Introduction to the aquatic realm, the origin of life, and the theory of evolution | AQ Marine Biology
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
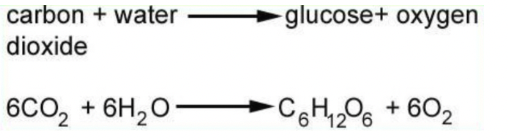
Photosynthesis formula
Photic zone
area where life can penetrate. Photosynthetic algae must live in this zone in order to contribute food and oxygen. The depth to which light can penetrate is affected by several things such as water quality or suspended sediment levels.
Photoinhibition
the light-induced reduction in photosynthetic capacity, meaning it's when excessive light exposure harms the photosynthetic machinery.
Thermocline
a layer in the ocean where temperature drops rapidly with depth, acting as a barrier that traps sinking food and supports marine life by concentrating nutrients. Uncommon in BVIS
Enzyme reaction rates
Enzyme reaction rates refer to how fast a chemical reaction happens when helped by an enzyme.
Enzyme reaction rates in the ocean double every 10°C increase in temperature, but if temperatures reach around 40°C (104°F), enzymes can break down and stop functioning. This is dangerous for marine life. However, because water has a high heat capacity, ocean temperatures change slowly, making such extreme heat rare — except in shallow lagoons or tide pools, which can approach this danger zone.
Temperature and dissolved oxygen levels
Oxygen levels in seawater depend mostly on temperature. As temperature increases, the amount of dissolved oxygen decreases, which is why warm Caribbean waters have less oxygen than cold deep waters.
Where does dissolved oxygen come from?
From waves mixing air into water and photosynthesis by primary producers.
Where does the oxygen go?
Used by organisms and lost during decay of dead organisms at the thermocline, forming oxygen minimum zones.
Theory of evolution
Darwin proposed that species evolved slowly over time through natural selection, where the best-adapted organisms survive and pass on traits. He noticed species vary slightly, and those better suited to their environment are more likely to survive. His findings showed how animals change over generations, though he couldn’t yet explain why species on different continents could still be similar.