6.7 Response to infection
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is a pathogen?
Organisms cause harm by invading and destroying host tissues and producing toxins
What are examples of pathogens?
Lamda phage
RNA viruses
TMV
Ebola
Staphylococcus Aureus
Stem rust fungus
Myobacterium
Influenza
Plasmodium
What are some barriers to non-specific infection?
Skin
Blood clotting
Stomach acid
Mucus and cilia
Antibacterial chemicals in sweat and tears
Skin
Physical and waterproof (keratin)
Blood clotting
Quick seal any breaks in skin
Stomach acid
Destroys ingested pathogens
Mucus and cilia
Trap + remove pathogens
Cilia waft mucus to stomach
Antibacterial chems
Lysozymes (digestive enzymes) found in sweat and tears
Kill bacteria
What are eosinophils
Parasitic function
Regulate allergic responses
What are monocytes?
Type of phagocytic cell
Macrophages
Phagocytic cells
Kidney chased nucleus
Mature from monocytes
Produced in bone marrow
Macrophage function
Engulf foreign cells, particles and infectious agents
Process them + present to lymphocytes
What cells are found in bone marrow?
WBCs and RBCs
Neutrophils
Phagocytic
lobed nucleus
Short live, large quant in bone marrow
Found in all tissues at site of injury
Neutrophil function
Engulf and destroy foreign cells, particles and infectious agents by phagocytosis
Lymphocytes
Non phagocytic cells
What do lymphocytes do?
Mature in bone marrow B for bone
or migrate to and mature in thymus gland T for thymus gland
Lymphocytes function
Differentiate into many different types of cells
Lymphocytes functions
Killing infected cells
Producing antibodies = providing immunity
Outline non-specific immune response
Offers protection against all pathogens encountered without any specificity
Lacks immunological mem, so rs are at same each time patho is encountered
Quicker than specific I r
What components of non-s defences are always present?
Barriers to infection - phagocytic less
How is non specific i r activated?
Histamine, complement and interferons
Where is histamine found?
Amine stored in granules of basophils
What happens when histamine is released from its granules?
Histamine = arterioles dilate + increase in permeability of capillaries
= plasma, leukocytes + blood plasma, proteins leak from bloodstream
Where do they leak from the bloodstream to?
Vessel walls + migrate to site of tissue injury of infection
Fight infection and help heal injured tissue
What is apoptosis?
Cell death
Complement
Complex system of more than 30 proteins
Eliminate infectious microorganisms
Where are the complement proteins produced?
Liver
What activates the complement?
Histamine
What happens to complement once activated?
Proteins = lysis of foreign and infected cells
Phagocytes of foreign particles, cell debris + inflammatory of surround tiss
What are interferons?
Group of proteins released by nucleus in response to presence of viruses
What do interferons do?
Virus infected cell will release interferons
= nearby cells heighten anti-viral defences
Are interferons cytokine?
Yes, used for communication bet cells to = protective defences of immune s
What is cytokine?
Cell signalling molecule
What do interferons do?
Infected cells = apoptosis = make infected cells = more obvs to killer cells = production of anti-viral enzymes in nearby cells
What are the anti-viral enzymes called?
Ribonuclease
Protein kinase
What are pseudopodia?
Fake feet
What type of reaction is digestion?
Hydrolysis as it requires water
Process of phagocytosis
Phagocyte extends its cell surf mem (forming pseudopodia) + pathogen
Cell surf mem meets + fuses = phagocytic vesicle
Lysosomes (containing lysozyme) move to + fuse w phagocytic vesicles
Hydrolytic enzymes from lysosomes digest pathogens
Products of digestion absorbed by cell
Undigested material is released by exocytosis
What can be antigens?
Glycoprotein, glycolipid and protein
What are antigens
Mols, usually on surface of a cell = immune r
How does a cell surface identify antigens?
Each cell has specific antigens on its surface
What do antigens enable immune s to do?
identify
pathogens
Cells from other organisms of same species
Abnormal body cells (infected or cancerous cells)
What is antigen variability?
