Human Nutrition Final
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Which nutrient is the most indispensable based upon the final slides lecture material?
Water
Which nutrient is typically the second most important to focus on ingesting when building a diet, especially when in negative energy balance or to maintain lean mass during weight loss?
Protein
Which nutrient is essential in the diet and contains the omega-3 and omega-6 types? -
Fats
Which nutrient in the list below is the one that both sodium and iron are contained within?
Minerals
How many grams of water does glycogen typically store with it?
3 to 4 grams of water for every one gram of glycogen
When someone does the Atkins, a low carbohydrate, or a ketogenic diet, a large portion of the initial body weight loss is due to which of the following?
Water loss
Which of the following are sources of water for our body?
Food, metabolism, liquids
Which of the following are sources of water loss?
Kidney (urine), skin (sweat), lungs (respiration), feces
How many calories does alcohol have per gram?
7 kcal/g
Alcohol is a ________ to the body
toxin
Which of the following is/are true regarding moderation and alcohol
May reduce the risk of
Heart attacks
Strokes
Dementia
Diabetes
Osteoporosis
Leads to lower mortality in adults older than 30
Which of the following is/are true regarding binge drinking
Binge drinking is at least four drinks in a row for women and five drinks in a row for men
Widespread on campuses, especially among 18 to 24 year olds
Can have serious health consequences
Alcohol can displace other nutrients in the diet
Does high blood cholesterol ALONE cause atherosclerosis?
No, it doesn’t solely cause atherosclerosis. Blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and poor gut health can trigger plaque buildup in the arteries that leads to atherosclerosis
When one loses body fat (weight loss), where does that fat exit the body (primarily)?
Through the mouth with respiration
The most important FACTOR to simply achieving weight loss over a short period of time
Remaining in negative energy balance
Things that screw up homeostatic eating
Food palatability
Food variety
Effort and resource cost
The social environment
Stress and Boredom
Homeostatic eating
Matching energy intake to expenditure
1 or more hours of physical activity helps with homeostatic eating
Non homeostatic eating is in part thought to be due to lack of physical activity.
True
BMI is an excellent predictor of disease risk for the individual.
False
BMI is still useful in assessing general risk of a population, but still has flaws in that application.
True
Most Americans should actively diet
False
Most American could benefit from mindful, knowledge based, intentional eating and physical activity endeavors, with grace and non-judgment to accept that health is more than any one number.
True
Carbohydrates must comprise the largest percent (AMDR) of your dietary intake for overall health
True
The ONLY sources of energy for metabolism during exercise are glucose and fatty acids.
False
When consuming a diet in energy balance, and comparing equal amounts of each, high fructose corn syrup is worse for your health than table sugar.
False
Overweight individuals (BMI 29), are always unhealthy, independent of other lifestyle factors.
False
Higher protein diets (1.8g/kg/day) are damaging to your kidneys and bone health even though you are otherwise healthy.
False
High carbohydrates are neither suitable nor healthy for anyone, not even competitive athletes.
False
No one can benefit from a low carbohydrate diet
False
Meeting nutritional needs (adequacy) is simple with the current food environment, and as such very few people have any nutrient deficiencies.
False
Which of the following is/are a component(s) or signs of malnutrition?
Overconsumption of calories with under consumption of nutrients
HIGH BMI and body fat mass with clinical or subclinical nutrient deficiencies
Leads to multiple health consequences
Primarily due to poor food quality
The development of chronic diseases is related to poor diet as well as lifestyle choices and:
genetics, environmental influences, stress, and socioeconomic conditions
In nutrition, the word “essential” means:
A nutrient that is essential for bodily functions but isn’t created by the body itself so it must be obtained from the food you eat
The primary site of absorption of most nutrients is the __________
Small intestine
Which of the following is/are TRUE regarding saturated fat and carbohydrate intake considering their link to poor health and atherosclerosis?
High saturated fat and carbohydrate content slowly builds plaque in the body (atherosclerosis) and can clog blood vessels, causing a large amount of issues in the body
Name the six categories of nutrients and how many calories they contain per gram (if no calories, put 0 kcal/g)
Carbohydrates – 4 kcal/g
Fats – 9 kcal/g
Proteins – 4 kcal/g
Minerals – 0 kcal/g
Water – 0 kcal/g
Vitamins – 0 kcal/g
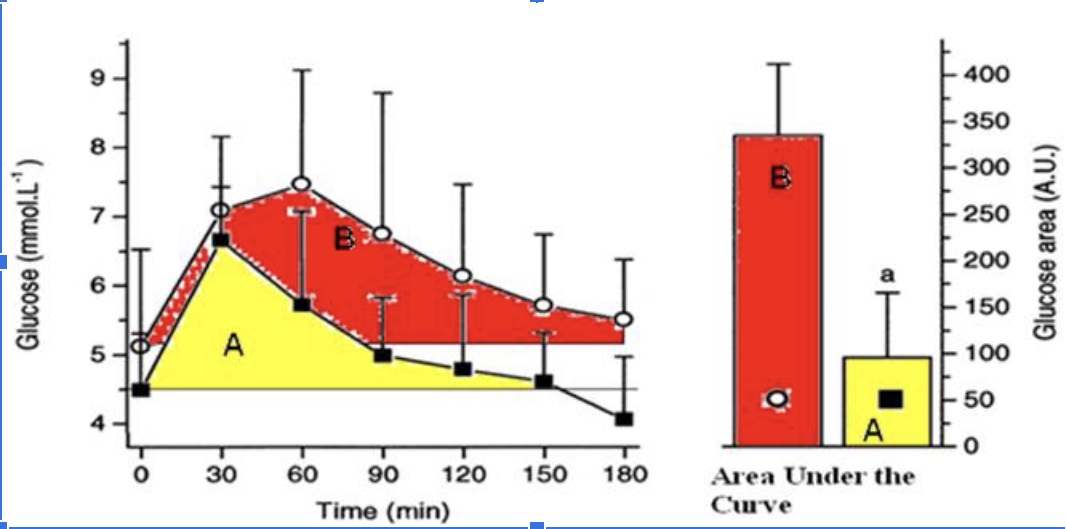
The athlete has a better response to a glucose meal because they are more sensitive to insulin when they eat a carbohydrate meal.
