bio 122L - animal disections
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
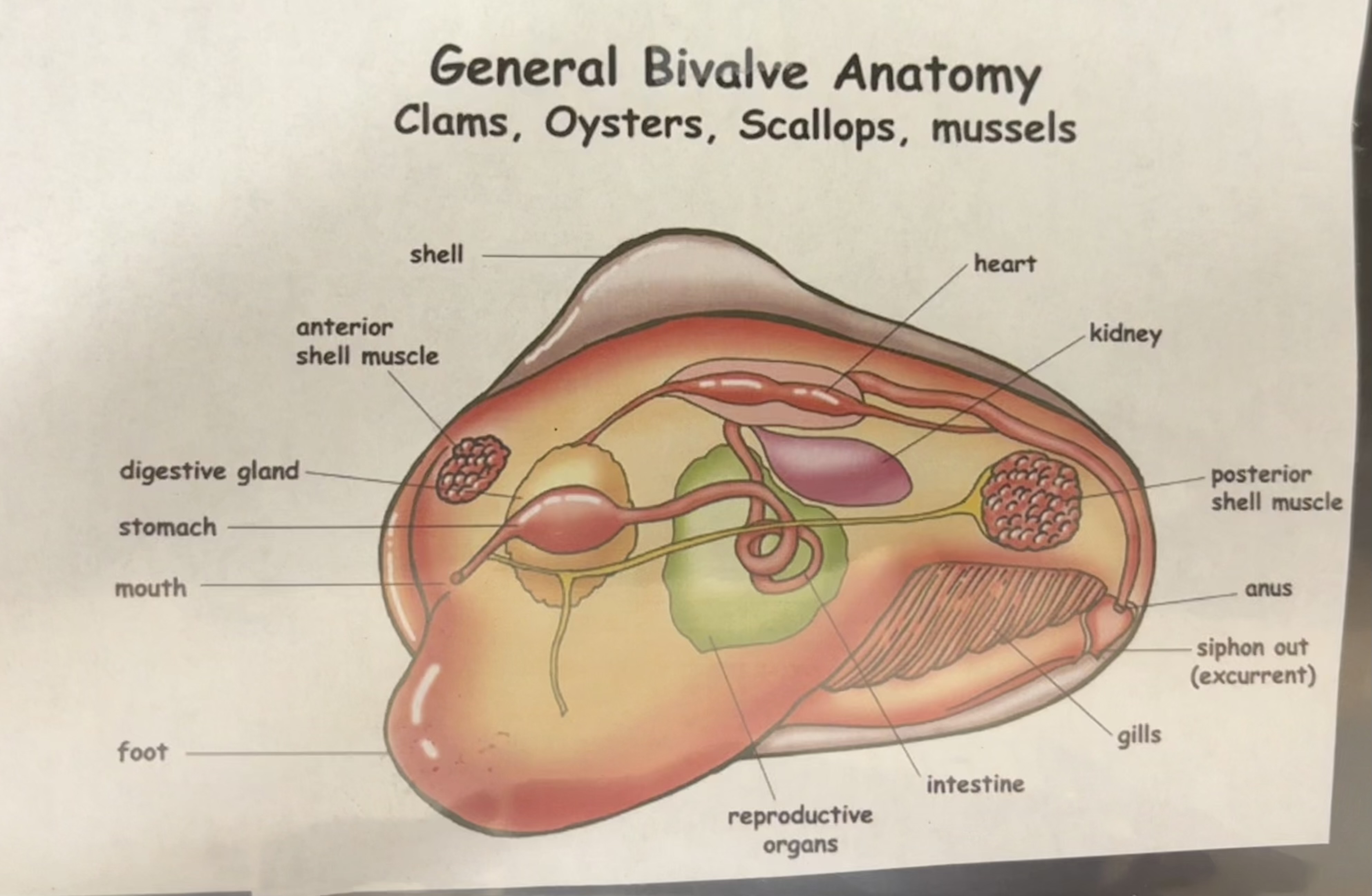
phylum mollusca
primarily aquatic
either marine or freshwater
basic body model:
muscular foot (how they move)
visceral mass
mantle
hard external shell
gills
what class of mollusks have 2 shells that open and close?
