4.14-4.16 Nitrogen Oxides & Sulfur Dioxide
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
NOx
General formula for nitrogen oxides (specifically nitric oxide, NO, and nitrogen dioxide, NO2). They are produced during combustion of fuel (or when there is lightning) and are harmful to the environment
2
New cards
How are nitrogen oxides formed?
High temperatures and pressures of internal combustion engines as well as blast furnaces, provide enough energy for nitrogen + oxygen to react. This leads to the formation of nitrogen oxides
N2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO (g)
N2 (g) + 2O2 (g) → 2NO2 (g)
Nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide can also be formed during the event of lightning, as vast quantities of thermal energy are provided which allows nitrogen and oxygen to react
N2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO (g)
N2 (g) + 2O2 (g) → 2NO2 (g)
Nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide can also be formed during the event of lightning, as vast quantities of thermal energy are provided which allows nitrogen and oxygen to react
3
New cards
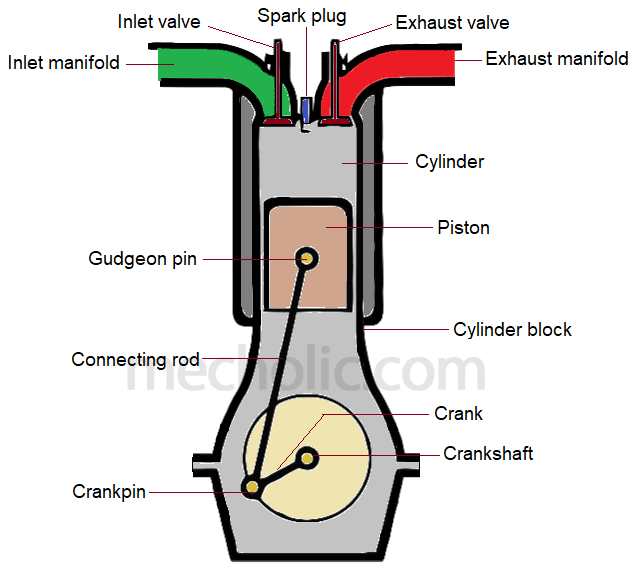
Internal combustion engines
Engine where fuel is combusted inside the engine, producing hot gases with an explosive force that drive pistons to generate motive power
4
New cards
Engine
Machine with mechanical (moving) components that uses energy from liquid fuel or steam to produce movement
5
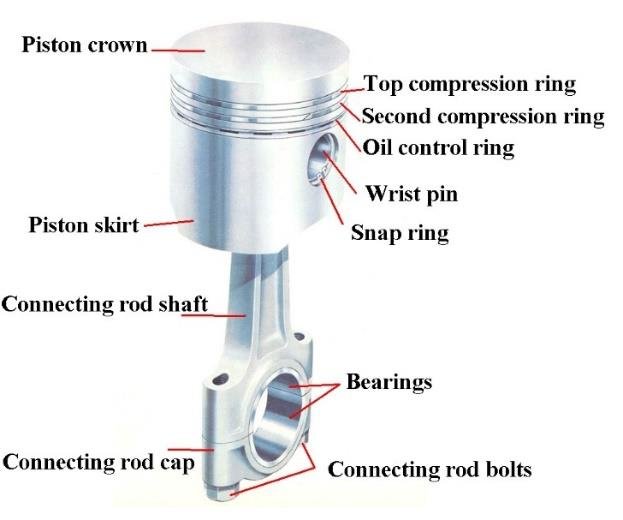
New cards
Piston
Metal disc or cylinder that is part of an engine. Pistons slide up and down inside tubes and cause various parts of the engine to move
6
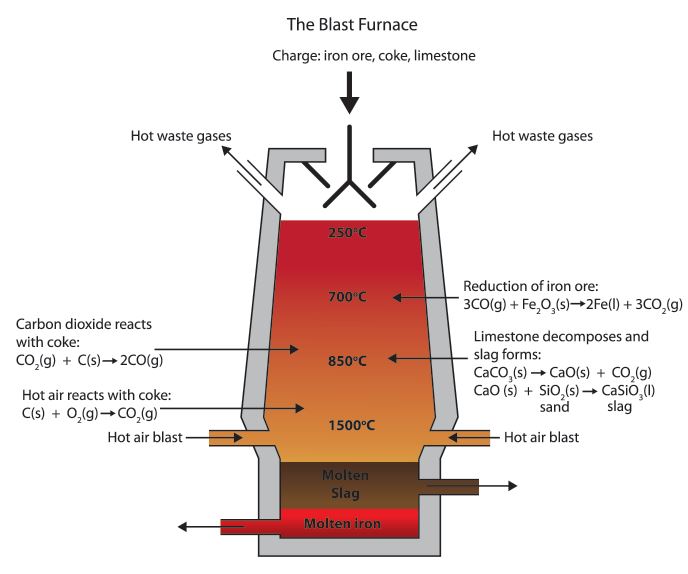
New cards
Blast furnace
Large machine made of steel. Hot air blown is blown into the blast furnace, enabling coke (a type of coal) to combust. This generates extremely high temperatures in the furnace
7
New cards
Exhaust gases
Waste gases from an engine
8
New cards
What do exhaust gases contain?