True
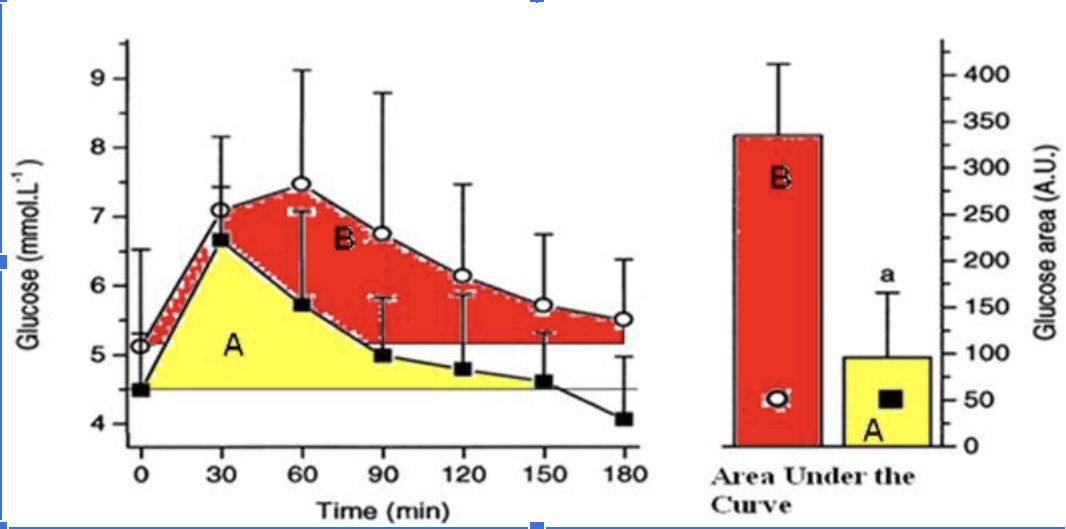
The athlete likely has less glycogen stored in their muscles compared to the sedentary individual when this glucose tolerance test (illustrated in the figure above) took place and thus has more “room” to store glycogen.
True
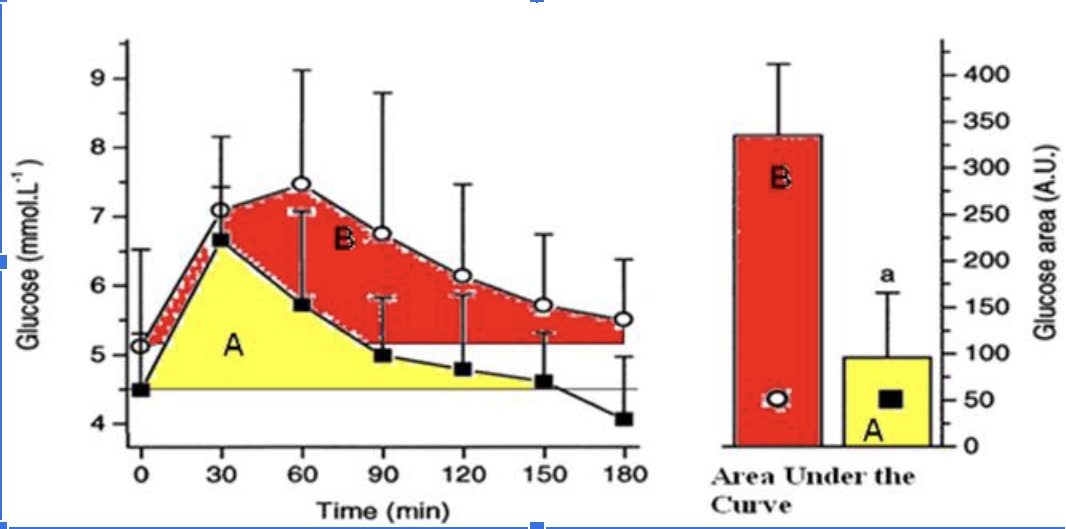
The athletes’ peak glucose response is lower than the sedentary individuals
True
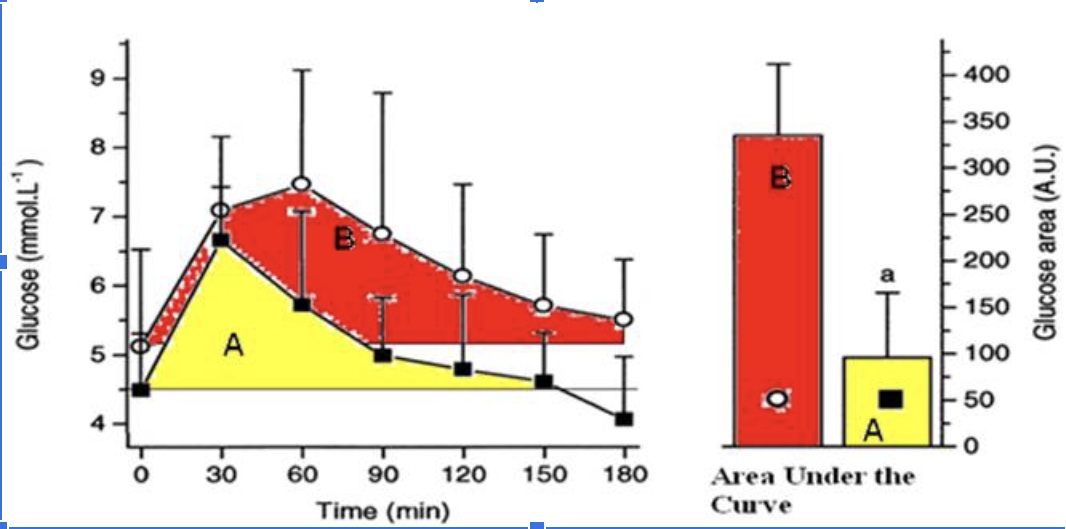
The hormone responsible for the glucose response curves is glucagon
False
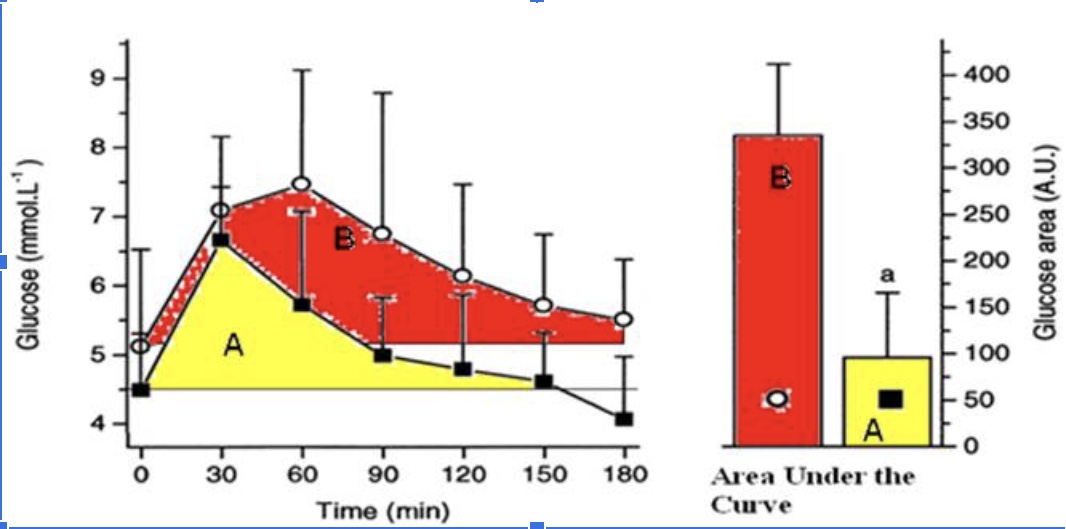
The protein that takes up the glucose into the muscle cells is GLUT5.
