HL Biology: Global Issues and Ecology
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Contains Stability and change, climate change, transfers of energy and matter
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
What are greenhouse gases?
Gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat from the sun.
Name some examples of greenhouse gases.
Includes CO2, Methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor.
Greenhouse effect
Natural situation in which heat is retained in Earth's atmosphere by carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and other gases
Climate
The long-term average weather condition at a particular location
Weather
the day-today variations in air temperature precipitation, cloud cover, and winder
Climate change
A long term change in global or regional climate patterns, caused by natural or human factors
What are the anthropogenic causes of climate change
Primarily attributed to increased levels of atmospheric greenhouse gases. Methane and carbon dioxide emissions being a primary concern.
How is carbon dioxide emitted? Through what?
Cellular respiration, combustion of fossil fuels, etc.
How methane is released
Released due to human activities such as extractions of fossil fuels, agricultural practices
Positive feedback cycles in global warming
1. O - increase of co2 from deep ocean
2. S - an increase absorption of solar radiation due to loss of reflection snow -> causing more heat melting more snow
3. D - an increase in decomposition of peat which release co2 -> causing rapid decomp
4. M - increase of methane from warm temps melting permafrost areas -> causing more greenhouse gases & heat
5. increase in droughts and fires -> causing more co2
tipping points in climate change
Boreal forests, polar habitat change, changes in ocean currents, range shift of temperate species
Boreal forests
- Play a crucial in absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere to use for photosynthesis
- Warmer temperatures and reduced winter snowfall contribute to drought conditions which result in water loss and increases forest fire conditions
Polar habitat change
Melting of polar ice leads to habitat loss
- Due to breakage of landfast and sea ice
Nutrient upwelling
When deep, nutrient-rich water rises to the surface of the ocean, supporting marine ecosystems.
How can warmer surface water affect nutrient upwelling?
