Chapter 26 - The Carbonyl Group
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Why does nucleophilic addition of aldehydes/ketones produce a racemic mixture (if a chiral carbon is present)
The carbonyl group is a planar bond where the nucleophile in nucleophilic addition can attack the double bond from above and below the bond with equal likelihood. This means that an equal amount of both enantiomers are made and a racemic mixture is made.
What is the carbonyl group?
The C=O bond.
Why is the carbonyl group reactive?
There is a large difference in electronegativity between carbon and oxygen making the bond strongly polar. This allows for nucleophiles to attack the delta positive carbon allowing the double bond to be broken simultaneously.
What reagent will reduce aldehydes and ketones back to alcohols and how is represented in equations?
Tetrahydridoborate (III) - NaBH₄ - [H]
Why is the addition of cyanide ions, to aldehydes and ketones, considered useful in industry?
It creates a longer hydrocarbon chain which then can be substituted for other more useful groups such as halogens or carboxylic acids.
Why are sodium/potassium cyanides used in preference to HCN for addition reactions?
HCN is toxic where as KCN and NaCN aren’t.
Why do carboxylic acids have relatively high boiling points?
The oxygens in the carboxylic acids have lone electron pairs which allow for hydrogen bonds to form with the hydrogens of another carboxylic acid. Hydrogen bonds are relatively strong and require a lot of energy to be broken giving carboxylic acids a relatively high boiling point.
Why are short carboxylic acids soluble?
The oxygen on a carboxylic acid can form a hydrogen bond with water allowing it to be dissolved in water as it can be surrounded with water molecules. However, this only happens with short chain carboxylic acids as the longer the longer hydrocarbon chain can’t be surrounded by water.
Why are carboxylic acids considered weak acids?
Carboxylic acids are considered weak acids because they do not completely dissociate in water. When dissolved, only a small fraction of the acid molecules release protons (H⁺ ions), resulting in a low concentration of hydrogen ions in solution and a higher pH than stronger acids.
Write a balanced equation for the reaction between ethanoic acid and sodium hydroxide.
H₃CCOOH + NaOH → H₃CCOONa + H₂O
Write a balanced equation for the reaction between ethanoic acid and Magnesium Carbonate.
H₃CCOOH + Mg₂CO₃ → 2(H₃CCOOMg) + H₂O + CO₂
What is the chemical test for carboxylic acids?
Add a metal Hydrogencarbonate
CO₂ will be made in the form of effervescence in solution.
What are the three uses for esters?
Solvents
Flavourings/Scents
Plasticisers
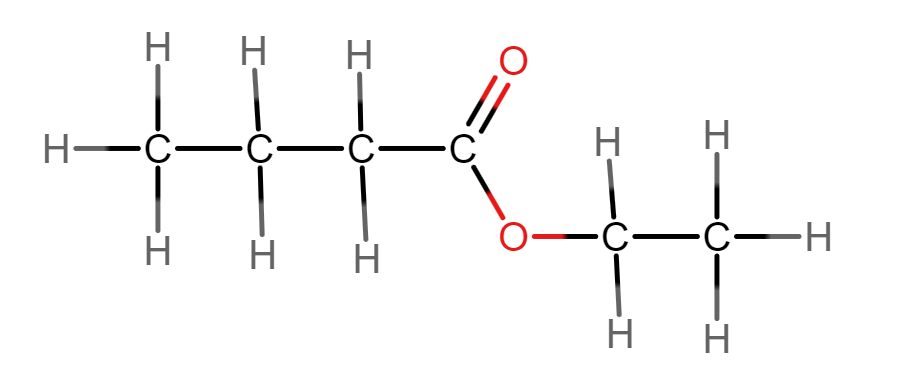
Name this ester.
Ethyl Butanoate
Write an equation for the formation of ethyl propanoate and give the conditions.
CH₃CH₂OH + CH₃CH₂CH₂COOH → CH₃CH₂CH₂COOCH₂CH₃ + H₂O
Concentrated sulfuric acid catalyst and heated under reflux.
Write an equation for the esterification reaction of ethanoic acid and propan-2-ol and name the ester formed.