False
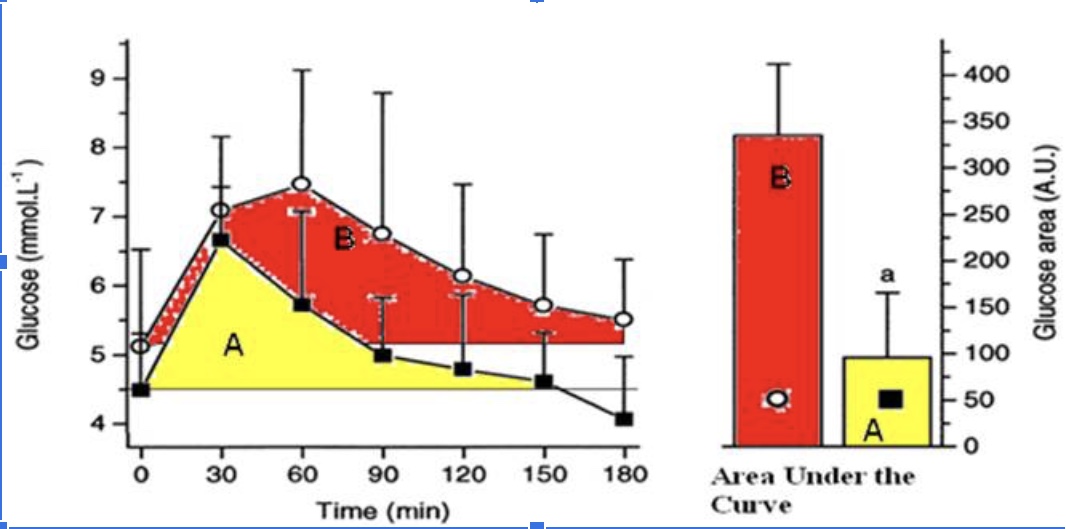
The athlete is metabolically flexible and can switch from carbohydrate metabolism back to a greater reliance on fat metabolism within 2 hours (120 minutes) of a large glucose meal.
True
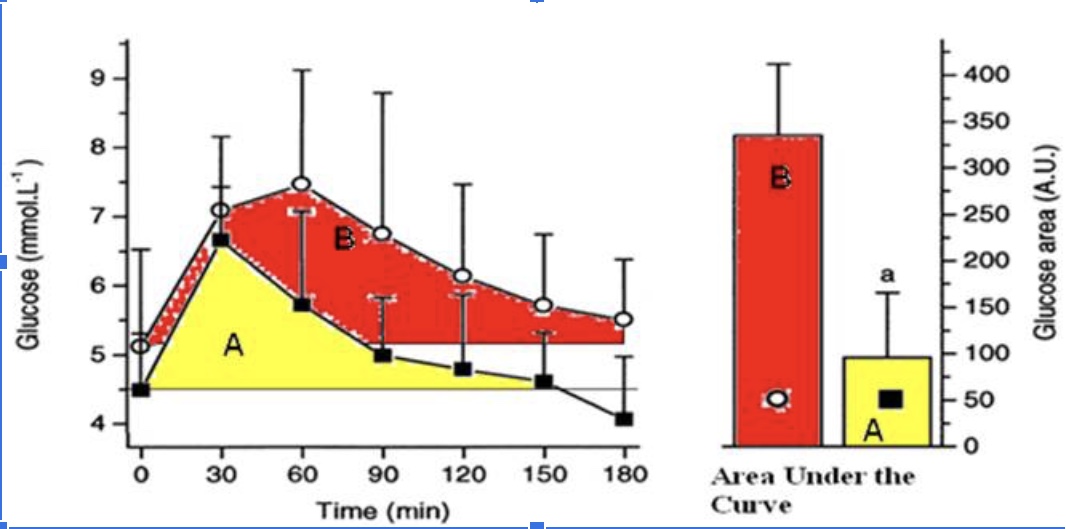
The sedentary individual has a better response to glucose because they are more sensitive to insulin.
False
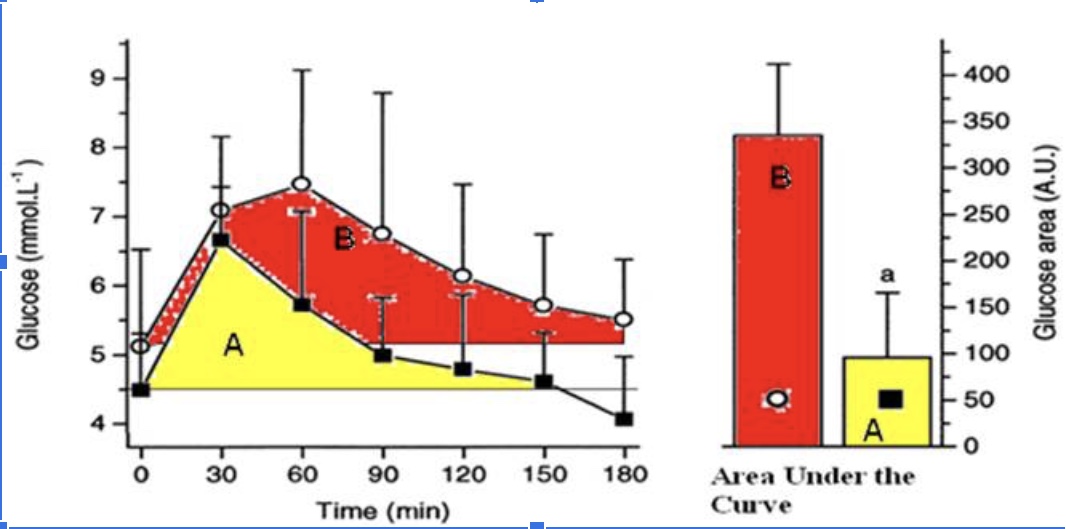
The sedentary individual likely has mostly fully stored glycogen in their muscle and thus has little ‘room.’