It can prevent nutrient upwelling to the surface
What is the impact of decreased nutrient availability?
Organisms that rely on nutrients may face a decrease in their availability
Temperate species
Organisms that are adapted to inhabiting temperate regions which are characterised by moderate climates with distinct seasons. As global temperatures rise, temperate species are moving into regions they couldn't previously inhibit.
Coral reefs
Vibrant underwater ecosystems built by tiny coral animals
Aka the "rainforests of the sea"
Carbon sequestration
the process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide
Afforestation
Planting trees on previously non-forested land
- Effective method of carbon sequestration
Phenology
the timing of seasonal events (biological events) and their relationship with season and environmental factors
What influences the timing of biological events?
Photoperiods and temperature patterns
Photoperiod
Day length (# of sunlight hours)
Seasonal temperatures can be affected by....
climate change
Budburst
When leaf buds swell, unfold, burst into leaves or flowers
Migration
Seasonal journeys of different animals across great distances
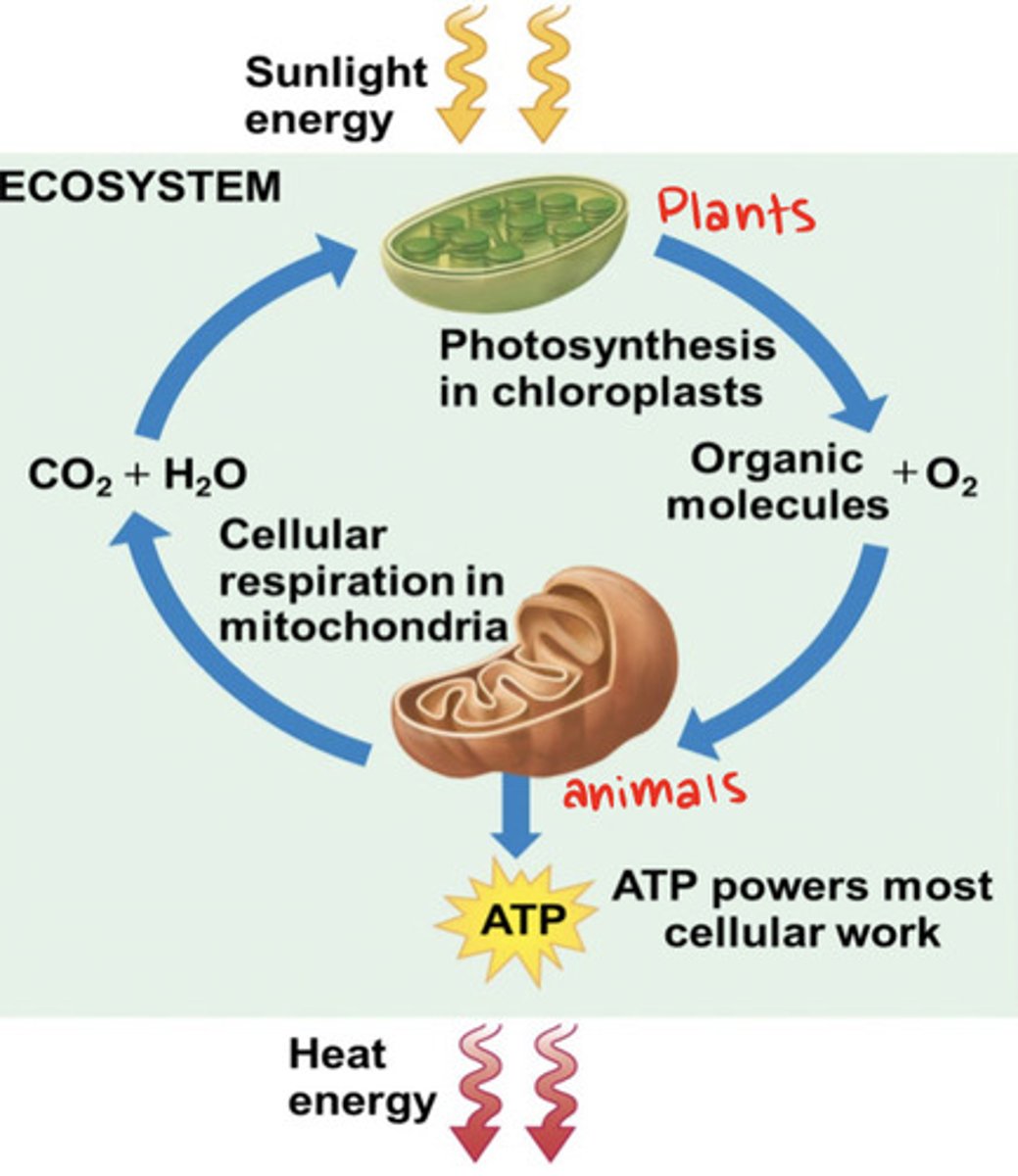
Photosynthesis
When producers convert light energy (from sunlight) to chemical energy through the absorption of CO2 and water, and release oxygen and glucose
Ecology
The study of the relationships between organisms and their environment.
Specieis
Groups of organisms that can potentially interbreed to produce offspring
Population
Includes all individuals of a species that live in the same area at the same time
Community (hows it formed)
Formed by populations of different species living together and interacting with eachother
Ecosystems
A community of organisms and their surroundings
What type of system are ecosystems
They are open systems
Types of biological systems and what they are
Open -> allows both energy and matter to be exchanged with its surroundings
Closed systems -> allows for exchange of energy with surrounding environment but restricts the flow of matter
isolated systems -> niether energy nor matter are exchanged with their surroundings
What is the primary source of energy that sustains most ecosystems?
Sunlight
Other sources of energy
H2S, which is an energy source in hydrothermal vent ecosystems
How is energy transferred through the food chain?
