Chapter 23, Lesson 7: Urine Storage and Elimination
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 23, Lesson 7 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Ureters
Muscular tubes that extend from the kidney to the urinary bladder; about 25 cm long with a flap of mucosa to prevent backflow
Urinary bladder
A muscular sac located on the floor of the pelvic cavity, has layers of the detrusor, trigone, and rugae
Detrusor
Three layers of smooth muscle in the urinary bladder wall
Trigone
A smooth triangular area marked by openings of the two ureters and the urethra
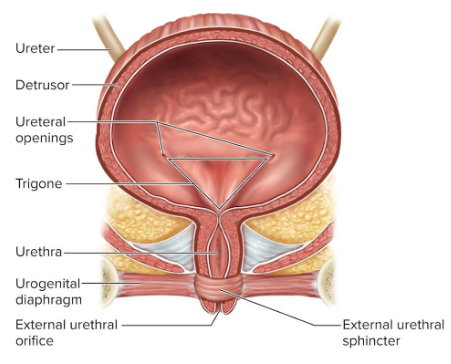
Rugae
Conspicuous wrinkles in the empty bladder for more surface area and extension

Renal calculus (kidney stones)
Hard deposits of minerals that form in the renal pelvis; can be small and pass unnoticed or larger, causing painful blockages in the renal pelvis or ureter
Kidney stone causes
Caused by:
Hypercalcemia
Dehydration
pH imbalances
Frequent UTIs
Enlarged prostate causing urine retention
Kidney stone treatments
Treated with:
Stone-dissolving drugs
Surgery
Shock wave lithotripsy (pulverization with ultrasound)
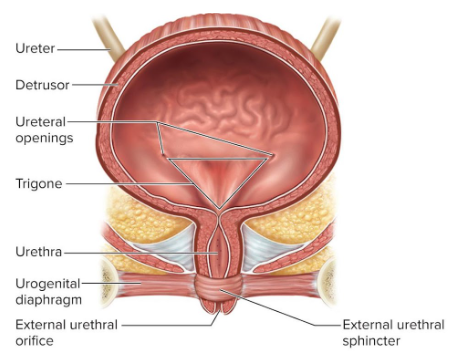
Urethra
A tube that conveys urine out of the body; female urethras as 3 to 4 cm long and male urethras are 18 cm long
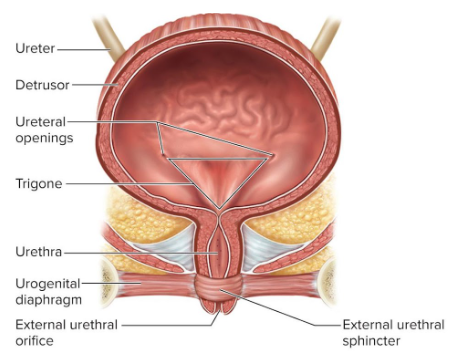