True
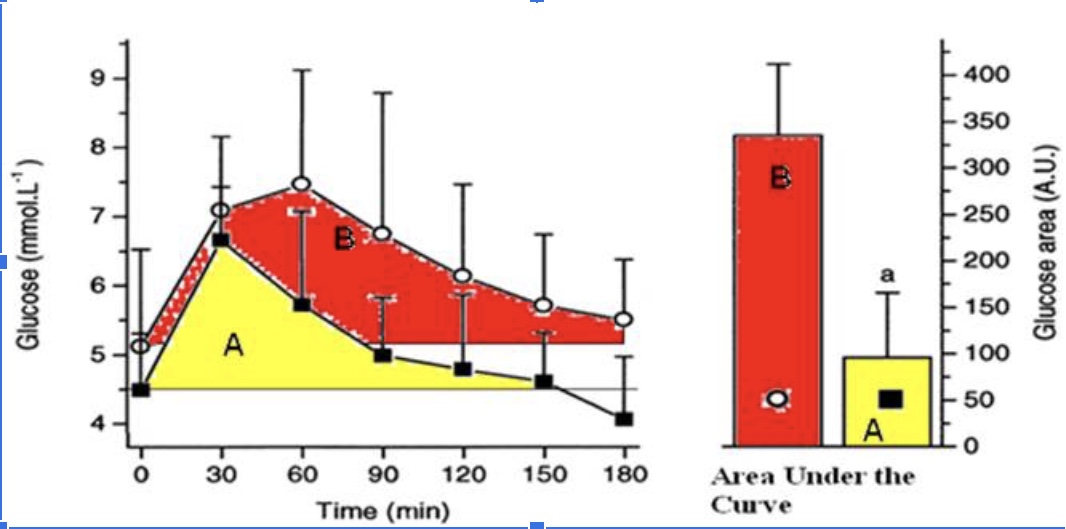
The sedentary individual’s peak glucose response is lower than the athletes peak response.
False
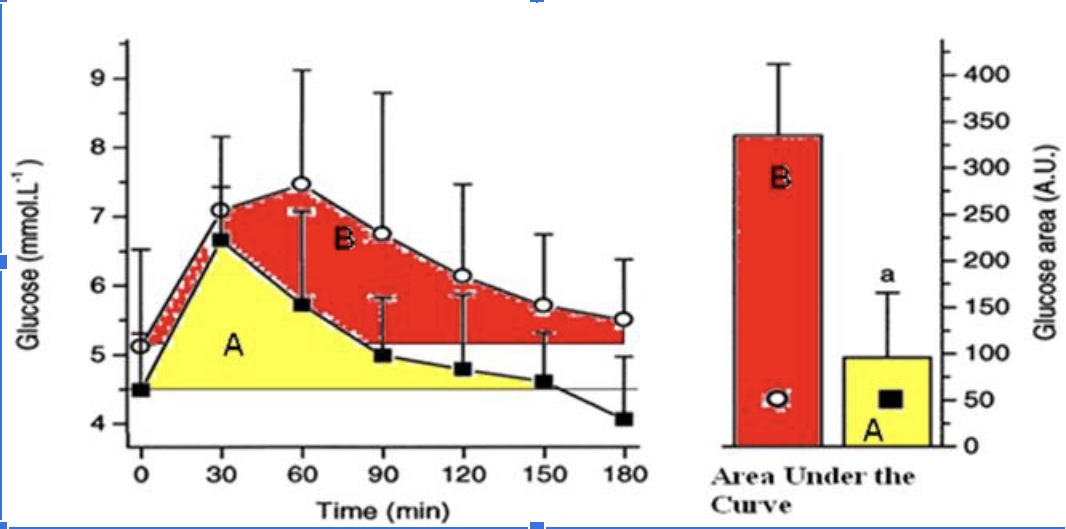
The sedentary individual arrives to do the test fasted, but their blood glucose levels are already elevated.
True
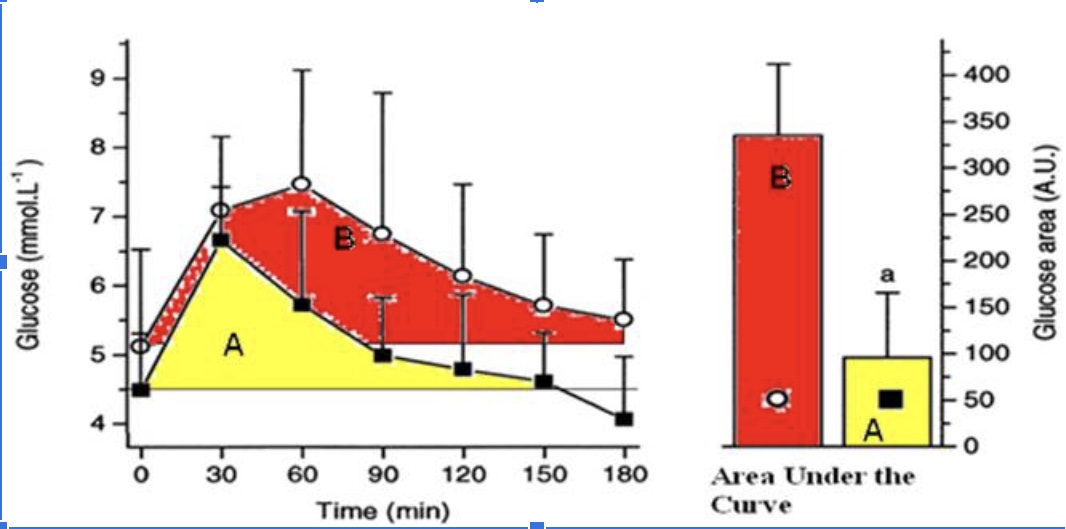
The sedentary individual’s blood glucose does not return back to baseline after 3 hours.
