nomenclature of organic chemicals
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
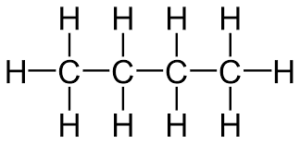
alkane
carbon atoms connected via all single bonds (saturated hydrocarbon).
suffix ‘-ane’, e.g. butane
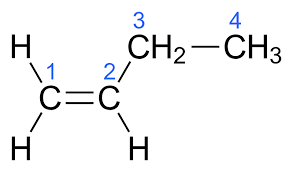
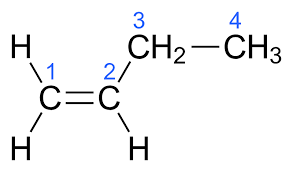
alkene
carbon atoms connected via at least one double bond (unsaturated hydrocarbon) .
for molecules larger than propane, a number must be used to indicate the position of the double bond.
suffix ‘-ene’, e.g. ‘but-1-ene’ or ‘1-butene’
alkyne
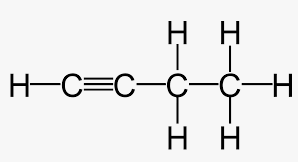
carbon atoms connected via at least one triple bond (unsaturated hydrocarbon) .
for molecules larger than propane, a number must be used to indicate the position of the triple bond.
suffix ‘-yne’, e.g. ‘but-1-yne’ or ‘1-butyne’
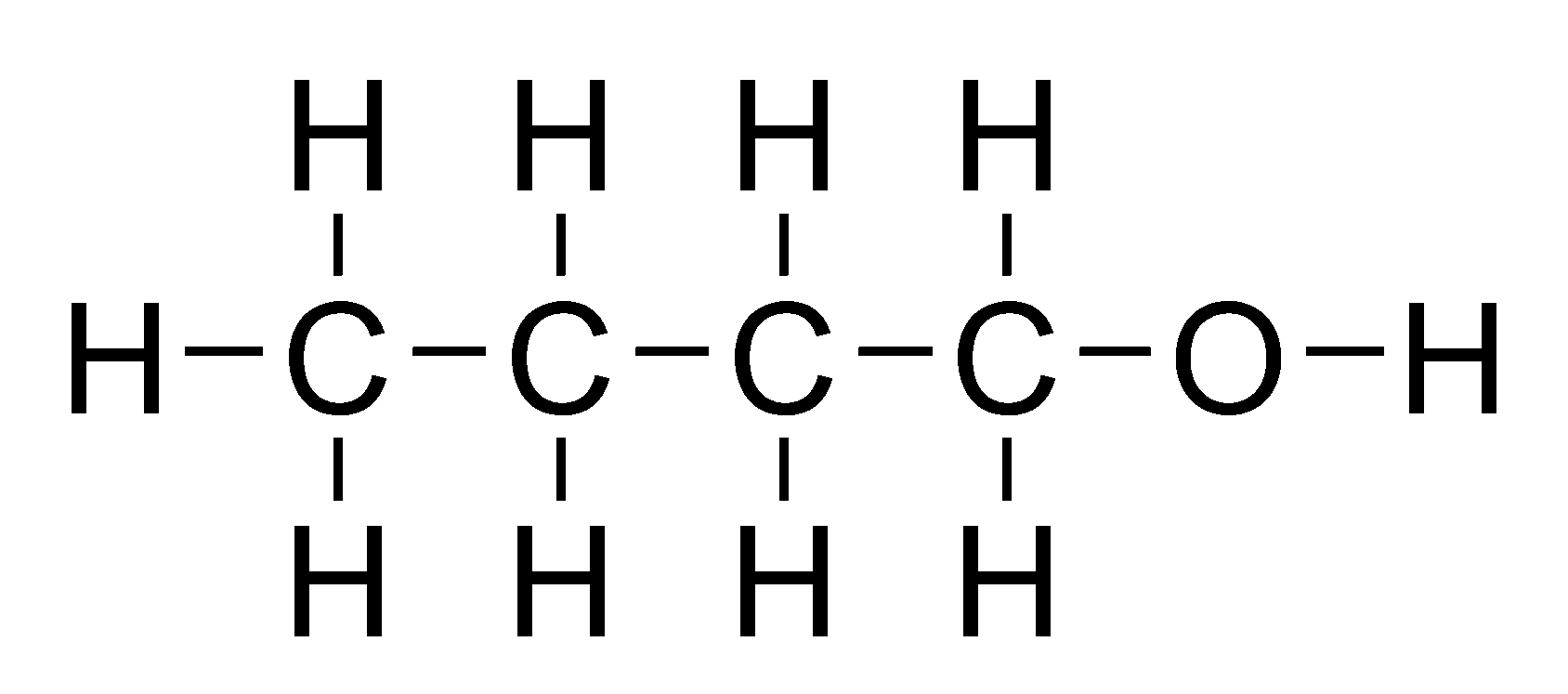
alcohol
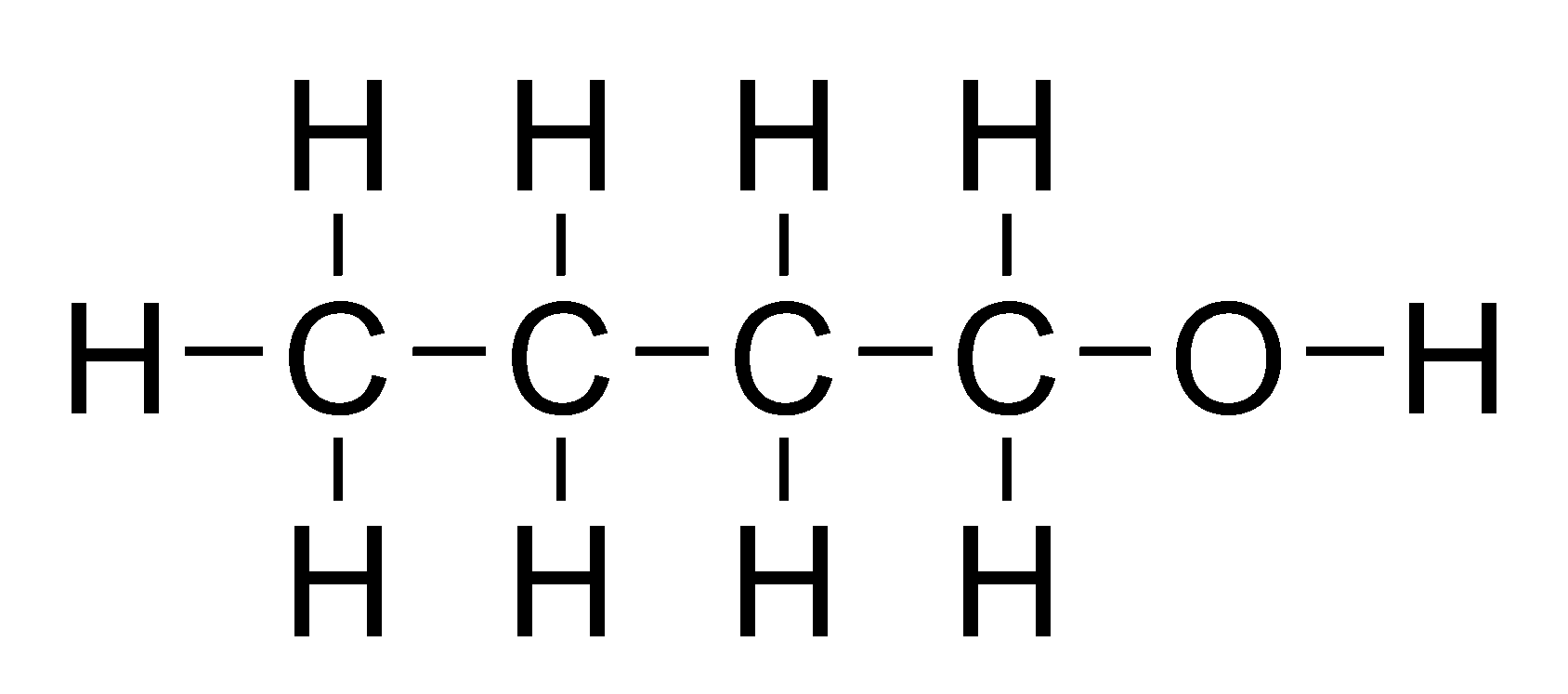
a hydroxyl functional group (OH) attached to a carbon chain.
for molecules larger than ethane, a number must be used to indicate the position of the OH group.
