Parasitology Exam 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
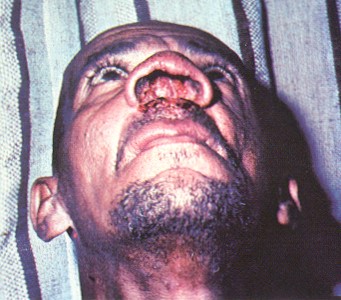
Leishmania braziliensis
Vector: Lutzomyia
Cardinal Sign: infection around nose and mouth (?)
Distribution: South America and Mexico
Cardinal Sign: infection around nose and mouth (?)
Distribution: South America and Mexico
2
New cards
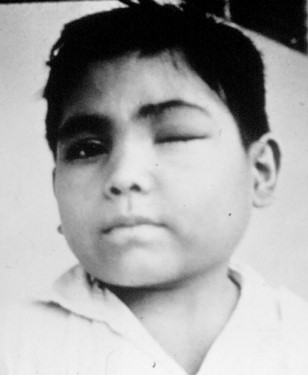
Trypanosoma cruzi
Vector: Triatoma gerstaeckeri and Triatoma sanguisuga
Cardinal Sign: Romana's Sign (swelling at bite site)
Distribution: coastal US, throughout South and Central America
Cardinal Sign: Romana's Sign (swelling at bite site)
Distribution: coastal US, throughout South and Central America
3
New cards
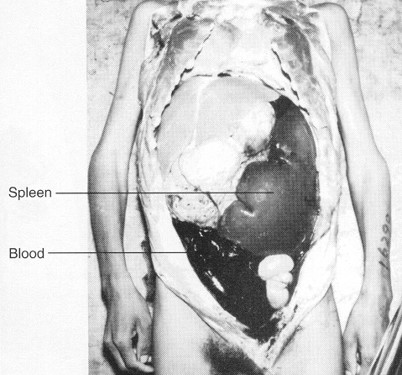
Leishmania donovani
Vector: Phelbotomus argentipes (sandfly)
Cardinal Sign: hepatosplenomegaly (enlargement of liver and spleen)
Distribution: eastern and central Africa, Eastern India, eastern and northern China
Cardinal Sign: hepatosplenomegaly (enlargement of liver and spleen)
Distribution: eastern and central Africa, Eastern India, eastern and northern China
4
New cards
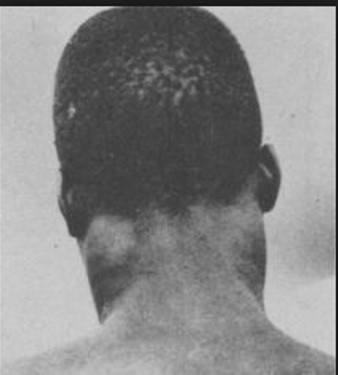
Trypanosoma brucei gambiense or Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense
Vector: Glossina palpalis (gambiense) or Glossina morsitans (rhodesiense)
Cardinal Sign: Winterbottom's Sign (enlargement of lymph)
Distribution: rhodesiense in eastern Africa and gambiense in western Africa
Cardinal Sign: Winterbottom's Sign (enlargement of lymph)
Distribution: rhodesiense in eastern Africa and gambiense in western Africa
5
New cards
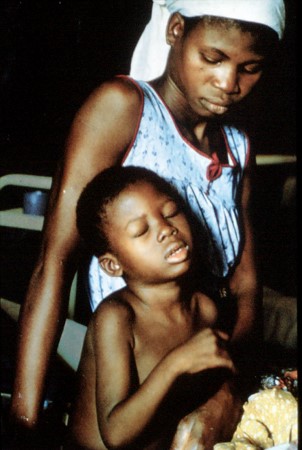
Trypanosoma brucei group
Vector: Glossina spp.
Cardinal Sign: African Sleeping Sickness (invasion of CNS)
Distribution: sub-saharan Africa
Cardinal Sign: African Sleeping Sickness (invasion of CNS)
Distribution: sub-saharan Africa
6
New cards
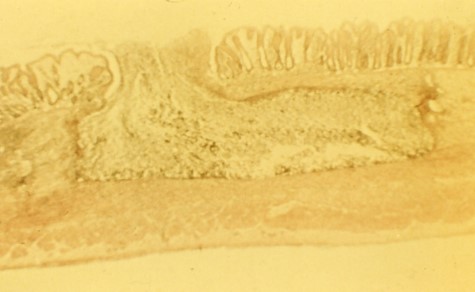
Entamoeba histolytica
Vector: contaminated water with cysts
Cardinal Sign: Flask shaped ulcer
Distribution: worldwise, most common in tropics and subtropics
Cardinal Sign: Flask shaped ulcer
Distribution: worldwise, most common in tropics and subtropics
7
New cards
How do you get infected with malaria
female mosquito infected with Plasmodium sporozoites takes a blood meal which injects those sporozoites
Vector: Anophelus quadrimaculatus
Vector: Anophelus quadrimaculatus
8
New cards
Paroxysm
time when many merozoites burst from RBCs releasing merozoites, pigements, hemoglobin, and metabolic byproducts into bloodstream; this causes the immune system to freak out
merozoites take time to repeat cycle
merozoites take time to repeat cycle
9
New cards
Steps of paroxysm
1. violent chills
2. high fever, headaches, nausea, vomiting, rapid pulse
3. intense sweating
4. symptoms subside and person is exhausted
5. repeats
2. high fever, headaches, nausea, vomiting, rapid pulse
3. intense sweating
4. symptoms subside and person is exhausted
5. repeats
10
New cards
protozoans in large intestine
Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba coli, Endolimax nana, Iodamoeba buetchlii, Dientamoeba fragilis, Trichomonas hominis, Chilomastix mesnili
11
New cards
protozoans in mouth
Entamoeba gingivalis, Trichomonas tenax
12
New cards
Protozoans in reproductive areas
Trichomonas vaginalis
13
New cards
Protozoans in small intestine
Giardia duodenalis
14
New cards
Beavers are a reservoir host for...
