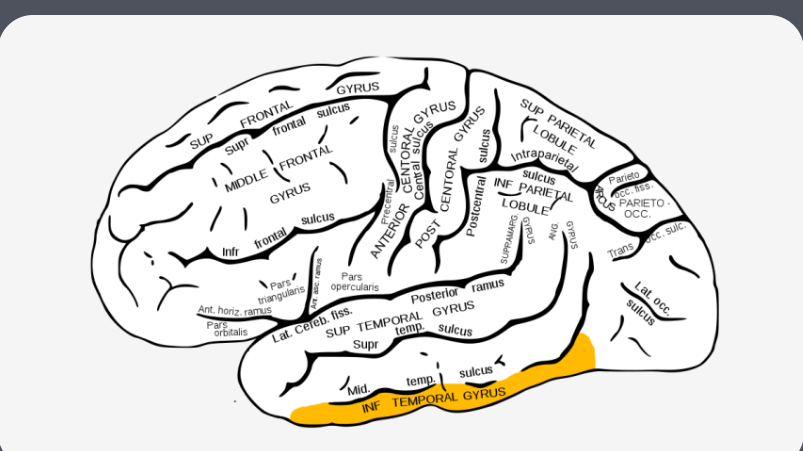
what is the highlighted area?…
temporal gyrus
wernickes aphasia VS Brocas Aphasia
WERNICKES APHASIAa
– Temporal
– Unable to understand language
– Fluent speech but - Makes no sense
– Little repetition
– Adequate syntax
– Adequate grammar
– Contrived or inappropriate speech
BROCAS APHASIAb
– Frontal
Understand language
•Cannot construct their own
– Halting speech – makes sense?
– Repetitive
– Disordered syntax
– Disordered grammar
– • Disordered structure individual words
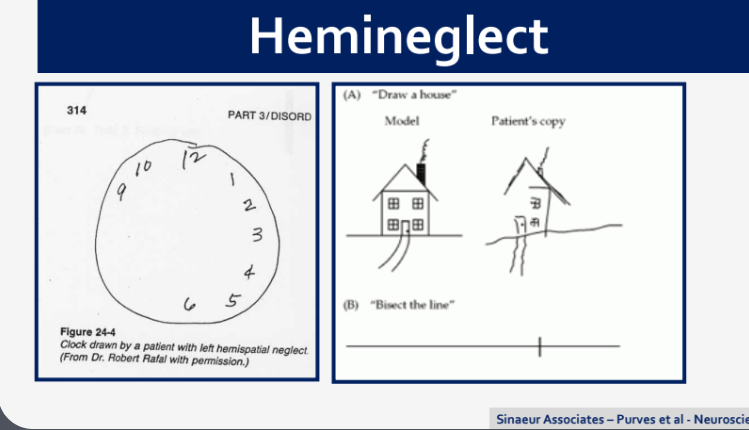
What is heminegelect?…
Hemineglect is a neurological condition characterized by a lack of awareness or attention to one side of space, often occurring after damage to the right parietal lobe.
What are the components of encoding?
Short-term memory, attention, working memory
What are the components of retrieval?
Learning and long-term memory
What is the sequence of the ascending sensory pathway?
Stimulus, first order neuron, spinal cord, spinothalamic tract (second order neuron), thalamus, thalamocortical projection (third order neuron), cortex
What structures are involved in the visual system?
Eye, optic nerve, optic chiasma, lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), primary visual cortex
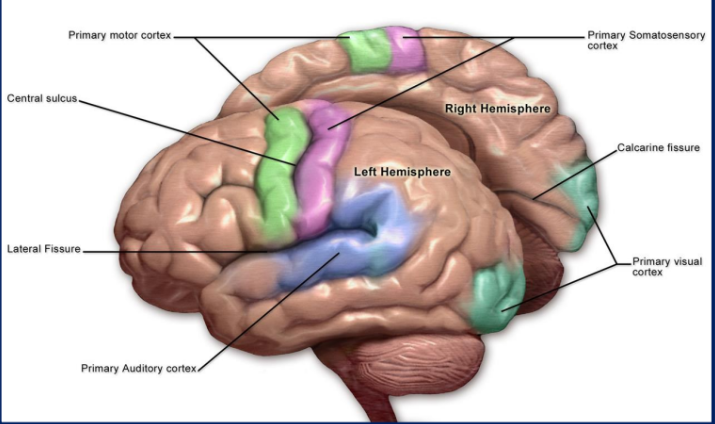
What are the four lobes of the brain?
Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital
What is the function of the parietal cortex?
Where is it?
What is the function of the temporal cortex?
Identifying nature of stimuli - What is it?
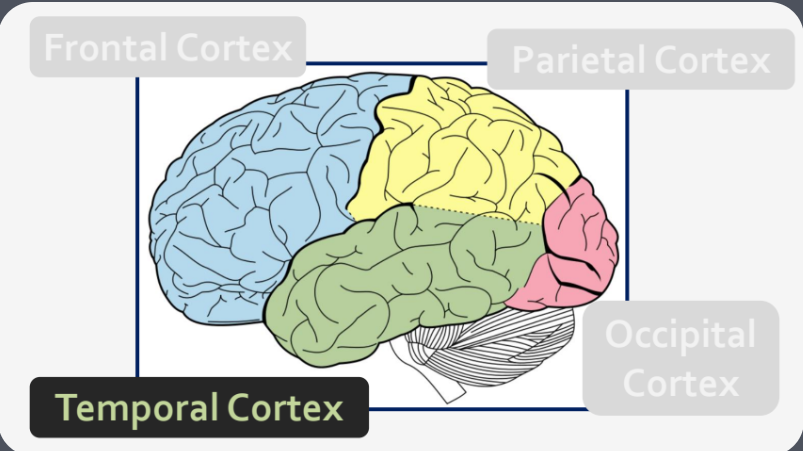
What is the function of the frontal cortex?
What do I do about it?
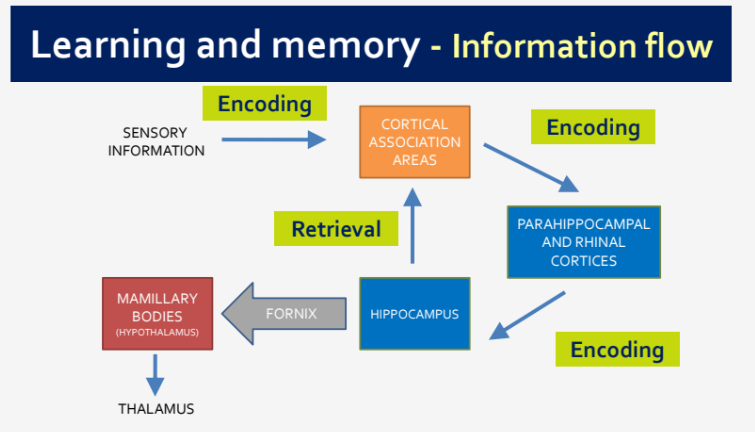
What is the information flow for learning and memory?
Information flow for learning and memory typically follows the pathway of sensory input to perception, followed by encoding in working memory, storage in long-term memory, and retrieval when needed.
What is the difference between a cortex and a lobe?
Lobe = A large anatomical region of the brain.
Each lobe contains multiple functional areas and is named by location (e.g., frontal lobe, parietal lobe).Cortex = The outer layer of the brain (made of grey matter) that covers the lobes.
Different cortical areas within lobes perform specific functions (e.g., visual cortex in the occipital lobe, motor cortex in the frontal lobe).
Define Sulcus (plural Sulci).
A sulcus is a groove or indentation on the surface of the brain that separates adjacent gyri. It plays a crucial role in increasing the surface area of the cerebral cortex.
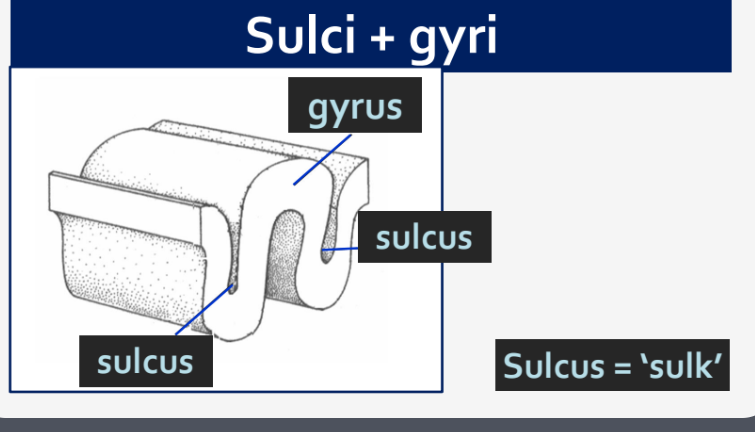
Define Gyrus (plural Gyri).
