AP Psych: Unit 1
1/170
Earn XP
Description and Tags
fu mr thomas
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
nature-nuture issue
Controversy over the relative contributions of genes and experience that affect the development of psychological traits and behaviors. Today psychologists agree that genes and environment both play parts of a person’s traits
Natural Selection
The principle that inherited traits enabling an organism to survive and reproduce in a particular environment will most likely pass onto other generations
Charles Darwin
‘Origin of Species’ Studied animals and how their specific traits are passed down. Claimed that natural selection shapes behaviors and bodies.
Evolutionary Psychology
Study of how evolution affected the brain and mind
Behavior Genetics
How much genes and environment affect behavior
Mutation
Errors in gene replication
Environment
Any non-genetic influence
Heredity
Passing down of traits
Genes
Biochemical units of heredity
Genome
instruction of an entire organism
Identical twins
Same fertilized egg, genetically identical
Fraternal twins
Two fertilized eggs, not identical-sibling like
Interaction
When the effect of one factor (environment) depends on another factor (heredity)
Epigenetics
Mechanisms in which environment can block or trigger gene expression
Nervous System
The body’s electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells in the CNS and PNS
Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord, body’s decision maker
Peripheral Nervous System
Sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
Nerves
Bundled axons that connect the CNS to muscles, glands and sensory organs
Sensory Neurons
Carries messages from body tissues and sensory receptors to the CNS
Motor Neurons
Carry messages outward from CNS to the muscles and glands
Interneurons
Help sensory and motor neurons communicate and process information, in the CNS
Somatic Nervous System
Controls body’s skeletal muscles
Autonomic Nervous System
controls glands and internal organs, self-regulating
Sympathetic Nervous System
arouses and spends energy, fight or flight
Parasympathetic Nervous System
calms the body, conserves energy
Reflexes
a simple autonomic response to a sensory stimulus, like a knee-jerk response
Neurons
Nerve cell, basic building block of nervous system
Cell body (soma)
Contains nucleus part of neuron
Dendrites
Recieves and integrates messages, conducting impulses to cell body
Axon
Passes messages through branches to other neurons or muscle and glands
Myelin Sheath
Fatty tissue layer, encasing axons helps transporting neural impulses to next node. Deterioration of this can lead to multiple sclerosis, where people experience less control and slower reactions
Glial cells
cells that support and nourish neurons, play a role in memory and thinking
Action potential
Brief electrical charge that travels down to axon, neural impulse.
Threshold
Level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
Refractory Period
Neural processing, brief resting pause after a neuron has fired
All or none response
Neuron’s reaction of either firing or not
Synapse
Junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or soma of the receiving neuron
Neurotransmitter
Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic cleft
Reuptake
A neurotransmitter’s reabsorption by a sending neuron
Agonist
Molecule that increases a neurotransmitter’s action
Antagonist
Molecule that inhibits or blocks a neurotransmitter’s action
Endocrine system
Glands and organs that make hormones release
Hormones
Chemical substances that act like messenger molecules
Psychoactive Drug
Chemicals that alter the brain, affecting mood and emotions
Substance use disorder
Disorder characterized by continued substance use despite disruption of life.
Depressants
Reduce neural activity and slows body functions, E.g: Alcohol, heroin
Tolerance
When the brain adapts to offset drug affects
Addiction
Caused by increased dosages of psychoactive drugs, to the point when users have to use to it to feel well.
Withdrawal
Difficulty to get off a drug and the symptoms that a person has when they abruptly stop drugs
Barbiturates
Tranquilizer, depress central nervous system activity
Opiods
Depress neural activity and lessens pain and anxiety.