True
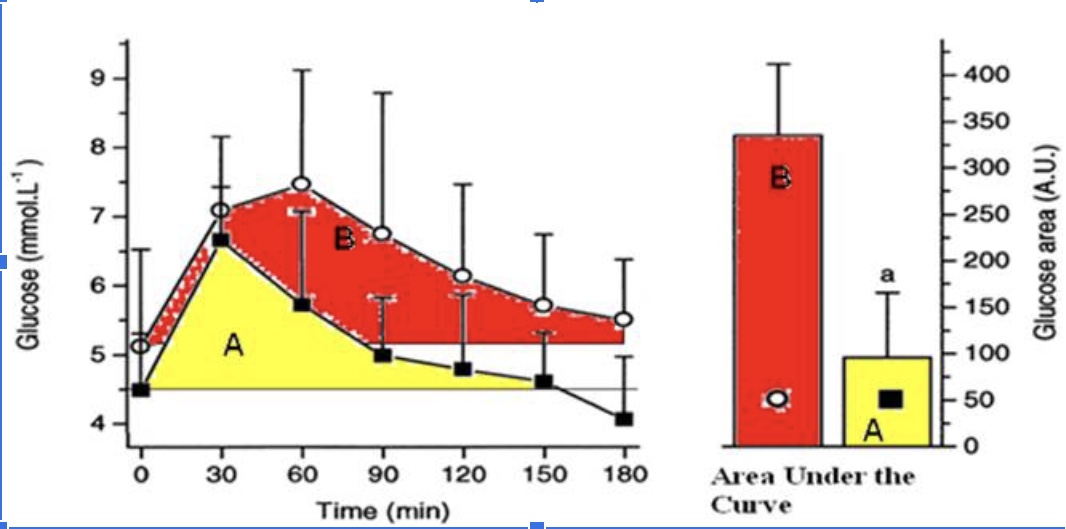
The sedentary individual is hungry 3 hours (180 minutes) after their glucose meal
True
![<p><span style="background-color: transparent;"><span>Answer briefly. What can a </span><strong><em><span>sedentary</span></em></strong><em><span> </span></em><strong><span>individual</span></strong><span> do SPECIFICALLY to lower the amount of stored glycogen in their muscles and potentially increase insulin sensitivity (depending on the intensity and duration) [Hint….The answer would require us to change the </span><strong><em><span>label</span></em></strong><em><span> </span></em><span>we had for them after they do this]</span></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2f11a24c-0025-400e-bd6d-a0f8cc6d0160.jpg)
Answer briefly. What can a sedentary individual do SPECIFICALLY to lower the amount of stored glycogen in their muscles and potentially increase insulin sensitivity (depending on the intensity and duration) [Hint….The answer would require us to change the label we had for them after they do this]
The individual who is sedentary could slowly start to increase their physical activity by going on short walks and begin eating refined carbohydrates and sugars
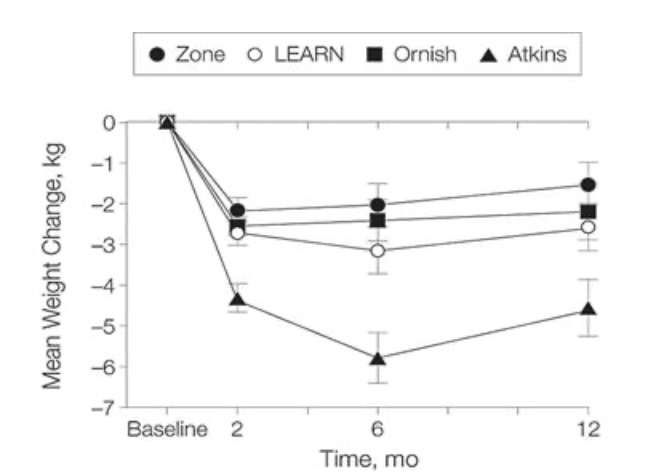
From the figure above, which diet had the BEST results for weight loss in this study over 12 months (blank below)?
Should everyone follow this diet?
Briefly, Why or why not?
The best diet in this study of free living individuals in the figure above was the Atkins
No
The diet causes people to lose more water weight than actual substrate. As a result, the patient has only lost good things and all the bad things that cause diseases in the body are still present.
Patient 45yo female, BMI 31, BF% 42, LDL-C 144, TG 220, Fasting BG 99 and 97 (two fasting tests). Has a German Sheppard & lives near a beautiful park. Divorced w/shared custody of kids (7 and 13 girls). Works as a secretary for Insurance agency
Know this I guess?
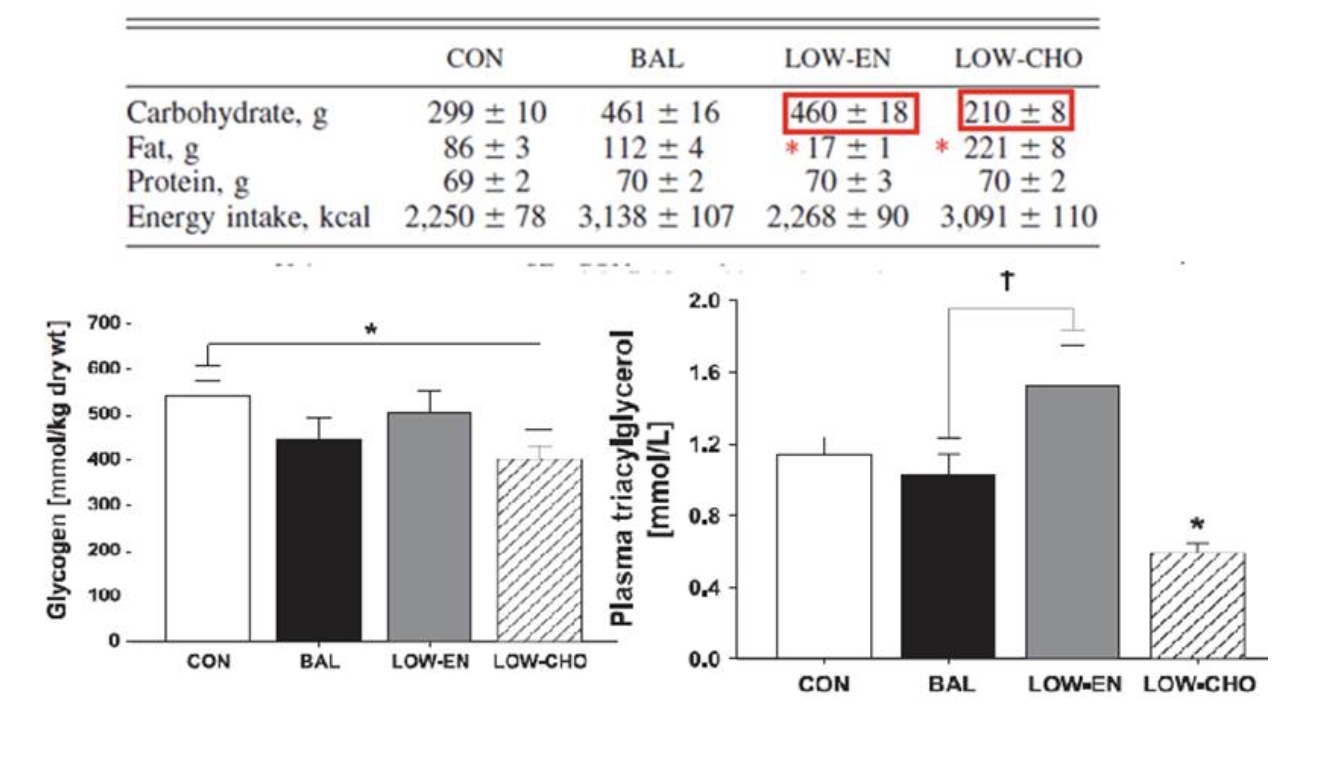
Which group had the lowest glycogen content the day after exercise?