bivalves - hatchet foot (ex. clam)
they use their foot for burrowing
have 2 shells
suspension feeders
breathe using gills
classes of mollusks (defined by shape + how they use their foot)
gastropods - belly foot
single shell or no shell
herbivores
radula - their teeth
ex: snail, slug
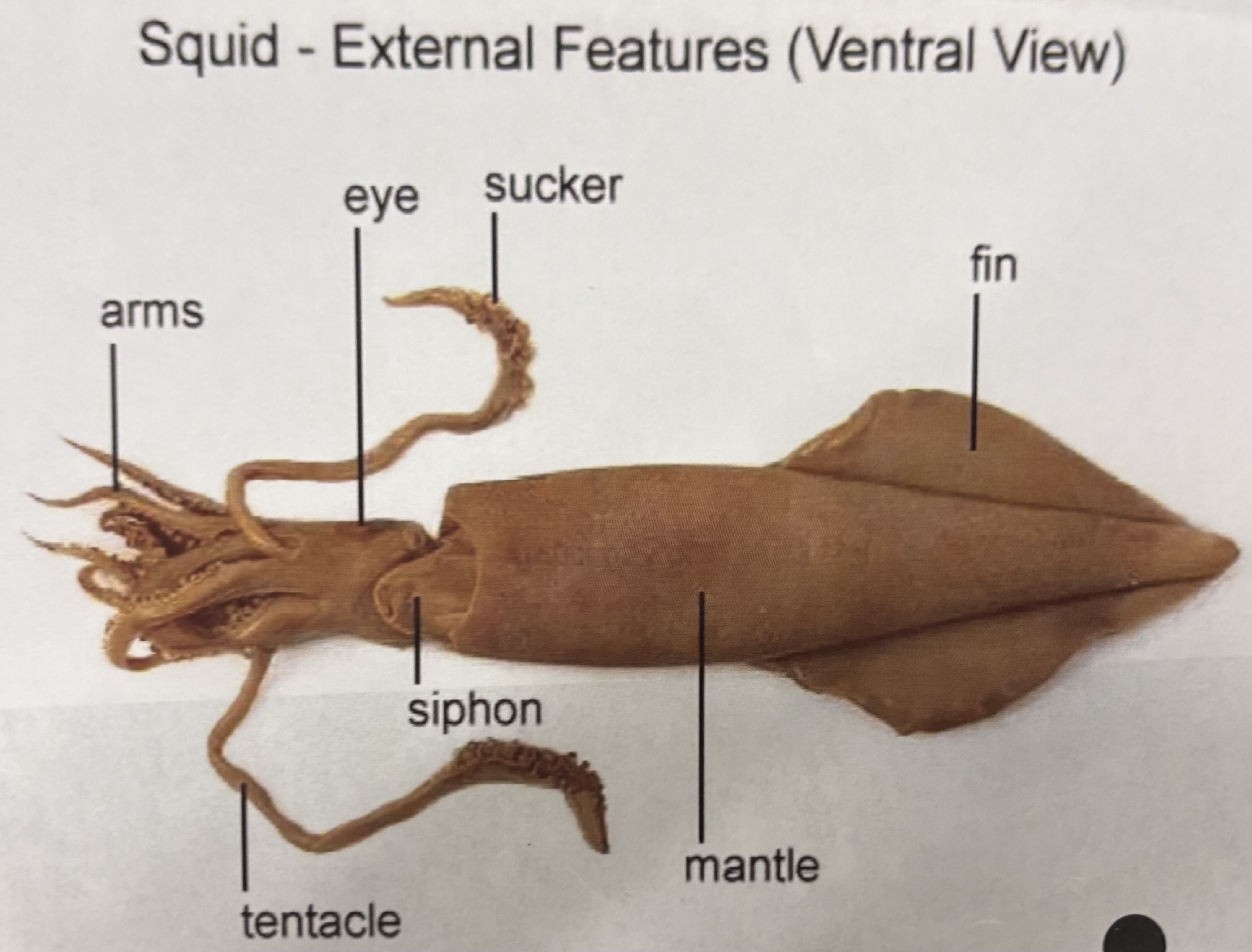
cephalopods - head foot
well developed head with advanced eyes
tentacles with suckers (foot is modified into tentacles)
carnivorous
siphon
ex: squid
bivalves - hatchet foot
they use their foot for burrowing
have 2 shells
suspension feeders
breathe using gills
ex: clams
general bivalve anatomy
general squid anatomy
phylum arthropoda
body segmented into head, thorax and abdomen
jointed appendages
bilateral symmetry
exoskeleton made of chitin, which they malt
major groups:
crustaceans
arachnids
insects
ex: crayfish
crayfish anatomy
body: cephalothorax (fused head and thorax), and abdomen
exoskeleton made of chitin
rostrum: hard triangle behind eyes
have an open circulatory system
green-gland: excretory system
have a pair of appendages on each body segment
2 pairs of antennas
4 pairs of walking legs and swimmerets
grasshopper anatomy
body: head, thorax and abdomen
tympanic membrane: eardrum, vibrates when they hear noise
Malpighian tubules: for excretion
spiracles: for respiration
if a female: will have ovipositor
what type of relationship do termites and protists have since they live in close association with one another?