Stimulants
Excites neural activity and speeds up body functions. E.g Caffeine, cocaine
Hallocinogens
Distort perceptions and evoke sensory images. E.g: LSD, marijuana
Near-death experience
Altered state of consciousness reported after a close brush with death.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Neurotransmitter that enables muscle action, learning and memory. E.g: This neurotransmitters deteriorate with Alzheimer’s disease, when the transmission is blocked it results in myasthenia gravis, where the muscles cannot contract
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter that influences movement, learning, attention and emotion. E.g: oversupply leads to schizophrenia and undersupply leads to Parkinson’s.
Serotonin
Neurotransmitter that affects mood, hunger, sleep and arousal. E.g: undersupply leads to depression
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter that controls alertness and arousal. E.g: undersupply leads to depression
GABA
Major INHIBITORY neurotransmitter
Glutamate
Major EXCITATORY neurotransmitter
Endorphins
Neurotransmitter that influence perception of pain or pleasure
Substance P
Neurotransmitter involved in pain perception and immune response.
Biological Psychologists
Scientific study of link between biological and psychological processes
Biopsychological Approach
Incorporates biological, psychological and socio-cultural levels of analysis
Levels of analysis
Different views for analyzing a phenomenon
Neuroplascity
The brain’s ability to change by reorganizing after damage or creating new pathways from new experiences.
Lesion
Tissue destruction, used by scientists to study how brain damage affects behavior.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity in the brain.
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
Brain imaging technique that measures magnetic fields of the brain.
(Computated Technology) CT Scan
X-ray photographs that combine to create an image of the brain
Positron Emission Topography (PET)
Detects brain activity where glucose goes in the brain during activity
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce images of soft tissues
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
Reveals blood flow and brain activity to reveal how the brain functions during activities, MRI images are compared
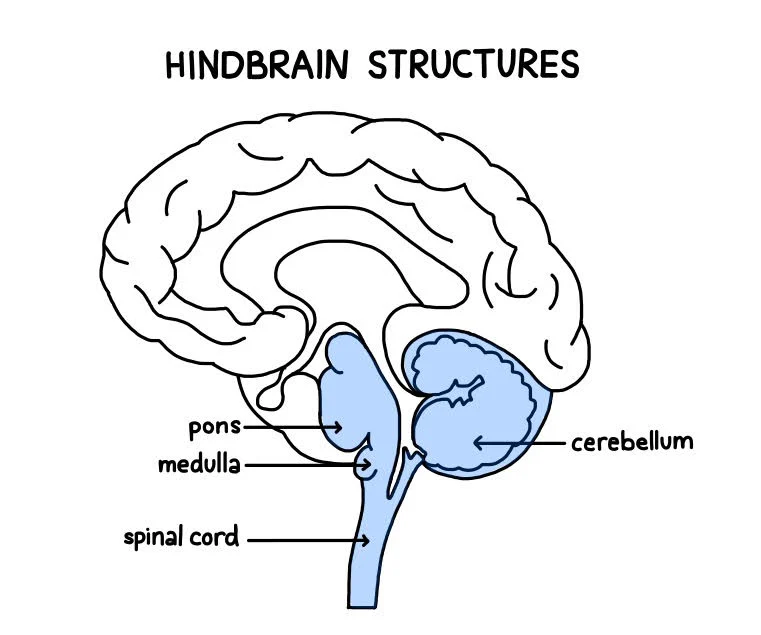
Hindbrain
Consists of medulla, pons, and cerebellum; directs essential survival functions like breathing, sleeping, and wakefulness, as well as coordination and balance.