Giardia duodenalis (colorado ski resorts)
15
New cards
Pigs (in Egypt and France) are a reservoir host for...
Iodamoeba buetchlii
16
New cards
Dogs are a reservoir host for...
Giardia duodenalis, Leishmania
17
New cards
Rat are a reservoir host for...
Leishmania, Trypanosoma cruzi
18
New cards
Monkeys are a reservoir host for...
Trypanosoma cruzi
19
New cards
Entamoeba histolytica
1. Morphology:
i. Troph is 20-30 um, amoeboid with blunt pseudopodia, one nucleus with smooth chromatin, small central endosome
ii. Cyst is 10-20 um, spereical, 4 nuclei, cigar-shaped chromatoidal bars
2. Taxonomy: Amoeba
3. Life Cycle: ineffective stage is the cyst, remain viable for up to a month, ingested in contaminated food or water; trophs live in large intestine within crypts of lining, may live indefinitely there
4. Geographic Distribution: worldwide but most common in tropics and subtropics
5. Symptoms: abdominal discomfort, intense pain localized on right side, dysentery; few actually ever have clinical signs
6. Pathology: primary ulcer, liver abscesses, heptic amebiasis, pulmonary amebiasis, cerebral amebiasis
7. Diagnosis: fecal smear, nested PCR, monoclonal antibody methods, biopsy, ELISA
8. Epidemiology: contaminated or polluted water, contaminated food, mechanical contamination
9. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: 90% recovery with flagyl (metronizazole)
i. Troph is 20-30 um, amoeboid with blunt pseudopodia, one nucleus with smooth chromatin, small central endosome
ii. Cyst is 10-20 um, spereical, 4 nuclei, cigar-shaped chromatoidal bars
2. Taxonomy: Amoeba
3. Life Cycle: ineffective stage is the cyst, remain viable for up to a month, ingested in contaminated food or water; trophs live in large intestine within crypts of lining, may live indefinitely there
4. Geographic Distribution: worldwide but most common in tropics and subtropics
5. Symptoms: abdominal discomfort, intense pain localized on right side, dysentery; few actually ever have clinical signs
6. Pathology: primary ulcer, liver abscesses, heptic amebiasis, pulmonary amebiasis, cerebral amebiasis
7. Diagnosis: fecal smear, nested PCR, monoclonal antibody methods, biopsy, ELISA
8. Epidemiology: contaminated or polluted water, contaminated food, mechanical contamination
9. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: 90% recovery with flagyl (metronizazole)
20
New cards
Entamoeba coli
1. Morphology:
i. Cysts have 8 nuclei, splinter-like chromatid bars
ii. Trophs have off centered endosome with lumpy chromatin
2. Taxonomy: Amoeba
3. Life Cycle: ineffective stage is the cyst, remain viable for up to a month, ingested in contaminated food or water; trophs live in large intestine within crypts of lining, may live indefinitely there
4. Geographic Distribution: worldwide but most common in tropics and subtropics
5. Epidemiology: contaminated or polluted water, contaminated food, mechanical contamination
i. Cysts have 8 nuclei, splinter-like chromatid bars
ii. Trophs have off centered endosome with lumpy chromatin
2. Taxonomy: Amoeba
3. Life Cycle: ineffective stage is the cyst, remain viable for up to a month, ingested in contaminated food or water; trophs live in large intestine within crypts of lining, may live indefinitely there
4. Geographic Distribution: worldwide but most common in tropics and subtropics
5. Epidemiology: contaminated or polluted water, contaminated food, mechanical contamination
21
New cards
Entamoeba gingiulis (non-pathogenic)
1. Morphology: troph only, no cyst
2. Taxonomy: Amoeba
3. Life Cycle: live in mouth on teeth and gums; hosts are humans, other primates, dogs, and cats
4. Epidemiology: transmission mouth to mouth, droplet spray, or sharing eating utensils
2. Taxonomy: Amoeba