Low carbohydrate group
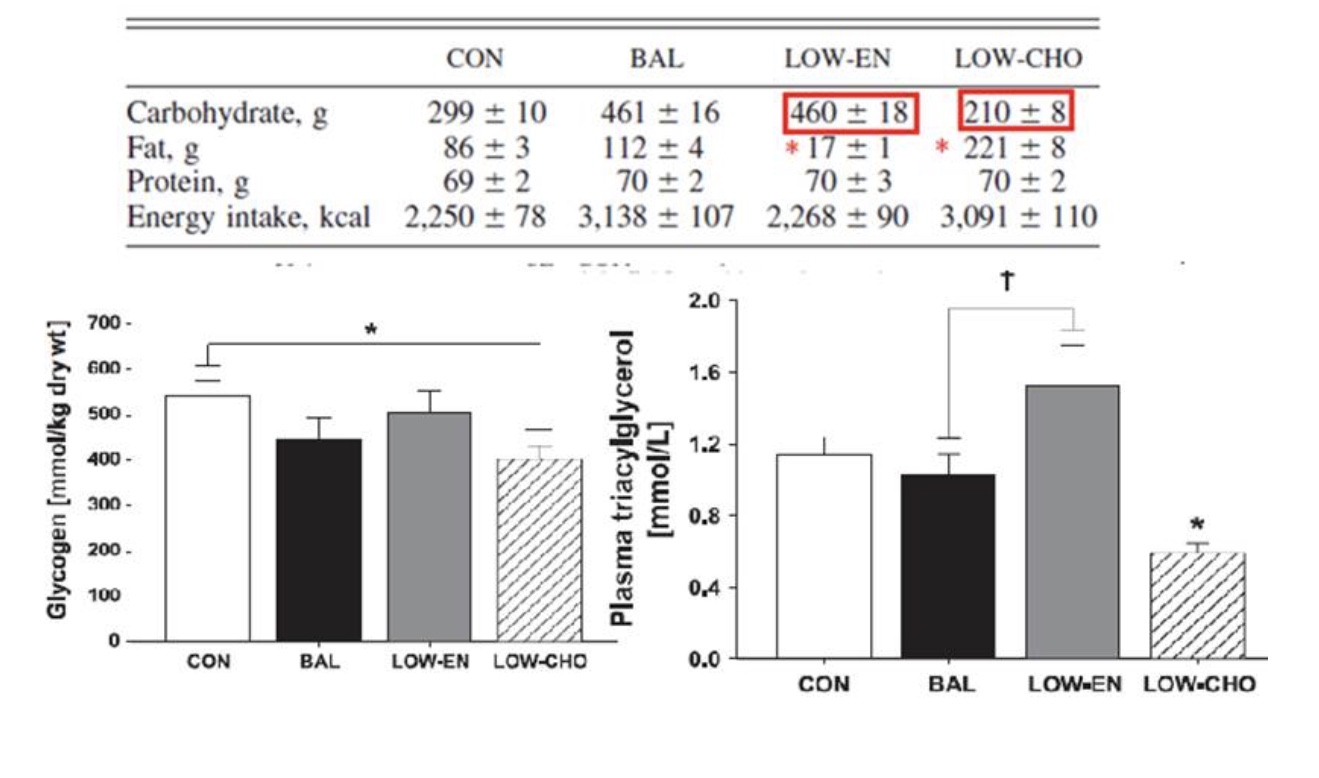
Which group also had the best insulin sensitivity due to this ‘room’ in the muscle?
Low carbohydrate group
Which group ate the most dietary fat?