External urethral orifice
Female urethra; between the vaginal orifice and clitoris
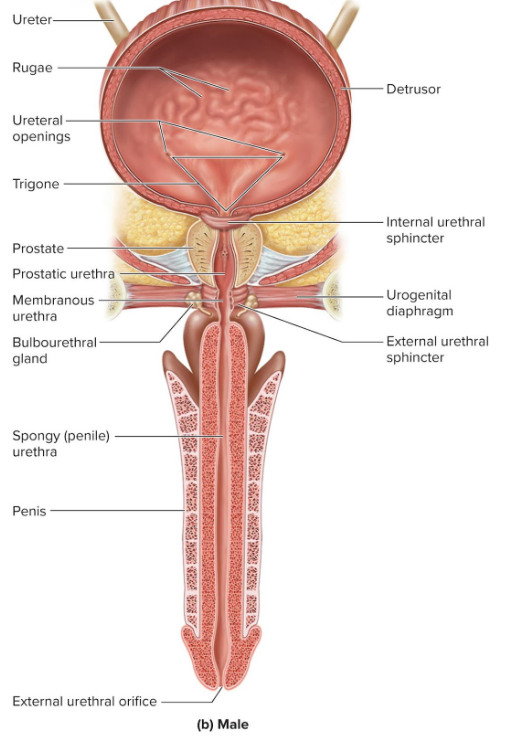
Male urethra region
Prostatic urethra (2.5 cm): passes through prostate
Membranous urethra (0.5 cm): passes through muscular pelvic cavity floor
Spongy urethra (15 cm): passes through penis in corpus spongiosum
Internal urethral sphincter
Urethral sphincter only in males with a thickened collar of muscle around the neck of the bladder, nearby urethra
External urethral sphincter
Urethral sphincter in both sexes where the urethra passes through the pelvic floor
Cystitis
Infection of the urinary bladder; common in females due to short urethra and an be triggered by sexual intercourse
Pyelitis
Infection of the renal pelvis
Pyelonephritis
Infection that reaches the cortex and nephrons; can result from blood-borne bacteria
Micturition
The act of urinating following the filling of the bladder; controlled by pons with stretch receptor signals to either relax or contract the sphincter for voiding or retention
Renal insufficiency
A state in which the kidneys cannot maintain homeostasis due to extensive nephron destruction; kidneys can regenerate or hypertrophy to compensate
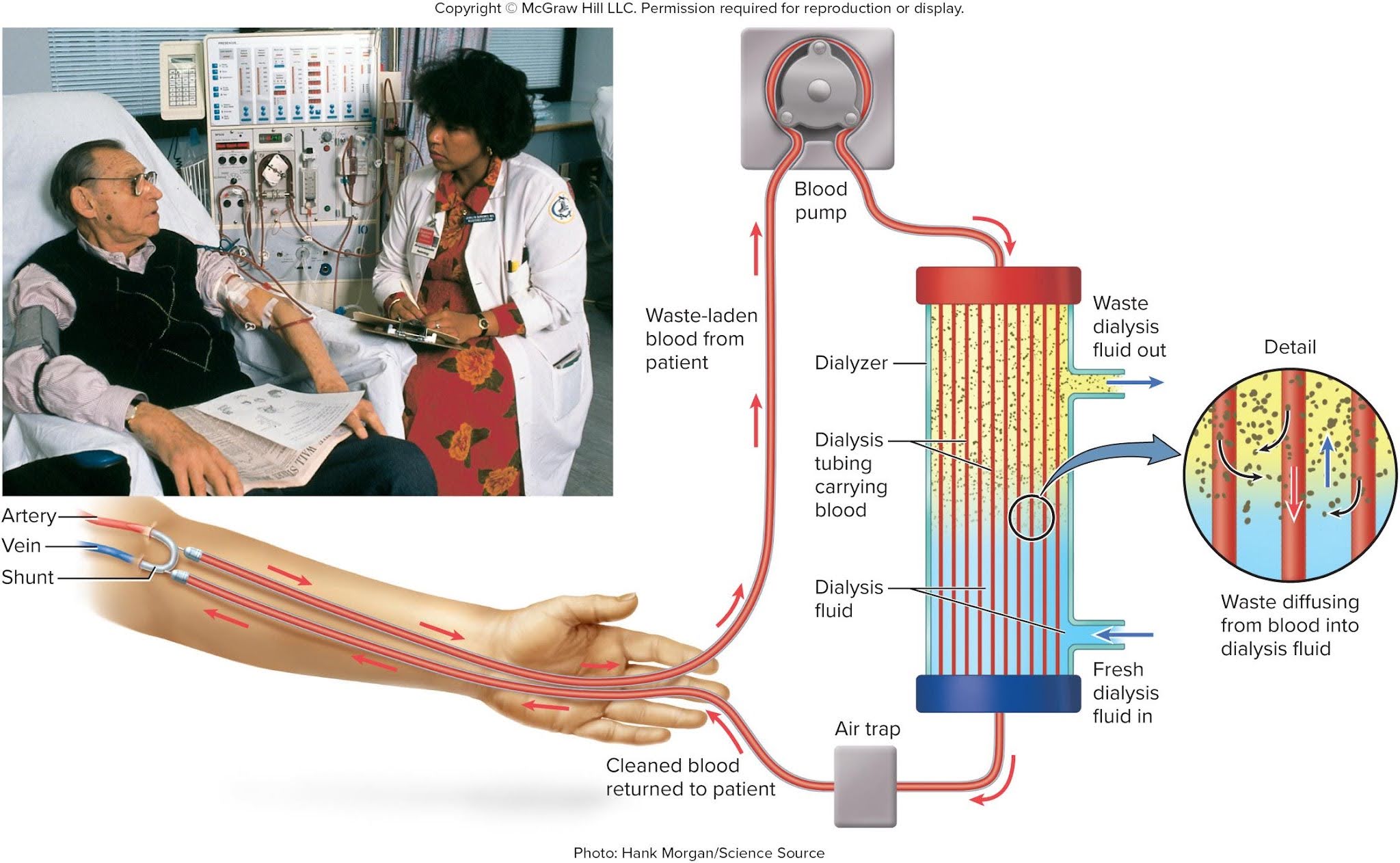
Hemodialysis
A procedure for artificially clearing wastes from the blood; it is cleaned by a machine with dialysis fluid