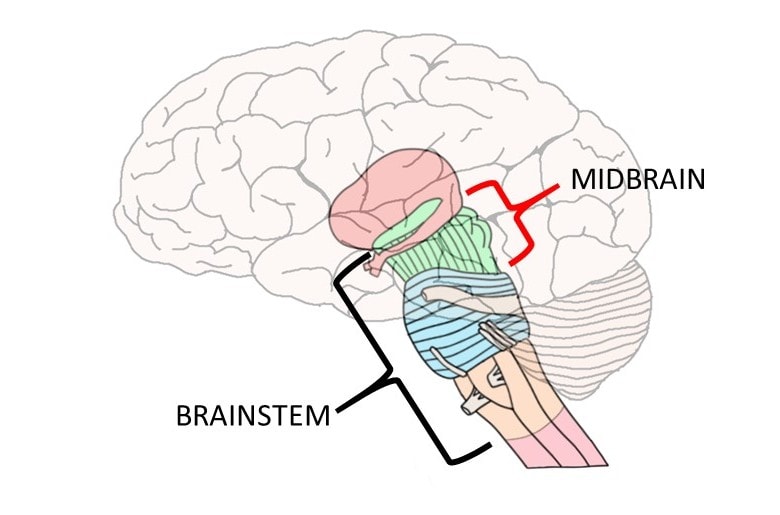
Midbrain
Atop the brainstem; connects the hindbrain with the forebrain, controls some motor movements and transmits auditory and visual information.
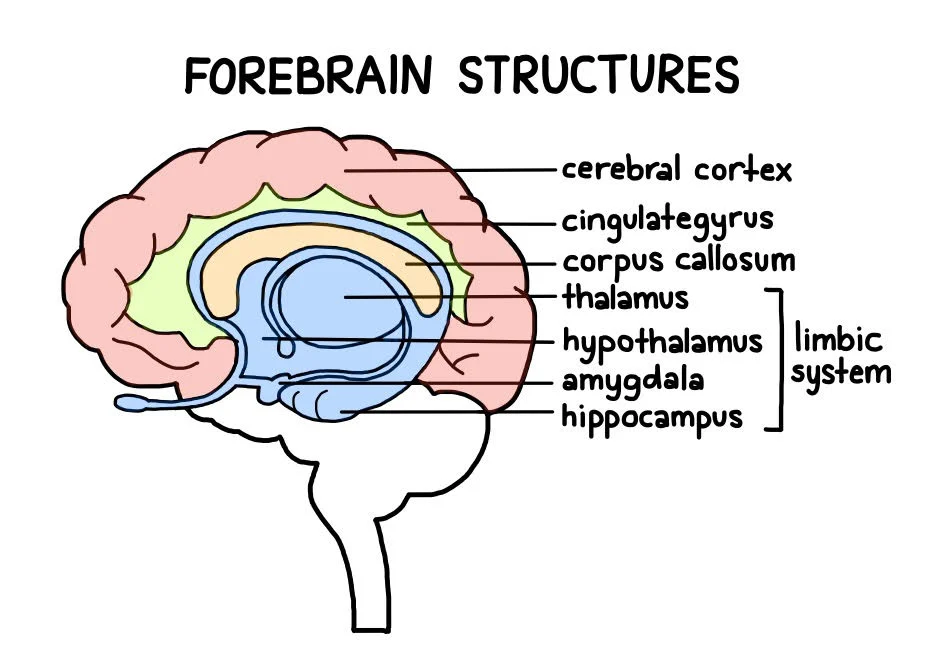
Forebrain
Consists of cerebral cortex, thalamus, and hypothalamus; manages complex cognitive functions and voluntary motor activites.