Key Term
What is a Brodmann Area?
‘Map’ of the cortex
Define White Matter Tracts.
White matter tracts are bundles of myelinated axons in the central nervous system that facilitate communication between different brain regions. They play a crucial role in the transmission of signals and the integration of information.
What is Laterality?
Key Term - 2 hemispheres
What does the Central Sulcus separate?
Parietal and Frontal Cortices
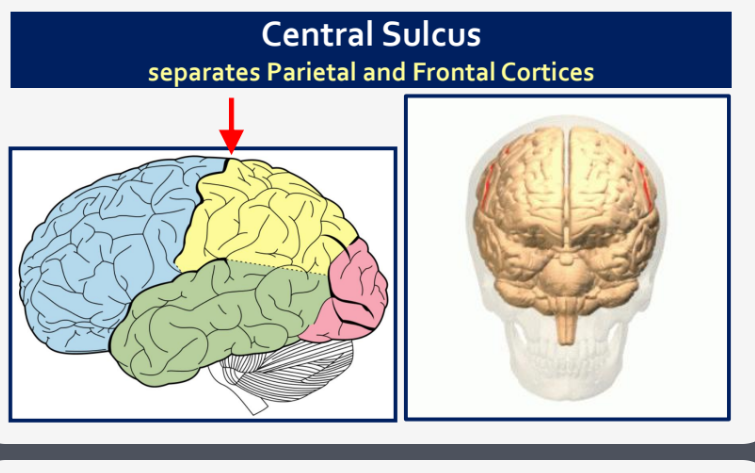
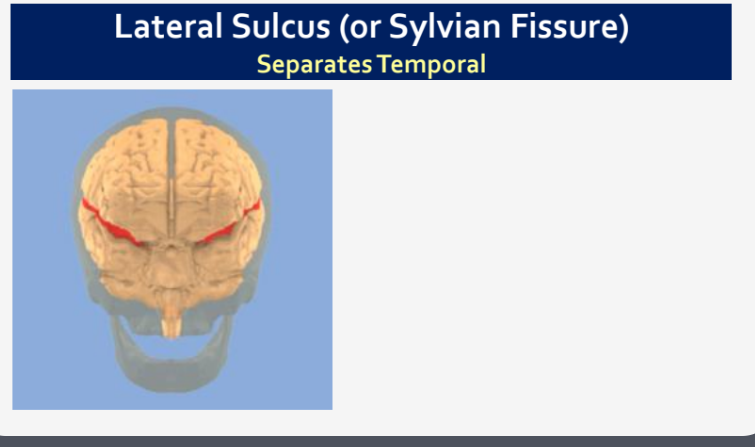
What does the Lateral Sulcus (or Sylvian Fissure) separate?
Temporal Lobe
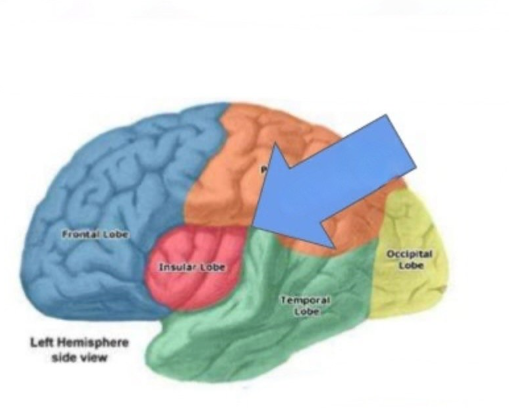
What is the Insula?
Insular Cortex
Who first mapped the cortex into Brodmann Areas?
Korbinian Brodmann in 1909
What is the basis for Brodmann Areas?
Areas of similarity in histology
How many Brodmann Areas are there?
