IB ESS Topic 2.2
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Productivity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Photosynthesis
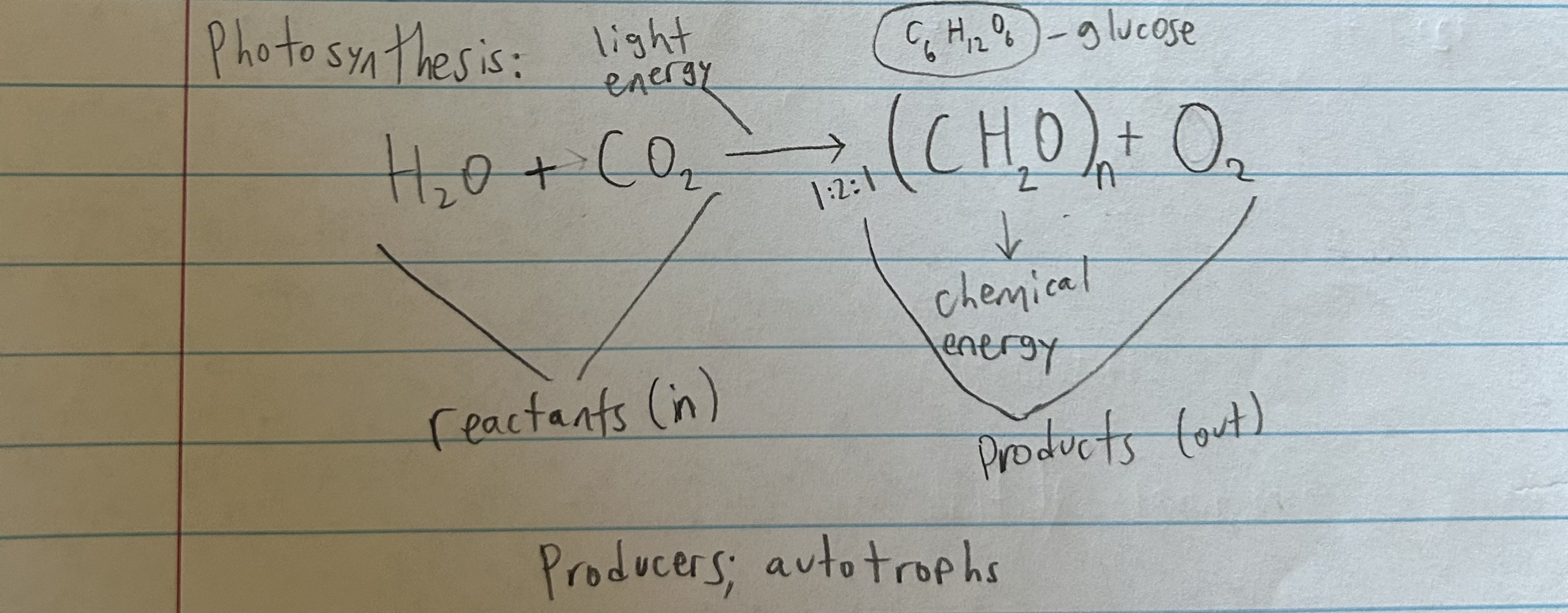
cellular process where CO2 and water are used w/ sunlight to form glucose and oxygen
What type of reaction is photosynthesis
chemical reaction that turns sun’s light energy into consumable chemical energy for organisms