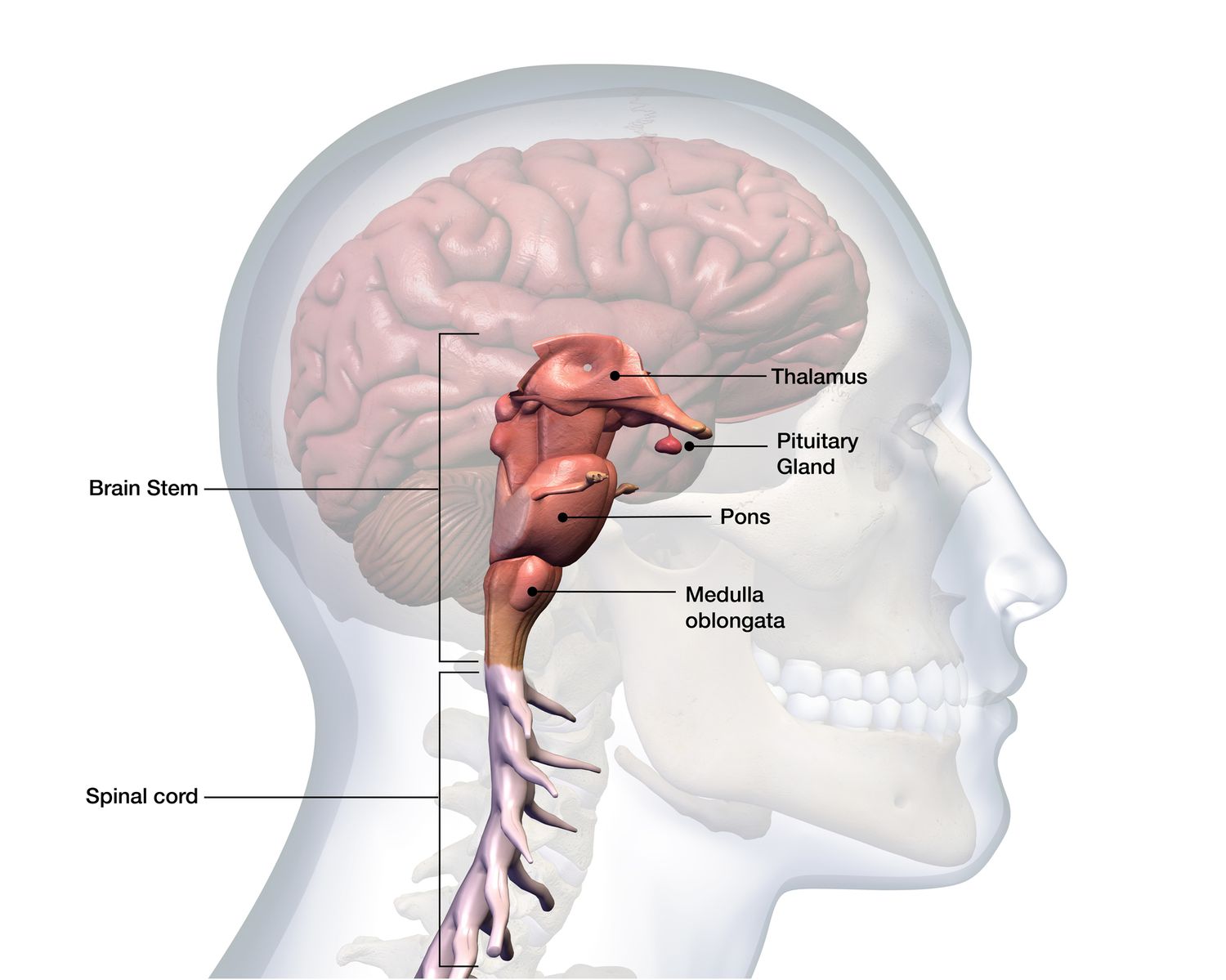
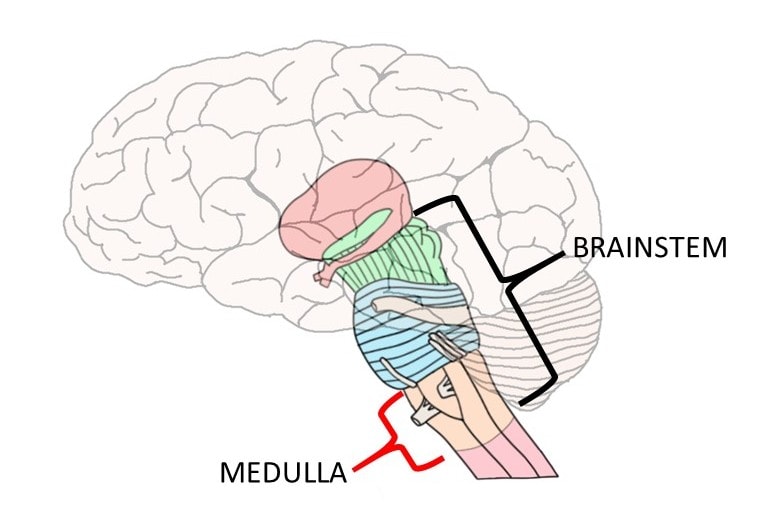
Brainstem
Central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull. It is responsible for automatic survival functions. For example, if the cat’s brainstem is cut off then they won’t purposefully run or climb for food.