3. Life Cycle: live in mouth on teeth and gums; hosts are humans, other primates, dogs, and cats
4. Epidemiology: transmission mouth to mouth, droplet spray, or sharing eating utensils
22
New cards
Endolimax nana (non-pathogenic)
1. Morphology: trophs are tiny (6-15 um), large glycogen vacuoles; cysts are 5-14 um, 4 nuclei and elliptical; endosome big and blobby
2. Taxonomy: Amoeba
3. Life Cycle: found in large intestine near cecum, feed on bacteria
4. Geographic Distribution: 30% worldwide
2. Taxonomy: Amoeba
3. Life Cycle: found in large intestine near cecum, feed on bacteria
4. Geographic Distribution: 30% worldwide
23
New cards
Iodamoeba buetschii
1. Morphology: endosome has tiny vacuoles around it; trophs are 9-4um; cysts are 6-15um with very large vacuole and one nuclei
2. Taxonomy: Amoeba
3. Life Cycle: lives in large intestine
4. Geographic Distribution: France and Egypt
5. Epidemiology: no very common endocommensal in people but very common in pigs
2. Taxonomy: Amoeba
3. Life Cycle: lives in large intestine
4. Geographic Distribution: France and Egypt
5. Epidemiology: no very common endocommensal in people but very common in pigs
24
New cards
Dientamoeba fragilis
1. Morphology: no cyst cycle; 2 fragmented nuclei; very small
2. Taxonomy: not actually an amoeba
3. Life Cycle: does not form cysts; trophs cannot survive passage through small intestine; humans most likely get infected when ingesting pinworm eggs
2. Taxonomy: not actually an amoeba
3. Life Cycle: does not form cysts; trophs cannot survive passage through small intestine; humans most likely get infected when ingesting pinworm eggs
25
New cards
Hisomonas meleagridis
1. Morphology: only trophs, no cyst stage; irregular shape
2. Taxonomy:
3. Life Cycle: transmission is within the egg of the cecum nematode that young birds then eat
4. Symptoms: ruffled feathers, dark skin pigment, hang wings/tail
5. Pathology: young turkeys are more susceptible to the infection than chickens; mortality can reach 100%
2. Taxonomy:
3. Life Cycle: transmission is within the egg of the cecum nematode that young birds then eat
4. Symptoms: ruffled feathers, dark skin pigment, hang wings/tail
5. Pathology: young turkeys are more susceptible to the infection than chickens; mortality can reach 100%
26
New cards
Naegleria fowleri
1. Morphology: free living in water and soil; heat loving; can be found in river/lake sediment
2. Taxonomy: Percolozoa
3. Life Cycle: contains cyst and troph
4. Geographic Distribution: worldwide in warm/hot freshwater
5. Symptoms: headache, fever, neck rigidity, mental confusion, coma, and death
6. Pathology: enters nose and naval cavities, trophs migrate to the cranium, trophs rapidly divide and cause brain tissue destruction; death usually occurs due to brain destruction; Primary Amebic Mengoencephalitis (PAM)
7. Epidemiology: person going swimming in infected water and getting water up their nose
8. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: 97% fatality rate, some drugs are affective however to what extent is unknown as most patients die
2. Taxonomy: Percolozoa
3. Life Cycle: contains cyst and troph
4. Geographic Distribution: worldwide in warm/hot freshwater
5. Symptoms: headache, fever, neck rigidity, mental confusion, coma, and death
6. Pathology: enters nose and naval cavities, trophs migrate to the cranium, trophs rapidly divide and cause brain tissue destruction; death usually occurs due to brain destruction; Primary Amebic Mengoencephalitis (PAM)
7. Epidemiology: person going swimming in infected water and getting water up their nose
8. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: 97% fatality rate, some drugs are affective however to what extent is unknown as most patients die
27
New cards
Acanthamoeba spp.