Low carbohydrate group
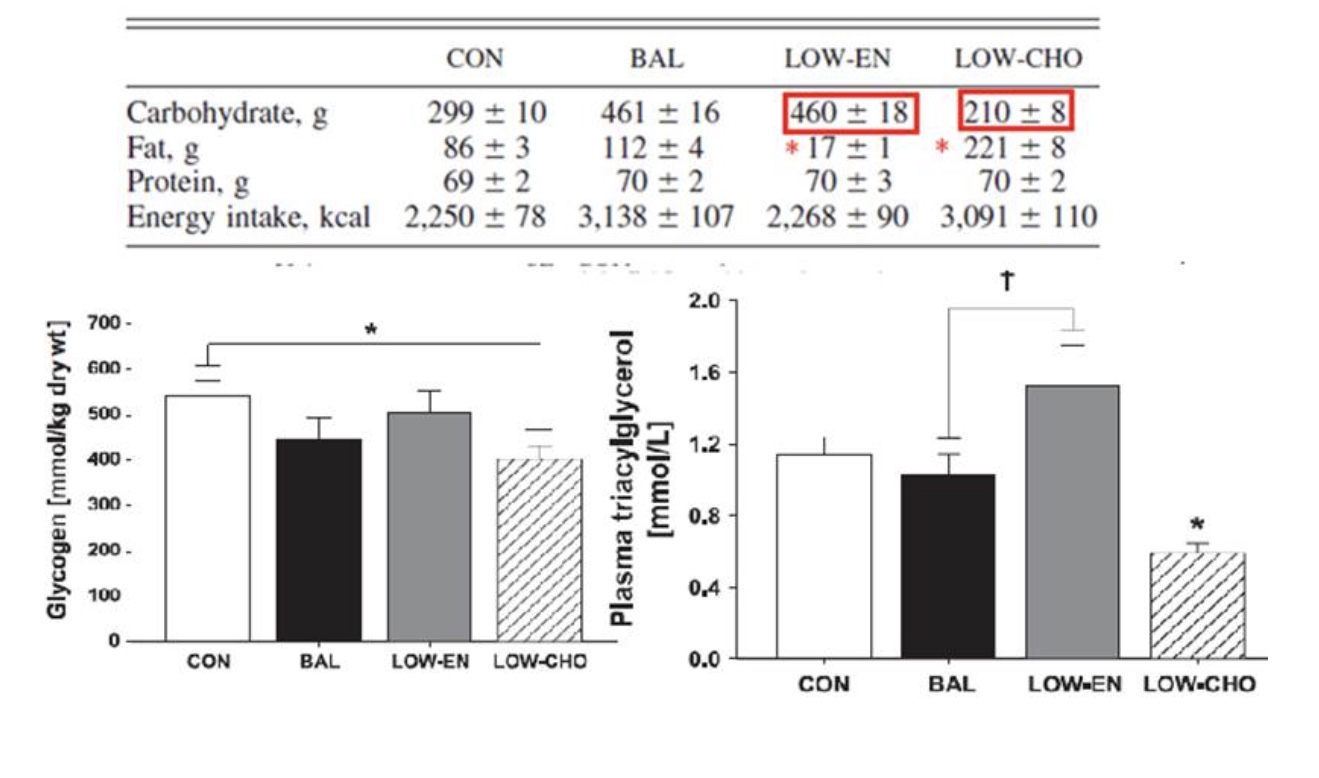
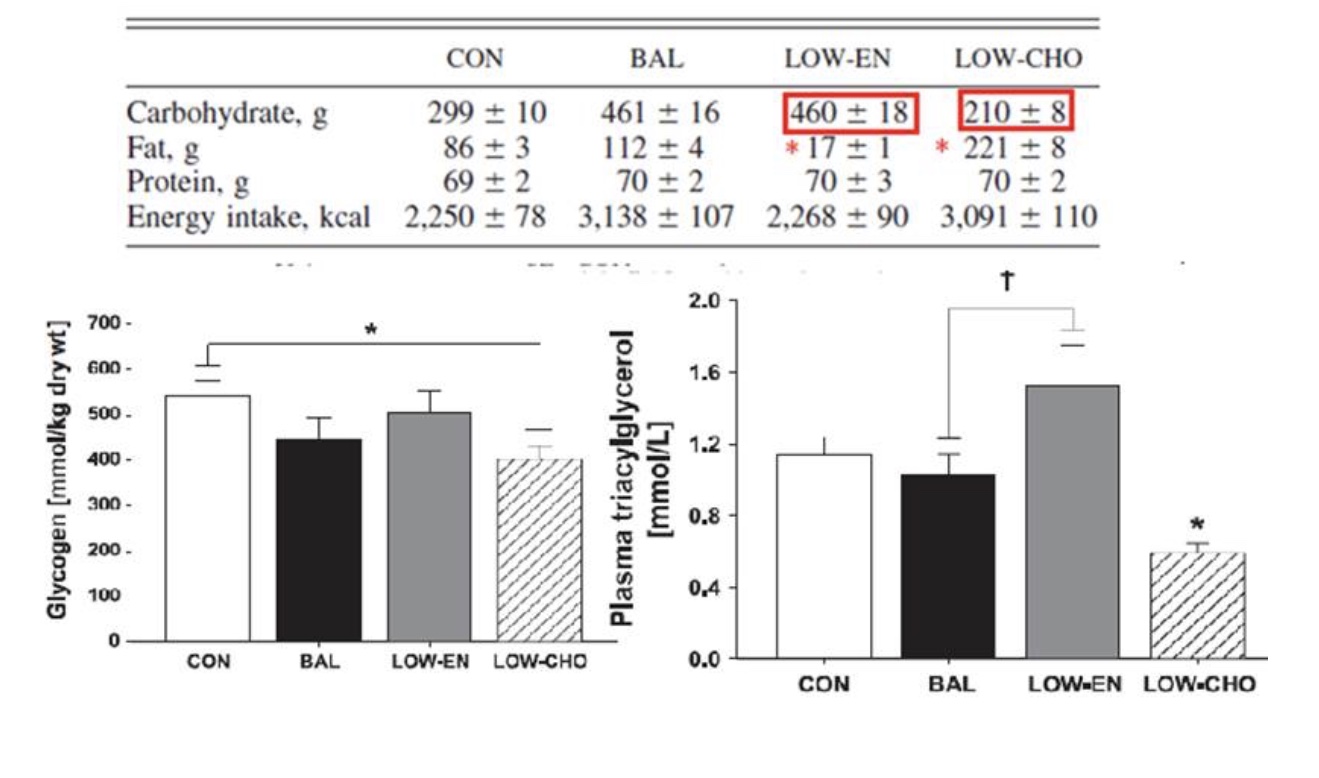
Which group had the lowest plasma triacylglycerol?