Medulla
Hindbrain structure, base of the brainstem. Controls heartbeat and breathing
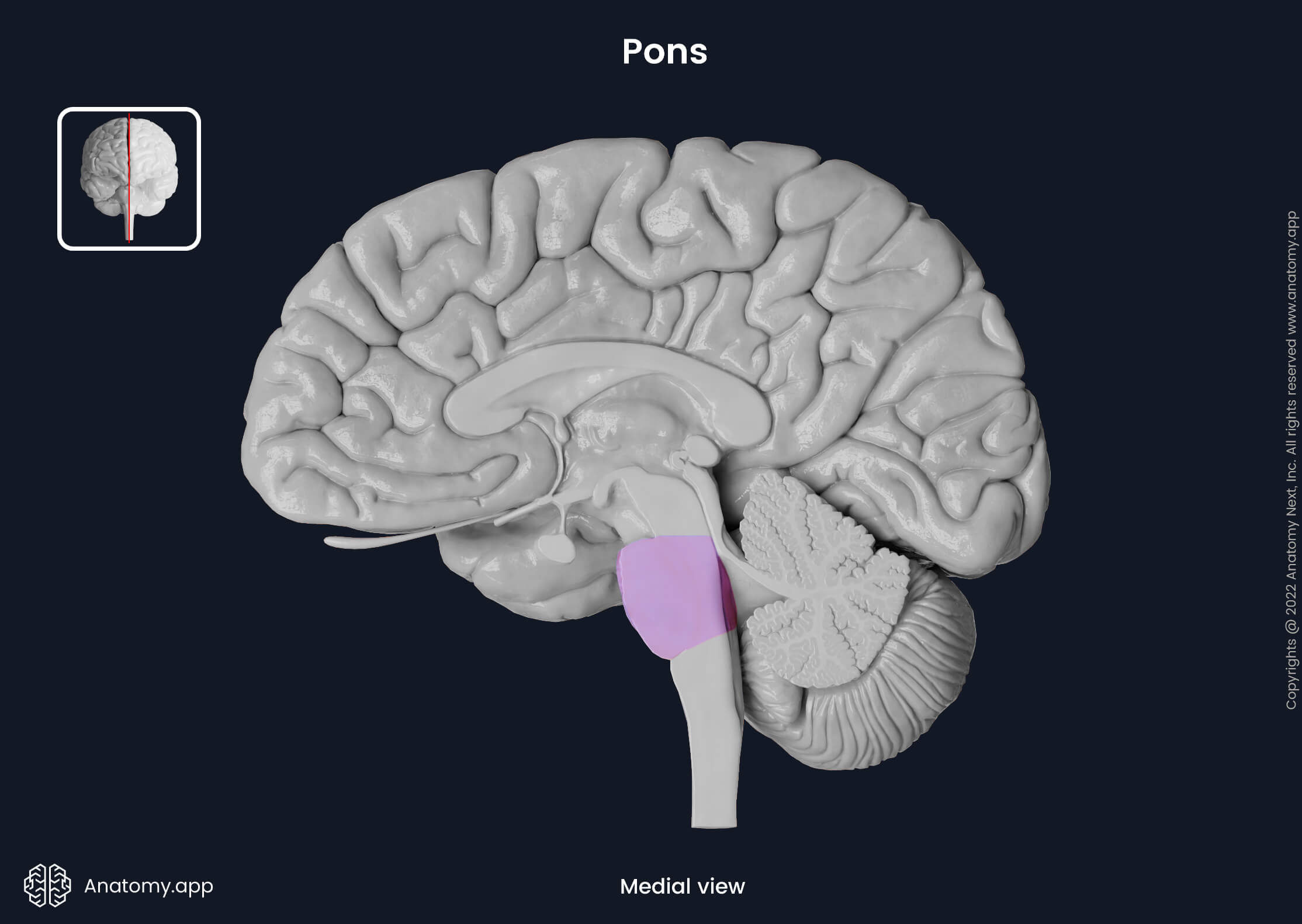
Pons
Above medulla, helps coordinate movement, control sleep, and feel relaxed.
