Ultimate Knowt Guide: AP Physics C, 2023
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/303
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics
Vector and Scalar
One-Dimensional Kinematics
Two-Dimensional Kinematics
Newton's Laws
Work, Energy and Power
Linear Momentum and Center of Mass
Rotation I - Kinematics, Force, Work, and Energy
Rotation II - Inertia, Equilibrium, and Combined Rotation
Simple Harmonic Motion
Universal Gravitation
Coulomb’s Law and Electric Fields Due to Point Charges
Calculating Electric Fields and Potentials
Gauss's Law
Circuits Containing Batteries and Resistors
Capacitors
RC Circuits
Magnetic Fields
Faraday's Law
Lenz's Law
Inductors
Maxwell’s Equations
12th
Last updated 1:53 AM on 3/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
304 Terms
1
New cards
Vectors
These specify the magnitude and direction.
2
New cards
Scalars
These specify the magnitude and no direction.
3
New cards
Speed
indicates how fast an object is moving but not in what direction.
4
New cards
Velocity
indicates both how fast an object is moving and in what direction.
5
New cards
arrow
A vector is generally represented by an \_____ whose direction is in the direction of the vector and whose length is proportional to the vector’s magnitude.
6
New cards
positive
To multiply a vector by a \_________ scalar , simply multiply the vector’s magnitude by the scalar.
7
New cards
negative
To multiply a vector by a \________ scalar , change the vector’s magnitude and reverse the direction of the vector.
8
New cards
Speed
Indicates how fast an object is moving but not in what direction.
9
New cards
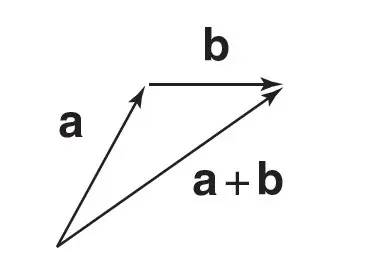
Vector Addition
10
New cards
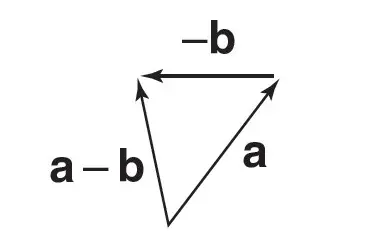
Vector Subtraction
11
New cards
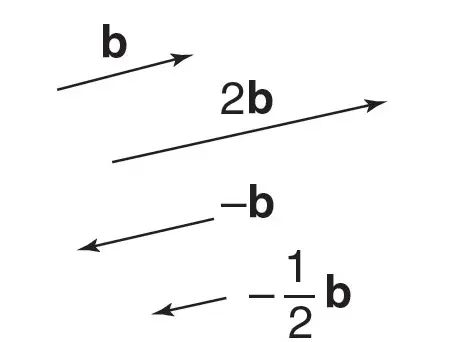
Scalar Multiplication
12
New cards
perpendicular
If two vectors are \________ , their dot product will equal zero [cos(π/2) \= 0].
13
New cards
parallel
If two vectors are \_______ , their dot product will equal the product of their magnitudes (cos 0 \= 1).
14
New cards
antiparallel
If two vectors are \_________ , their dot product will be the negative of the product of their magnitudes [cos(π) \= −1].
15
New cards
Scalar Product
Dot product is also known as?
16
New cards
third
The cross product of two vectors yields a \____ vector.
17
New cards
Vector Product
Cross product is also known as?
18
New cards
units
All measurements and observable quantities have \________; otherwise they would be meaningless.
19
New cards
Multiplication and division
Units are multiplied and divided just as variables are.
20
New cards
Addition and subtraction
The sum or difference of two quantities with the same units has those same units.
21
New cards
Exponential function
The argument x of an \__________, such as ex, must be dimensionless, such as the ratio of two lengths.
22
New cards
dimensionless
Arguments of trigonometric functions, such as sinx and tan−1x , also must be \___________
23
New cards
Velocity
Indicates both how fast an object is moving and in what direction.