By feeding interactions
Explain the energy pyramid/transfer of energy
Herbivores consume plants, carnivores consume herbivores
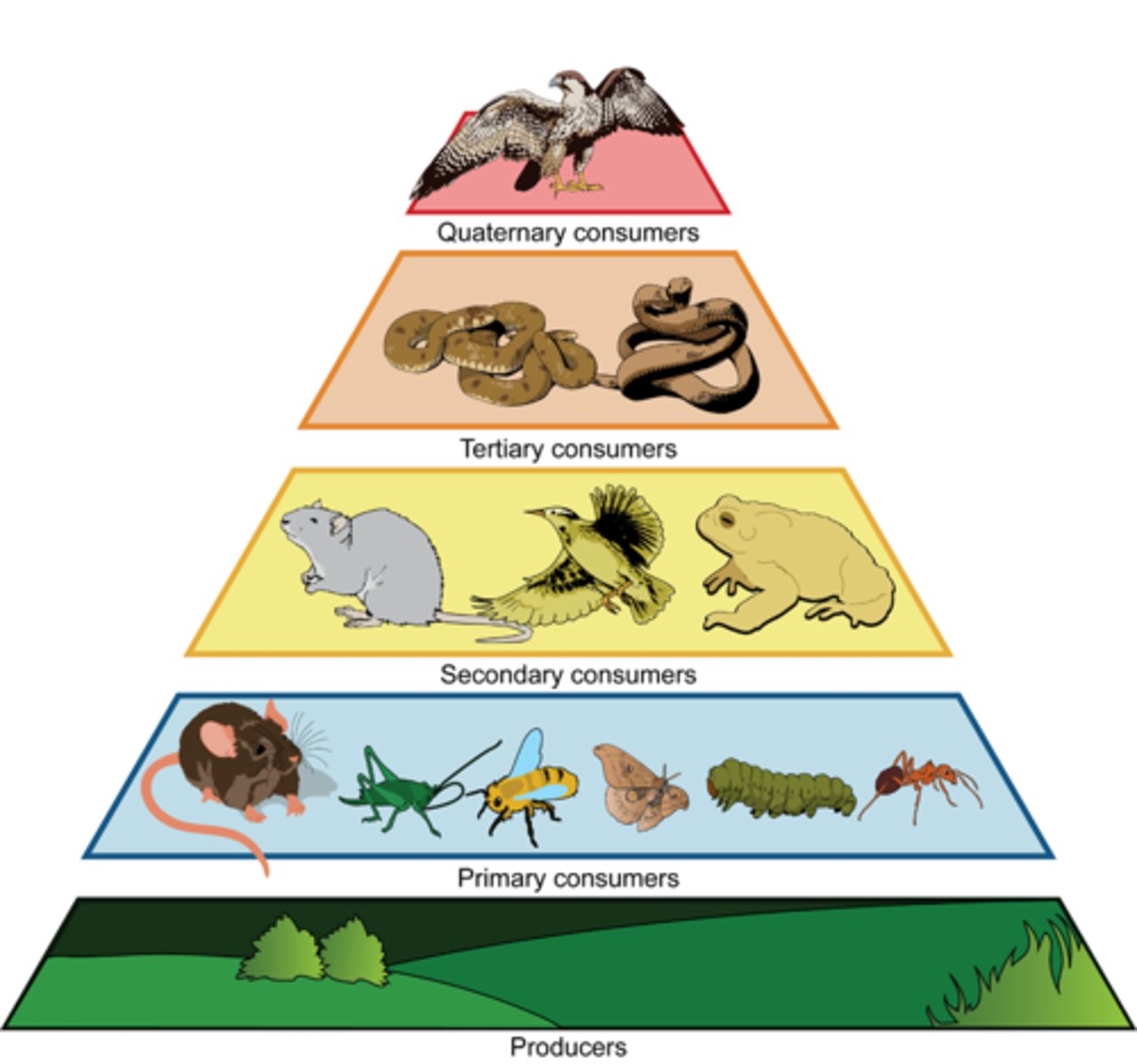
Food chains and food webs
As organisms eat other organisms, they get energy. Food chains and food webs show us how that energy moves from one organism to another in an ecosystem.
- Arrows indicate the direction of energy flow
What does biomass refer to?
Total dry mass of organisms in an ecosystem
How is biomass created by organisms?