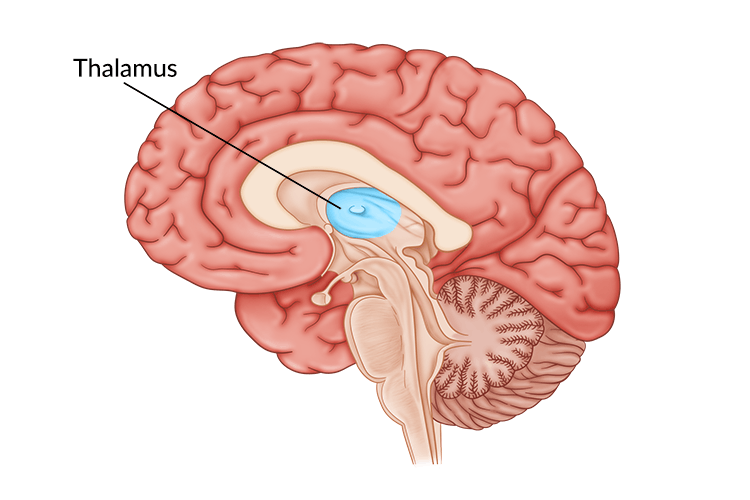
Thalamus
Part of the forebrain, sensory control center, on top of the brainstem; directs messages to sensory recieving areas in cortex and transmits replies to cerebellum and medulla.
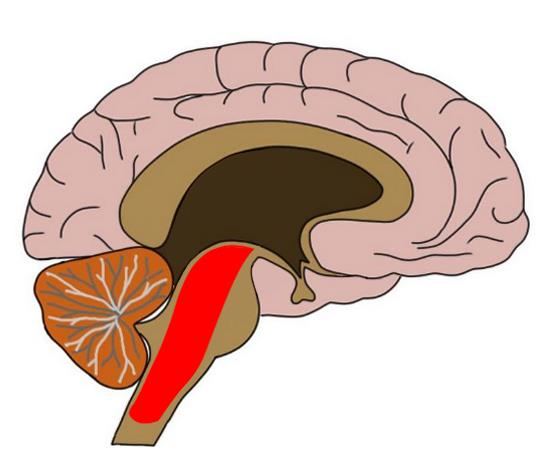
Reticular formation
Nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus; plays an important role in controlling arousal and alertness.