24
New cards
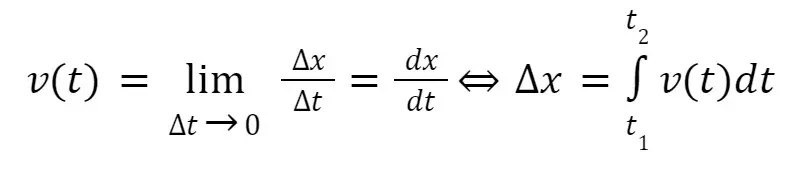
Instantaneous velocity (2D Kinematics)
25
New cards
Instantaneous speed
The magnitude of instantaneous velocity.
26
New cards
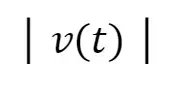
Instantaneous speed (2D Kinematics)
27
New cards
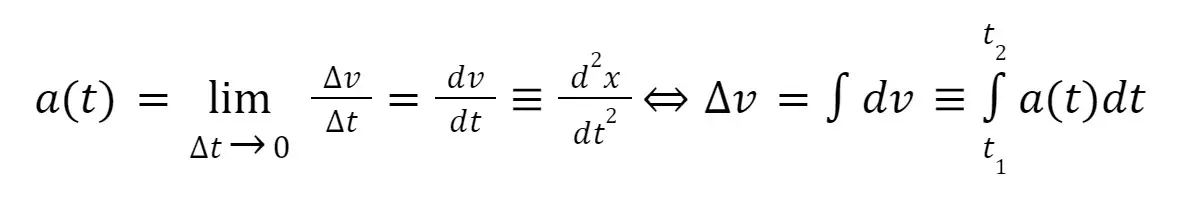
Instantaneous acceleration (2D Kinematics)
28
New cards
Displacement
The net difference in the location of an object independent of how the object got there.
29
New cards
Average quantities
These are often denoted as the variable with a bar over it (v, a)
30
New cards
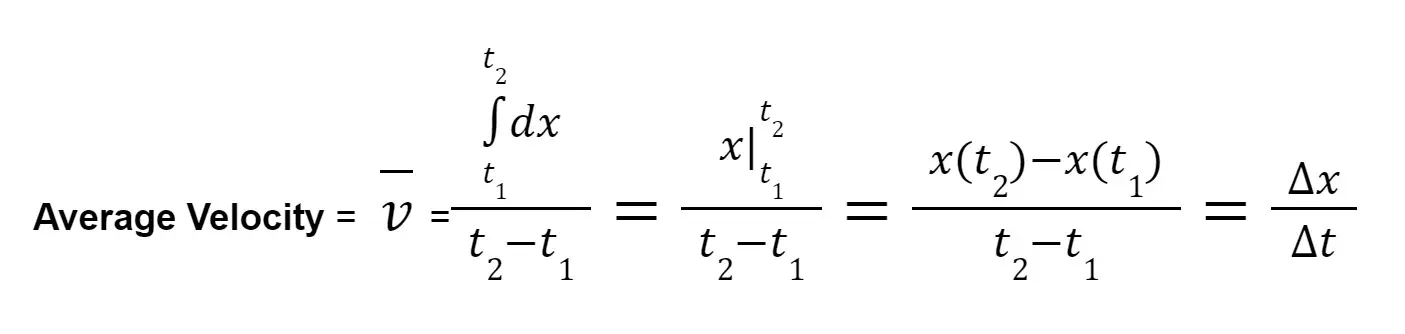
Derivation of Average Velocity
31
New cards
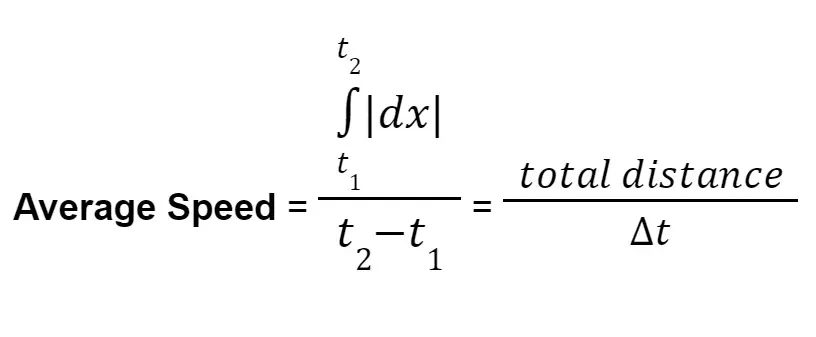
Derivation of Average Speed
32
New cards
Total Distance
The distance traveled irrespective of direction
33
New cards
vectors
Velocities and displacements are \__________
34
New cards
scalars
speeds and distances are \_________
35
New cards
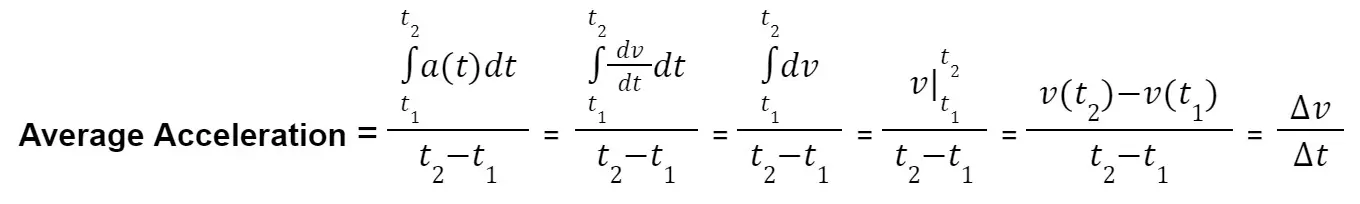
Derivation of Average Acceleration
36
New cards
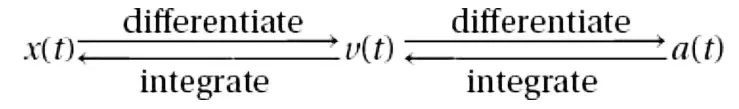
fundamental schematic
37
New cards
positive curvature