symbiotic relationship
phylum echinodermata
strictly marine organisms
radial symmetry as adults
many have spines
water vascular system used for locomotion
endoskeleton
ex: sea urchins, sea cucumber, sea dollar
starfish anatomy
carnivorous
have tube feet that extend or retract by water pressure in the water vascular system
tube feet help the starfish move and capture prey
madreporite: small, porous opening that allows for water to enter body for water vascular system
pyloric ceca: digestive glands
jelly like stuff in the middle: gonads, for reproduction
ambulacral ridge + ampullae: involved in water vascular system
dermal ossicles: part of skeletal system
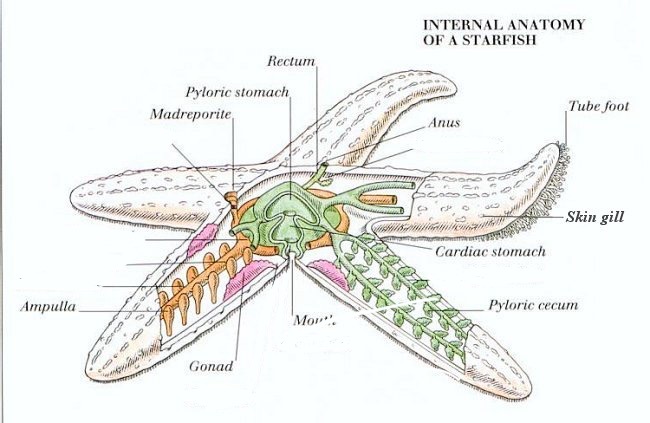
what organ do starfish invert out of their body to hunt?
their stomach
phylum chordata
4 basic features in development:
nerve chord