suffix ‘-ol’, e.g. ‘1-butanol’ or ‘butan-1-ol’
primary: C atom OH group is bonded to one other carbon, e.g. ‘1-butanol’
secondary: C atom OH group is bonded to two other carbons, e.g. ‘2-butanol’
tertiary: C atom OH group is bonded to three other carbons, e.g. ‘2-3dimthyl-butan-1-ol’
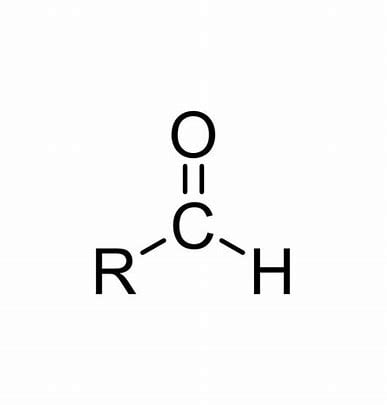
aldehyde
carbonyl (double bonded O) group connected to a carbon bonded to a hydrogen.
number to indicated position of carbonyl group.
suffix ‘-al’, e.g. butanal
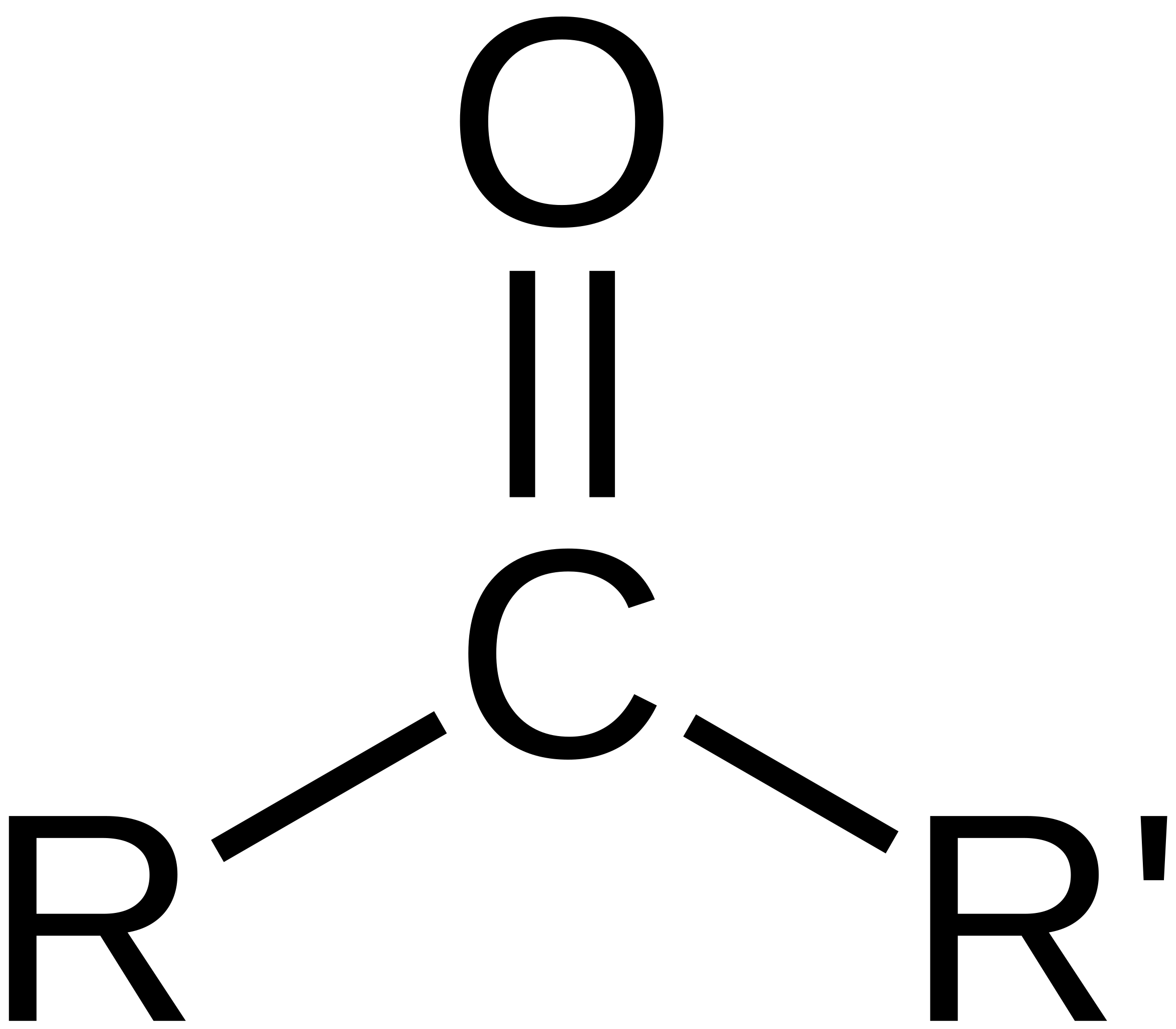
ketone
carbonyl (double bonded O) group connected to a carbon NOT bonded to a hydrogen.
