lecture 5: men's reproductive history and physical exam
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
corpus spongiosium
ventral column of erectile tissue containing the urethra (cavernosum urethra)
tunica albuginea of testis
fibrous envelope of the corpus cavernosum
-thinner, whiter in color, more elastic
sperm, testosterone--> secondary sex characteristics
what do the testes produce?
•Travel from testes & epididymis to vas deferens to seminal vesicles, out ejaculatory duct
path of spermatogenesis
prostate issues
urinary hesitancy in males suggests
•If you could spend rest of your life with your sexual function just as it is, how would that be?
•How is it compared to when you were ____?
•How does your partner feel about it?
•Do you have interest in sexual intercourse?
question to assess degree of sexual satisfaction
erectile dysfunction
-can be an early symptom of coronary artery disease
-precedes cardiac symptoms by 10 years
1.Inspect pubic hair characteristics & distribution
2.Retract foreskin if patient uncircumcised
3.Inspect the glans noting: color, smegma, external meatus of urethra, urethral discharge
inspection steps of male GU exa
•Palpate length of shaft, ventrally along the corpus spongiosum, & laterally both corpora cavernosa to detect nodules or plaques
how should you palpate the penis?
•Compress the glans anteroposteriorly between the thumb and forefinger
•Open & inspect the meatus and terminal urethra
how should you assess for penile discharge?
•Rugae produced by contractions of dartos muscle (only muscle besides platysma not to attach to a joint)
what produces the rugae of the scrotum?
•(a) testes
•(b) tunica vaginalis
•(c) epididymis (head, body, & tail)
•(d) spermatic cord
•(e) inguinal lymph nodes.
sequence to examine the scrotum
•Compare the spermatic cords by simultaneously grasping each at neck of scrotum. With thumb in front & forefinger behind scrotum, GENTLY compress cord