who can perform photosynthesis
only autotrophs
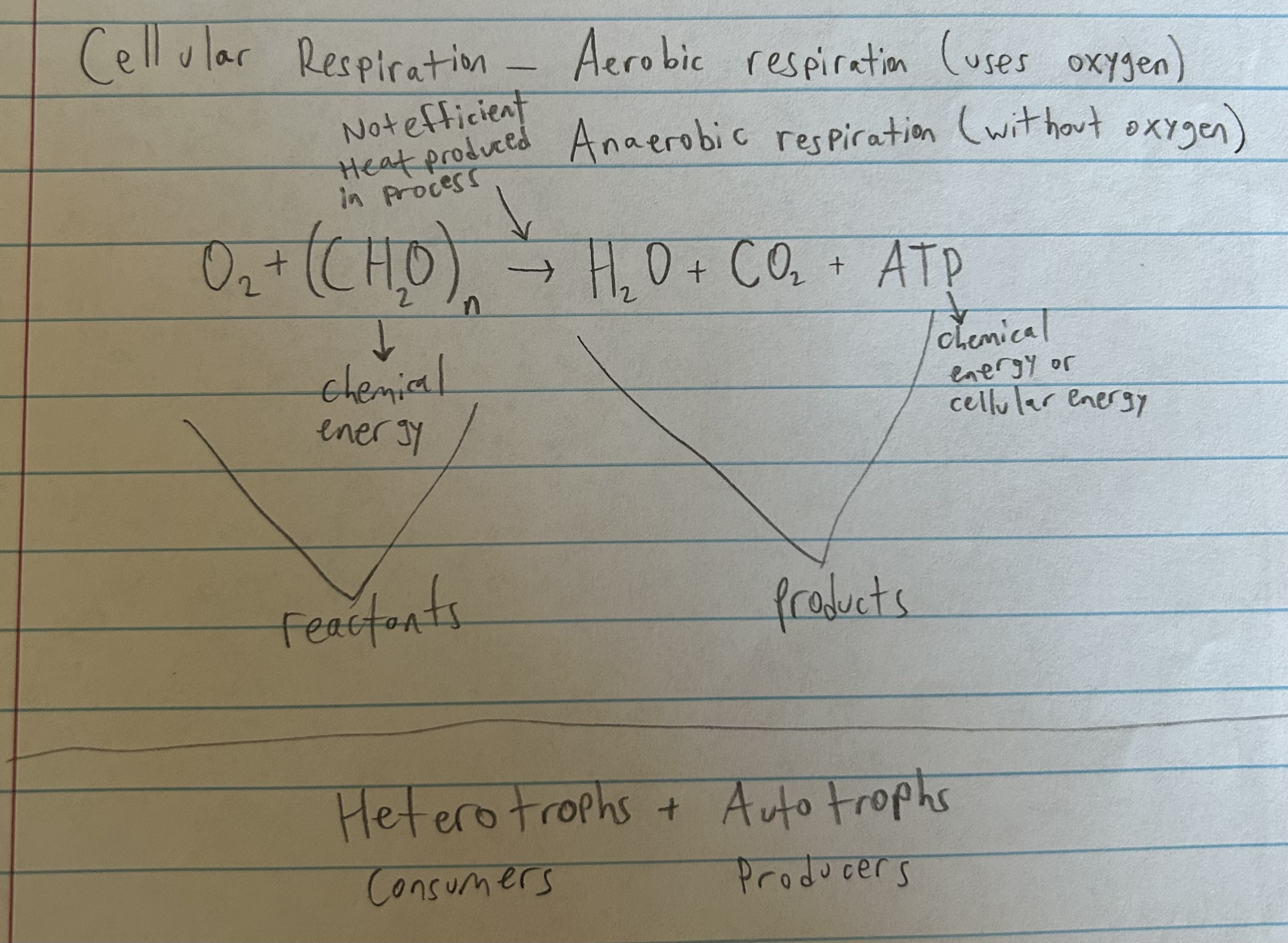
aerobic respiration
uses oxygen and glucose to create ATP, CO2 and water
what organisms use cellular respiration to turn glucose into ATP
heterotrophs and autotrophs
what is released as extra in cellular respiration
heat energy
what is ATP
cellular energy
what do photosynthesis and cellular respiration have in common?
