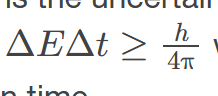Chapter 29: Quantum Physics
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
atomic spectra
the electromagnetic emission from atoms and molecules
binding energy
also called the work function; the amount of energy necessary to eject an electron from a material
blackbody
an ideal radiator, which can radiate equally well at all wavelengths
blackbody radiation
the electromagnetic radiation from a blackbody
bremsstrahlung
German for braking radiation; produced when electrons are decelerated
characteristic x-rays
x rays whose energy depends on the material they were produced in
Compton Effect
the phenomenon whereby x rays scattered from materials have decreased energy
Correspondence Principle
in the classical limit (large, slow-moving objects), quantum mechanics becomes the same as classical physics
de Brogile wavelength
the wavelength possessed by a particle of matter, calculated by 𝜆=ℎ/𝑝
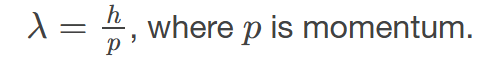
gamma ray
also 𝛾-ray; highest-energy photon in the EM spectrum
Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle
a fundamental limit to the precision with which pairs of quantities (momentum and position, and energy and time) can be measured
infrared radiation
photons with energies slightly less than red light
ionizing radiation
radiation that ionizes materials that absorb it
microwaves
photons with wavelengths on the order of a micron (μm)
particle-wave duality
the property of behaving like either a particle or a wave; the term for the phenomenon that all particles have wave characteristics
photoelectric effect
the phenomenon whereby some materials eject electrons when light is shined on them
photon
a quantum, or particle, of electromagnetic radiation
photon energy
the amount of energy a photon has; 𝐸=hf
photon momentum
the amount of momentum a photon has, calculated by 𝑝=ℎ𝜆=𝐸𝑐
Planck’s Constant
ℎ=6.626×10–34J⋅s
Probability Distribution
the overall spatial distribution of probabilities to find a particle at a given location
Quantized
the fact that certain physical entities exist only with particular discrete values and not every conceivable value
Quantum Mechanics
the branch of physics that deals with small objects and with the quantization of various entities, especially energy
Ultraviolet Radiation
UV; ionizing photons slightly more energetic than violet light
Uncertainty in energy
lack of precision or lack of knowledge of precise results in measurements of energy
Uncertainty in momentum
lack of precision or lack of knowledge of precise results in measurements of momentum
Uncertainty in position
lack of precision or lack of knowledge of precise results in measurements of position
Uncertainty in time
lack of precision or lack of knowledge of precise results in measurements of time
visible light
the range of photon energies the human eye can detect
x ray
EM photon between 𝛾-ray and UV in energy
maximum kinetic energy KE𝑒 of ejected electrons (photoelectrons)
achieved by increasing the frequency of incident light in the photoelectric effect.
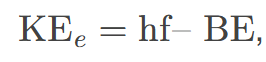
Photons have momentum,
which is the product of their energy and the speed of light, allowing them to exert pressure.

Photon energy and momentum are related
through the equation E = pc, where E is energy, p is momentum, and c is the speed of light.
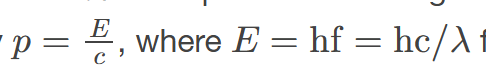
Uncertainty Principle for Energy and time
states that the more precisely the energy of a system is known, the less precisely its time duration can be known, and vice versa.