notochord
pharyngeal slits
post-anal tail
can have vertebrates and invertebrates
invertebrate lancelet
belongs to phylum chordata
marine animal
retains the 4 characteristics
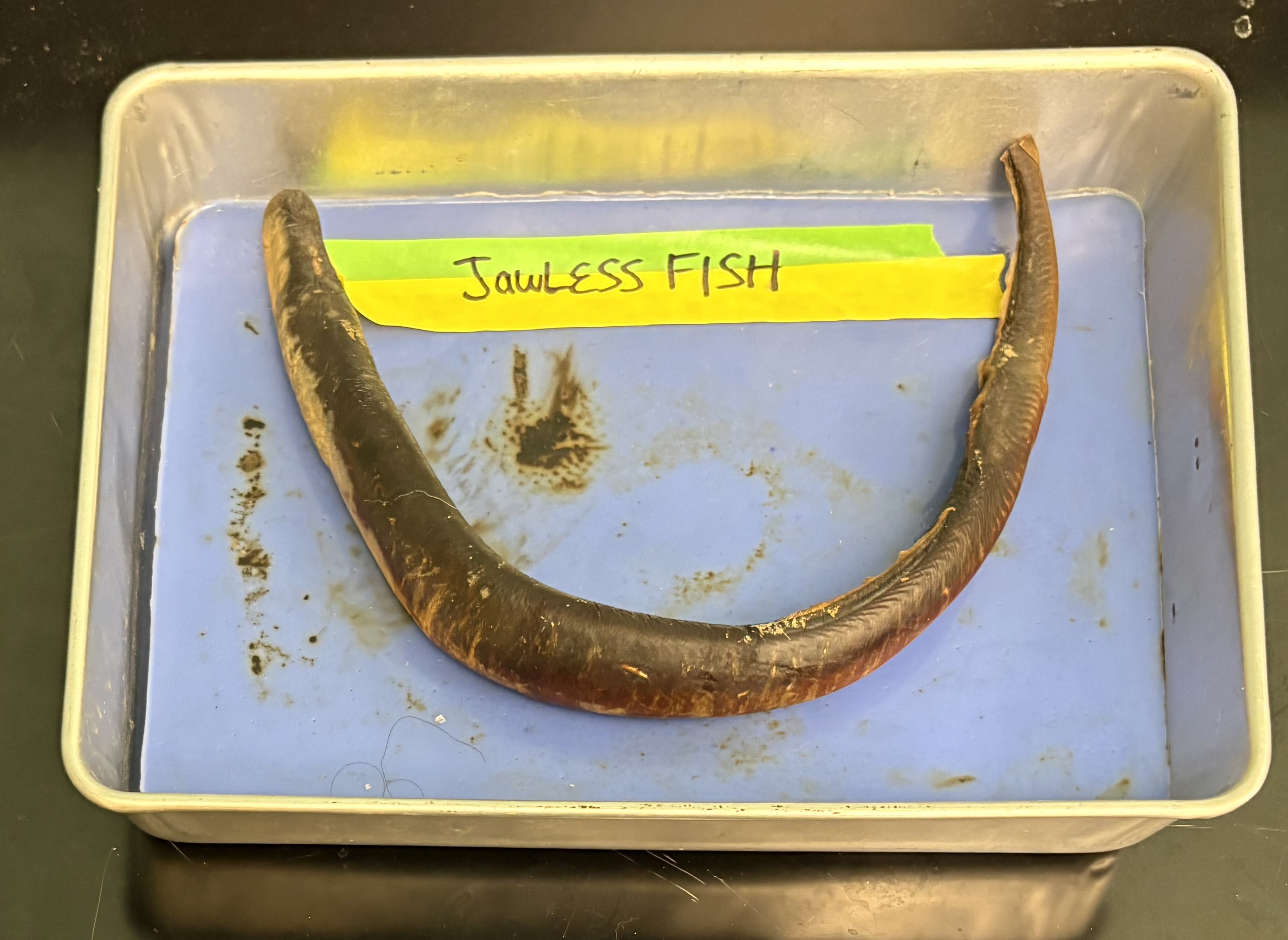
jawless fish (lamprey and hagfish)
vertebrate in phylum chordata
has: cartilaginous endoskeleton, notochord, and pharyngeal gill slits

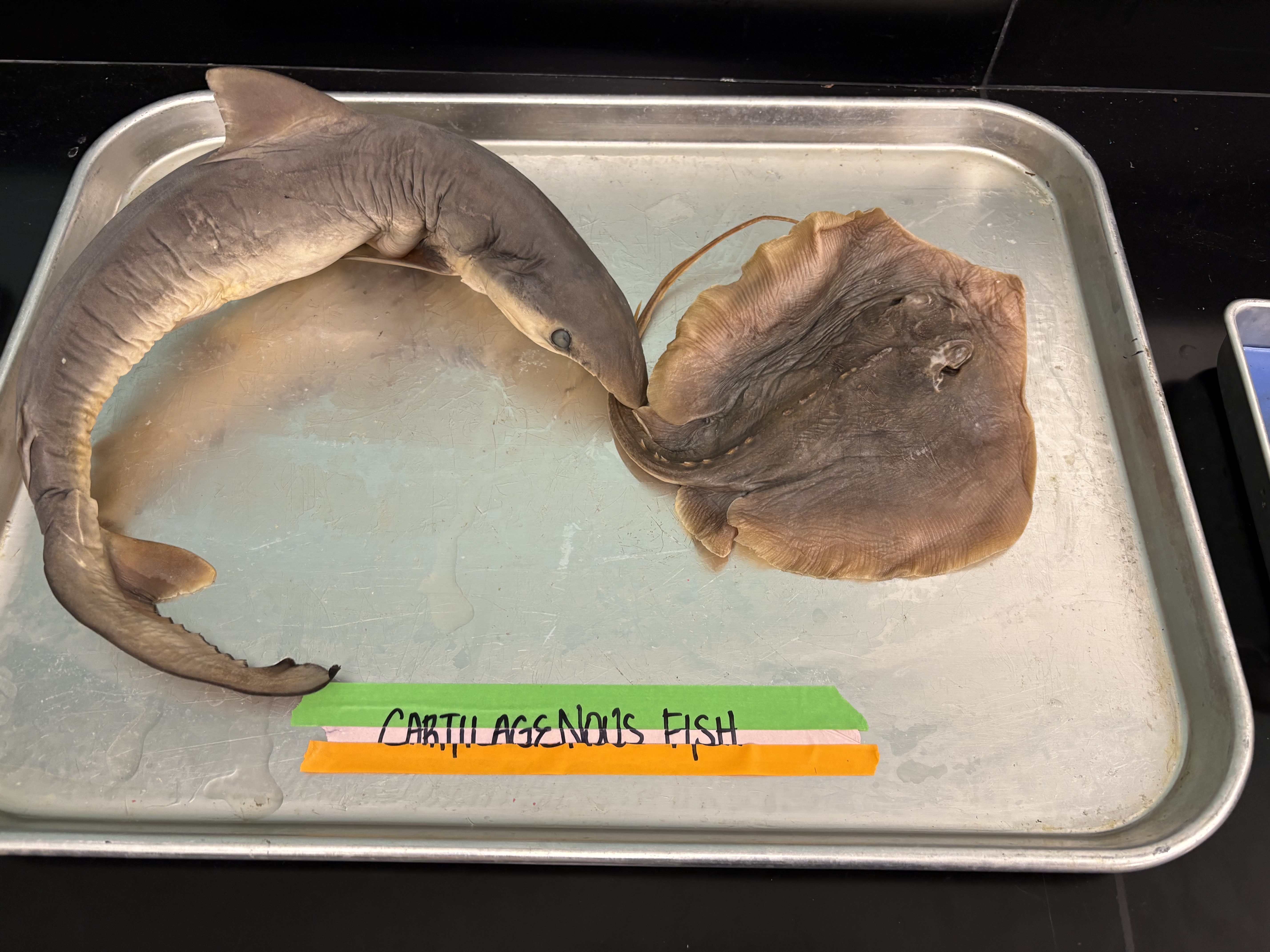
sharks, rays, etc.
