last min PHYSICS stuffies u should knoww otherwise u'll CRY
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Earthing (Method of user protection)
provides a low resistance path to the earth so if some one does come into contact with a current instead of flowing through them to the earth giving them a shock it flows through the earthing wire.
four methods of protecting the user in domestic electrical appliances
insulation, double insulation, fuses, circuit breakers, earthing (WHOops thats five)
resistors turn ____ energy into _____ energy
electrical, heat
can james very well afford cookies sadly james was already rich
friction is a force that ___________ __________
opposes motion
the "f" in f=ma stands for
UNBALANCED force
stopping distance =
Thinking distance + braking distance
factors affecting stopping distance
speed, mass, road condition and reaction time
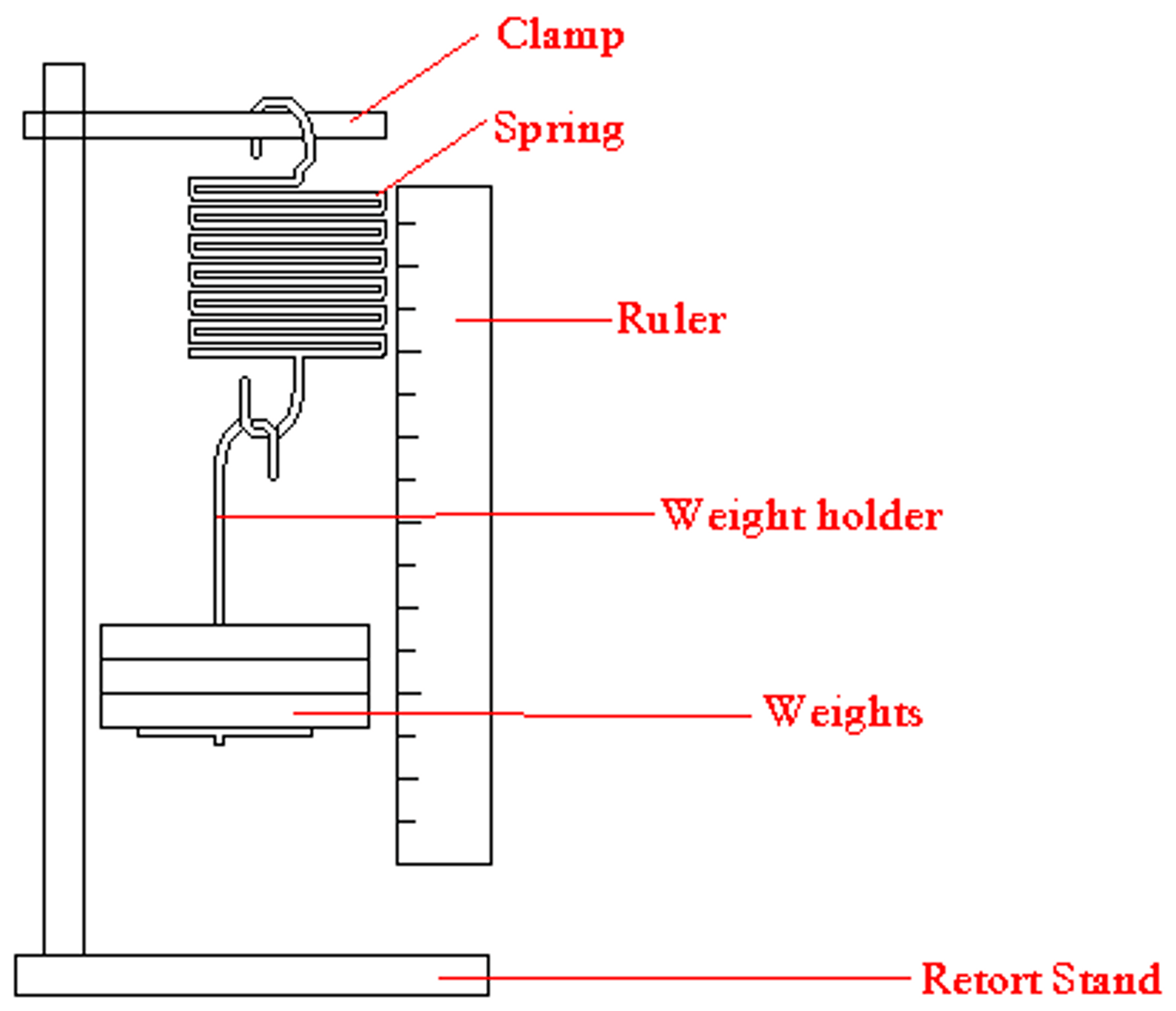
practical investigate how extension varies with applied force for helical springs, metal wires and rubber bands
1) Set up your apparatus as shown in the diagram, use a set square to get a vertical ruler
2) Measure the length of your spring without any hanging masses.
3) Hang a mass of 100g on the spring
4) Measure the new length of the spring
5) Calculate the extension of the spring
6) Repeat steps 3-5 for increasing the mass In increments of 100g
7) Take note of your results in the table.
spring extension diagram
hooke's law on a graph
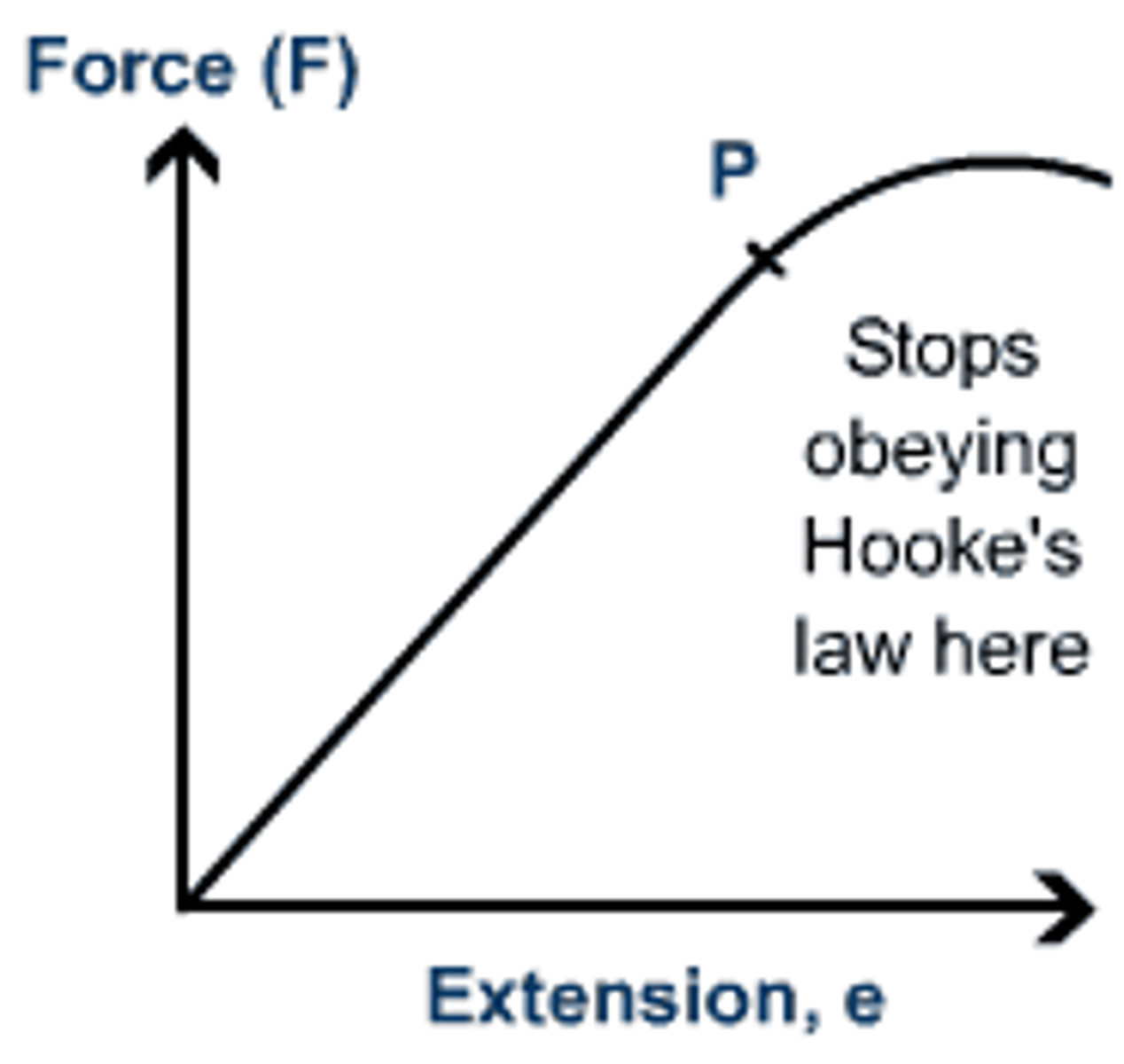
- Spring is elastic: force and extension are directly proportional
-Limit of proportionality: the point at which force and extension stop being directly proportional

elastic behaviour
The ability of a material to recover its original shape after the forces causing deformation have been removed.