Positive acceleration corresponds to \____________
38
New cards
negative curvature
Negative acceleration corresponds to \_________
39
New cards
Non Uniform accelerated motion problems
These generally involve conversion between position, velocity, and acceleration via differentiation or integration .
40
New cards
UAM problems
These problems give you a set of values (such as x0, v0, a, t1, and t2) and ask you to calculate other values from them.
41
New cards
position vector
A natural way to describe the position of an object in more than one dimension is to define a \_______ that points from the origin to the location of the object.
42
New cards
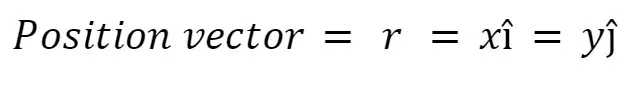
Position Vector Definiton
43
New cards
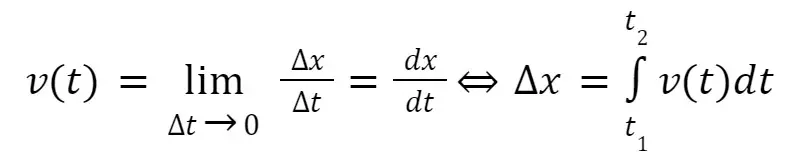
Instantaneous velocity (2D Kinematics)
44
New cards
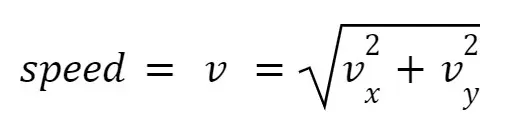
Instantaneous speed (2D Kinematics)
45
New cards
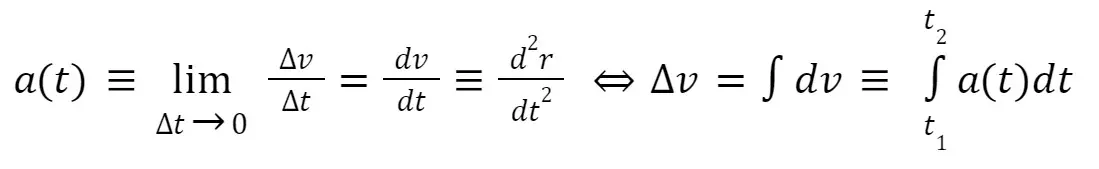
Instantaneous acceleration (2D Kinematics)
46
New cards
two-dimensional vector equations
The definitions of velocity and acceleration are \____________ , each of which is equivalent to a set of two one-dimensional equations.