CH₃COOH + CH₃CHOHCH₃ → CH₃COOC(CH₃)CH₃ + H₂O
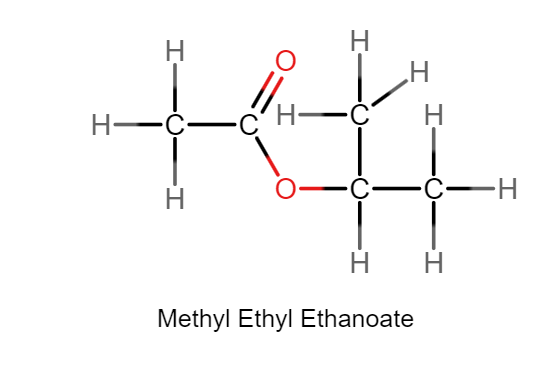
Write an equation for the acid hydrolysis of methyl propanoate and give the conditions.
CH₃CH₂COOCH₃ + H₂O ⇌ CH₃CH₂COOH + CH₃OH
Heated under reflux with acid catalyst.
Write an equation for the base hydrolysis of methyl propanoate and give the conditions.
CH₃CH₂COOCH₃ + NaOH → CH₃CH₂COONa + CH₃OH
Heat with strong base.
Why is base hydrolysis often used in preference to acid hydrolysis?
The carboxylate salt can be removed easier than the carboxylic acid.
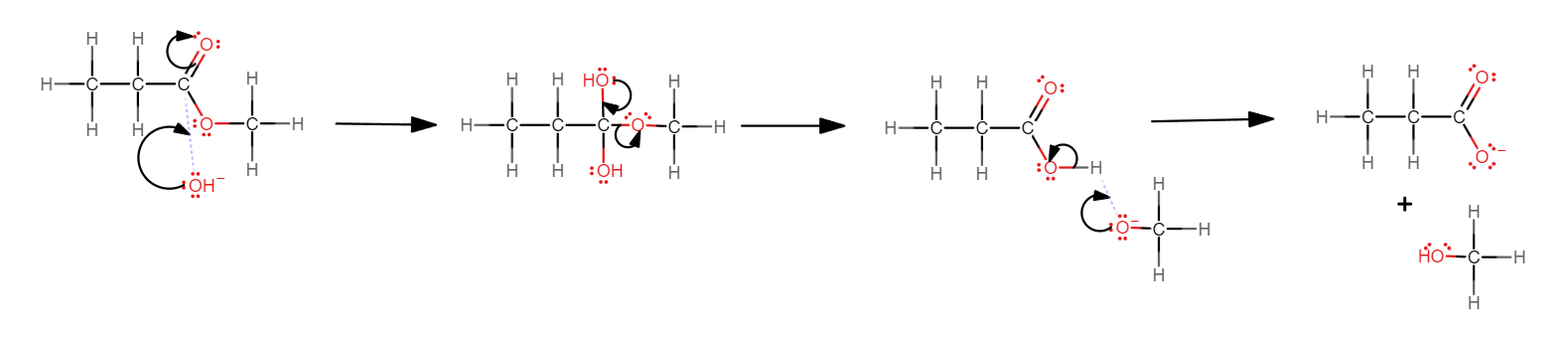
Name and outline the mechanism for the base hydrolysis of methyl propanoate.
Nucleophilic addition-elimination
Describe the structure of a triglyceride.
A glycerol body with three polar fatty acid tails which can either be saturated (straight with no double bonds) or unsaturated (has double bonds and therefore kinks)
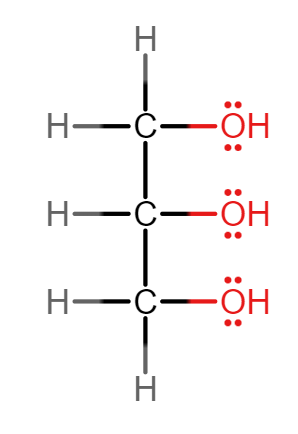
Draw the structure of glycerol and give its IUPAC name.
Propan-1,2,3-triol
Explain why fats have higher melting points than oils.
Fats have no double bonds in their fatty acid tails which means that they are in a more uniform formation and have more points where they can form van de waals forces with other molecules and therefore have higher melting points.
What is the general formula for glycerol and a fatty acid?
CH₂OHCHOHCH₂OH + 3 HOOC-R → CH₂OOC-RCHOOC-RCH₂OOC-R + 3H₂O
What is the general formula for the acid hydrolysis of a triglyceride?
Triglyceride + 3H₂O → Glycerol + 3 HOOC-R
What is the general formula for the base hydrolysis of a triglyceride?
Triglyceride + 3NaOH → Glycerol + 3 NaOOC-R
What is another name for base hydrolysis and what is the main use for the porduct?
Saponification
Long Chain Carboxylate Salt - Soap
Define biodiesel
Biodiesel is a mixture of methyl esters of long-chain carboxylic acids. It is produced by reacting vegetable oils with methanol in the presence of a catalyst.