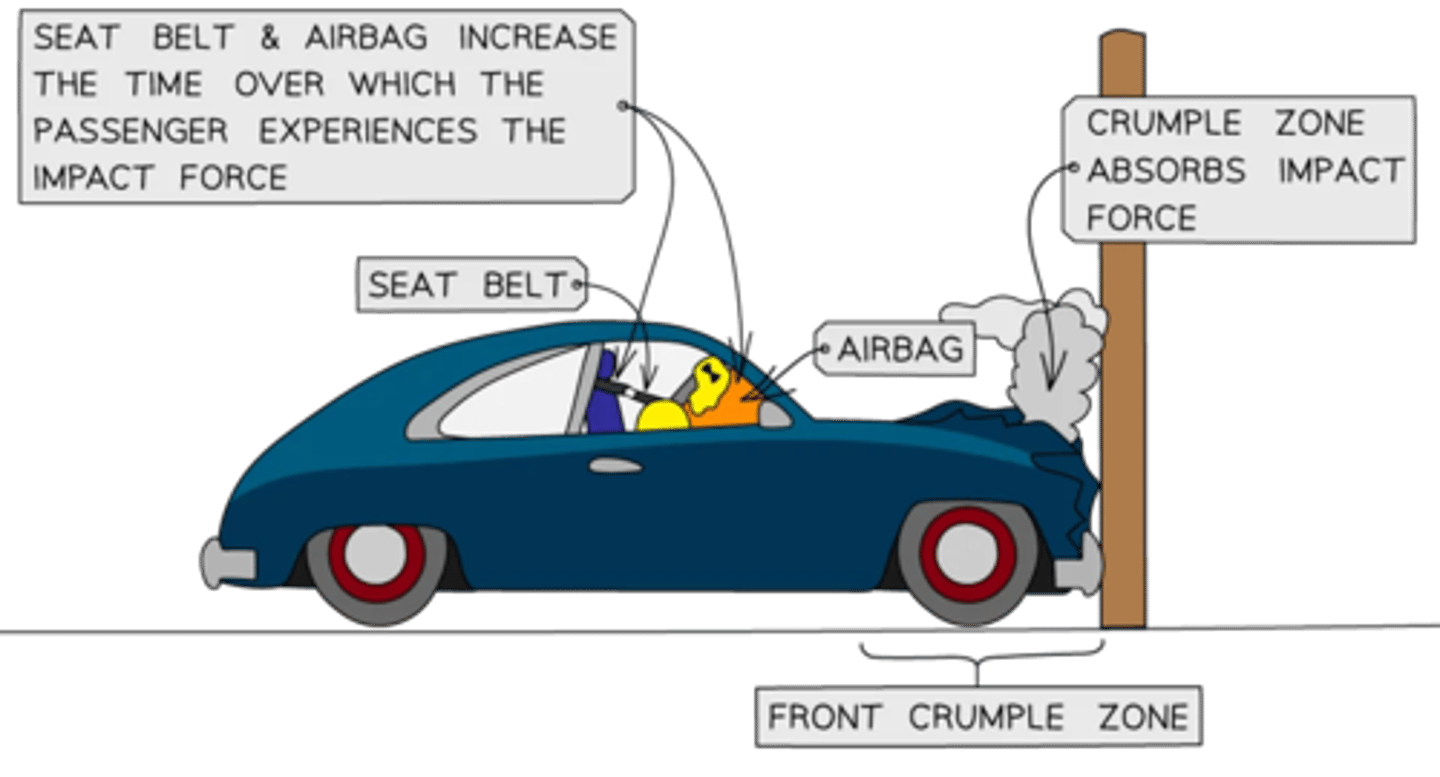
momentum safety features
- seat belts are designed to stop a passenger from colliding with the interior of a vehicle by keeping them fixed to their seat in an abrupt stop
- they are designed to stretch slightly to increase the time for the passenger's momentum to reach zero and reduce the force on them in a collision
- airbags are deployed at the front on the dashboard and steering wheel when a collision occurs to act as a soft cushion to prevent injury on the passenger when they are thrown forward upon impact
- crumple zones are designed into the exterior of vehicles
- they are at the front and back and are designed to crush or crumple in a controlled way in a collision
- the crumple zones increase the time over which the vehicle comes to rest, lowering the impact force on the passengers
newtons third law
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
newtons second law
Force equals mass times acceleration
newtons first law
An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
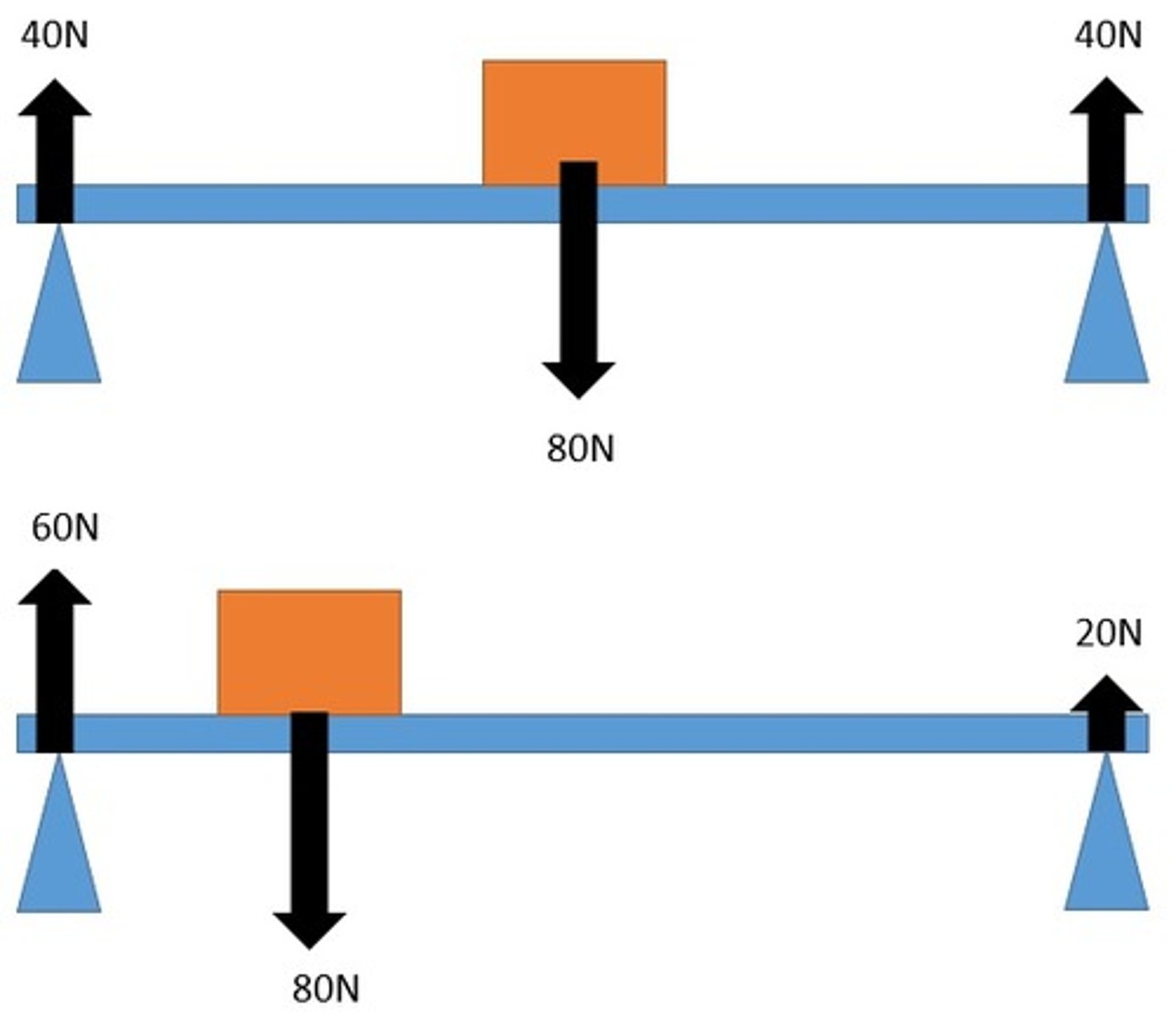
understand how the upward forces on a light beam, supported at its ends, vary with the position of a heavy object placed on the beam
when moments are taken from the right hand side as the block is a greater distance the force from the left hand pivot must be bigger to counteract it. The opposite is true for the left hand side.
how does a current in a resistor results in the electral transfer of energy and an increase in temperature
converts the electricial energy to heat energy, which can be used in products like heaters where there are a lot of resistors where the temperature gets really high
fuses sizes
The most common for domestic appliances in the UK are 3 A, 5 A and 13 A. The correct fuse for a circuit is the one that allows the correct current but blows if the current is a little larger.
mains electricity is an _____ supply
ac
battaries and cells are ___________ supply
dc
current dependance on voltage in a series circuit
- As voltage increases the current also increases.