both are chemical reactions that transfer energy between trophic levels
what are trophic levels
represent the transfer of energy through an ecosystem or food chain from one level to next
what is the basic order of trophic levels
sun to autotrophs to heterotrophs
autrophs
auto=automatic, troph=energy. make their own food/energy. producers in an ecosystem
what do autotrophs eat
food made of glucose molecules broken down to release energy. 1st trophic level
photoautotrophs
use sunlight to make energy (plants, algae, etc). contain highest level of energy of all organisms in an ecosystem
chemoautotrophs
use chemical to make energy (all are bacteria). live in guts of organisms or in deep sea waters around ocean vents with no light
heterotrophs
hetero=other, troph=energy. obtain energy from source other than themselves. eat other organisms (auto and heterotrophs). make up all trophic levels other than first level. consumers that do aerobic respiration
photoheterotrophs
use carbon-based organic molecules from other organisms to make food. small % of living organisms. normally only secondary consumers. live in oxygen rich environments w/ little carbon dioxide (rely on other organisms). Ex: carnivorous plants
chemoheterotrophs
majority of heterotrophs and consumers. obtains both its energy and carbon from organic compounds. must eat other organisms. Ex: animals, protists, decomposers, etc
sun as trophic level
provides energy for nearly all organisms on earth. energy flow of life starts w/ sun (solar energy) which is combo of light and radiation energy
producers as trophic level
1st trophic level. organisms that harness sun’s energy via photosynthesis
primary consumers as trophic level
2nd level. organisms that eat producers (herbivores and detritivores). detritivores eat decaying plant material. use aerobic respiration to break down food to release energy
secondary consumers as trophic level
third level. eat primary consumers. small carnivores and some omnivores. use aerobic respiration
tertiary consumers as trophic level
4th level. eat secondary consumers. large carnivores and scavengers. use aerobic respiration
quaternary consumers as trophic level
5th level. eat tertiary consumers. large carnivores or scavengers. ex: humans
decomposers as trophic level
final trophic level that can affect everything at same time. break down dead organisms into biomolecules that can be further broken down to release energy and nutrients into soil. use aerobic respiration. help in nutrient cycling. ex: fungus, mold, bacteria
energy pyramid
simple schematic that visually represents how much energy (biomass), population and productivity levels exist at each trophic level
10% rule
moving from one trophic level to next loses 90% of energy as heat and kinetic energy (respiration) and feces too. kinetic energy used for hunting, hiding, reproduction, etc. Each trophic level only has 10% roughly stored energy from the level before. Causes a decrease in population too. DONT USE 10% RULE IF ACTUAL PERCENT IS GIVEN
food chain
linear depiction of how producers are consumed and how consumers are consumed. small part of giant food web. arrows always go to organism receiving energy from eating
food web
collection of food chains showing different pathways in which energy flows from one organism to the next
what should you do when naming organisms
UNDERLINE SCIENTIFIC NAMES
gross productivity
gain in all biomass of an organism before losses
Net productivity
gross productivity - losses. the actual amount of biomass after respiration
where is gross productivity greatest
coral reefs (shallow water close to land)
where is gross productivity lowest
deserts and deep ocean (little water and high heat)
ecological efficiency equation
(energy used in growth / energy supplied) X 100
Primary productivity is highest where
in areas where conditions for growth are the highest. high levels of insolation, good water supply, warm temperature, high nutrients, constant grow seasons
what are the levels of the ocean and where grows best
photic (top 200 m) has most light and plants grow here (most life), disphotic has less light (twilight), and aphotic (no light). There is a conveyor belt for the oceans to move water around
how does agricultural land connect to productivity
highly maintained and modified ecosystems. goal is to increase npp and biomass of crops. add water and nutrients. nitrogen and phosphorus are most limiting to plant growth. npp in agricultural land is less than other ecosystems despite modifications
total primary productivity
it is gross primary productivity. amount of light energy converted to chemical energy by photosynthesis per unit time (J m^-2 yr^-1)
net primary productivity
GPP - R. R is respiration. energy storage available for whole community of consumers
standing crop
total live material at a trophic level
consumer GSP
food eaten - fecal losses
consumer NSP
change in mass over time. GSP - R
efficiency of assimilation
(gross productivity / food eaten) X 100
efficiency of biomass productivity
(net productivity / gross productivity) X 100
photosynthesis equation
cellular respiration equation
primary productivity
gain in biomass for producers
secondary productivity
gain in biomass by consumers using carbon compounds absorbed and assimilated from ingested food
biomass
total mass of a living organism/amount of living material. always dry weight
respiration
breaking down food often in the form of glucose to release energy which is used in living processes
chemosynthesis
a process where microorganisms use chemical energy from inorganic molecules instead of sunlight to create food
1st law of thermodynamics
principle of conservation of energy. as energy flows through ecosystems, it can be transformed from one form to another but cannot be created nor destroyed
2nd law of thermodynamics
as energy is transferred or transformed in a system, it’s degraded to a less useful form of energy such as heat energy. entropy (disorder) also increases
productivity
the conversion of energy into biomass over time. it’s the rate of growth or biomass increase in plants and animals. measured for plants as mass per unit area per unit time (g m^-2 yr^-1)
biocides
substances or microorganisms that destroy, deter or render harmless living things (ex: disinfectants, pesticides (can include DDT) and don’t break down quickly/at all)