52 regions, some subdivided
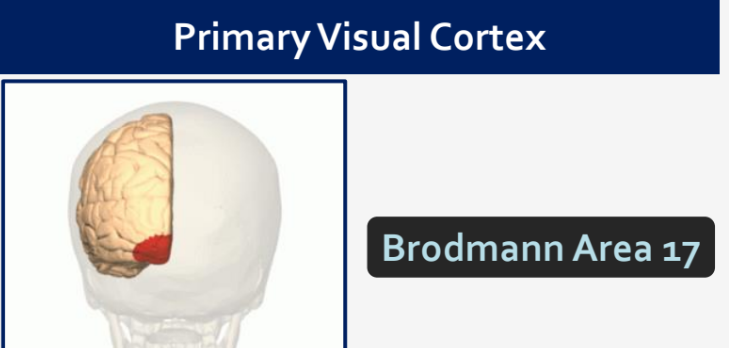
What Brodmann Area is the Primary Visual Cortex?
Area 17
What Brodmann Area is part of the Fusiform Face Area?
Area 37
Association cortices are not the?..
Not the primary cortices
What is the function of the Posterior Parietal Cortex?
Attending to stimuli (Where is it?)
What Brodmann areas comprise the Posterior Parietal Cortex?
Areas 5, 7, 39, 40
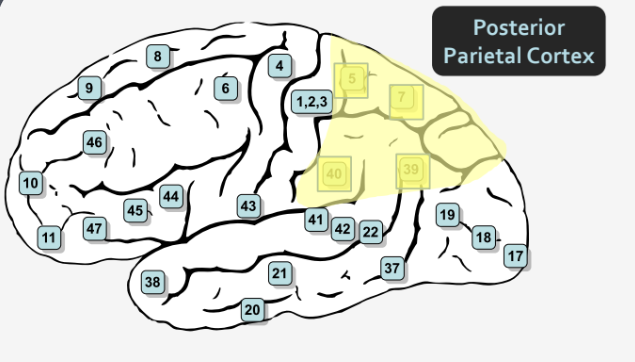
What is the Posterior Parietal Cortex important for?
Attention, especially spatial attention
What information does the Posterior Parietal Cortex integrate?
Visual, auditory, and somatosensory info
What can damage to the posterior parietal cortex result in?
“Neglect”
What is sensory neglect?
Incoming sensory information from the contralateral hemispace is ignored
What is conceptual neglect?
Neglect of the body and the external world in the contralateral hemifield
What is Hemiasomatognosia?
Patient denies that affected side of body belongs to them
What is motor neglect?
Fewer movements in the contralateral space
What is the function of the Temporal Cortex?
Identifying the nature of stimuli (What is it?)
What is Agnosia?
Inability to recognise sensory stimuli
What can damage to the inferior temporal cortex cause?
Visual agnosia (“Psychic blindness”) - patient can see but not identify
What area of the temp?
Face Blindness - inability to recognise individuals from their faces
What area of the brain is affected in Prosopagnosia?
Fusiform gyrus
What can damage to the middle temporal cortex cause?
Movement agnosia - cannot distinfuish btwn moving and stationary
What is the result of the integration of sensory streams?
Allows us to assemble one coherent perspective on the world
What is brain's role in consciousness?
Brain predicts a view of the world based upon perception and prior knowledge
What is the McGurk Effect?
Vision is the dominant sense
What Brodmann areas comprise the Auditory Cortex?
Areas 41+42
What area of the brain integrates audio and visual information in speech processing?
Superior Temporal Sulcus
Damage to which Brodmann Area(s) is associated with Prosopagnosia?
Area 37
What is the function of the Frontal Cortex?
Selecting and planning an appropriate response (What to do about it?)
Where is the Prefrontal cortex located?
Rostral to Primary Motor Cortex
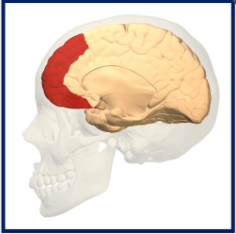
When does the Prefrontal cortex develop?
Develops very late 20-30
What are the dorsal functions of the Prefrontal cortex?
Thoughts, attention
What are the ventral functions of the Prefrontal cortex?
Emotion
What are the functions of the Prefrontal cortex?
Restraint, Initiative, Order
What are some symptoms of frontal cortex damage?
Difficulty planning, loss of interactions, loss of flexibility, perseveration, inability to focus, emotional lability, abulia, behavior change, problem solving difficulty, aphasia, hemiplegia
Where does executive function reside?
Prefrontal cortex
What is executive function?