- In general, the more components in a circuit, the lower the current.
sc,vp
(security council, vice president)
series current (is the same in every branch)
voltage parallel (voltage is the same in every branch)
resistance total in series
r1+r2+r3...
resistance total in parallel
1/r1 + 1/r2 + 1/r3...
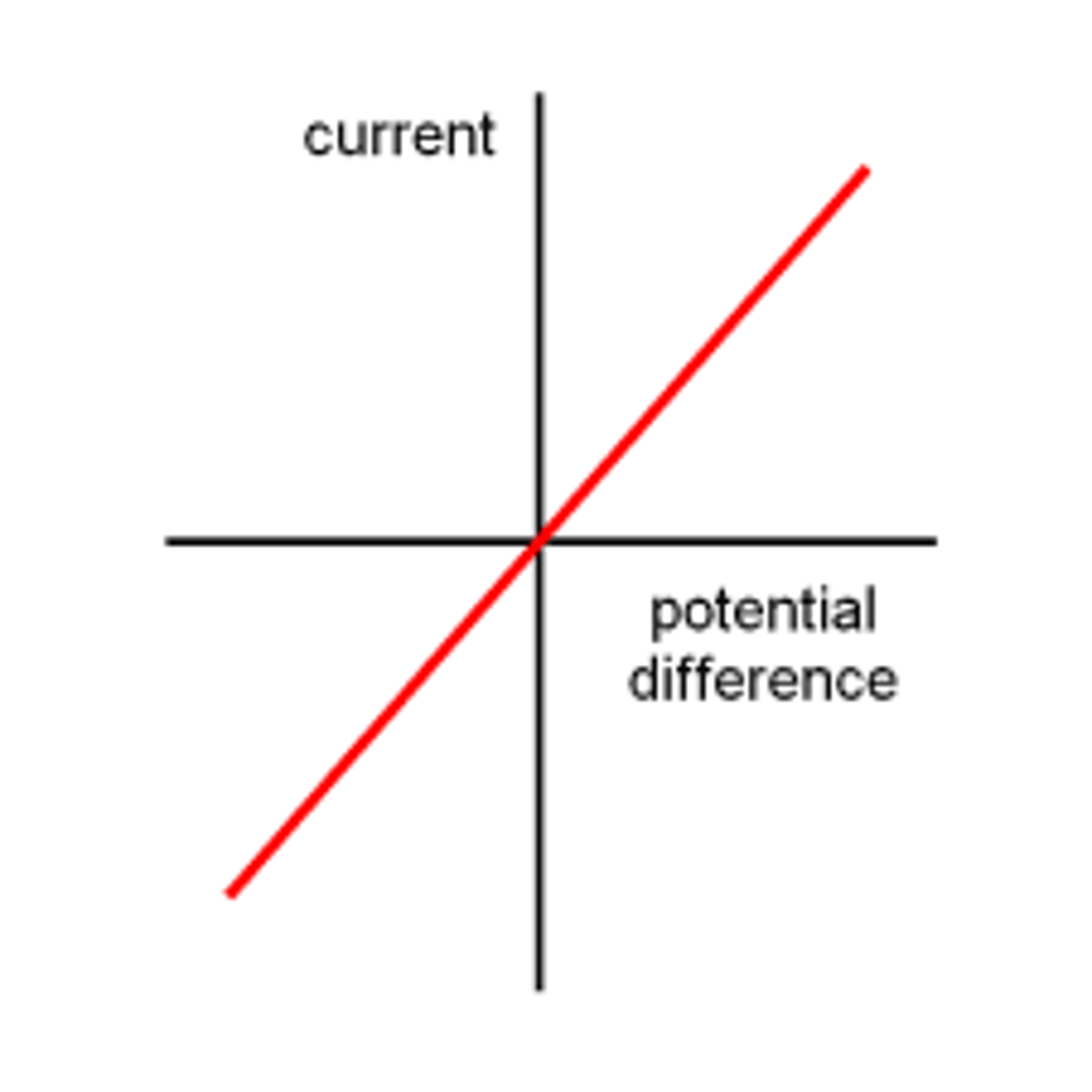
current/voltage graph
current and voltage are directly proportional through a resistor when it is at a constant temperature
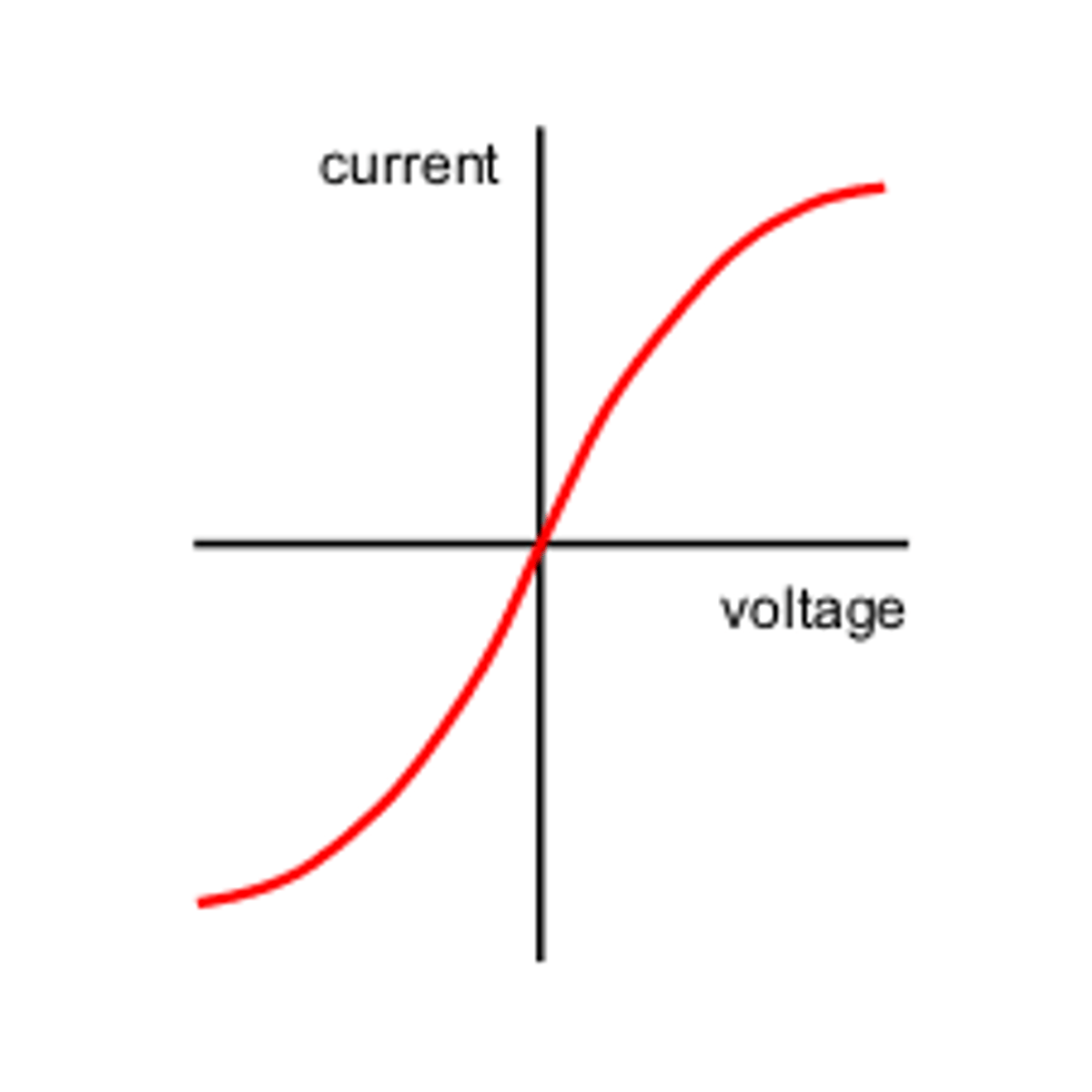
Filament lamp graph (current/voltage)
in this graph, the current and voltage are not directly proportional since the filament lamp gets hotter, which increases the resistance, more voltage is required to push the current through so it increases, but the current doesn't increase by as much.