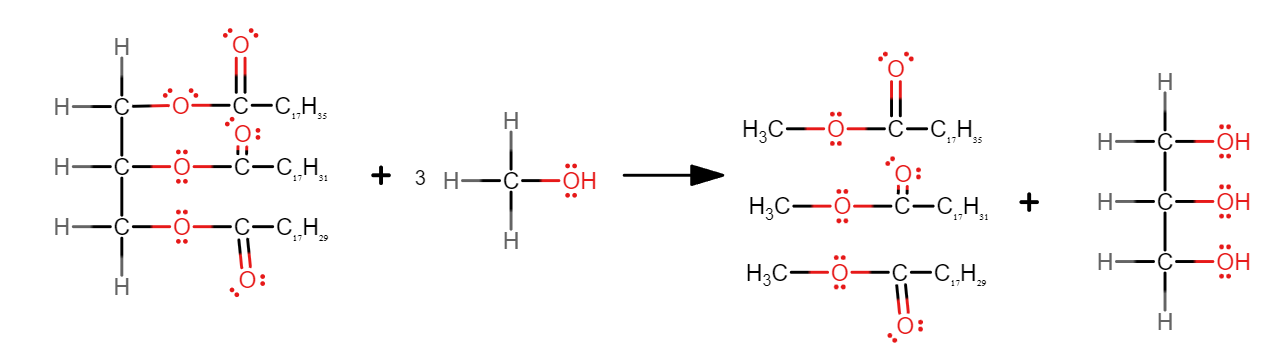
Write the general equation for how biodiesel is formed from an oil.
Triglyceride (Oil) + CH₃OH → 3CH₃OOC-R + CH₂OHCHOHCH₂OH
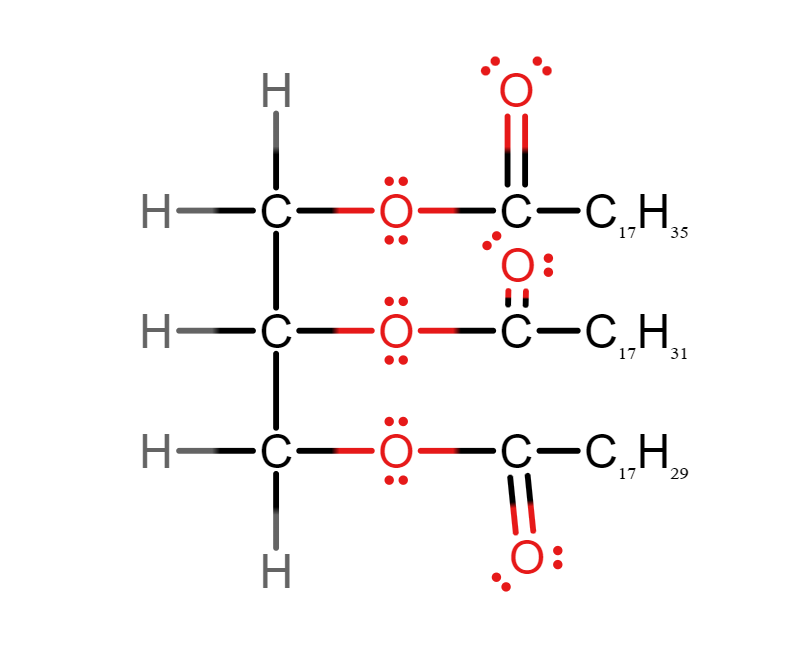
Write an equation to show how biodiesel could be produced from an oil.
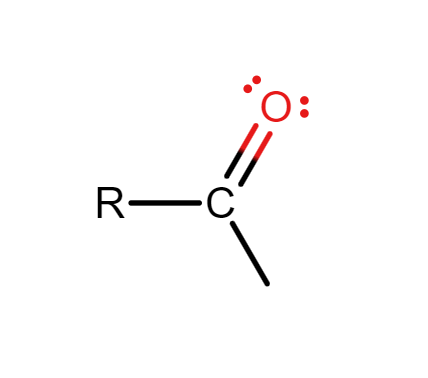
What is the acyl group?
Hydrocarbon group attached to a carbon with a double bond to oxygen.
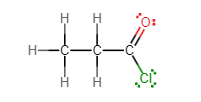
Give the displayed formula of propanoyl chloride.