47
New cards
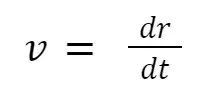
definition of velocity
48
New cards
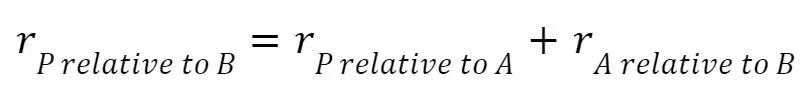
Vector addition relates the position of an object relative to two different frames of reference
49
New cards
Tangential Acceleration (a∥)
Affects only the magnitude of the velocity vector.
50
New cards
Radial Acceleration (a⊥)
Affects only the direction of the velocity vector.
51
New cards
ω
determines the sense of rotation
52
New cards
magnitude of ω
determines how quickly the r(t) vector rotates.
53
New cards
Phase shift angle (ϕ)
A parameter that determines the initial angle and thus the initial position.
54
New cards
Nonuniform circular motion
Refers to motion in a circular path with nonconstant velocity.
55
New cards
Newton’s First Law
When the net force acting on a body is zero, its acceleration must be zero, meaning that the velocity remains constant.
56
New cards
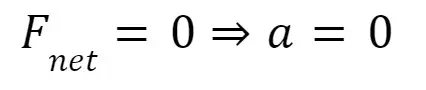
Newton’s First Law
57
New cards
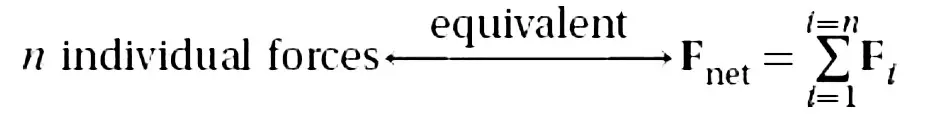
Superposition of Forces
58
New cards
Inertia
It refers to how much an object resists a change in its velocity and is measured by mass.
59
New cards
Newton’s Second Law
This law reveals that force is a vector parallel to the acceleration.
60
New cards
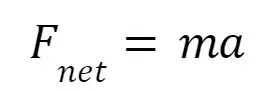
Newton’s Second Law
61
New cards
pounds or newtons
Force is measured in \____________.
62
New cards
Newton’s Third law
For every force exerted by one object on another, there is another force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction that is exerted back by the second object on the first.
63
New cards
Mass
A measure of inertia and is the proportionality constant that relates force to acceleration in Newton’s second law.
64
New cards
Kilograms
SI Unit of Mass
65
New cards
Weight
The magnitude of the force exerted on an object by the closest nearby planet (typically Earth) according to the formula.
66
New cards
Gravitational Force
The most prevalent force in the universe, pulling together on any two objects with mass in the universe.
67
New cards
Normal Force
Denotes FN. Its magnitude is determined by Newton’s second law. Always perpendicular.
68
New cards
Frictional Force
Force that resists the sliding or rolling of one solid object over another.
69
New cards
Static Friction
Objects are not sliding relative to each other.
70
New cards

Static Friction
71
New cards
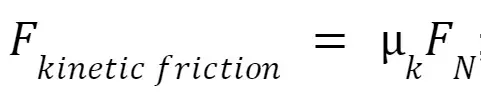
Kinetic Friction
72
New cards
Kinetic Friction
Objects are sliding relative to each other.