method to examine the spermatic cord
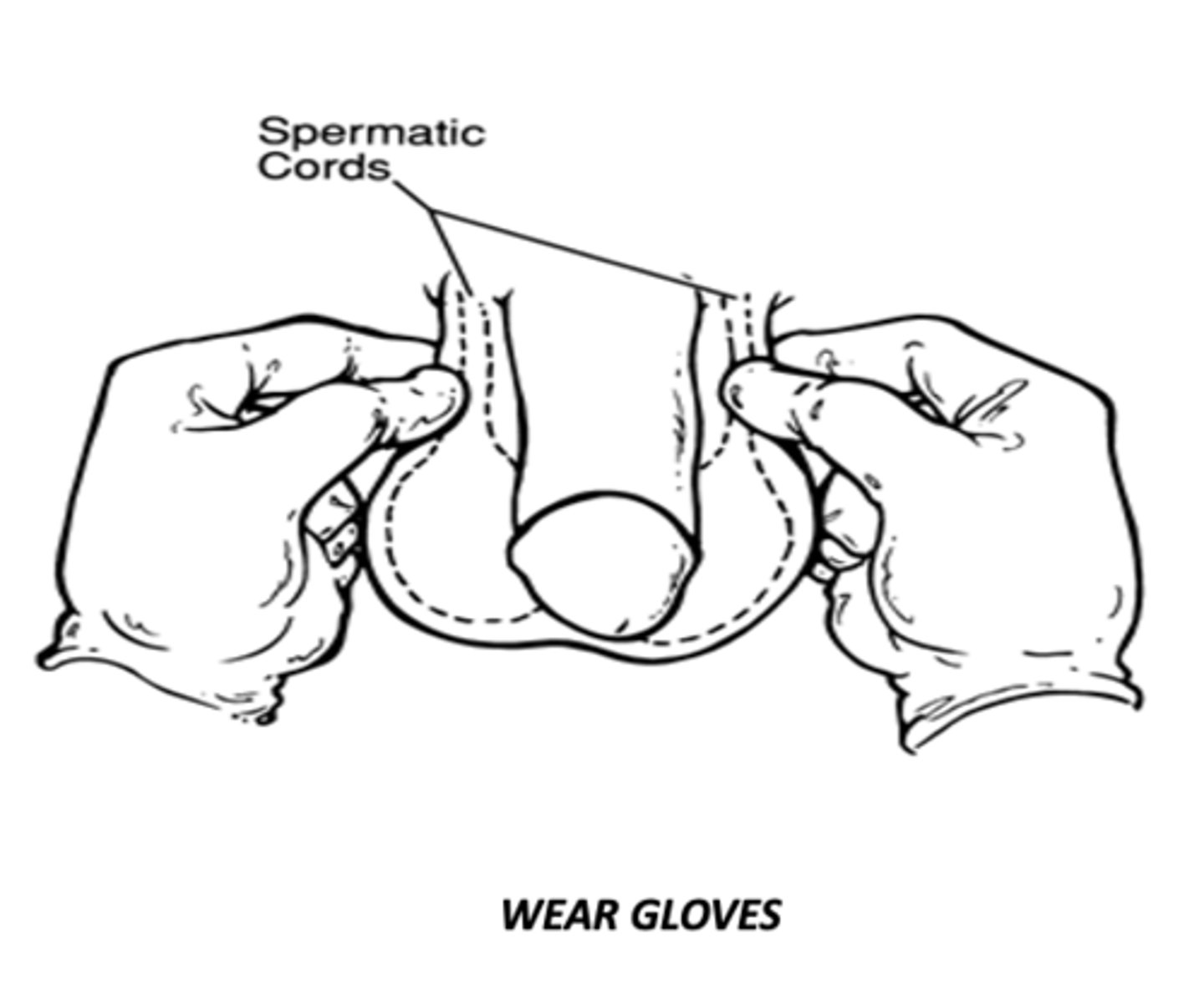
vas deferens
felt as a distinct hard cord, which can be separated from other cord structures
the spermatic cord & testes, so identify these structures & anatomic relations to the mass
inguinal hernias always descend in front of
Indirect inguinal hernia
what type of hernia?
•follows the pathway that the testicles made during prebirth development. It descends from the abdomen into the scrotum. This route is normally closed by birth but remains a potential space.
-more common with age, but can occur with any age
direct inguinal hernia
what type of hernia?
-occurs slightly to the inside of the site (medial), comes through weakened abdomen muscles
-rarely protrudes into the scrotum; almost ALWAYS in middle aged and elderly bc the abdominal walls weaken
femoral hernnia
what type of hernia?
-abdominal contents (usually intestine) can slip into the canal
- causes bulge below the inguinal crease in roughly the middle of the thigh
-HIGH RISK OF BECOMING irreducible and strangulated
small: by age 2
large: 2-4 years old
when do umbilical hernias usually close by?
•Disruption of the conjoined tendon
•Weakening of the transversalis fascia
•Tears in the internal oblique muscles
•Tear in oblique aponeurosis causing dilation of the superficial inguinal ring
etiologies of sports hernias
place light against posterior wall of scrotum, shining anteriorly through mass
how do you perform scrotal transillumination?
-most appear opaque
how do hernias appear on scrotal transillumination?
active hemorrhoids
relative contraindication to rectal exam
values below 4.0 are considered good
-above 4.0 is a risk for prostate cancer
normal PSA finding
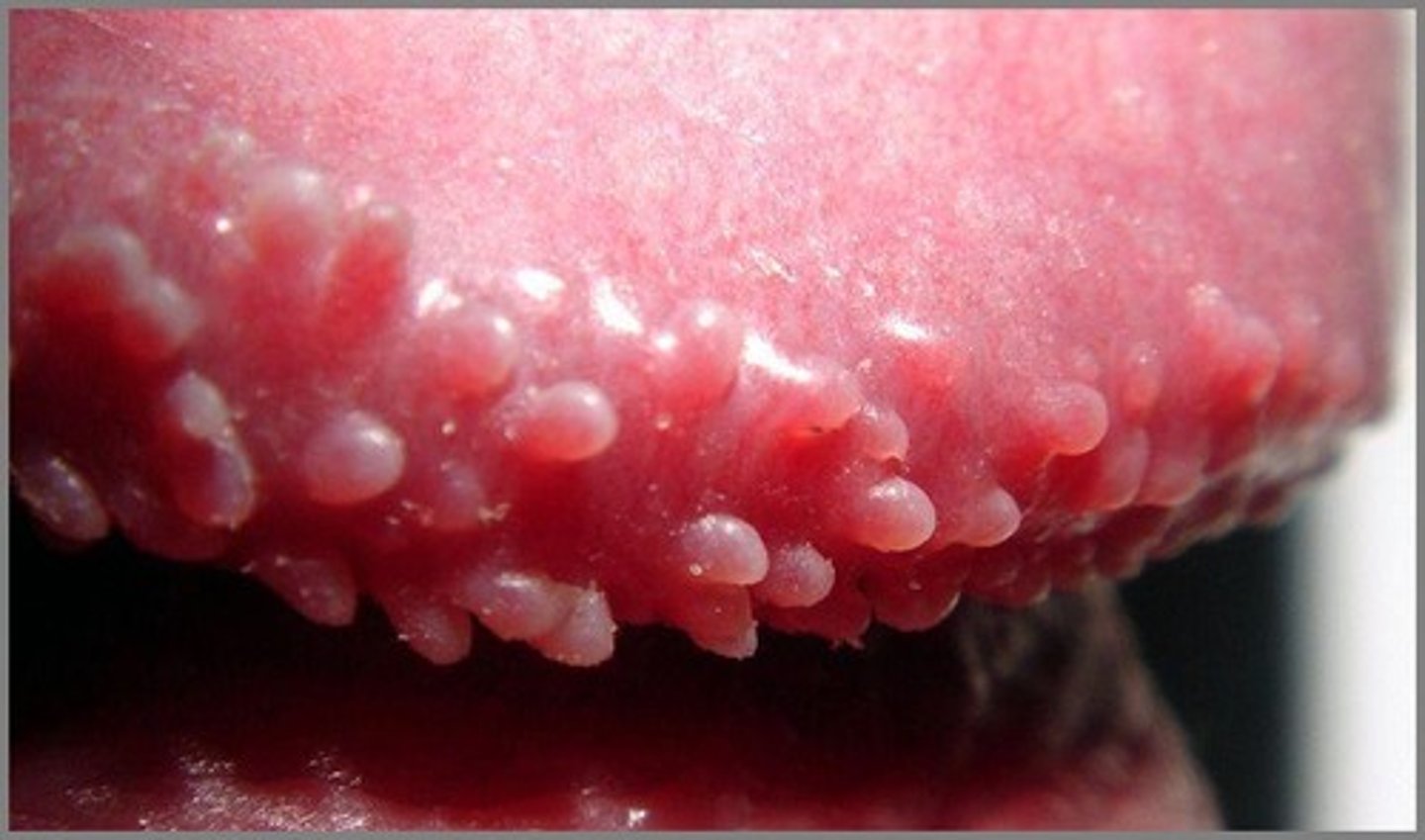
pearly penile papules
Small skin colored bumps that often form in rows around the glans. Considered a normal anatomic variant, not contagious, and are asx
