Electricity
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Direct current
Cells and batteries supply electric current which always flows in the same direction
Alternating current
Constantly changing direction
Conductor
Allows current to flow / pass through
Insulator
Stops current from flowing
Fuse
When the current becomes too high, the fuse will melt and break the circuit
Formula involving current, time, and charge
Q = I x T
Charge © = current (A) x time (t)
Current
Rate of flow of charge
Equation linking voltage, current, and resistance
V = I x R
Voltage (v) = current (A) x resistance (Ω)
If you increase the voltage …
Then more current will flow
If you increase the resistance …
Then less current will flow (more voltage is needed to keep the same current flowing)
Series circuit
In a series circuit, current is the same everywhere; voltage is distributed over the components (doesn’t have to be equal amounts)
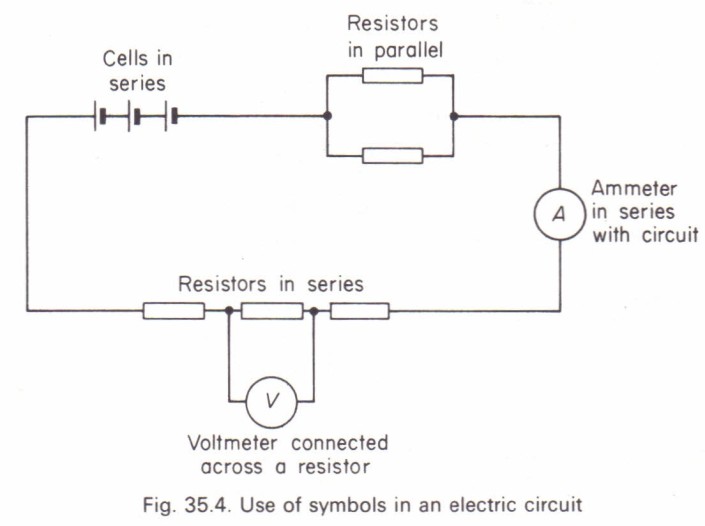
Switch
Opens or closes circuit
Voltmeter
Measures potential difference (volts) (must be parallel / over)
Variable resistor
Changes resistance
Battery
Power source
Ammeter
Measures current (must be placed in series)
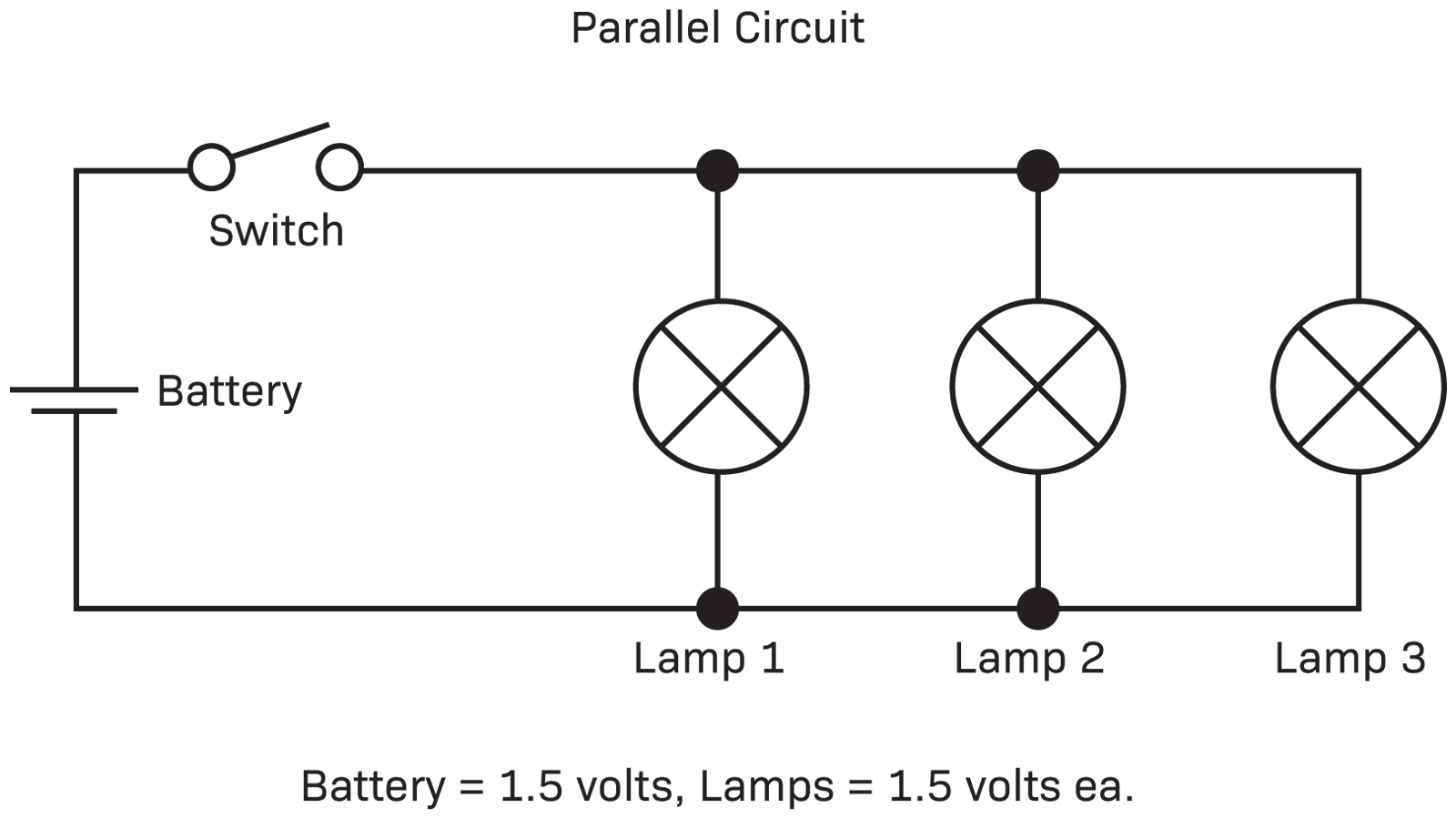
Parallel circuit
Voltage in each branch is equal to the voltage over the battery
Resistance
Resistance is a measure of how hard it is for the electrons to move in an electrical circuit
What causes resistance?
1.) As the electrons move along the wire they collide with the metal ions in the wire
2.) These collisions make the atoms vibrate more, which makes the metal hotter
3.) All wires and components have some resistance, so electrical appliances always waste some energy as heat
Special resistors (don’t obey ohm’s law)
-Thermistors
-Light-dependent resistors (LDR)
-Diode
-Filament bulbs
Thermistor
The resistance of a thermistor decreases as the temperature increases
Light-dependent resistor (LDR)
The resistance of a light-dependent resistor decreases as light intensity increases
Diode
A diode only allows current to flow in one direction through it. No current is allowed to flow the other way in a diode.
Static electricity
Charges which are not free to move. This causes them to build up in one place and it often ends with a spark or a shock when they do move.
Like charges…
Repel
Unlike charges…
Attract