73
New cards
Tension Force
A force that develops in a rope, thread, or cable as it is stretched under an applied force.
74
New cards
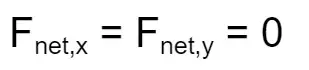
Static equilibrium (object at rest)
75
New cards
centripetal force
The \_________ is the net force required for circular motion . It can be provided by any number of forces such as tension, normal force, gravity, or friction.
76
New cards
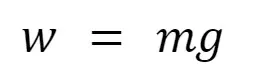
Weight formula
77
New cards
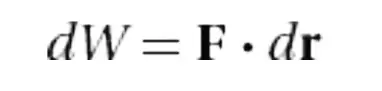
Work by One Force
78
New cards
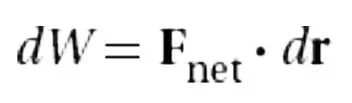
Work due to multiple forces
79
New cards
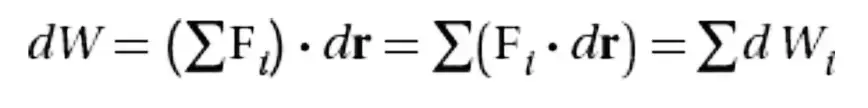
Work due to multiple forces expanded
80
New cards
Joule
The unit of work and energy
81
New cards
Work
the change in an object’s kinetic energy due to the action of a given force.
82
New cards
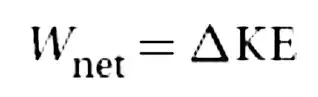
Work–kinetic energy theorem
83
New cards
Work–kinetic energy theorem
This is the first and most fundamental of a number of equations we will soon derive relating various types of work and energy. This theorem is a restatement of Newton’s laws, and it is always valid.
84
New cards
Energy
never created or destroyed; it merely changes form.
85
New cards
Conservative forces
Are involved in reversible energy conversions, where we can get our kinetic energy back.
86
New cards
Nonconservative forces
Are involved in irreversible energy conversions; though the total energy is always conserved, energy is converted to forms from which we cannot recover
87
New cards
Conservative forces
kinetic energy ⇒ potential energy ⇒ kinetic energy
88
New cards
Nonconservative forces
kinetic energy ⇒ sound, heat, etc. ⇒ cannot be easily recovered
89
New cards
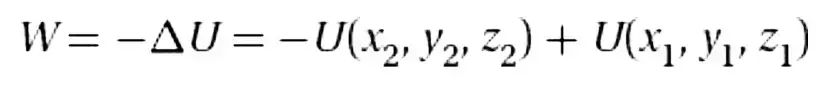
General definition of a potential energy function
90
New cards

Gravitational potential energy
91
New cards
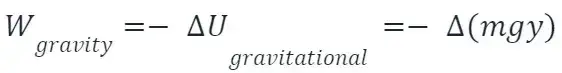
Work done by gravitational force
92
New cards
spring constant
The proportionality constant k , called the \_____________ or force constant, is a property of the particular spring.
93
New cards
negative
The direction of the spring force is opposite the displacement, as indicated by the \______ sign.
94
New cards
restoring force
Because the force always tries to restore the spring to its relaxed state, whether it has been stretched or compressed, it is called a \_______________ .
95
New cards
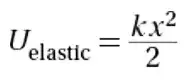
Elastic Potential Energy
96
New cards
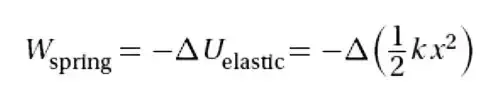
Work Done by Spring Force
97
New cards

general form of the energy conservation equation
98
New cards
Power
The rate at which a force does work on a system
99
New cards
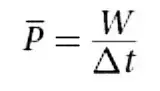
Average power
100
New cards
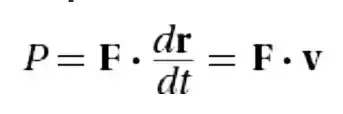
Constant power