increase in temp = electrons + ions collide more = increase in resistance
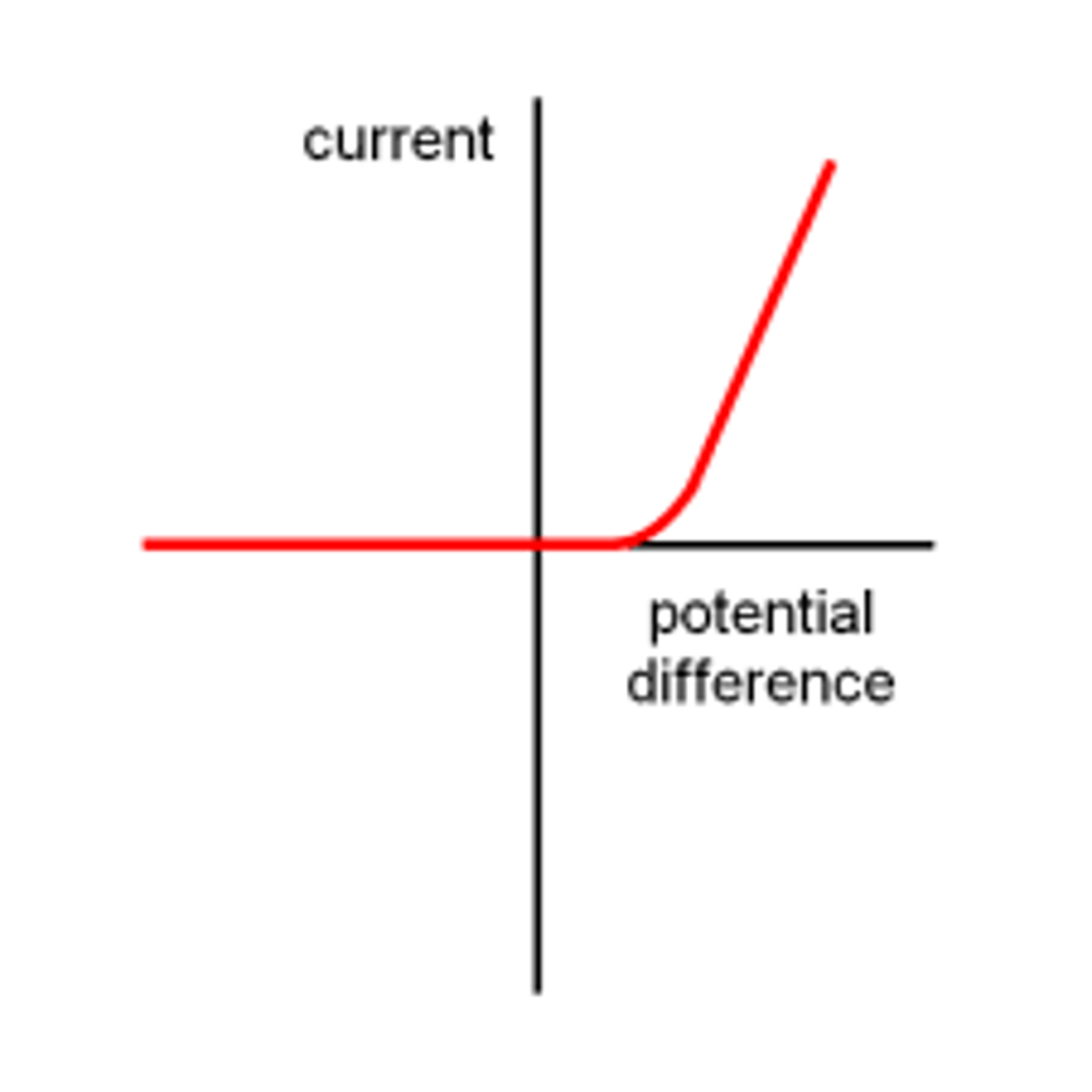
diode graph
current cannot flow in the opposite direction with a diode in a circuit, but in the normal direction the current still increases with voltage
cells/batteries contain
chemical energy whcih is transferred to electrical energy in a circuit
increase in resistance
decrease in current since the current needs more energy to be able to pass through
decrease in resistance
increase in current
in both an LDR, and thermistor, the resistance ___________ as their light/temperature ___________________
resistance decreases == light/temp increases
electric current in solid metals
negative, free flowing electrons
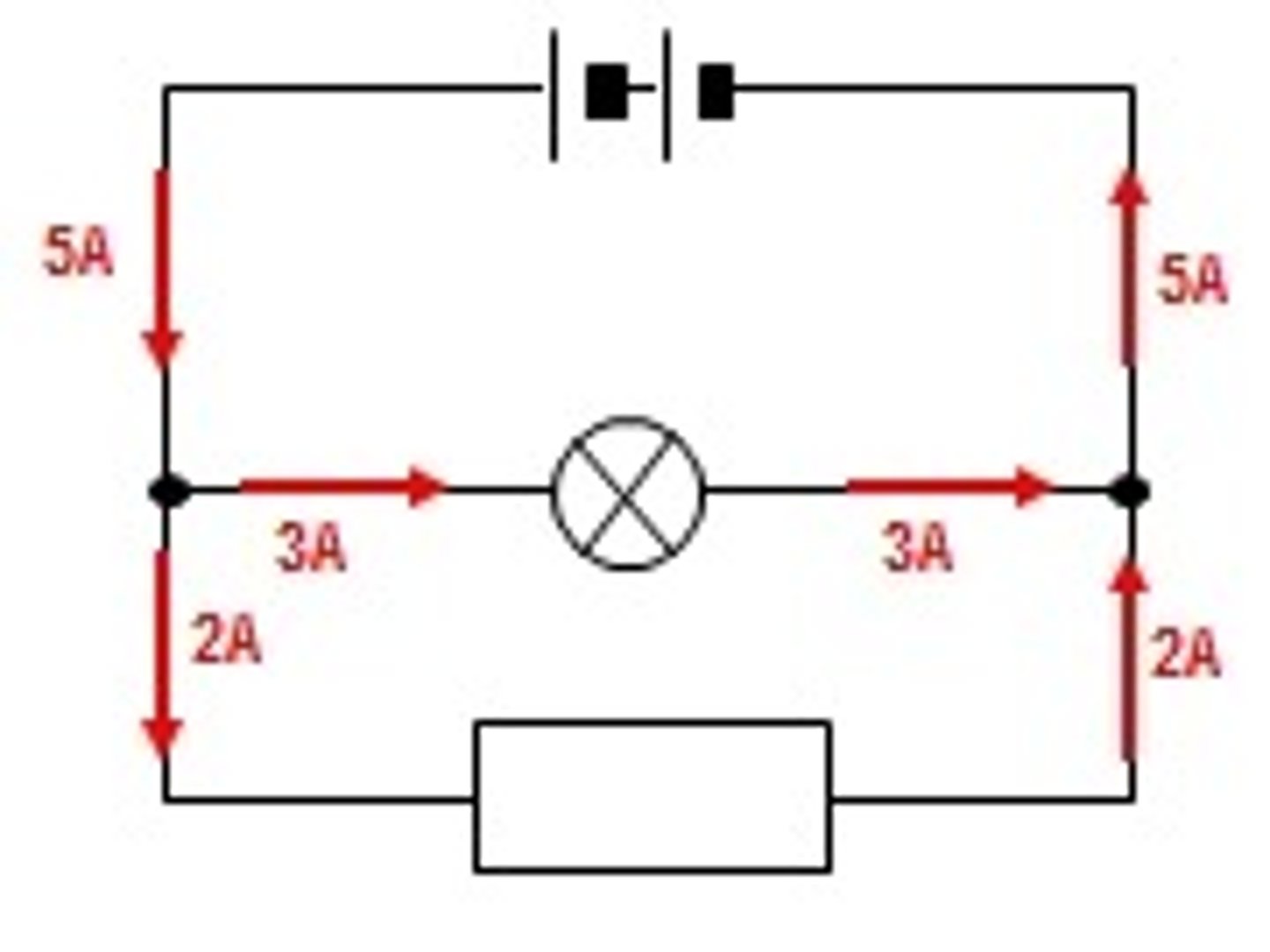
current conserved at junctions
this is because current is never used up, it splits at the junctions and comes back together when the paths meet again
investigate how insulating materials can be charged by friction
- Hold polythene rod and cloth next to up small pieces of paper one at a time, observe.
- Now rub the rod with the cloth
- Again hold close to small pieces of paper, observe.