vertebrate in phylum chordata
endoskeleton made of cartilage
jaws: great for chomping on other meaty specimens
fins: pelvic and pectoral

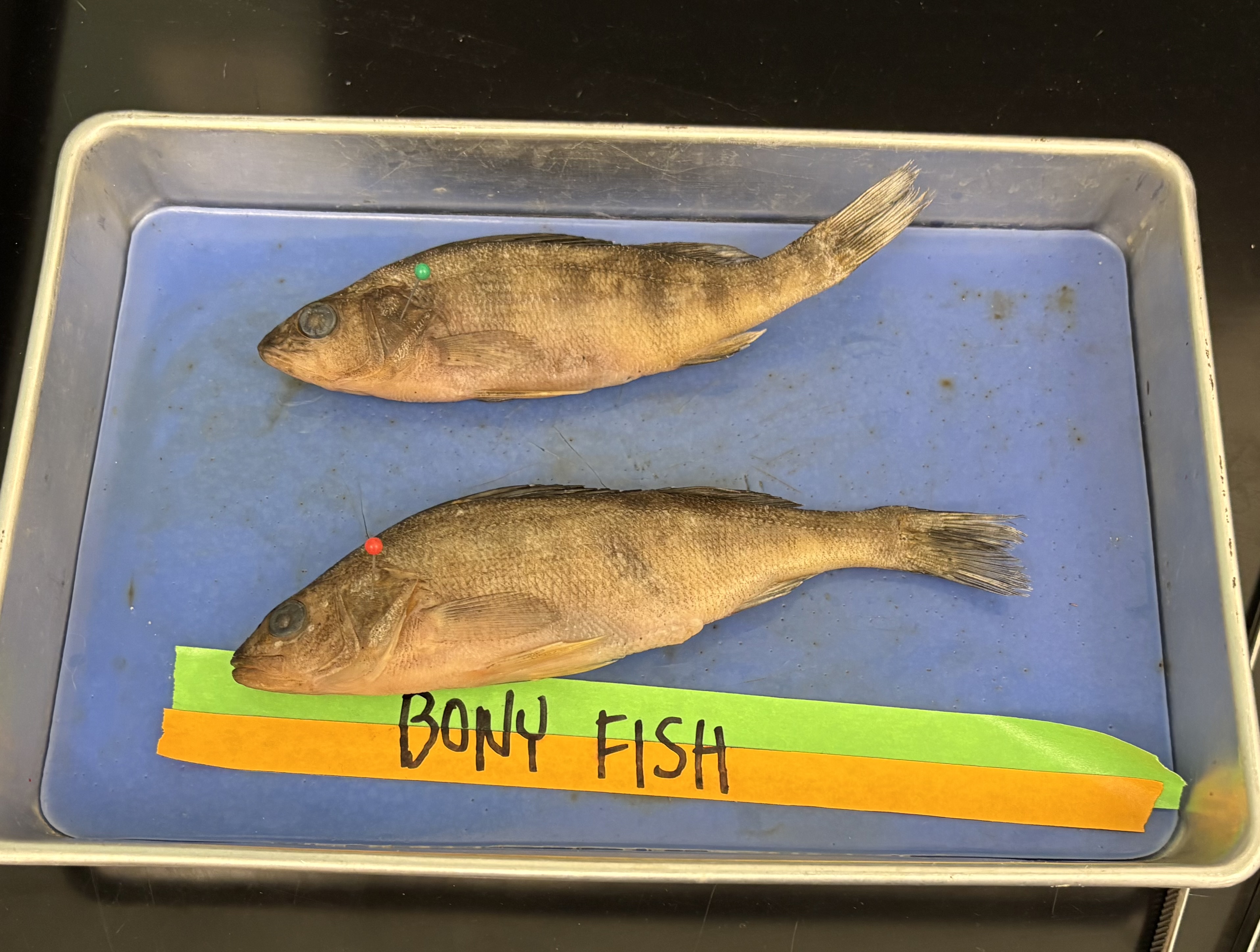
salmon, goldfish, etc.
vertebrate in phylum chordata
endoskeleton of bones
internal air bladders for balance and buoyancy
lateral line system
operculum: a gill cover in some fish (the pin in the pic)

amphibians
vertebrates in phylum chordata
live in terrestrial and aquatic areas
egg incased in jelly so it doesn’t dry out
require moisture for reproduction
most are carnivorous
ex: frog, toads, salamanders
frog dissection

reptiles
vertebrates in phylum chordata
produce eggs that have a shell
egg contains food and moisture
internal fertilization
amniotic egg that can adapt to living on land
dry, scaly skin - protects against dehydration
lungs
advanced circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems
ex: snakes, lizards, turtles, alligators and crocodiles
birds
wings (with feathers for flight and insulation), and horny beaks
evolutionary advance of hollowing bones
lay eggs (amniotic)
specialized digestive organs: crop, gizzard and stomach
carnivorous, herbivorous, and insectivorous
beak is adapted to the type of food that they eat
feet
mammals
vertebrates in phylum chordata
expansive group - can sly, swim, climb, burrow, run and walk
all mammals have fur or hair, and nourish their young with milk
have mammary glands
adaptations reflect:
the animals food sources
their digestive tract (length of it)
teeth
ex: human, hippo, etc.