Unburned hydrocarbons
Carbon monoxide
Oxides of nitrogen and sulfur dioxide
Carbon monoxide
Oxides of nitrogen and sulfur dioxide
9
New cards
Negative effects of NOx (oxides of nitrogen)\`
Acid rain (similar effects of acid rain with sulfur dioxide)
Produces photochemical smog
Produces breathing difficulties, especially for asthmatic people
Produces photochemical smog
Produces breathing difficulties, especially for asthmatic people
10
New cards
Photochemical smog
Mixture of pollutants formed when oxides of nitrogen and volatile (easily vaporize) organic compounds (VOCs) react to sunlight, creating a brown haze above cities
11
New cards
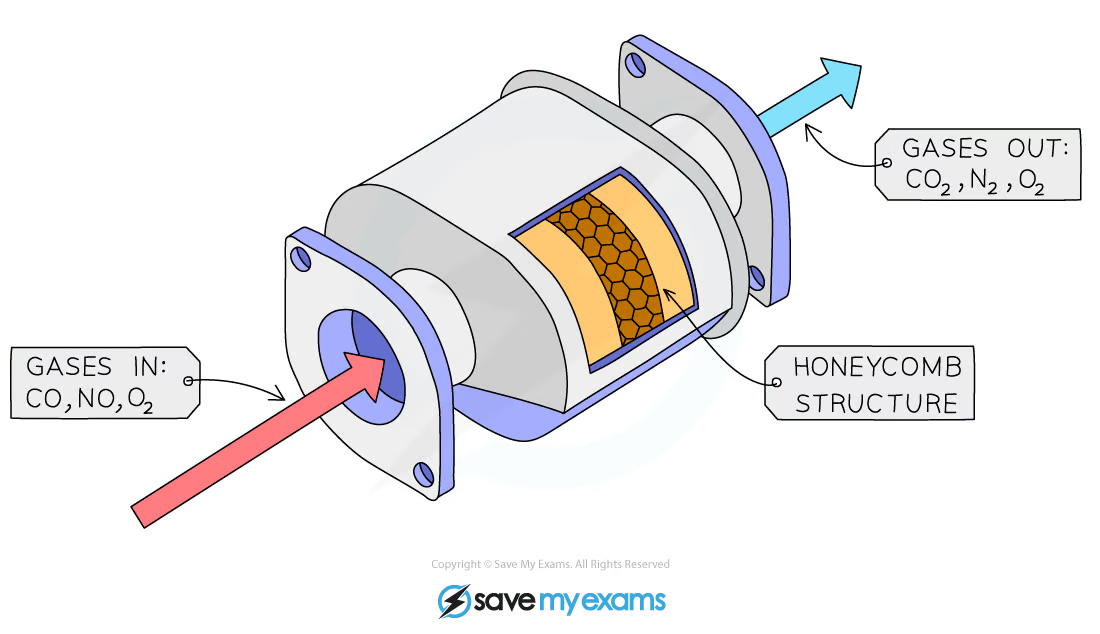
Catalytic converters
Device incorporated in exhaust systems of a motor vehicle. They contain catalysts that convert pollutant gases into less harmful gases. Catalytic converters are designed to reduce polluting gases produced in vehicle exhaust systems
Transition metal catalysts such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium are used in a honeycomb structure to maximize surface area for reactions
Many redox reactions occur, which neutralize the pollutant gases;
* Carbon monoxide is oxidized into carbon dioxide
* 2CO + O2 → 2CO2
* Nitrogen oxides are reduced into nitrogen gas
* 2NO → N2 + O2
* 2NO2 → N2 + 2O2
* Unburned hydrocarbons are oxidized into carbon dioxide and water by complete combustion
* 2C8H18 + 25O2 → 16CO2 + 18H2O
Transition metal catalysts such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium are used in a honeycomb structure to maximize surface area for reactions
Many redox reactions occur, which neutralize the pollutant gases;
* Carbon monoxide is oxidized into carbon dioxide
* 2CO + O2 → 2CO2
* Nitrogen oxides are reduced into nitrogen gas
* 2NO → N2 + O2
* 2NO2 → N2 + 2O2
* Unburned hydrocarbons are oxidized into carbon dioxide and water by complete combustion
* 2C8H18 + 25O2 → 16CO2 + 18H2O
12
New cards
Exhaust system
Component of a vehicle or machinery which removes exhaust gases produced during the combustion process and directs them out of the engine in a safe, noise-reducing manner
13
New cards
How is sulfur dioxide formed?
Hydrocarbon fuels (e.g. fossil fuels) often contaminated with small amounts of sulfur impurities
Combustion of fossil fuels (especially coal) oxidizes the sulfur into sulfur dioxide:
S(s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