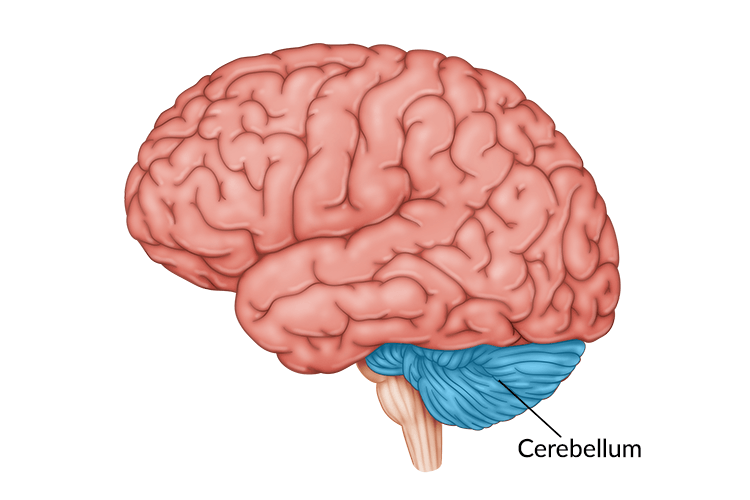
Cerebellum
Hindbrains “little brain” at the rear, processes sensory inputs, coordinating movement output and balance and enables nonverbal learning and memory.
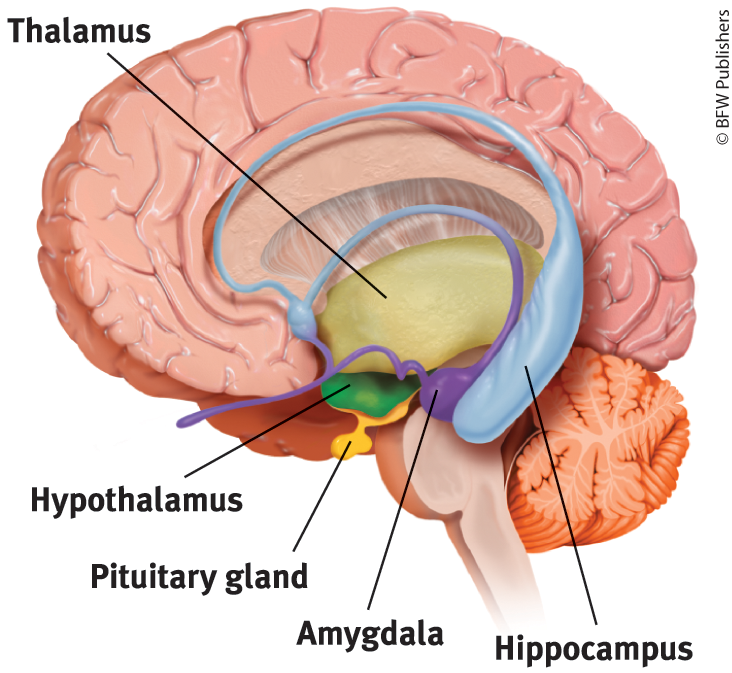
Limbic System
Neural system mostly the forebrain; assosciated with emotions and drive
Amygdala
Part of the limbic system, linked to emotions like aggression and fear
Hypothalamus
Below thalamus, directs maintenance activities that promote homeostasis (eating, drinking, temperature), controls endocrine system
Hippocampus
Helps process explicit memories for storage
Cerebral Cortex
Interconnected neural cells covering forebrain, ultimate control system and information processing center
Frontal Lobes
Behind the forehead, enables linguistic processing, muscle movements, higher-order thinking and executive functioning.
Parietal Lobes
On top of the head in the rear, receives sensory input
Occipital Lobes
Back of the head, receives visual information
Temporal Lobes
Roughly above the ears, includes auditory information enables linguistic processing.
Motor Cortex
Controls voluntary movements, behind frontal lobes
Somatosensory Cortex
In front of parietal lobes registers body touch and movement sensations
Association Areas
Enables higher order thinking
Neurogenesis
Creation of new neurons
Corpus Callosum
Long band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres
Split brain
surgery that isolates both brain hemispheres by cutting corpus callosum.
Left hemisphere- Language and speech, controls right side of body
Right hemisphere- Interpreting visual information and spatial processing, controls left side of body
Conciousness
Subjective awareness of ourselves and our environment
Cognitive Neuroscience
Study of brain activity linked with cognition
Dual Processing
Principle that information is often processed simultaneously on separate conscious and unconscious tracks. Example: Driving a car while talking