Change antigens through mutation
= immunity + disease protection diffi
Would an MHC be similiar to family members
Yes
What does MHC stand for
Major histocompatibility complex
What is MHC
Collection of glycoproteins on surf of cell that identifies it as self
Why is MHC unique to individual
Gen determined and inherited f
Where are genes for MHC found
Found on chromosome 6
What is role of MHC?
prevents immune s attacking its own cells
Used in antigen presentation
What do lymphocytes have antigen receptors that can…
recognise MHC antigens
Differentiate bet these + foreign antigens
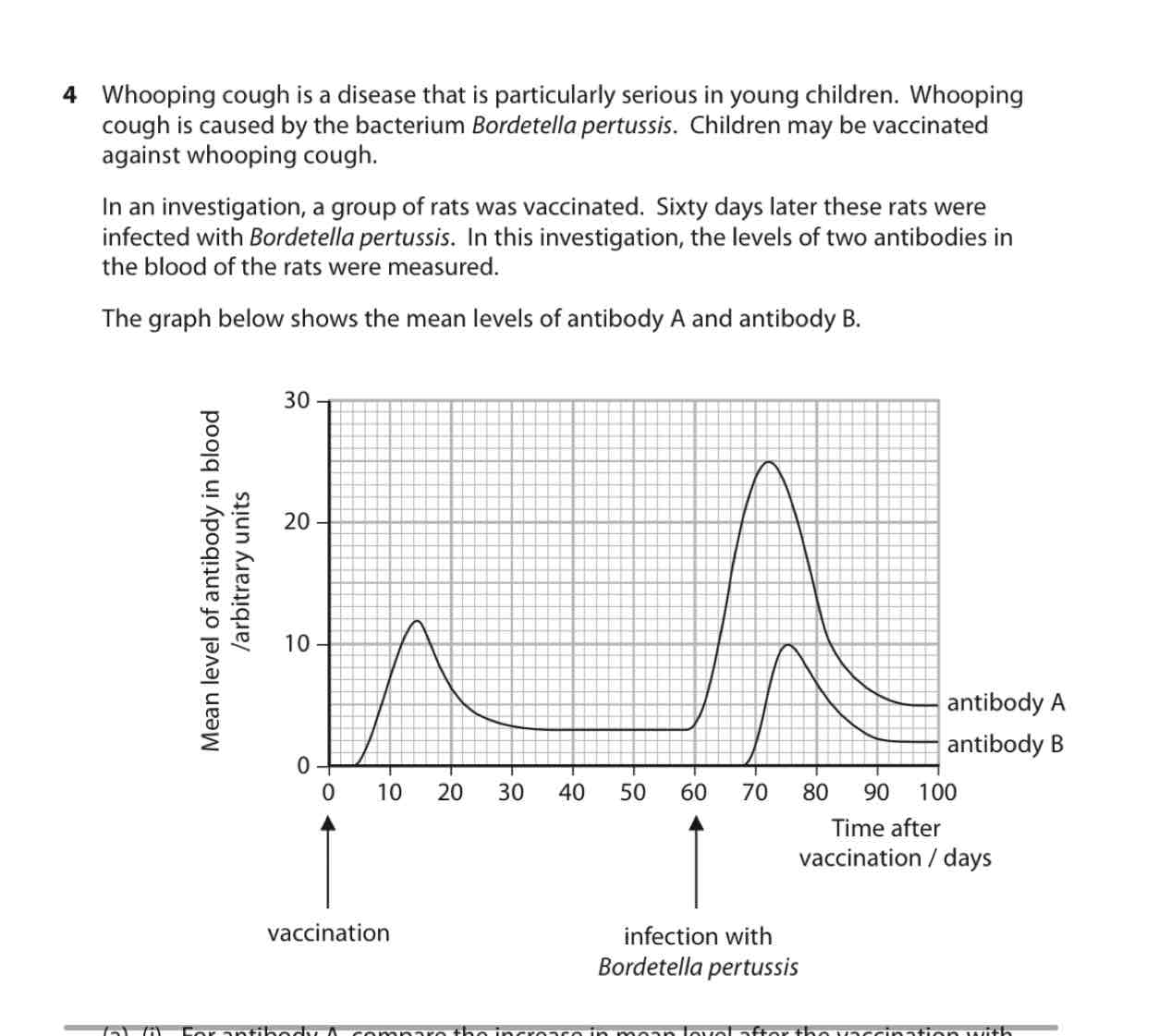
(A) (I) For antibody A, compare increase in mean level after vaccination with mean level after infection of Bortella pertussis
B) (I) Explain the changes in mean level of antibody A after infection with Bordtella pertussis
B (ii) Suggest why antibody B was not present in blood of these rats until after infection with Bordetella pertussis
C) Comment on reliability
(A) Levels of antibody rise sooner higher and faster after infection
(A) (I) sec I. R memory cells, 2nd exposure mem cells stimulated, sec r antibodies produced from plasma cells
B I) antibodies present if antigen is present antigen is not present in vaccine
C) no error bars, no control variables, stats analysis