Chemical energy (aka food) is used by organisms to create biomass
Decomposers
breaks down dead organisms and organic matter
- examples: bacteria, fungi, invertebrates
What are Saprotrophs
Heterotrophs that obtain organic nutrients from dead organic matter by external digestion
Detritivores (Scavengers)
Heterotrophs that obtain nutrients from Detritus by internal digestion
- Directly ingest and consume dead organic matter, internally breaking it down using digestive enzymes
Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs
Autotrophs - "self feeders" that produce organic compounds (key example - glucose) (producers)
Heterotrophs - organisms who must obtain their energy source by ingesting or absorbing nutrients from other living things (consumers)
Photoautotrophs
Derives their energy through photosynthesis, which involves converting sunlight, CO2, & water into glucose & oxygen gas
Chemoautotrophs
Obtain energy through oxidization of inorganic compounds (iron, sulfur, mg)
example: iron-oxidising bacteria
Explain trophic levels
Represents an organisms position in food chain/web
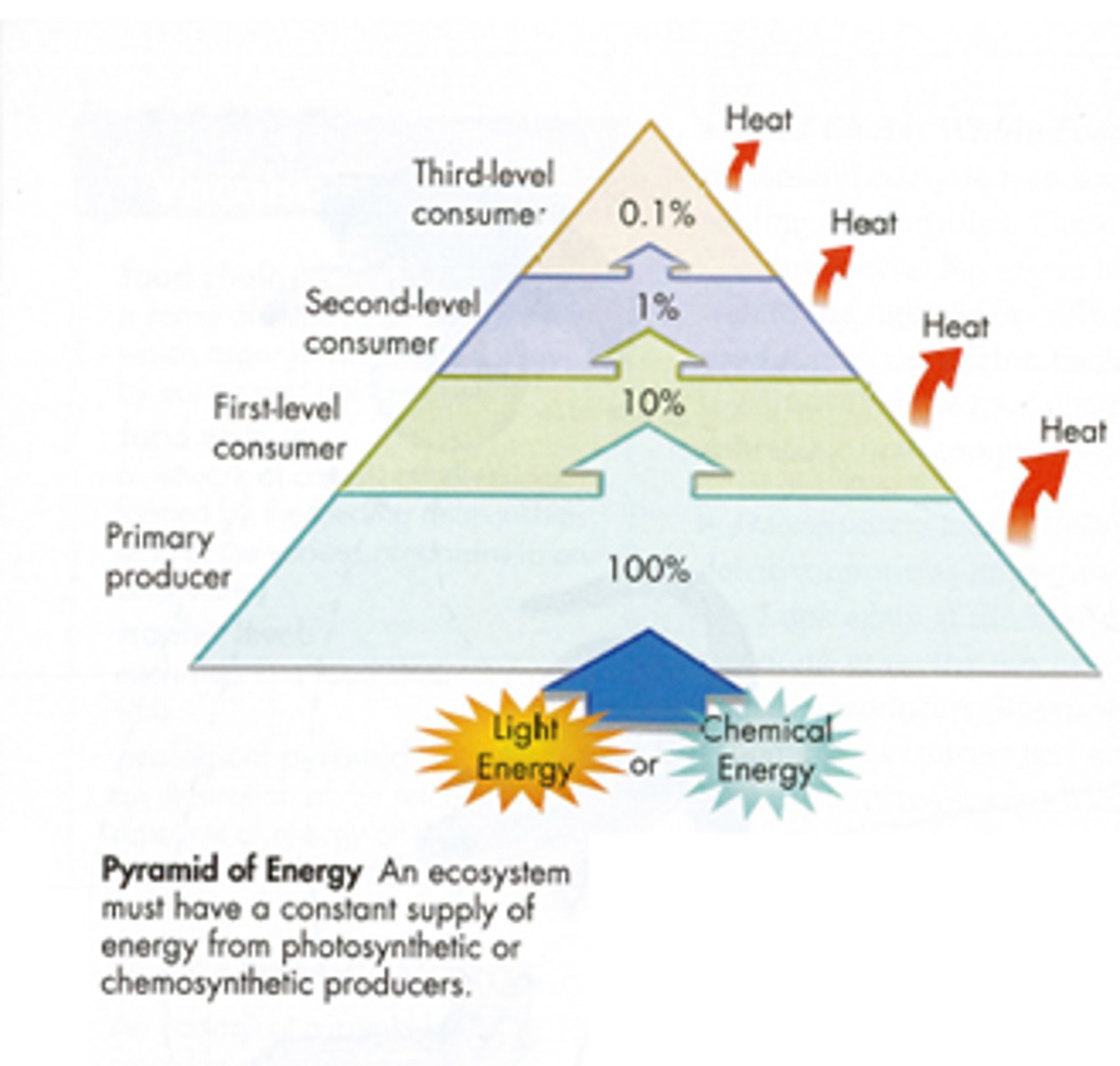
Explain the energy flow in a food chain (energy pyramids)
- Energy decreases as it moves up the pyramid due to inefficiencies like heat loss
- Only about 10% of the heat is transferred to the next, 90% is lost
- When biomass is consumed, energy is transferred from the food source to the consumer
Factors of energy losses between trophic levels
Incomplete consumption
Inefficient digestion
Inefficient energy conversion & storage
Used in metabolic processes
Heat dissipation
Majority of energy is lost as heat
Primary production
The rate at which producers accumulate carbon compounds in their biomass
- Measured in units of mass per unit area per unit time (gm^-2yr^-1)
Gross primary Productivity (GPP)
Rate at which an ecosystem's producers capture and store a given amount of chemical energy as biomass in a given length of time.