Long term planning, Withholding impulsive behaviour, Cognitive control
What are associ
Connect the Association Cortices,Connect the brain
What type of neurons are White Matter Tracts?
Myelinated neurons
How are White Matter Tracts mapped?
Use Diffusion Tensor Imaging to map
What are the three types of White Matter Tracts?
Association fibres, Commissural fibres, Projection fibres
What is the function of Association fibres?
Connect cortical areas in the same hemisphere
What is the function of Commissural fibres?
Connect across hemispheres
What is the function of Projection fibres?
Connect cortex to other brain regions
What is the Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus?
An example of an Association tract
What is the Corpus Callosum?
An example of a Commissural tract
What are the Corticospinal and Corona-radiata?
Examples of Projection tracts
What cortical areas are working together in language?
Temporal cortex and Frontal cortex
What is Dysarthria?
Difficulty moving the muscles of the face + tongue that mediate speaking
What is Aphasia?
Difficulty in naming objects. Repetition of words is impaired.
What structures are related to Language?
superior temporal gyrus, Temporal Cortex
What Brodmann Area is Wernicke's Area?
Area 22
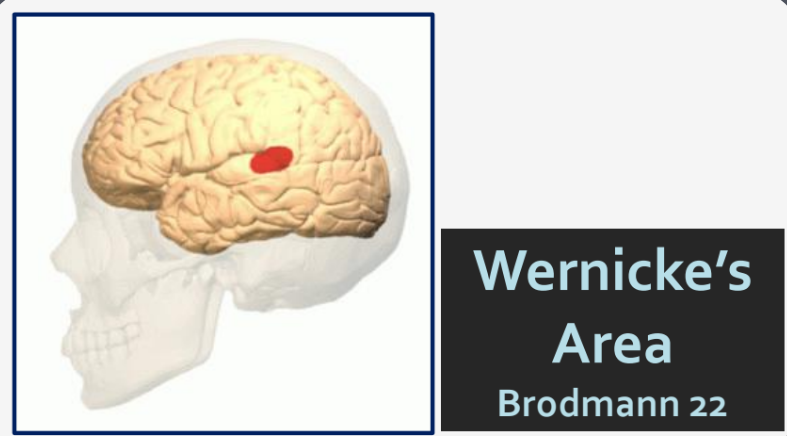
What is the function of Wernicke's Area?
Understanding language
What is Wernicke’s Aphasia?
Unable to understand language. Fluent speech, but makes no sense.
What is Wernicke's Aphasia also called?
Fluent, sensory or receptive aphasia
What does Fluent Aphasia mean?
A type of aphasia (language disorder after stroke) with poor comprehension. Speech is effortless, but the meaning is impaired.
What area of the brain is related to language?
Inferior Frontal Gyrus
What Brodmann Areas comprise Broca's Area?
Areas 44+45
What is the function of Broca's Area?
Creating language
What is Broca’s Aphasia?
Difficulty constructing their own language. Halting speech.
What is Broca’s Aphasia also called?
Non-fluent, motor, expressive, or production aphasia
What are the consequences of damage to Broca's area?
Understand language, cannot construct their own, halting speech, repetitive, disordered syntax, grammar, structure of individual words
What are the consequences of damage to Wernicke's area?
Unable to understand language, fluent speech, makes no sense, little repetition adequate syntax, grammar, contrived or inappropriate speech
What is affected in Aphasias?
Recognition of ‘conversation cues’, reading, writing, sign language
What areas does the Arcuate Fasiculus Connect?
Broca's + Wernicke's areas
What type of fiber is the Arcuate Fasciculus?
Association Fibres
Damage to which Brodmann Area is associated with Wernicke's Aphasia?
Area 22
What association cortex associated with 'where is it?'
Posterior Parietal Cortex
What association cortex associated with 'what is it?'
Temporal Cortex
What association cortex associated with 'what do I do about it?'
Prefrontal Cortex
List some symptoms of frontal cortex damage…
Difficulty planning sequence needed to complete a task (eg. make a cup of tea)
– Requires working memory
• Loss of spontaneous interactions
• Loss of flexibility in thought
• Perseveration – persistence of a single thought or action
• Inability to focus on the task in hand
• Emotional lability #
• Abulia – passivity, apathy
• Socially inappropriate behaviour
• Personality change
• Difficulty with problem solving
• Expressive aphasia
• Hemiplegia