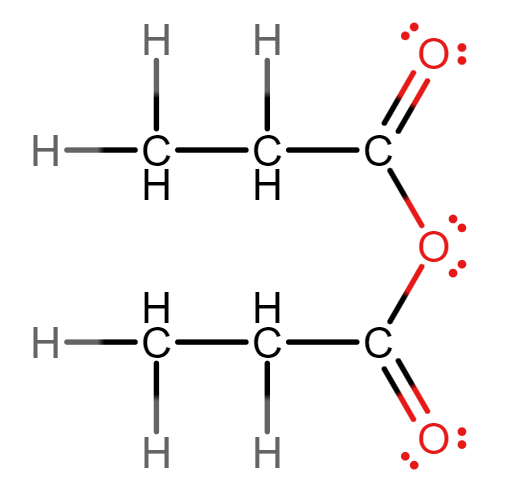
Give the displayed formula of propanoic anhydride.
What is the name of the mechanism that acyl chlorides undergo?
Nucleophilic addition-elimination
Order the four nucleophiles that react with acyl chlorides.
Ammonia (NH₃) → Amines (RNH₂) → Alcohols → Water
What is the general formula for the reaction of acyl chloride and ammonia?
acyl chloride + ammonia → amine + hydrogen chloride gas
What is the general formula for the reaction of acyl chloride and amines?
acyl chloride + amine → N-Substituted Amine + hydrogen chloride gas
What is the general formula for the reaction of acyl chloride and alcohol?
acyl chloride + alcohol → ester + hydrogen chloride gas
What is the general formula for the reaction of acyl chloride and water?
acyl chloride + water → carboxylic acid+ hydrogen chloride gas
Outline the mechanism for the reaction of ethanoyl chloride with methyl amine and name the organic product formed.
N-methylethylamide
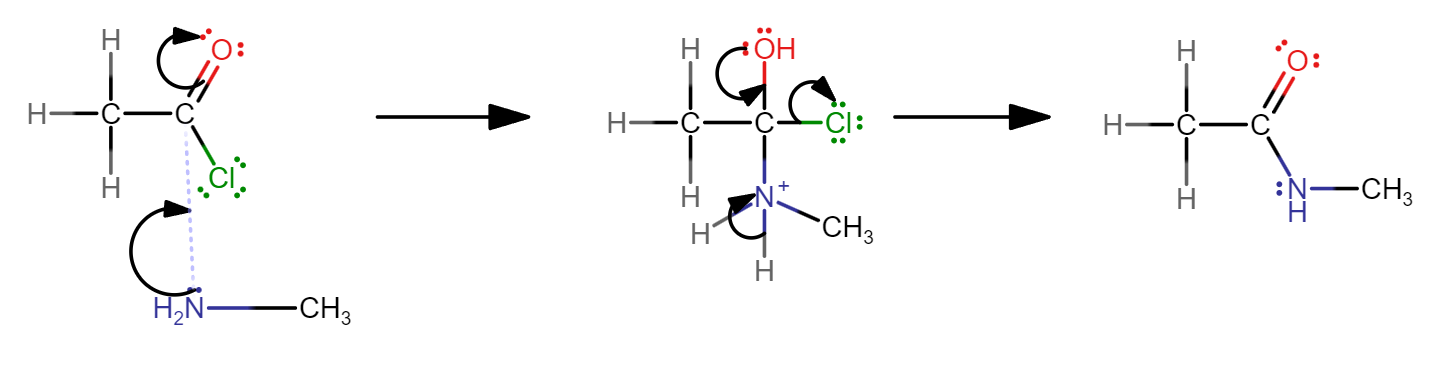
Write an equation for the reaction of ethanoyl chloride and methyl amine.
CH₃COCl + NH₂CH₃ → CH₃CONH₂CH₃ + HCl
What is the general formula for the reaction of acid anhydride and ammonia?
acid anhydride + ammonia → amide + carboxylic acid
What is the general formula for the reaction of acyl anhydride and an amine?
acid anhydride + amine → N-substituted amide + carboxylic acid
What is the general formula for the reaction of acid anhydride and alcohol?
acid anhydride + alcohol → ester + carboxylic acid
What is the general formula for the reaction of acid anhydride and water?
acid anhydride + water → carboxylic acid + carboxylic acid
Name 3 advantages to using acid anhydrides instead of acyl chlorides for acylation reactions.
Cheaper
Less corrosive
Doesn’t produce the hydrogen chloride by product
Name one advantage to using acyl chlorides instead of acid anhydrides.
It is more reactive
What is the IUPAC name of aspirin?
2-ethanoyl oxybenzenecarboxylic acid
Write an equation to represent the formation of aspirin.
Salicylic Acid + Ethanoic anhydride → 2-ethanoyl oxybenzenecarboxylic acid + ethanoic acid