National 5 Chemistry Unit 1 - Chemical Changes and Structure
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What are the three subatomic particles?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons
What are the four main ways of increasing the rate of reaction?
Increasing the temperature, increasing the concentration, increasing the surface area/decreasing the particle size, and adding a catalyst
Does increasing the size of the beaker increase the rate of reaction?
No
What is collision theory?
A theory that explains that reactions only take place when the reactant particles collide with the correct orientation and sufficient energy, leading to “effective collisions” that form products
Using collision theory, explain how increasing the temperature increases the rate of reaction.
Because it gives the reactant particles more energy
Using collision theory, explain how increasing the concentration increases the rate of reaction.
It means there will be a greater number of reactant particles
Using collision theory, explain how increasing the surface area increases the rate of reaction.
It means there will be more area for reactant particles to collide
What effect does decreasing the particle size have on surface area?
The surface area will increase
What is the formula used to calculate the average rate of reaction?
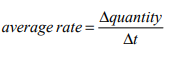
What is a catalyst?
A substance that increases the rate of reaction whilst remaining chemically unchanged in the process
What are four examples of ways to monitor the progress of a chemical reaction?
Measuring the volume of gas produced, measuring the change in mass over time, monitoring changes in pH, measuring changes in concentration
What apparatus can be used to measure the volume of gas produced, other than a gas syringe?
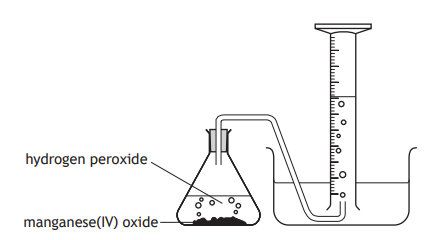
What apparatus can be used to measure the volume of gas produced, other than an upturned measuring cylinder?
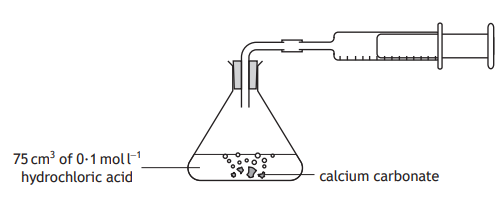
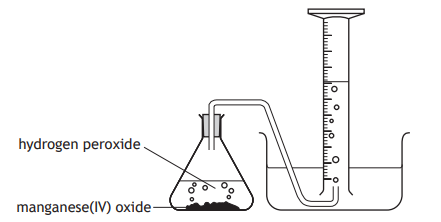
What property must a gas have in order for it to be collected via the apparatus shown?
It must be insoluble or have low solubility
How are elements on the Periodic Table arranged?
In order of increasing atomic number
What is an atom?
The smallest unit into which an element can be divided and still retain its characteristic chemical properties
What is an ion?
An ion is a particle formed when an atom loses or gains and electron to become positively or negatively charged
What is an isotope?
A different form of an element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons/the same atomic number but a different mass number
Why are atoms neutral?
Because they have the same number of protons and electrons
How can you calculate the mass number of an element?
Add the number of protons (the atomic number) and the number of neutrons
What does an element’s atomic number tell us?
The number of protons in an atom of that element
What is meant by the relative atomic mass (RAM)?
The average atomic mass of all known isotopes of an element
What is valency?
The combining power of an element i.e. how many bonds an atom of that element can form with other elements
How many electrons can the first energy level hold?
2
How many electrons can the outermost energy level hold?
8
Why do atoms bond?
To achieve a stable electron configuration
Why do atoms lose or gain electrons to become ions?
To achieve a stable electron configuration
What is meant by a stable electron configuration?
An atom that has a full outer shell of electrons
What mass does a neutron have?
1 amu
What mass does a proton have?
1 amu
What mass does an electron have?
0 amu
What charge does a neutron have?
0
What charge does a proton have?
1+
What charge does an electron have?
1-
Where are protons found?
The nucleus
Where are neutrons found?
The nucleus
Where are electrons found?
Orbiting the nucleus in energy shells
What does the top number in nuclide notation tell us?
The atom’s mass number
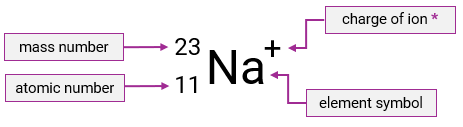
What does the bottom number in nuclide notation tell us?
The atom’s atomic number
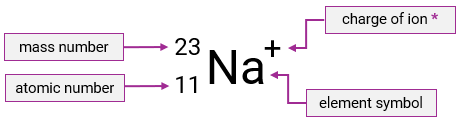
What is a covalent bond?
The electrostatic attraction between positively charge nuclei and a shared pair of electrons
What mnemonic can be used to memorise the 7 diatomic elements?
Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer
What are the 7 diatomic elements?
Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Fluorine, Oxygen, Chlorine, and Bromine
What is a diatomic element?
An element that exists naturally as diatomic molecules
What is a diatomic molecule?
A molecule consisting of only two atoms
What does a linear molecule look like?
The atoms are in a line

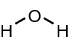
What does an angular molecule look like?
The atoms are arranged in a bent shape
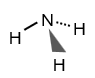
What does a trigonal pyramidal molecule look like?
There are four atoms arranged in a pyramid shape
What does a tetrahedral molecule look like?
There is one central atom surrounded by four other atoms
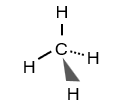
What is an ionic bond?
The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
What structure is formed when ions bond?
An ionic lattice
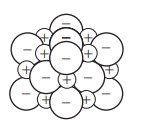
When do ionic compounds conduct electricity?
When molten or in solution
Why do ionic compounds only conduct electricity when molten or in solution?
Because their ions become free to move
Why do ionic compounds not conduct electricity when solid?
Because their ions are not free to move
Do ionic compounds have high or low melting boiling points, and why?
Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points as they contain strong ionic bonds which must be broken in order to change state
Are ionic compounds soluble in water?
Yes, as they dissolve the lattice structure breaks up, allowing water molecules to surround the separated ions
What is the pH scale?
A measurement of how acidic or alkaline a solution is that goes from below 1 to above 14
What is pH a measurement of?
pH stands for “potential of hydrogen” because pH is essentially a measurement of the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution
In terms of ions, what makes a substance acidic?
An acid has a greater concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) than hydroxide ions (OH-)
In terms of ions, what makes a substance neutral?
A neutral substance has an equal concentration of hydrogen (H+) and hydroxide (OH-) ions
In terms of ions, what makes a substance alkaline?
An alkaline substance has a greater concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) than hydrogen ions (H+)
What is meant by the dissociation of water?
The dissociation of water is the reversible chemical process where water molecules naturally dissociate into hydrogen (H+) and hydroxide (OH-)
Write the equation for the dissociation of water.
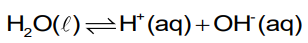
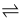
What does this symbol mean?
That a reaction is reversible i.e. it can take place in both directions
What is the difference between an alkali and a base?
A base is any substance that neutralises an acid and an alkali is a soluble base that will dissolve in water to form an alkaline solution
What is the definition of an alkali?
A soluble base that will dissolve in water to form an alkaline solution
What is the definition of a base?
Any substance that neutralises an acid
What are the three main bases at National 5?
Metal carbonates, metal hydroxides, and metal oxides
Write the word equation for a metal oxide reacting with water.
Metal oxide + water —→ metal hydroxide