AP Euro Topic 6.3 2nd Wave Ind and its effects (terms/names AMSCO)
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Second Industrial Revolution
Steel, chemicals, electricity. This is the name for the new wave of more heavy industrialization starting around the 1860s.
3 multiple choice options
Internal Combustion Engine
an engine that burns fuel inside cylinders within the engine
3 multiple choice options
Manchester Capitalism
the idea that free trade could raise the living standard of all workers
3 multiple choice options
Krupp Family
German family famous for their steel production and for their manufacture of ammunition and armaments (weapons).
3 multiple choice options
telegraph
A device that used electrical signals to send messages quickly over long distances
2 multiple choice options

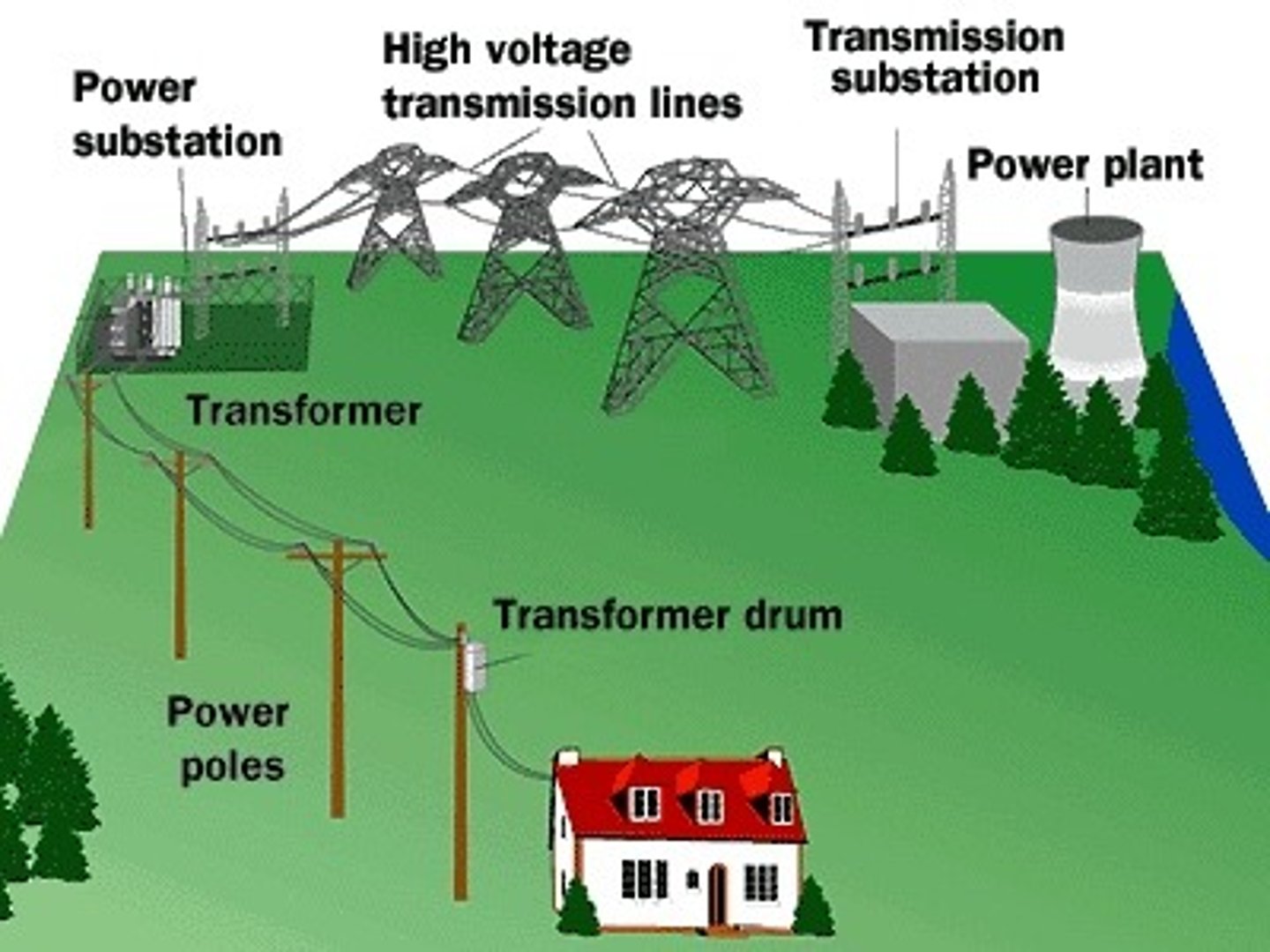
electric grid
an interconnected network for delivering electricity from suppliers to consumers..
3 multiple choice options
telephone
communication device that communicates voice between two people over long distance via wires
3 multiple choice options

radio
the wireless transmission and reception of electric impulses or signals by means of electromagnetic waves
3 multiple choice options

steam ships
technological innovation allowed Europeans to reach distant Asian and African ports quickly and predictably without relying on wind
3 multiple choice options
streetcar
wheeled vehicle that moves along rails using electricity in city streets and is used to carry passengers within the city
3 multiple choice options

protectionism
the theory or practice of shielding a country's domestic industries from foreign competition by taxing imports.
3 multiple choice options
cartels
an association of manufacturers or suppliers in an industry with the purpose of maintaining prices at a high level and restricting competition.
3 multiple choice options
trusts
Firms or corporations that combine for the purpose of reducing competition and controlling prices
3 multiple choice options
monopoly
Complete control of sales of a product or service by one person or group
3 multiple choice options
free trade agreements
Pacts between countries that make it easier to trade goods across national boundaries
3 multiple choice options
most favored nation
trading status describes a condition in which a country grants other countries special trading treatment such as the reduction of import duties
3 multiple choice options
department stores
Also called Emporiums, they are larger stores that offered a wide array of goods within one building, rather than specializing in one product/product type
3 multiple choice options
mail-order catalog
a publication that contains pictures and descriptions of items so that people can order by mail
3 multiple choice options
refrigerated railroad cars
this invention allowed animals to be slaughtered before shipping. This helped cut transportation costs and helped cattle ranching become a big business
3 multiple choice options
Zollverein Agreement
economic cooperation between states in German Confederation - no taxes on imports, encouraged growth of railroads/transportation
3 multiple choice options
National System
Set of ideas by German Economist Friedrich List arguing for government involvement in economic growth including protective tariffs, investment in education, and in infrastructure such as railroads.
3 multiple choice options
Friedrich List
wrote National System of Political Economy, which advocated fast and large-scale industrialization to develop nation's strength and the use of protective tariffs to make people buy domestic goods.
3 multiple choice options
infrastructure
Fundamental facilities and systems serving a country, city, or area, such as transportation and communication systems, power plants, and schools
3 multiple choice options