1. Morphology: trophs only occur as amoeboid forms
2. Life Cycle: free living trophs and cysts occur in both soil and freshwater
3. Symptoms: foreign body sensations, severe ocular pain, photophobia, blurred vision
4. Pathology: enlarged corneal nerve (keratoneuritis), scleritis in advanced cases
5. Epidemiology: people who wear contact lenses trying to make their own saline
6. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: early diagnosis important; topical anti-amoeba agents; penetrating keratoplasy in severe cases
2. Life Cycle: free living trophs and cysts occur in both soil and freshwater
3. Symptoms: foreign body sensations, severe ocular pain, photophobia, blurred vision
4. Pathology: enlarged corneal nerve (keratoneuritis), scleritis in advanced cases
5. Epidemiology: people who wear contact lenses trying to make their own saline
6. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: early diagnosis important; topical anti-amoeba agents; penetrating keratoplasy in severe cases
28
New cards
Trichomonas vaginalis
1. Morphology: troph is the only stage present; 7-32um long and 5-12um wide
2. Taxonomy: Metamonada
3. Life Cycle: trophs only, no cysts
4. Geographic Distribution: worldwide
5. Symptoms: usually none; males do not show any symptoms; in women: chaffing, itching, frothing/clear/creamy discharge (Leuhurrhea)
6. Pathology: severe cases lead to disintegration of vaginal epithelial lining; tophs can survive in low pH; does not explain stillbirths, spontaneous abortions, or death in women
7. Diagnosis: vaginal smear
8. Epidemiology: sexual contact, soiled clothing, sharing towel; can live for up to a day in clothing
9. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Flagyl for 4-5 days; reinfection can happen almost immediately so partner also needs to take drug; 100% recovery
2. Taxonomy: Metamonada
3. Life Cycle: trophs only, no cysts
4. Geographic Distribution: worldwide
5. Symptoms: usually none; males do not show any symptoms; in women: chaffing, itching, frothing/clear/creamy discharge (Leuhurrhea)
6. Pathology: severe cases lead to disintegration of vaginal epithelial lining; tophs can survive in low pH; does not explain stillbirths, spontaneous abortions, or death in women
7. Diagnosis: vaginal smear
8. Epidemiology: sexual contact, soiled clothing, sharing towel; can live for up to a day in clothing
9. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Flagyl for 4-5 days; reinfection can happen almost immediately so partner also needs to take drug; 100% recovery
29
New cards
Trichomonas tenax
1. Pathology: associated with periodontal disease but does not cause this, non-pathogenic
2. Epidemiology: transmitted orally by kissing, sharing food/drinks
2. Epidemiology: transmitted orally by kissing, sharing food/drinks
30
New cards
Trichomonas hominis
1. Morphology: undulating membrane, free flagella, 5 anterior flagella
2. Life Cycle: non-pathogenic, endocommensal, found in large intestine/cecum
3. Epidemiology: ingestion of troph in contaminated water; indicates poor hygeiene and sanitation
2. Life Cycle: non-pathogenic, endocommensal, found in large intestine/cecum
3. Epidemiology: ingestion of troph in contaminated water; indicates poor hygeiene and sanitation
31
New cards
Chilomastix mesnili
1. Morphology: trophs have 4 flagella and is tear drop shaped; cysts have single nucleus and retracted flagella and are lemon shaped
2. Life Cycle: water-borne endocommensal, non-pathogenic
3. Epidemiology: indicates poor hygeiene and sanitation
2. Life Cycle: water-borne endocommensal, non-pathogenic
3. Epidemiology: indicates poor hygeiene and sanitation
32
New cards
Giardia duodenalis
1. Morphology:
i. Troph: bi nucleated, 12-15um, ventral adhesive disk, 8 flagella, median bodies
ii. Cysts: oval shape, 8-12um long, 4 nuclei, flagella shorten and retract, axonemes
2. Taxonomy: Metamonada (also called G. lamblia or G. intestinalis)
3. Life Cycle: Trophs live in upper small intestine and attach to epithelail cells, feed on mucus, absorbs vitamins and amino acids; cysts form when trophs become dehydrated while passing through large intestine; cysts can stay in external environment for several months
4. Geographic Distribution: worldwide (ex. Colorado ski resorts, daycare centers)
5. Symptoms: ranges from none to abdominal discomfort causing acute/chronic diarrhea (grey, greasy, voluminous, malodorous diarrhea)
6. Pathology: nutrient malabsorption and physical blockage with damage to microvilli; fat/CHO digestion decreases, absorption decreases, both cause malabsorption and maldigestion
7. Diagnosis: at least 3 exams before determination, ELISA test, PCR
8. Epidemiology: ingesting cyst through contaminated water, most common intestinal flagellate of people, reservoir hosts are beavers, cats, and dogs
9. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: flagyl; not hard to treat but have to keep those who were infected from becoming reinfected
i. Troph: bi nucleated, 12-15um, ventral adhesive disk, 8 flagella, median bodies
ii. Cysts: oval shape, 8-12um long, 4 nuclei, flagella shorten and retract, axonemes
2. Taxonomy: Metamonada (also called G. lamblia or G. intestinalis)
3. Life Cycle: Trophs live in upper small intestine and attach to epithelail cells, feed on mucus, absorbs vitamins and amino acids; cysts form when trophs become dehydrated while passing through large intestine; cysts can stay in external environment for several months
4. Geographic Distribution: worldwide (ex. Colorado ski resorts, daycare centers)