- Turn on a tap so a thin stream of water is flowing
- Hold the rod about 1cm away from the water just below the nozzle, observe
- Repeat with different material rods and cloths
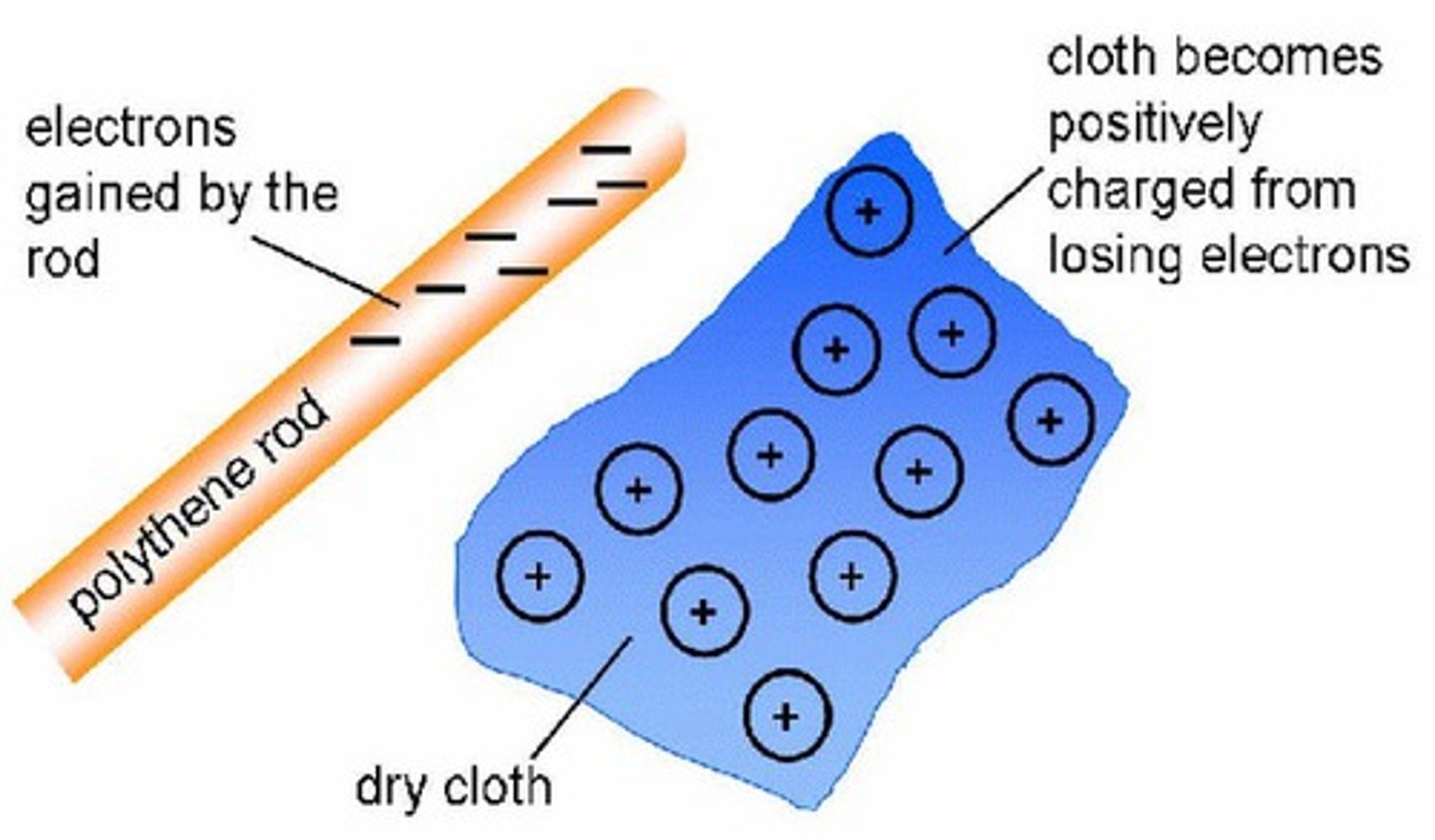
electrostatic charges
the electrons from a plastic rod rub onto the cloth, creating an electrostatic charge. the rod becomes positive
sparking (electrostatic stuff)
when a plane is flying through the air, electrons come onto it thanks to friction OR when refuelling a plane, electrostatic charge can build up in the fuel pipe and cause a spark, therefore the refuelling truck and the plane are both earthed.
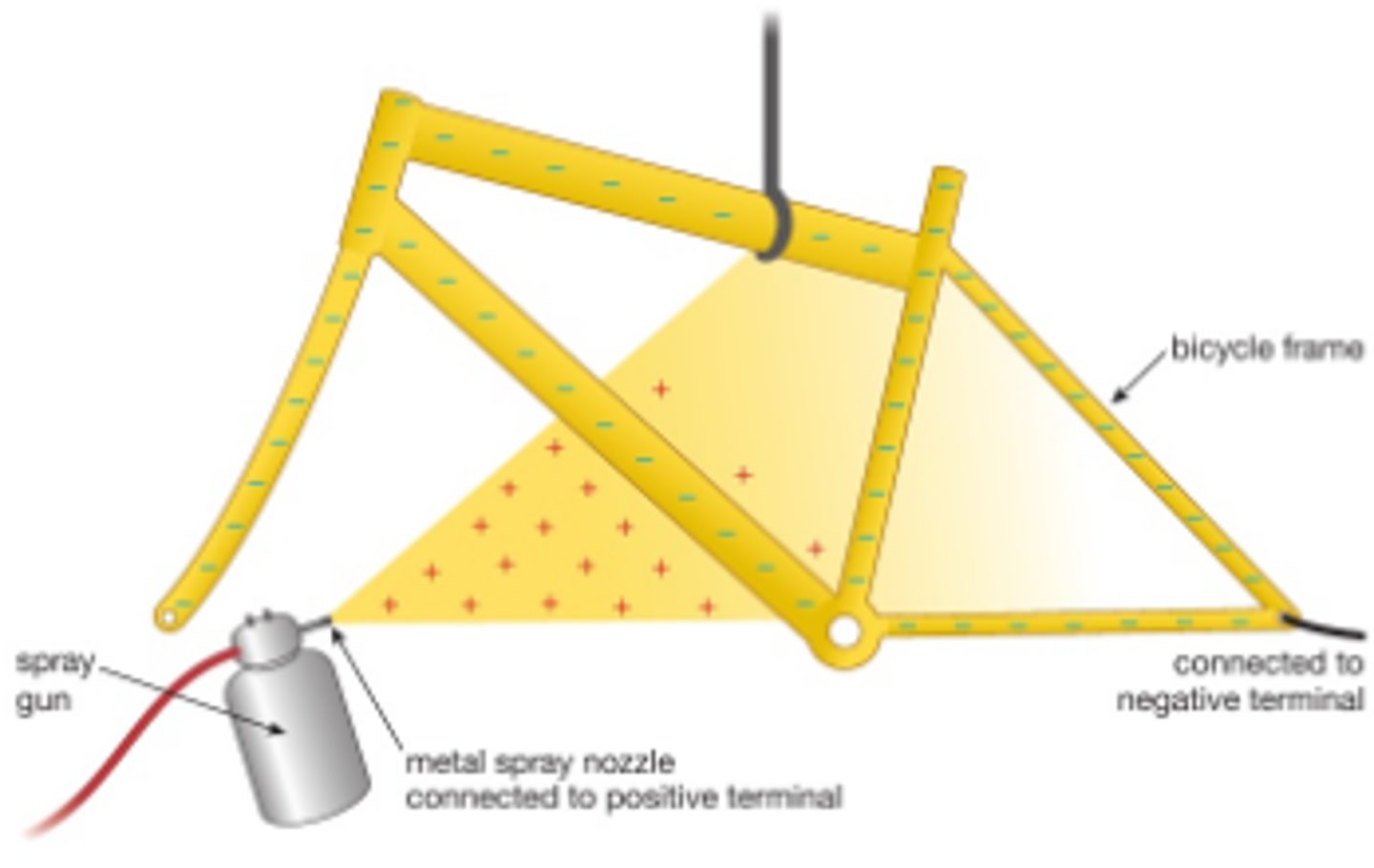
electrostatic paint sprayer
- a bike frame is given a positive charge
- a paint sprayer with negatively charged paint droplets is used to spray the paint.
- this gives an even coating and reduces the amount of paint wasted.