Combustion of fossil fuels (especially coal) oxidizes the sulfur into sulfur dioxide:
S(s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
14
New cards
Negative effects of SO2 (sulfur dioxide)
Sulfur dioxide, like oxides of nitrogen (NOx; e.g. NO or NO2) can lead to acid rain which can cause:
* Corrosion of metal structures (e.g. iron), buildings (e.g. limestone buildings), statues made of carbonate rocks (e.g. calcium carbonate), etc
* Buildings and statues can both be made of calcium carbonate (limestone)
* Their corrosion by acid rain can be dangerous as it weakens the foundation of industrial infrastructure
* Calcium carbonate (a.k.a. Limestone) + Sulfuric acid → Calcium sulfate + Water + Carbon dioxide
* CaCO3 (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → CaSO4 (s) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
* Damage to aquatic organisms
* Pollution of crops and water supplies
* Lung, throat, and eye irritation
* Corrosion of metal structures (e.g. iron), buildings (e.g. limestone buildings), statues made of carbonate rocks (e.g. calcium carbonate), etc
* Buildings and statues can both be made of calcium carbonate (limestone)
* Their corrosion by acid rain can be dangerous as it weakens the foundation of industrial infrastructure
* Calcium carbonate (a.k.a. Limestone) + Sulfuric acid → Calcium sulfate + Water + Carbon dioxide
* CaCO3 (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → CaSO4 (s) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
* Damage to aquatic organisms
* Pollution of crops and water supplies
* Lung, throat, and eye irritation
15
New cards
Rain’s usual pH and reason for this pH
5\.6
Naturally slightly acidic because carbon dioxide reacts with water vapor in the atmosphere (once these water vapor droplets get large and heavy enough they fall down as rain) or directly with rain, forming a weak carbonic acid
Naturally slightly acidic because carbon dioxide reacts with water vapor in the atmosphere (once these water vapor droplets get large and heavy enough they fall down as rain) or directly with rain, forming a weak carbonic acid
16
New cards
Acid rain
Rain with a pH of less than about 5.6 due to water and oxygen in the atmosphere reacting with sulfur dioxide to produce sulfuric acid or with NOx (various oxides of nitrogen) to produce nitric acid
17
New cards
How does sulfur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen contribute to and form acid rain?