5. Symptoms: ranges from none to abdominal discomfort causing acute/chronic diarrhea (grey, greasy, voluminous, malodorous diarrhea)
6. Pathology: nutrient malabsorption and physical blockage with damage to microvilli; fat/CHO digestion decreases, absorption decreases, both cause malabsorption and maldigestion
7. Diagnosis: at least 3 exams before determination, ELISA test, PCR
8. Epidemiology: ingesting cyst through contaminated water, most common intestinal flagellate of people, reservoir hosts are beavers, cats, and dogs
9. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: flagyl; not hard to treat but have to keep those who were infected from becoming reinfected
33
New cards
Leishmania donovani
1. Morphology: amastigotes (round, internal flagellum) in humans and promastigotes (flagellum at anterior end of flagulate) in sand flies
2. Taxonomy: Euglenozoa
3. Life Cycle: Amastigotes and promastigotes
4. Geographic Distribution: eastern and central Africa, Eastern India, Eastern and Northern China
5. Symptoms: Kala-Azar: headache, fever, wasting disease, emancipation, bleeding from mucous membrane, dysentery, anemia, Hepatosplenomegaly (Cardinal symptom, enlargement of liver and spleen)
6. Pathology: visceral leishmanisis: invasion of white blood cells (macrophages), body cannot produce RBC because all energy is going towards making more macrophages, hyperplasia (excessive proliferation of normal cells in the normal tissue of an organ), amastigotes
7. Diagnosis: ELISA, IFA (indirect fluorescent antibody test), best way is to do a biopsy of liver or spleen (invasive and uncomfortable)
8. Epidemiology: vector is Phlebotomus argentipes (sand fly), female sand fly ingest macrophage with amastigotes, sand fly becomes infected with promastigotes and ingests fruit juice, proboscises becomes filled with promastigotes, female sand fly takes blood meal from human ejecting promastigotes into bloodstream, promastigotes then infect macrophages turning into amastigotes
9. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: antimony compounds (arsenic, extremely toxic), Pentamidine, without treatment it will lead to fatality, however you might also die from the treatment itself
2. Taxonomy: Euglenozoa
3. Life Cycle: Amastigotes and promastigotes
4. Geographic Distribution: eastern and central Africa, Eastern India, Eastern and Northern China
5. Symptoms: Kala-Azar: headache, fever, wasting disease, emancipation, bleeding from mucous membrane, dysentery, anemia, Hepatosplenomegaly (Cardinal symptom, enlargement of liver and spleen)
6. Pathology: visceral leishmanisis: invasion of white blood cells (macrophages), body cannot produce RBC because all energy is going towards making more macrophages, hyperplasia (excessive proliferation of normal cells in the normal tissue of an organ), amastigotes
7. Diagnosis: ELISA, IFA (indirect fluorescent antibody test), best way is to do a biopsy of liver or spleen (invasive and uncomfortable)
8. Epidemiology: vector is Phlebotomus argentipes (sand fly), female sand fly ingest macrophage with amastigotes, sand fly becomes infected with promastigotes and ingests fruit juice, proboscises becomes filled with promastigotes, female sand fly takes blood meal from human ejecting promastigotes into bloodstream, promastigotes then infect macrophages turning into amastigotes
9. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: antimony compounds (arsenic, extremely toxic), Pentamidine, without treatment it will lead to fatality, however you might also die from the treatment itself
34
New cards
Sylvan-enzaotic cycle
transmission in wild animals (foxes, coyotes, armadillos, monkeys, rodents, raccoons)
35
New cards
Peridomestic-zoonotic cycle
transmission in around the house animals (dogs, cats, humans,) (chickens cannot get infected but are good food sources)
36
New cards
Domestic-endemic cycle
transmission just between bugs and humans
37
New cards
Leishmania tropica
a. Morphology: amastigotes (round, internal flagellum) in humans and promastigotes (flagellum at anterior end of flagulate) in sand flies
b. Taxonomy: Euglenozoa
c. Life Cycle: female sand fly ingest macrophage with amastigotes, sand fly becomes infected with promastigotes and ingests fruit juice, proboscises becomes filled with promastigotes, female sand fly takes blood meal from human ejecting promastigotes into bloodstream, promastigotes then infect macrophages turning into amastigotes
d. Geographic Distribution: Middle East (Turkey, Iraq, Iran, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Northern Africa)
e. Symptoms: “Oriental sore”, open sore occurs where the fly bit the person
f. Pathology: Cutaneous leishmaniasis, infection of macrophages of the skin
g. Diagnosis: ELISA, IFA (indirect fluorescent antibody test)
h. Epidemiology: vector is Phlebotomus sergenti (sandfly)
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Antimony compounds (arsenic, extremely toxic)
b. Taxonomy: Euglenozoa
c. Life Cycle: female sand fly ingest macrophage with amastigotes, sand fly becomes infected with promastigotes and ingests fruit juice, proboscises becomes filled with promastigotes, female sand fly takes blood meal from human ejecting promastigotes into bloodstream, promastigotes then infect macrophages turning into amastigotes
d. Geographic Distribution: Middle East (Turkey, Iraq, Iran, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Northern Africa)
e. Symptoms: “Oriental sore”, open sore occurs where the fly bit the person
f. Pathology: Cutaneous leishmaniasis, infection of macrophages of the skin