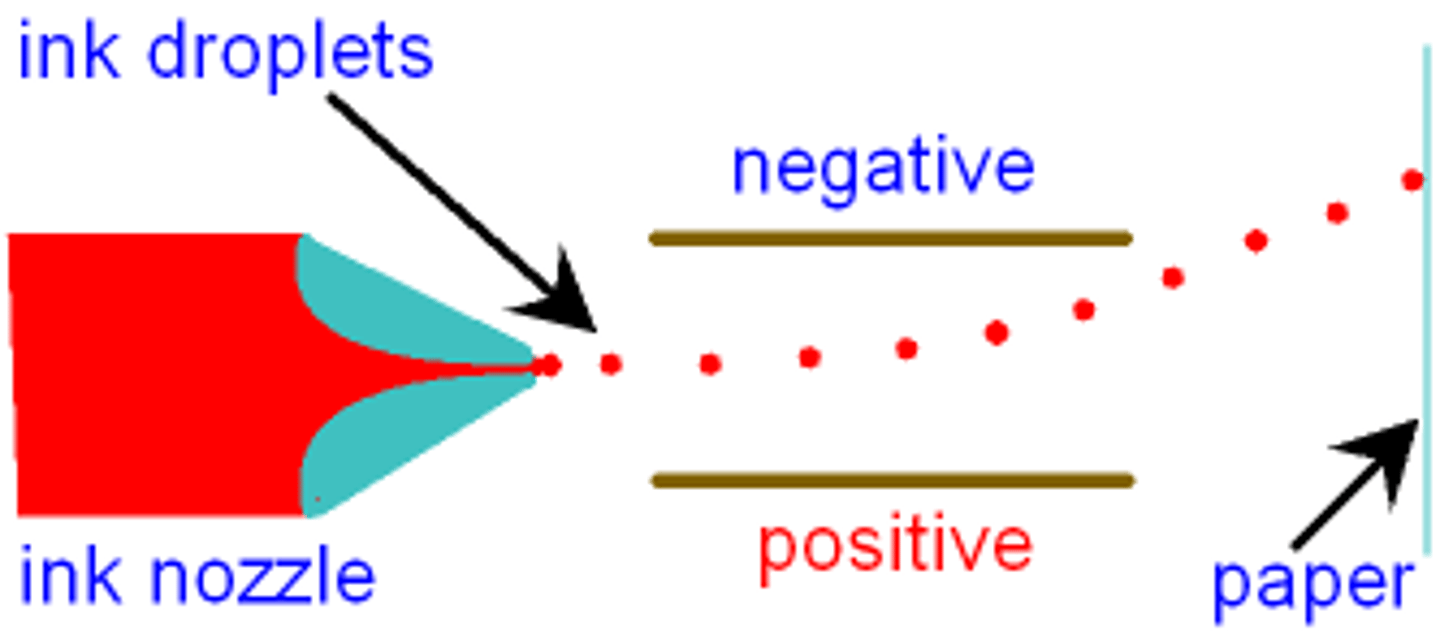
inkjet printer electrostatic
- each ink drop gains a charge
- this charge is guided to the right part of the paper by deflecting plates, which also have charges to guide the ink droplet to the correct position