Considered harmless, they will decrease with age, but can last throughout ones lifetime
fordyce's spots
-sebacous glands found on shaft and scrotum of penis
-cosmetic concern only
inguinal adenopathy
swelling associated with shaving
•Usually congenital in children
•Due to trauma in adults
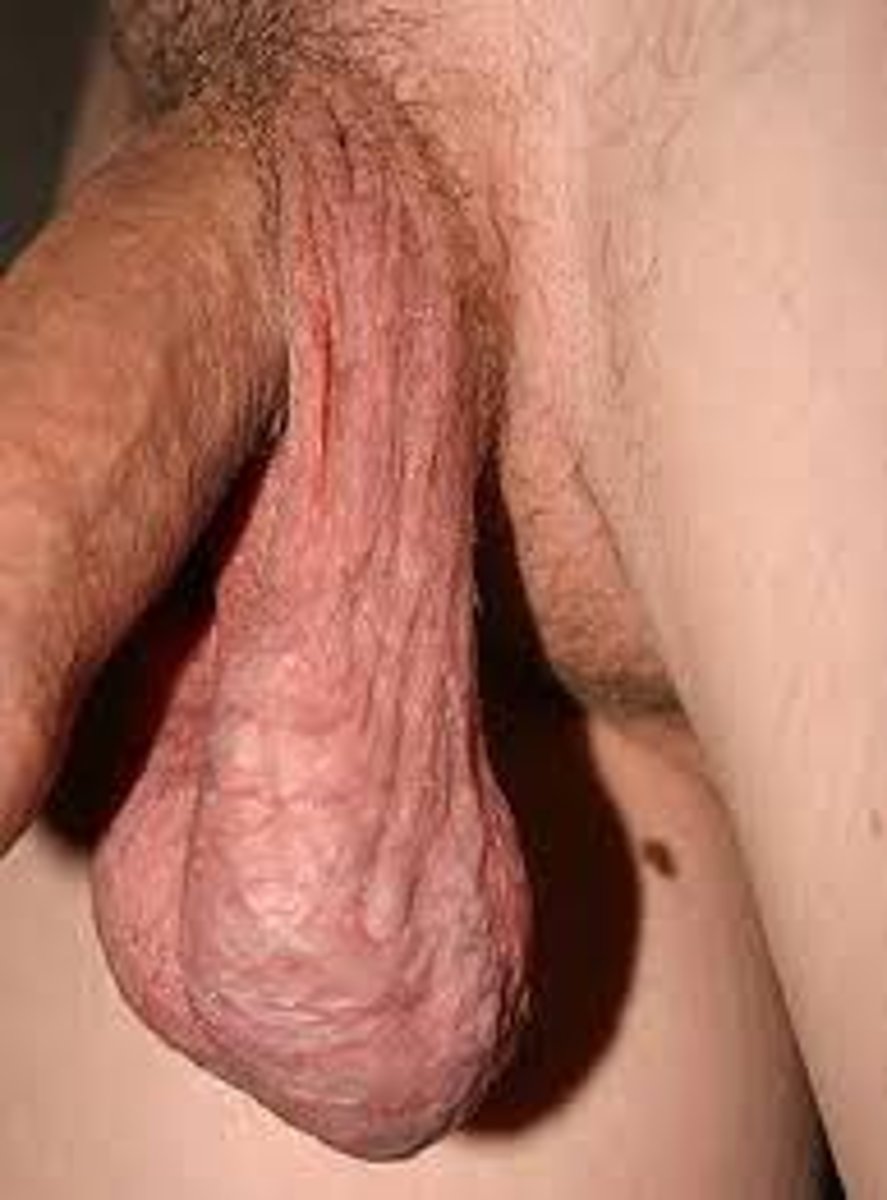
etiology of hydrocele
•When scrotum is investigated with focused beam of light, scrotum transilluminates, revealing a homogenous glow, without internal shadows
transillumination findings of hydrocele
scrotal ultrasonography
if suspect hydrocele after transillumination, whhat do you do next?
orichitis
-testes bilateral swollen, tender, and usually extremely painful
-associated with mumps
-mumps (unimmunized)
-primary or secondary epididymitis
-hydrocele
associated diseases of orchitis
Paraphimosis
condition in which a retracted prepuce cannot be pulled forward to cover the glans
gonorrhea
-purulent discharge 7-10 days after sex exposure usually indicates
herpes simplex
-small group of vesicles on erythematous base, frequently occuring on glans or prepuce
-when vesicles rupture, produces painful superficial ulcers that heal in 5 to 7 days
-ulcers may serve as portals of entry for bacteria
carcinoma of the penis
-appears as irritation or inflammation of the foreskin or glans, commonly the dorsal corona or the inner lip of foreskin
-a warty growth develops, ulcerates, and discharges watery pus
inguinal lymph nodes
penile carcinoma most often metastases to
primary lesion of syphilis
-hard chancre commonly occuring on glans or inner leaves of foreskin, occasionally on the shaft or scrotum
•The chancre begins as a silvery papule that gradually erodes to form a superficial ulcer with a serous discharge containing Treponema pallidum
progression of syphilitic chancre
condyloma latum
-cauliflower like plaque in genital area; manifestation of secondary syphilis