Is that crazy
Low carbohydrate group
Yes
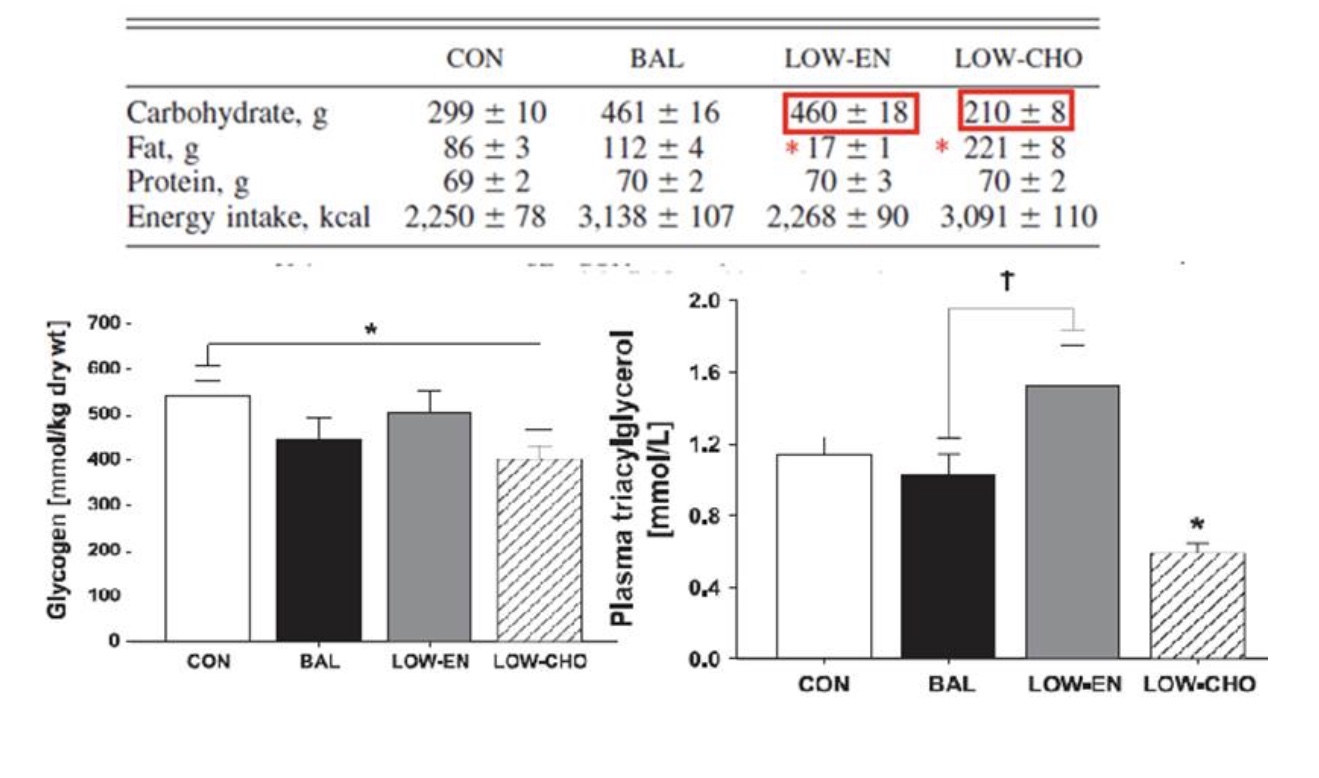
PART 1: If these are athletes with a competition today, what might be bad about eating a lower carbohydrate, higher fat diet the night before that competition? {Think piles and needs}
Athletes need carb piles full before competition because carbs are the fast, high-power fuel — fat isn’t.
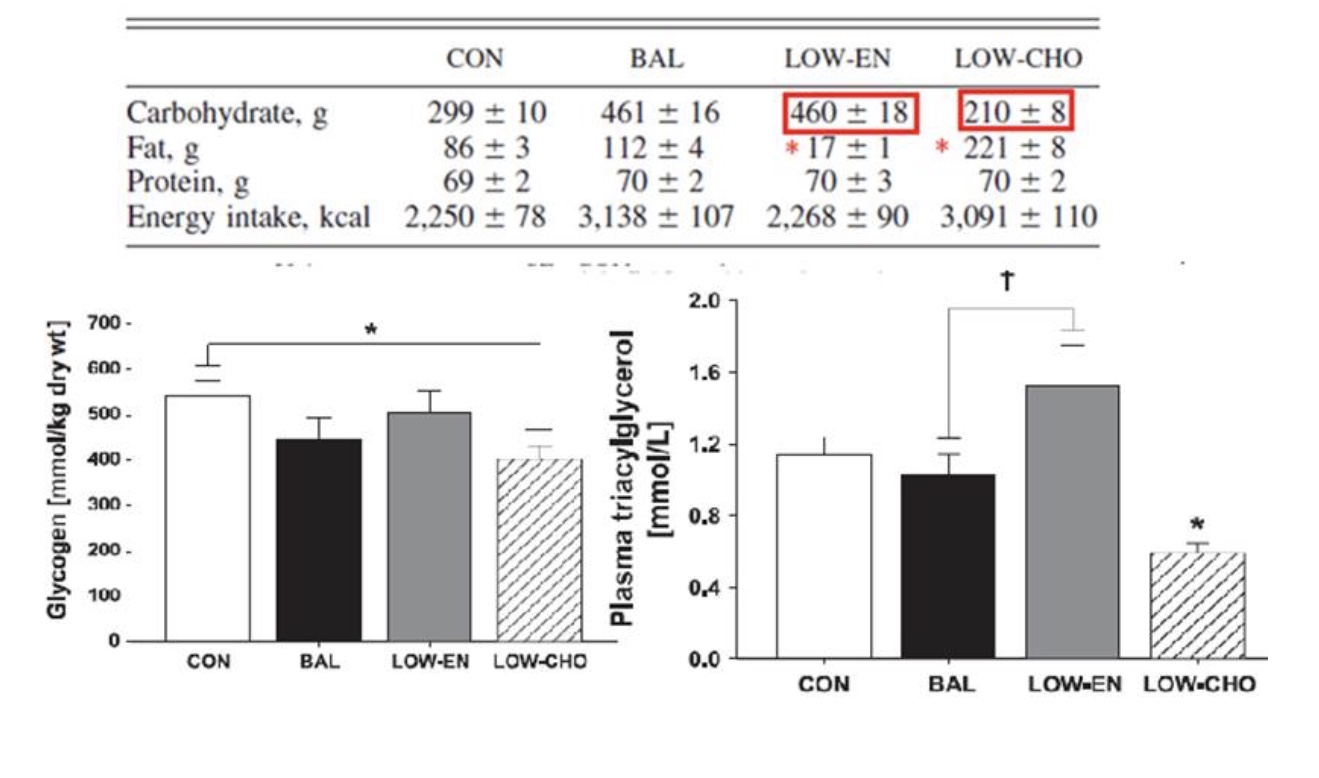
PART 2: If these are athletes with a competition today, what might be bad about eating a lower carbohydrate, higher fat diet the night before that competition? {Think piles and needs}
Just answer this: What might be sub-optimal?
The athlete’s performance as they would not be able to burn any fat while performing as they cannot burn what they don’t have