g. Diagnosis: ELISA, IFA (indirect fluorescent antibody test)
h. Epidemiology: vector is Phlebotomus sergenti (sandfly)
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Antimony compounds (arsenic, extremely toxic)
38
New cards
Leishmania braziliensus
a. Morphology: amastigotes (round, internal flagellum) in humans and promastigotes (flagellum at anterior end of flagulate) in sand flies
b. Taxonomy: Euglenozoa
c. Life Cycle: female sand fly ingest macrophage with amastigotes, sand fly becomes infected with promastigotes and ingests fruit juice, proboscises becomes filled with promastigotes, female sand fly takes blood meal from human ejecting promastigotes into bloodstream, promastigotes then infect macrophages turning into amastigotes
d. Geographic Distribution: South America, Mexico, Southern US
e. Symptoms: Chiclero’s ulcer (biting the ears of people)
f. Pathology: Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, infection of mucous layers and membranes around mouth, nose cartilage, and pharynx region
g. Diagnosis: ELISA, IFA (indirect fluorescent antibody test)
h. Epidemiology: Vector is Lutzomyia (sand fly)
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Antimony compounds (arsenic, extremely toxic)
b. Taxonomy: Euglenozoa
c. Life Cycle: female sand fly ingest macrophage with amastigotes, sand fly becomes infected with promastigotes and ingests fruit juice, proboscises becomes filled with promastigotes, female sand fly takes blood meal from human ejecting promastigotes into bloodstream, promastigotes then infect macrophages turning into amastigotes
d. Geographic Distribution: South America, Mexico, Southern US
e. Symptoms: Chiclero’s ulcer (biting the ears of people)
f. Pathology: Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, infection of mucous layers and membranes around mouth, nose cartilage, and pharynx region
g. Diagnosis: ELISA, IFA (indirect fluorescent antibody test)
h. Epidemiology: Vector is Lutzomyia (sand fly)
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Antimony compounds (arsenic, extremely toxic)
39
New cards
Trypanosoma brucei gamiense
a. Morphology: Trypomastigotes in humans and epimastigotes in tsetse fly
b. Taxonomy: Euglenozoa
c. Life Cycle: uninfected tsetse fly bites infected vertebrate and ingests trypomastigotes that were in the bloodstream; binary fission and they migrate the salivary glands where they transform to epimastigotes; epimastigotes transform to metacyclic trypomastigotes and hang out in salivary glands; tsetse fly bites host and trypomastigotes go into bloodstream; trypomastigotes multiply in blood and lymph nodes
d. Geographic Distribution: West Africa
e. Symptoms: itching and inflammation of skin; fever, headache, skin rash; general weakness; emaciation, severe headaches, apathy, drowsiness, coma; death from asthenia, heart failure, meningitis, severe falls
f. Pathology: Chronic Sleeping Sickness; Winterbottom’s Sign (enlargement of lymph nodes); hyper stimulated immune system; host lyses own RBC
g. Diagnosis: find trypanosomes in plasma
h. Epidemiology: vector is Glossina palpalis (tsetse fly)
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Eflornithine (DFMO), well tolerated, effective against CNS form, expensive
b. Taxonomy: Euglenozoa
c. Life Cycle: uninfected tsetse fly bites infected vertebrate and ingests trypomastigotes that were in the bloodstream; binary fission and they migrate the salivary glands where they transform to epimastigotes; epimastigotes transform to metacyclic trypomastigotes and hang out in salivary glands; tsetse fly bites host and trypomastigotes go into bloodstream; trypomastigotes multiply in blood and lymph nodes
d. Geographic Distribution: West Africa
e. Symptoms: itching and inflammation of skin; fever, headache, skin rash; general weakness; emaciation, severe headaches, apathy, drowsiness, coma; death from asthenia, heart failure, meningitis, severe falls
f. Pathology: Chronic Sleeping Sickness; Winterbottom’s Sign (enlargement of lymph nodes); hyper stimulated immune system; host lyses own RBC
g. Diagnosis: find trypanosomes in plasma
h. Epidemiology: vector is Glossina palpalis (tsetse fly)
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Eflornithine (DFMO), well tolerated, effective against CNS form, expensive
40
New cards
Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense
a. Morphology: Trypomastigotes in humans and epimastigotes in tsetse fly
b. Taxonomy: Euglenozoa
c. Life Cycle: uninfected tsetse fly bites infected vertebrate and ingests trypomastigotes that were in the bloodstream; binary fission and they migrate the salivary glands where they transform to epimastigotes; epimastigotes transform to metacyclic trypomastigotes and hang out in salivary glands; tsetse fly bites host and trypomastigotes go into bloodstream; trypomastigotes multiply in blood and lymph nodes
d. Geographic Distribution: East Africa
e. Symptoms itching and inflammation of skin; fever, headache, skin rash; general weakness; emaciation, severe headaches, apathy, drowsiness, coma; death from asthenia, heart failure, meningitis, severe falls
f. Pathology: Acute Sleeping Sickness; Winterbottom’s Sign (enlargement of lymph nodes); hyper stimulated immune system; host lyses own RBC
g. Diagnosis: find trypanosomes in plasma
h. Epidemiology: vector is Glossina morsitans (tsetse fly)
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Eflornithine (DFMO), well tolerated, effective against CNS form, expensive
b. Taxonomy: Euglenozoa