Combustion of fossil fuels containing sulfur impurities:
* Sulfur + Oxygen → Sulfur dioxide
* S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
Sulfur dioxide reacts with oxygen and water in atmosphere, forming sulfuric acid (strong acid and important component of acid rain):
* Sulfur dioxide + Water + Oxygen → Sulfuric acid
* 2SO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) + O2 (g) → 2H2SO4 (aq)
When sulfur dioxide reacts with water, a weaker sulfurous acid forms:
* Sulfur dioxide + Water → Sulfurous acid
* SO2 (g) + H2O (l) → H2SO3 (aq)
High temperatures and pressures of internal combustion engines, as well as blast furnaces (or events of lightning and electrical storms), provide enough energy for nitrogen + oxygen to react. This leads to the formation of nitrogen oxides:
* Nitrogen + Oxygen → Nitric oxide
* N2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO (g)
* Nitrogen + Oxygen → Nitrogen dioxide
* N2 (g) + 2O2 (g) → 2NO2 (g)
Nitric oxide reacts with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide. This nitrogen dioxide dissolves in rainwater or reacts with atmospheric water vapor to form a mixture of nitric acid and nitrous acid:
* Nitric oxide + Oxygen → Nitrogen dioxide
* 2NO (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO2 (g)
* Nitrogen dioxide + Water → Nitric acid + Nitrous acid
* 2NO2 (g) + H2O (l) → HNO3 (aq) + HNO2 (aq)
Nitrogen dioxide may also react with atmospheric water vapor and oxygen to form nitric acid:
* 4NO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) + O2 (g) → 4HNO3 (aq)
The mixture of sulfuric, nitric, and nitrous acid results in acidic rain with a pH lower than normal rain’s pH of 5.6
Water vapor is less dense than dry air → water vapor rises → temperature decreases as they rise → water vapor condenses into water droplets → multiple water droplets collide and combine to form a larger droplet → droplets continually become larger and heavier → droplets cannot be contained in the clouds anymore so they fall to the ground as acid rain
* Sulfur + Oxygen → Sulfur dioxide
* S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
Sulfur dioxide reacts with oxygen and water in atmosphere, forming sulfuric acid (strong acid and important component of acid rain):
* Sulfur dioxide + Water + Oxygen → Sulfuric acid
* 2SO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) + O2 (g) → 2H2SO4 (aq)