number to indicate position
suffix ‘-one’, e.g. ‘butan-2-one’ or ‘2-butanone’
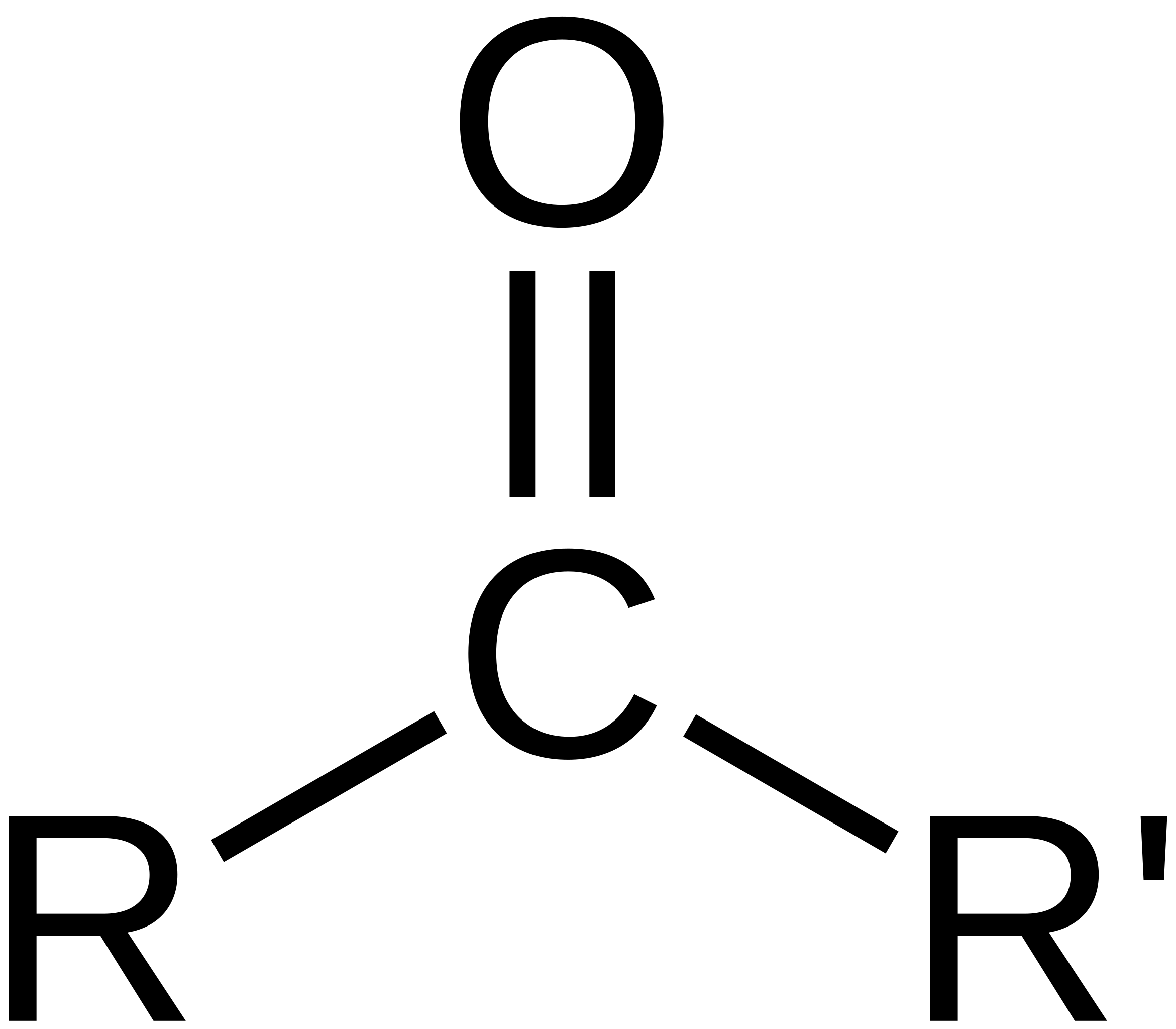
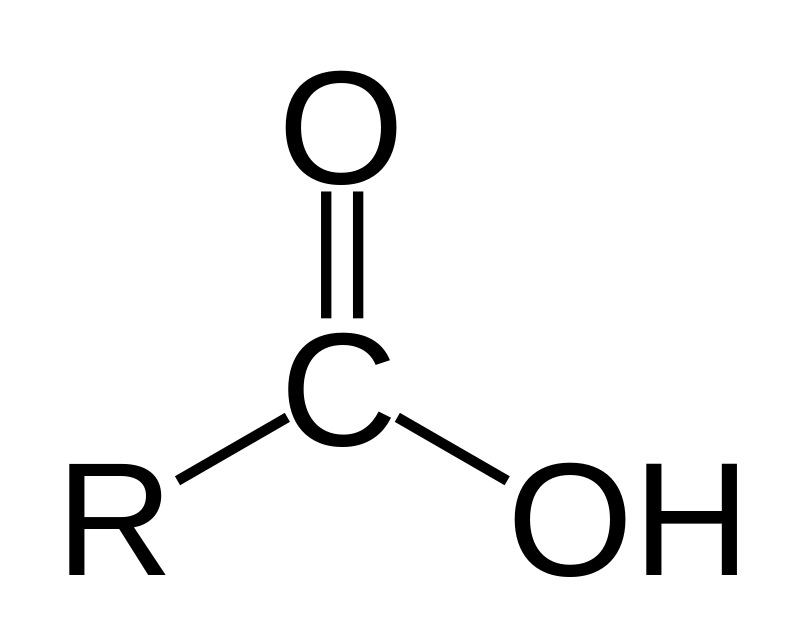
carboxylic acid
carbonyl and hydroxyl group (double bonded O and OH) on 1 carbon
number to indicate position
suffix ‘-oic acid’
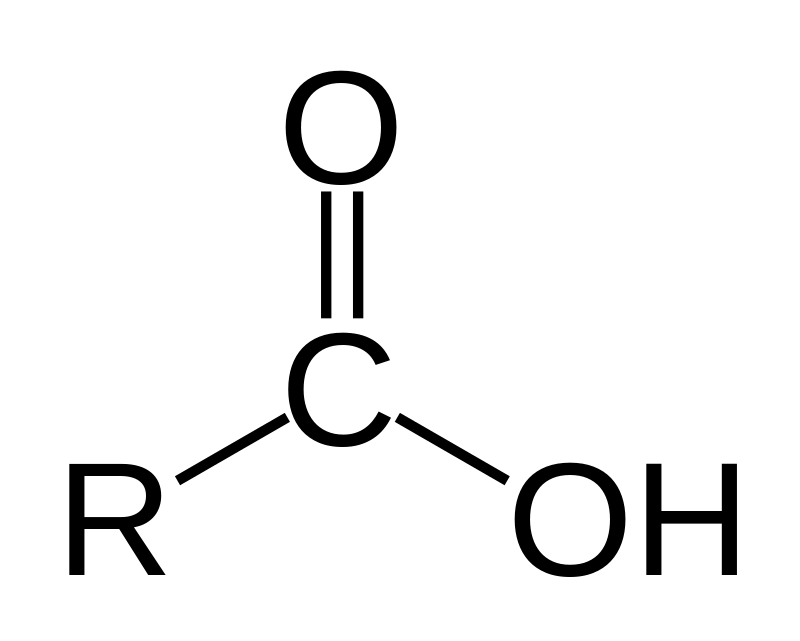

amine
nitrogen attached to a carbon chain

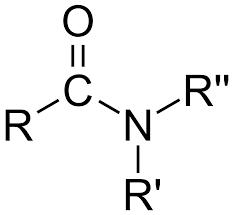
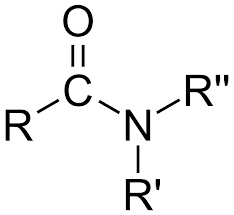
amide
nitrogen attached to a carbon which is double bonded to an oxygen atom
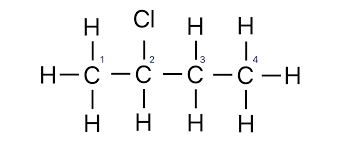
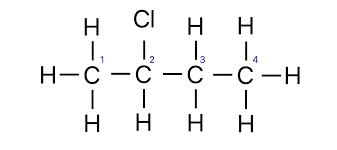
halogenated organic compounds
halogens replacing a hydrogen along a carbon chain