c. Life Cycle: uninfected tsetse fly bites infected vertebrate and ingests trypomastigotes that were in the bloodstream; binary fission and they migrate the salivary glands where they transform to epimastigotes; epimastigotes transform to metacyclic trypomastigotes and hang out in salivary glands; tsetse fly bites host and trypomastigotes go into bloodstream; trypomastigotes multiply in blood and lymph nodes
d. Geographic Distribution: East Africa
e. Symptoms itching and inflammation of skin; fever, headache, skin rash; general weakness; emaciation, severe headaches, apathy, drowsiness, coma; death from asthenia, heart failure, meningitis, severe falls
f. Pathology: Acute Sleeping Sickness; Winterbottom’s Sign (enlargement of lymph nodes); hyper stimulated immune system; host lyses own RBC
g. Diagnosis: find trypanosomes in plasma
h. Epidemiology: vector is Glossina morsitans (tsetse fly)
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Eflornithine (DFMO), well tolerated, effective against CNS form, expensive
41
New cards
Trypanosoma cruzi
a. Morphology: epimastigotes in bugs (infective stage), amastigotes in muscle cells
b. Taxonomy: Euglenozoa
c. Life Cycle: trypomastigotes in human blood ingested by bug; epimastigotes transmitted through bug feces that gets into open wound or mucous membrane; trypomastigotes found in plasma; amastigotes reproduce in muscle cells
d. Geographic Distribution: coastal US, throughout South and Central America
e. Symptoms: Romana’s Sign (swelling at bite site), headache, fever, prostration; those symptoms subside; then edema (abnormal accumulation of fluid in the tissue spaces), inflamed lymph glands, enlarged spleen and liver
f. Pathology: apex of heart becomes very thin, impulses into ventricles are affected; megasophagus and peristalsis destroyed, organs increase their size, victim may not be able to swallow and may die from starvation; feces not formed efficiently
g. Diagnosis: demonstration of trypanosomes in blood but very difficult; ELISA; xenodiagnosis
h. Epidemiology: vector is the family Reduvidae (assassin bugs, kissing bugs); Triatoma infestans, Triatoma sanguisaga; stercorarian transmission
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: not good, no effective treatment
b. Taxonomy: Euglenozoa
c. Life Cycle: trypomastigotes in human blood ingested by bug; epimastigotes transmitted through bug feces that gets into open wound or mucous membrane; trypomastigotes found in plasma; amastigotes reproduce in muscle cells
d. Geographic Distribution: coastal US, throughout South and Central America
e. Symptoms: Romana’s Sign (swelling at bite site), headache, fever, prostration; those symptoms subside; then edema (abnormal accumulation of fluid in the tissue spaces), inflamed lymph glands, enlarged spleen and liver
f. Pathology: apex of heart becomes very thin, impulses into ventricles are affected; megasophagus and peristalsis destroyed, organs increase their size, victim may not be able to swallow and may die from starvation; feces not formed efficiently
g. Diagnosis: demonstration of trypanosomes in blood but very difficult; ELISA; xenodiagnosis
h. Epidemiology: vector is the family Reduvidae (assassin bugs, kissing bugs); Triatoma infestans, Triatoma sanguisaga; stercorarian transmission
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: not good, no effective treatment
42
New cards
Plasmodium vivax
a. Morphology:
i. Ring troph: enlarges RBC, ring ½ size of RBC
ii. Schizont: enlarges RBC, more than 12 merozoites inside
iii. Gametocyte: enlarges RBC
b. Taxonomy: Apicomplexa
c. Life Cycle: female mosquito takes blood meal and injects sporozoites into blood stream where they go to the liver; sporozoites under for schizogeny; merozoites released to infect RBCs; cycles between schizogeny and merozigony for ~3 weeks; merozoites turn into macro/microgametocytes; macro/microgametocytes infect RBC and stay there; female mosquito takes blood meal ingesting macro/microgametocytes; sexual reproduction occurs to form ookinete that burrows through stomach lining to form oocysts; oocysts form sporozoites that release to migrate to the salivary glands of mosquito
d. Geographic Distribution: widespread, temperate area, Asia, Northern Africa
e. Symptoms: paroxysm (violent chills, high fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, sweating, exhaustion, repeats)
f. Pathology: destruction of RBCs (loss of oxygen to tissues and cells); accumulation of iron pigment in liver, spleen, or brain; overactive immune system; anemia
g. Diagnosis
h. Epidemiology: Anophelus quadrimaculatus (N. American mosquito) vector
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Quinine, Chloroquine, Primaquine
i. Ring troph: enlarges RBC, ring ½ size of RBC
ii. Schizont: enlarges RBC, more than 12 merozoites inside
iii. Gametocyte: enlarges RBC
b. Taxonomy: Apicomplexa
c. Life Cycle: female mosquito takes blood meal and injects sporozoites into blood stream where they go to the liver; sporozoites under for schizogeny; merozoites released to infect RBCs; cycles between schizogeny and merozigony for ~3 weeks; merozoites turn into macro/microgametocytes; macro/microgametocytes infect RBC and stay there; female mosquito takes blood meal ingesting macro/microgametocytes; sexual reproduction occurs to form ookinete that burrows through stomach lining to form oocysts; oocysts form sporozoites that release to migrate to the salivary glands of mosquito
d. Geographic Distribution: widespread, temperate area, Asia, Northern Africa
e. Symptoms: paroxysm (violent chills, high fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, sweating, exhaustion, repeats)