-these lesionns are soft, flat topped, moist or macerated reddish brown to grayish
-coalesce into larger plaques
•X-ray taken using a broken chicken bone on top of penis
how do you xray the penis for a fracture?
fractured penis
•Defined as rupture of the tunica albuguinea of corpus cavernosum when penis is in an erect state
-urologic emergency
peyronie disease
•Chronic disease of unknown cause, characterized by irregular fibrosis of the septum or sheath of the corpus cavernosum penis, extending into tunica albuginea
•Never affects corpus spongiosom
peyronie disease
considered a component of dupuytren diathesis along with palmar and solar fibrosis
epispadias
•Urethral opening along the dorsum of the penis on the glans, penile shaft, and penopubic angle
•Proximal forms are common and associated with incontinence
hypospadias
•Ectopic urethral opening which may be located ventrally on the glans, penile shaft, scrotum, or perineum
spermatocele
•Benign cystic accumulation of sperm
•Often found in the head of the epididymis
•Usually a smooth, firm, well-circumscribed mass of the scrotum
•Usually develop slowly and usually have no symptoms
•Common cause of infertility in men
presentation of varicocele
varicocele
•Incompetent or inadequate valves within the veins along the spermatic cord cause a varicocele.
•The abnormal valves obstruct normal blood flow causing a backup of blood, resulting in enlargement of the veins

Cryptochordism
•During fetal development, descent of one or both testis arrested in abdomen, inguinal canal, or at puboscrotal junction
•Testes is palpable in the inguinal canal or at the puboscrotal junction, but frequently is atrophied
•Testicular maldescent may decrease fertility and is frequently associated with a congenital inguinal hernia on the same side as a result of persistence of part of the saccus vaginalis
testicular cancer
maldescended testis (cryptochordism) carry an increased risk of this cancer