G12 Physics
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Underlinned saya nai
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
In a circular motion, the object _____
In a circular motion, the object just moves in a circle.
In a rotational motion, the object _____
In a rotational motion, the object rotates about an axis.
A rigid body
A rigid body is a body that does not deform or change shape.
When is angular acceleration constant?
When an object (rigid body) rotates, it speeds up or slows down. During these time intervals, the angular velocity is changing therefore it has an angular acceleration. If its angular velocity changes at a constant rate then we can say that the angular acceleration is constant and the motion is called the rotational motion under constant angular acceleration.
Under what condition the angular acceleration of a rotating object is equal to zero?
When the angular velocity is constant or when the object is at rest.
Relation between linear and angular quantities
s = rθ
v = rω
𝑎𝑡 = rα
Linear velocity is also known as ____
Tangential velocity
Where is angular velocity?
It’s on the Z axis
If the magnitude of the angular velocity of a rotating object changes, the magnitude of _____ will also change and the object will have a tangential acceleration.
linear velocity / tangential velocity
The direction of tangential acceleration is always ____ to the circular path.
tangent
The direction of the angular velocity vector is ______ to the plane of rotation, and along the axis of the rotation.
perpendicular
When the angular velocity is increasing, the angular acceleration vector points in the ______ direction.
same
When the anuglar velocity is decreasing, the angular acceleratino vector poitns in the _____ to the angular velocity.
opposite
The bigger the radius, the bigger the velocity when angular velocity is constant for both cases.
The carousel question
circular motion of a particle of the object (diagram)
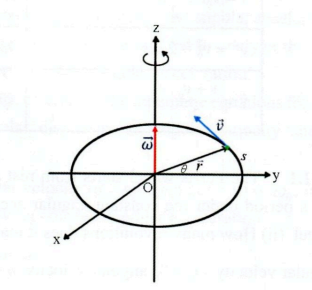
If the object is ______, angular velocity and the angular acceleration have same direction.
velocity is increasing / speeding up
If the object is ______, angular velocity and the angular acceleration have opposite direction.
velocity is decreasing / slowing down
The cause of V’s value = _____
tangential acceleration
The cause of V’s direction = ______
centripetal acceleration
If an object rotates with constant angular velocity, its acceleration is zero.
False because every circular motion (angular quantities) has centripetal acceleration.
Angular velocity is the rate of ______ with respect to displacement.
rotation
In non-uniform circular motion, an object is moving in a circular path with a varying ______
speed