f. Pathology: destruction of RBCs (loss of oxygen to tissues and cells); accumulation of iron pigment in liver, spleen, or brain; overactive immune system; anemia
g. Diagnosis
h. Epidemiology: Anophelus quadrimaculatus (N. American mosquito) vector
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Quinine, Chloroquine, Primaquine
43
New cards
Plasmodium falciparum
a. Morphology:
i. Ring troph: rings 1/3 the size of cell, may be multiple in cell
ii. Schizont: present in muscle cells
iii. Gametocyte: banana shaped
b. Taxonomy: Apicomplexa
c. Life Cycle: female mosquito takes blood meal and injects sporozoites into blood stream where they go to the liver; sporozoites under for schizogeny; merozoites released to infect RBCs; cycles between schizogeny and merozigony for ~3 weeks; merozoites turn into macro/microgametocytes; macro/microgametocytes infect RBC and stay there; female mosquito takes blood meal ingesting macro/microgametocytes; sexual reproduction occurs to form ookinete that burrows through stomach lining to form oocysts; oocysts form sporozoites that release to migrate to the salivary glands of mosquito
d. Geographic Distribution: Tropics
e. Symptoms: paroxysm (violent chills, high fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, sweating, exhaustion, repeats)
f. Pathology: destruction of RBCs (loss of oxygen to tissues and cells); accumulation of iron pigment in liver, spleen, or brain; overactive immune system; anemia
g. Diagnosis
h. Epidemiology: Anophelus quadrimaculatus (N. American mosquito) vector
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Quinine, Chloroquine, Primaquine
i. Ring troph: rings 1/3 the size of cell, may be multiple in cell
ii. Schizont: present in muscle cells
iii. Gametocyte: banana shaped
b. Taxonomy: Apicomplexa
c. Life Cycle: female mosquito takes blood meal and injects sporozoites into blood stream where they go to the liver; sporozoites under for schizogeny; merozoites released to infect RBCs; cycles between schizogeny and merozigony for ~3 weeks; merozoites turn into macro/microgametocytes; macro/microgametocytes infect RBC and stay there; female mosquito takes blood meal ingesting macro/microgametocytes; sexual reproduction occurs to form ookinete that burrows through stomach lining to form oocysts; oocysts form sporozoites that release to migrate to the salivary glands of mosquito
d. Geographic Distribution: Tropics
e. Symptoms: paroxysm (violent chills, high fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, sweating, exhaustion, repeats)
f. Pathology: destruction of RBCs (loss of oxygen to tissues and cells); accumulation of iron pigment in liver, spleen, or brain; overactive immune system; anemia
g. Diagnosis
h. Epidemiology: Anophelus quadrimaculatus (N. American mosquito) vector
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Quinine, Chloroquine, Primaquine
44
New cards
Plasmodium malariae
a. Morphology:
i. Ring troph: does not enlarge RBC, ring ½ the size of cell
ii. Schizont: less than 12 merozoites (usually like 8)
iii. Gametocyte: pigmented cell, does not enlarge RBC
b. Taxonomy: Apicomplexa
c. Life Cycle: female mosquito takes blood meal and injects sporozoites into blood stream where they go to the liver; sporozoites under for schizogeny; merozoites released to infect RBCs; cycles between schizogeny and merozigony for ~3 weeks; merozoites turn into macro/microgametocytes; macro/microgametocytes infect RBC and stay there; female mosquito takes blood meal ingesting macro/microgametocytes; sexual reproduction occurs to form ookinete that burrows through stomach lining to form oocysts; oocysts form sporozoites that release to migrate to the salivary glands of mosquito
d. Geographic Distribution: rare, localized but widespread
e. Symptoms: paroxysm (violent chills, high fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, sweating, exhaustion, repeats)
f. Pathology: destruction of RBCs (loss of oxygen to tissues and cells); accumulation of iron pigment in liver, spleen, or brain; overactive immune system; anemia
g. Diagnosis
h. Epidemiology: Anophelus quadrimaculatus (N. American mosquito) vector
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Quinine, Chloroquine, Primaquine
i. Ring troph: does not enlarge RBC, ring ½ the size of cell
ii. Schizont: less than 12 merozoites (usually like 8)
iii. Gametocyte: pigmented cell, does not enlarge RBC
b. Taxonomy: Apicomplexa
c. Life Cycle: female mosquito takes blood meal and injects sporozoites into blood stream where they go to the liver; sporozoites under for schizogeny; merozoites released to infect RBCs; cycles between schizogeny and merozigony for ~3 weeks; merozoites turn into macro/microgametocytes; macro/microgametocytes infect RBC and stay there; female mosquito takes blood meal ingesting macro/microgametocytes; sexual reproduction occurs to form ookinete that burrows through stomach lining to form oocysts; oocysts form sporozoites that release to migrate to the salivary glands of mosquito
d. Geographic Distribution: rare, localized but widespread
e. Symptoms: paroxysm (violent chills, high fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, sweating, exhaustion, repeats)
f. Pathology: destruction of RBCs (loss of oxygen to tissues and cells); accumulation of iron pigment in liver, spleen, or brain; overactive immune system; anemia
g. Diagnosis
h. Epidemiology: Anophelus quadrimaculatus (N. American mosquito) vector
i. Prognosis/Drug of Choice: Quinine, Chloroquine, Primaquine