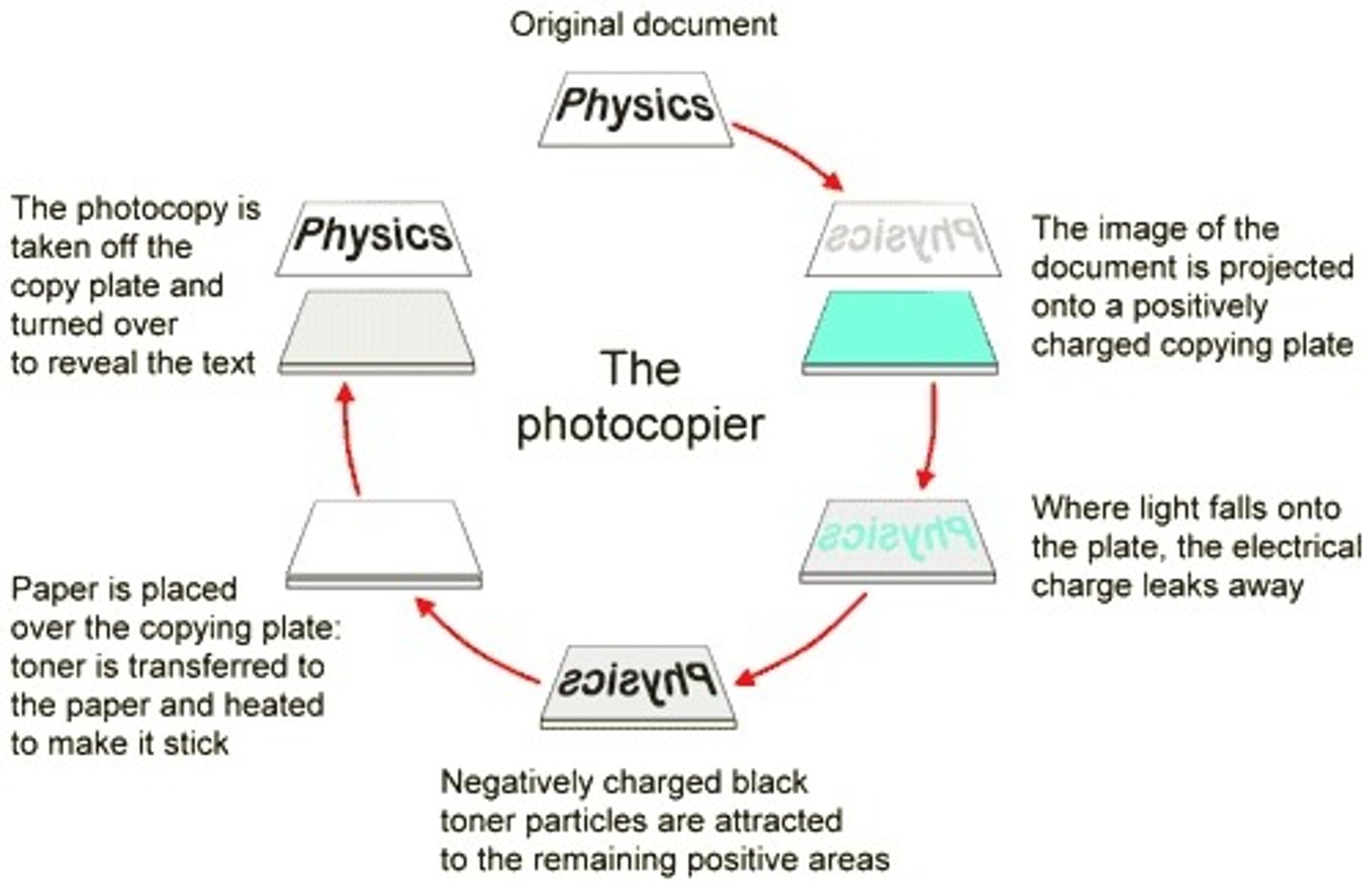
photocopier electrostatic
dangerous effects of four em waves
microwaves: internal heating of body tissue
infrared: skin burns
ultraviolet: damage to surface cells and blindness
gamma rays: cancer, mutation
protective measures against dangerous em waves
wear sun glasses, sun cream and stay in shade for UV
Wear led clothing for Gamma
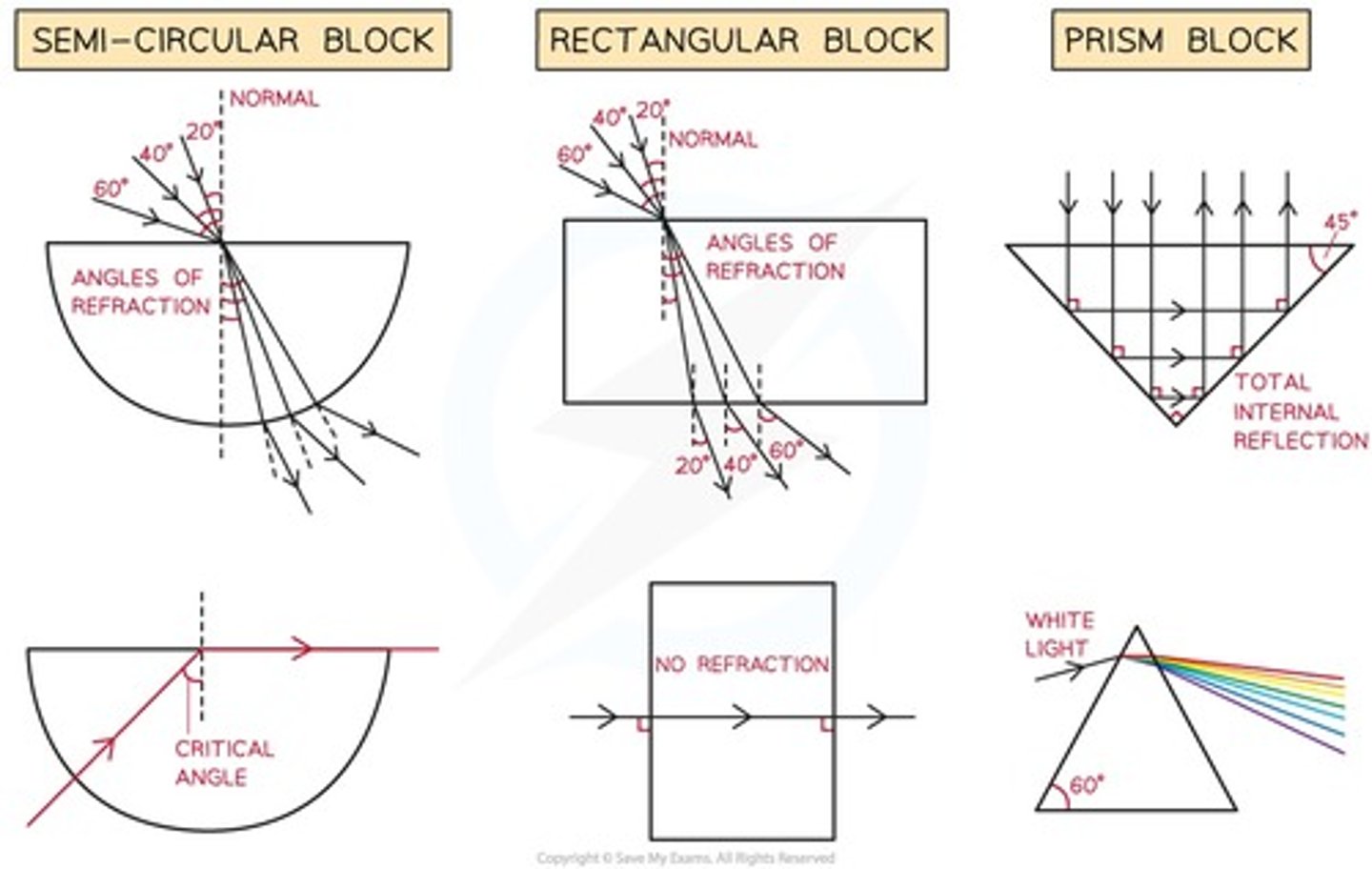
practical: investigate refraction
1. Set up your apparatus as shown in the diagram using a rectangular block.
2. Shine the light ray through the glass block
3. Use crosses to mark the path of the ray.
4. Join up crosses with a ruler
5. Draw on a normal where the ray enters the glass block
6. Measure the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction and add these to your results table
7. Comment on how the speed of the light has changed as the light moves between the mediums.
8. Repeat this for different angles of incidence and different glass prisms.
refractive index=
sin i / sin r
snells law
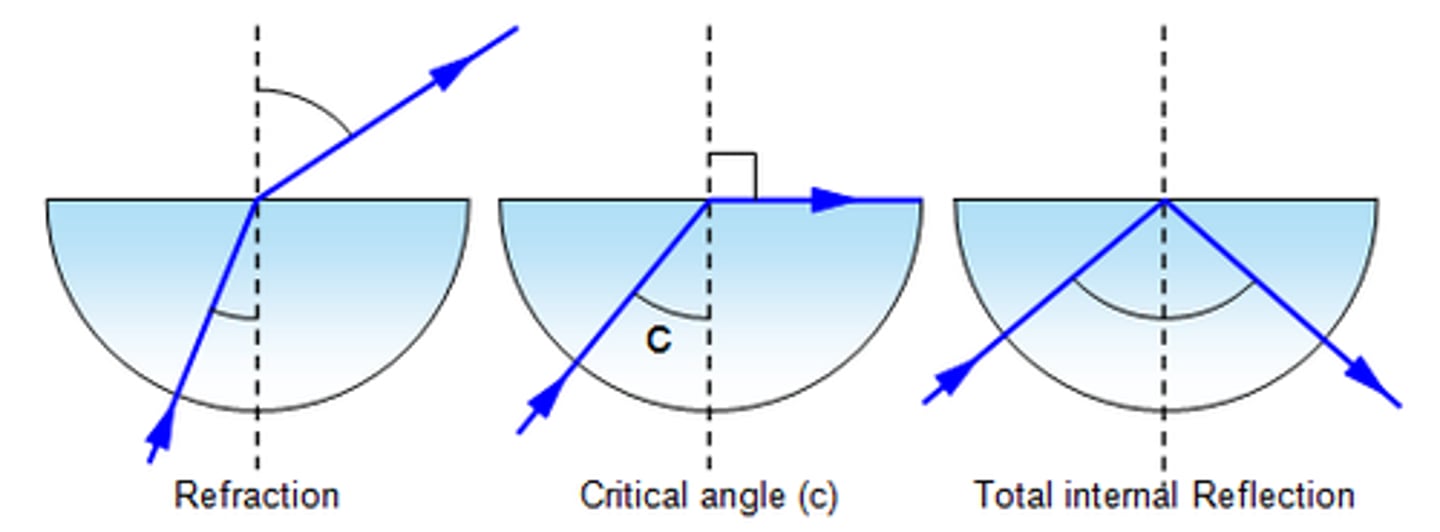
total internal reflection
The angle of incidence must be greater than (not less than) the critical angle.
It occurs when light travels from a medium with a higher refractive index to one with a lower refractive index.
It happens at the boundary between two different media, not within a single substance.
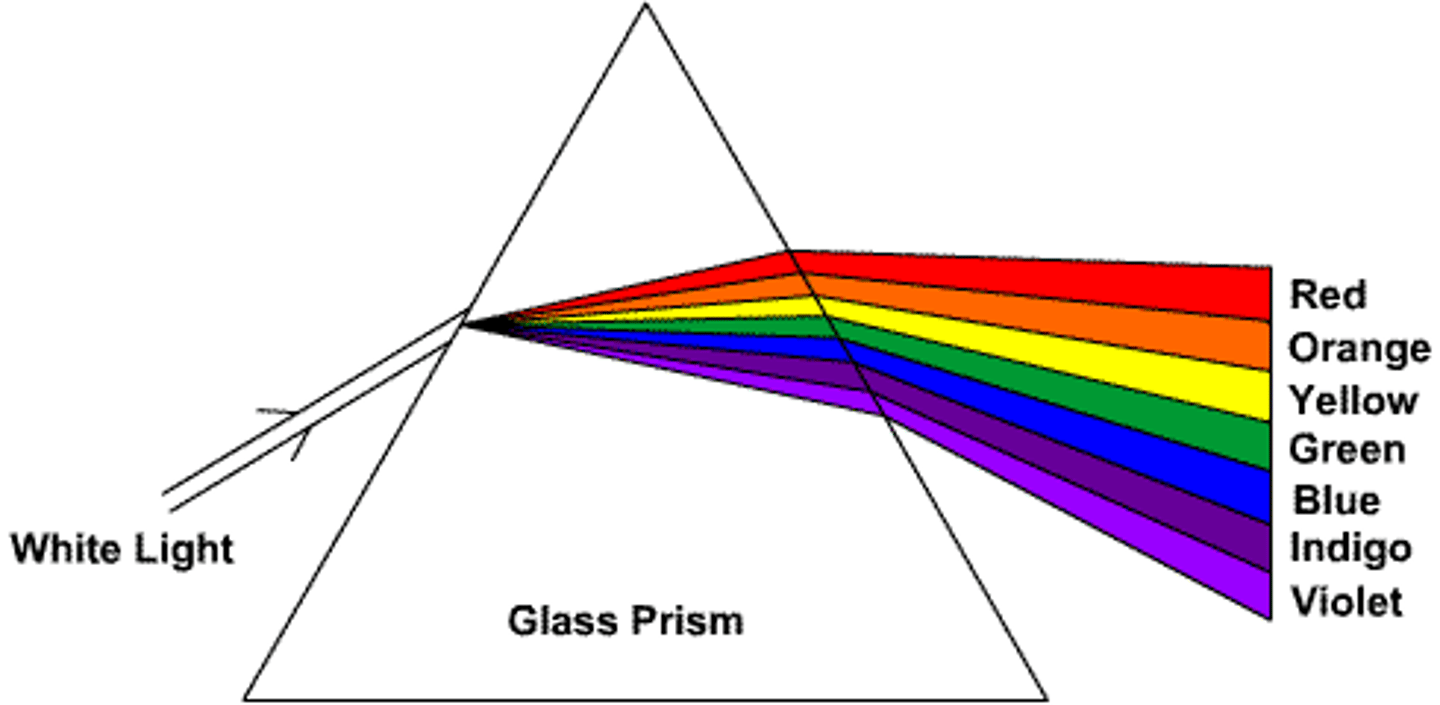
prism splitting
White light is actually a mixture of all the colors of the visible spectrum
Different colors of light have different wavelengths
When light enters the prism, it slows down and bends (refracts)
Each color bends by a different amount because they travel at different speeds through the glass
Violet light bends the most, while red light bends the least
As the light exits the prism, it bends again, further separating the colors
tir in optical fibres
Light enters one end of the fibre and travels through it by bouncing off the sides
The light undergoes repeated total internal reflection as it moves along the fibre
This allows the light to travel long distances without significant loss of intensity.