When sulfur dioxide reacts with water, a weaker sulfurous acid forms:
* Sulfur dioxide + Water → Sulfurous acid
* SO2 (g) + H2O (l) → H2SO3 (aq)
High temperatures and pressures of internal combustion engines, as well as blast furnaces (or events of lightning and electrical storms), provide enough energy for nitrogen + oxygen to react. This leads to the formation of nitrogen oxides:
* Nitrogen + Oxygen → Nitric oxide
* N2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO (g)
* Nitrogen + Oxygen → Nitrogen dioxide
* N2 (g) + 2O2 (g) → 2NO2 (g)
Nitric oxide reacts with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide. This nitrogen dioxide dissolves in rainwater or reacts with atmospheric water vapor to form a mixture of nitric acid and nitrous acid:
* Nitric oxide + Oxygen → Nitrogen dioxide
* 2NO (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO2 (g)
* Nitrogen dioxide + Water → Nitric acid + Nitrous acid
* 2NO2 (g) + H2O (l) → HNO3 (aq) + HNO2 (aq)
Nitrogen dioxide may also react with atmospheric water vapor and oxygen to form nitric acid:
* 4NO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) + O2 (g) → 4HNO3 (aq)
The mixture of sulfuric, nitric, and nitrous acid results in acidic rain with a pH lower than normal rain’s pH of 5.6
Water vapor is less dense than dry air → water vapor rises → temperature decreases as they rise → water vapor condenses into water droplets → multiple water droplets collide and combine to form a larger droplet → droplets continually become larger and heavier → droplets cannot be contained in the clouds anymore so they fall to the ground as acid rain
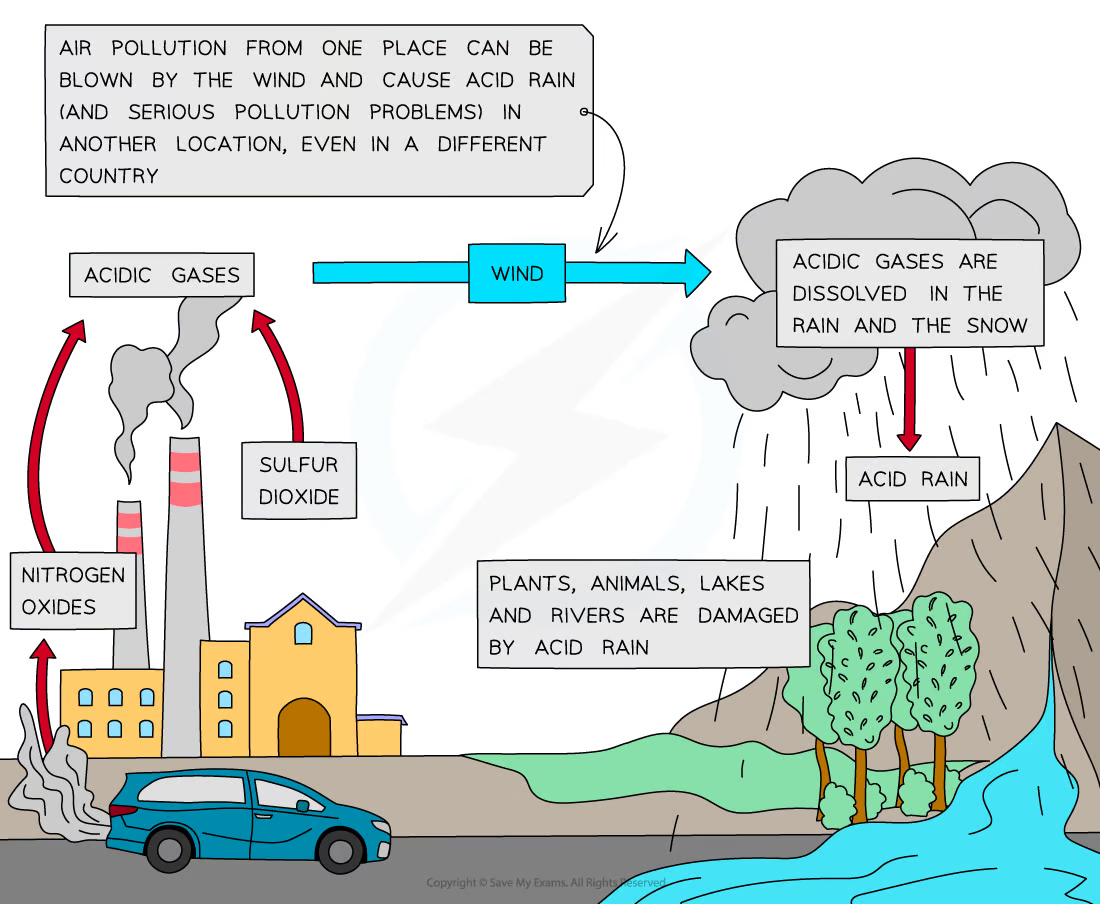
18
New cards
Acid rain effects
Damage to plants, animals (especially aquatic organisms), rivers, lakes, etc
Corrosion of limestone buildings
Corrosion of limestone buildings
19
New cards
Scrubbing
Process whereby pollutant gases are removed from exhaust gases produced during combustion reactions
20
New cards
Examples of solutions to acid rain
Removing sulfur from fuels (usually done for petrol, a.k.a. gasoline, used in cars)
Scrubbing gases from power stations and factories to remove sulfur dioxide (SO2) as well as oxides of nitrogen (NOx)
Using catalytic converters in the exhaust systems of car engines
Scrubbing gases from power stations and factories to remove sulfur dioxide (SO2) as well as oxides of nitrogen (NOx)
Using catalytic converters in the exhaust systems of car engines