- The amount of energy captured as biomass by primary producers
ie. rate of photosynthesis
Net primary production
The remaining energy after losses to cellular respiration(R)
- Represents the energy available to consumers at higher trophic levels
NPP = GPP - R
Secondary production
The rate at which consumers accumulate carbon compounds as part of their biomass
- Heterotrophs also experience biomass loss during cell respiration
Cell respiration (R)
The process where cell derives energy from glucose
glucose+oxygen --> CO2 + H2O + ATP
Gross secondary production (GSP_
The total biomass assimilated by heterotrophs in an ecosystem
- Determined by measuring the mass of food eaten by consumers subtracted mass lost from poopp
GSP = food eaten - fecal loss
Net secondary productivity
Biomass that remains after accounting for respiration losses
- Represents energy available to sustain higher trophic levels
Carbon sinks
absorb more carbon than they release
Carbon sources
Locations or processes that release more carbon into the atmosphere than they absorb
How are photosynthesis and respiration linked together?
Photosynthesis uses CO2 released by cellular respiration, aerobic respiration relies on oxygen released by photosynthesis
Biodiversity
The variet of living organisms including plants, animals, microorganisms
Genetic biodiversity
Variations in species are caused by genetics
Stability
The ability to maintain the ecosystem’s structure and function over time, despite changes or disturbances
If disturbance affects structure or function, then what should a stable ecosystem do?
It should be able to restore itself back to its original state
What are some examples of stable ecosystems?
Tropical rainforests, coral reefs, boreal forests, Sonoran desserts
An ecosystem requires ____ and ____ to maintain its stability over time
Resistance and resilience
Resistance
The ability of an ecosystem to remain stable in the face of disturbances
Resilience
The ability of an ecosystem to recover after a disturbance
Factors contributing to the stability of an ecosystem
Supply of energy, recycling of nutrients, biodiversity, climatic factors
Tipping points
The critical threshold of a change that results in a significant and irreversible change in an ecosystems structure, function, composition
Transpiration
The loss of water vapor from plant leaves
Causes of deforestation
Farming, logging, mining, road building, energy development, settlement, population growth
Keystone species
A species on which other species in an ecosystem largely depend, such that if it were removed the ecosystem would change drastically.
They help define an entire ecosystem
Sustainability
The ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level
Agriculture
The practice of cultivating plants and livestock
Soil erosion
A process that involves the detachment, movement, transportation of soil particles from one location to another
Agrochemicals
Chemicals used in agriculture
Leaching
Occurs when water-soluble minerals in soil are washed away by rain
Carbon footprint
The amount of CO2 released into atmosphere
Eutrophication
Algae overgrowth — A process which water bodies are enriched with excessive nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) leading to overgrowth of algae and other aquatic plants
Bioaccumulation
The gradual buildup of chemical substances in tissues of organisms over time
Biomagnification
The tendency of pollutants to concentrate as they move up the food chain
Microplastics
Small plastic pieces or fragments, measure less than 5mm in size
Rewilding
Reintroducing and restoring natural processes and biodiversity to ecosystems that have been degraded/altered by human activities
Ecological succession
Sequences of changes that progressively transforms ecosystems
Primary succession
The formation of an ecosystem in an environment devoid of vegetation and lacking soil
Secondary succession
Ecological change in an area that previously had life but was destroyed
Cyclic succession
Community composition changes rapidly, continuous cycle of change and regeneration, can be seasonal
Climax community
A stable and mature ecological community, remains unchanged for a long period of time
Arrested succession
Disruption/interruption in normal progression of ecological succession
Examples of keystone species
Beavers, elephants, wolves, bees