conditions for tir in optic fibres
The core of the fibre (where light travels) must be denser than the surrounding cladding
The angle at which the light hits the boundary between the core and cladding must be greater than the critical angle
critical angle
the angle of incidence that produces an angle of refraction of 90 degrees
critical angle and refractive index
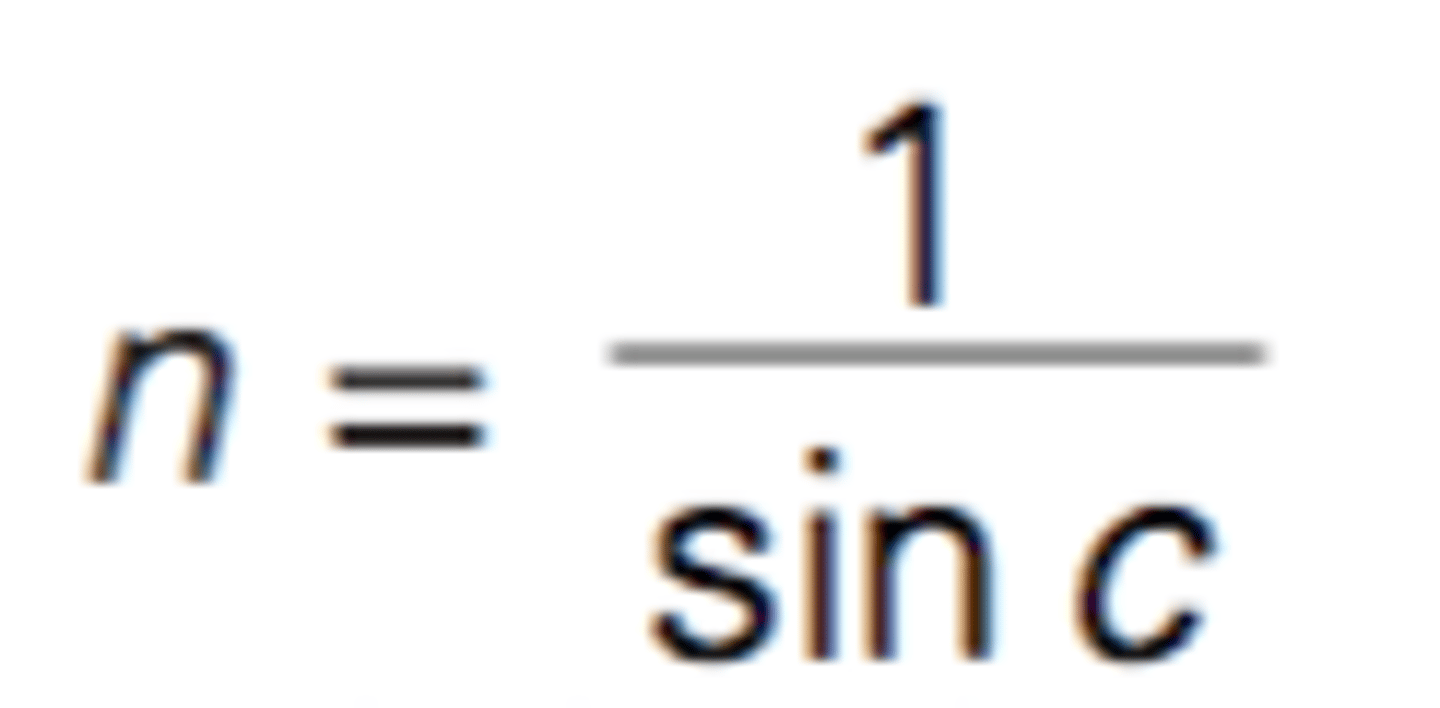
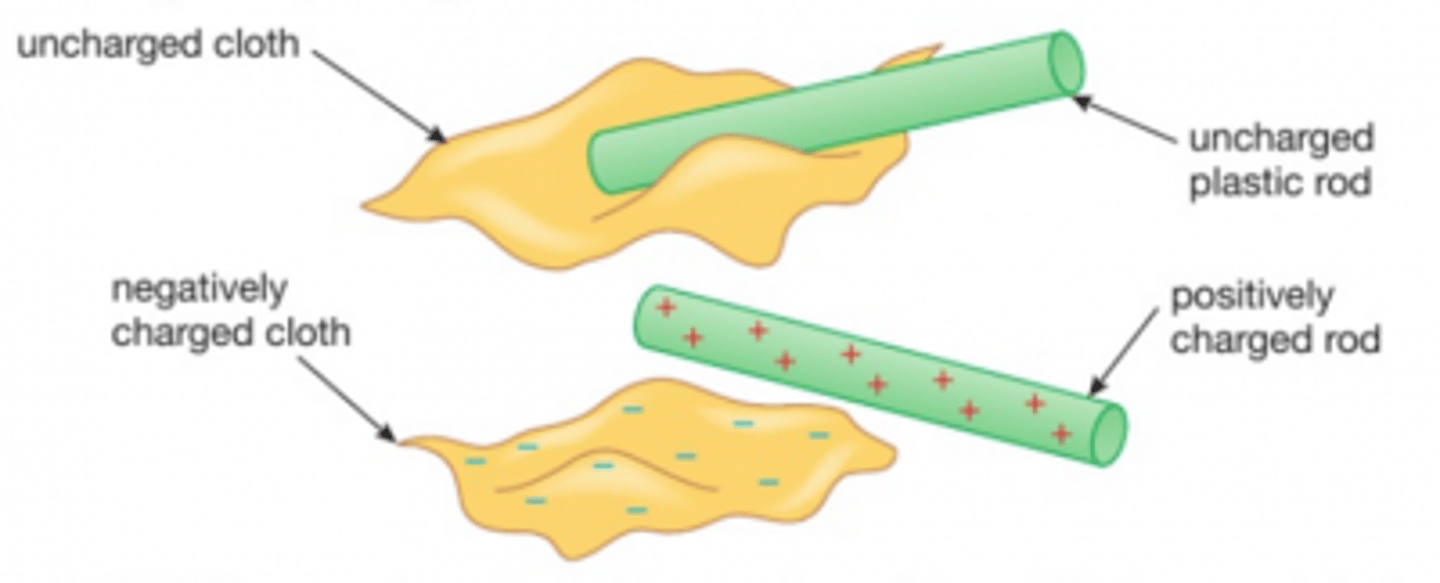
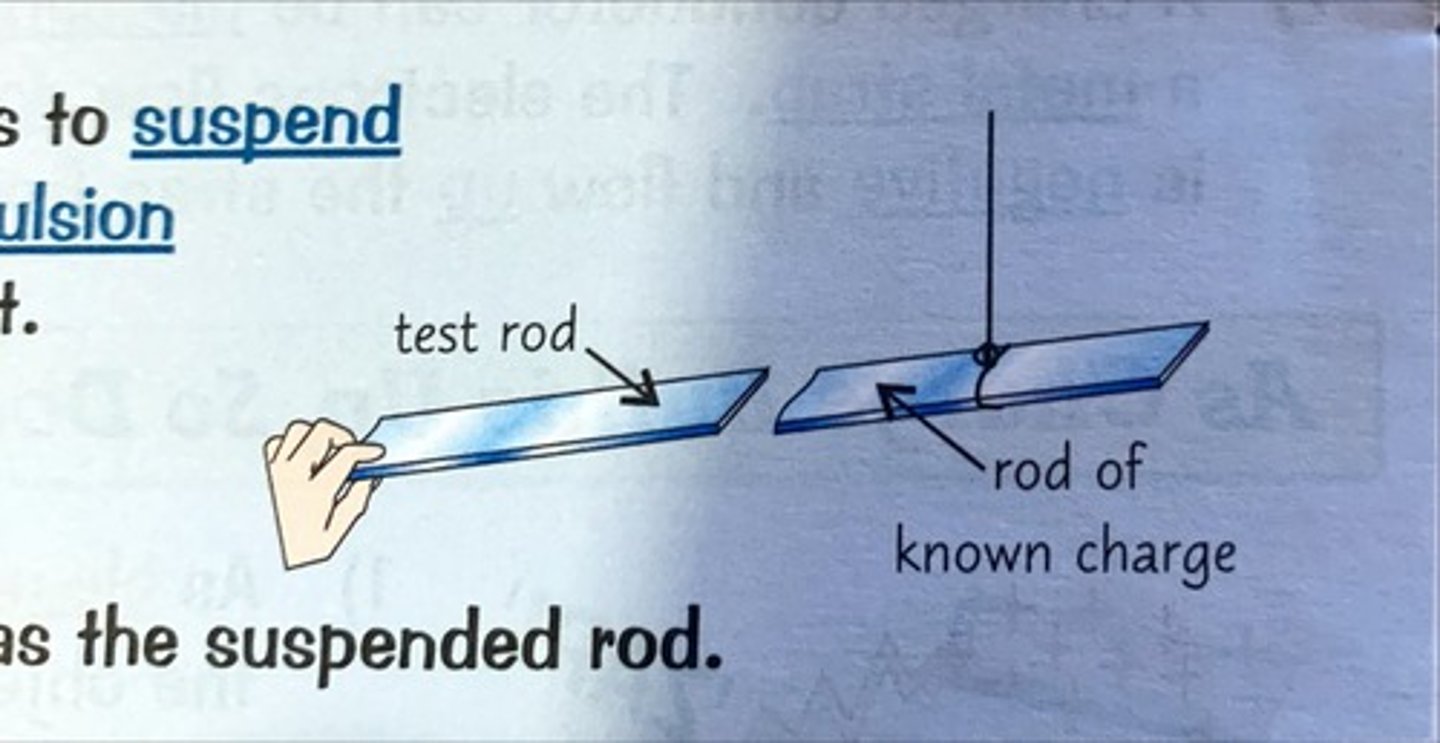
suspending a charged rod
1) Another way of testing whether a rod of material is charged is to suspend a rod with a known charge on a thread and see if there is repulsion or attraction when the rod you're testing is brought close to it.
2) If there is attraction, then the test rod has the opposite charge to the suspended rod
3) If there is repulsion, then the test rod has the same charge as the suspended rod.
Celsius to kelvin
K=C+273
Kelvin to celsius
C=K-273
moon orbit shape
circular
planets orbit shape
slightly eliptical
comet orbit shape
highly eliplitical orbit