TV2102 - Parasitology Ruminant Prac
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:46 AM on 10/26/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
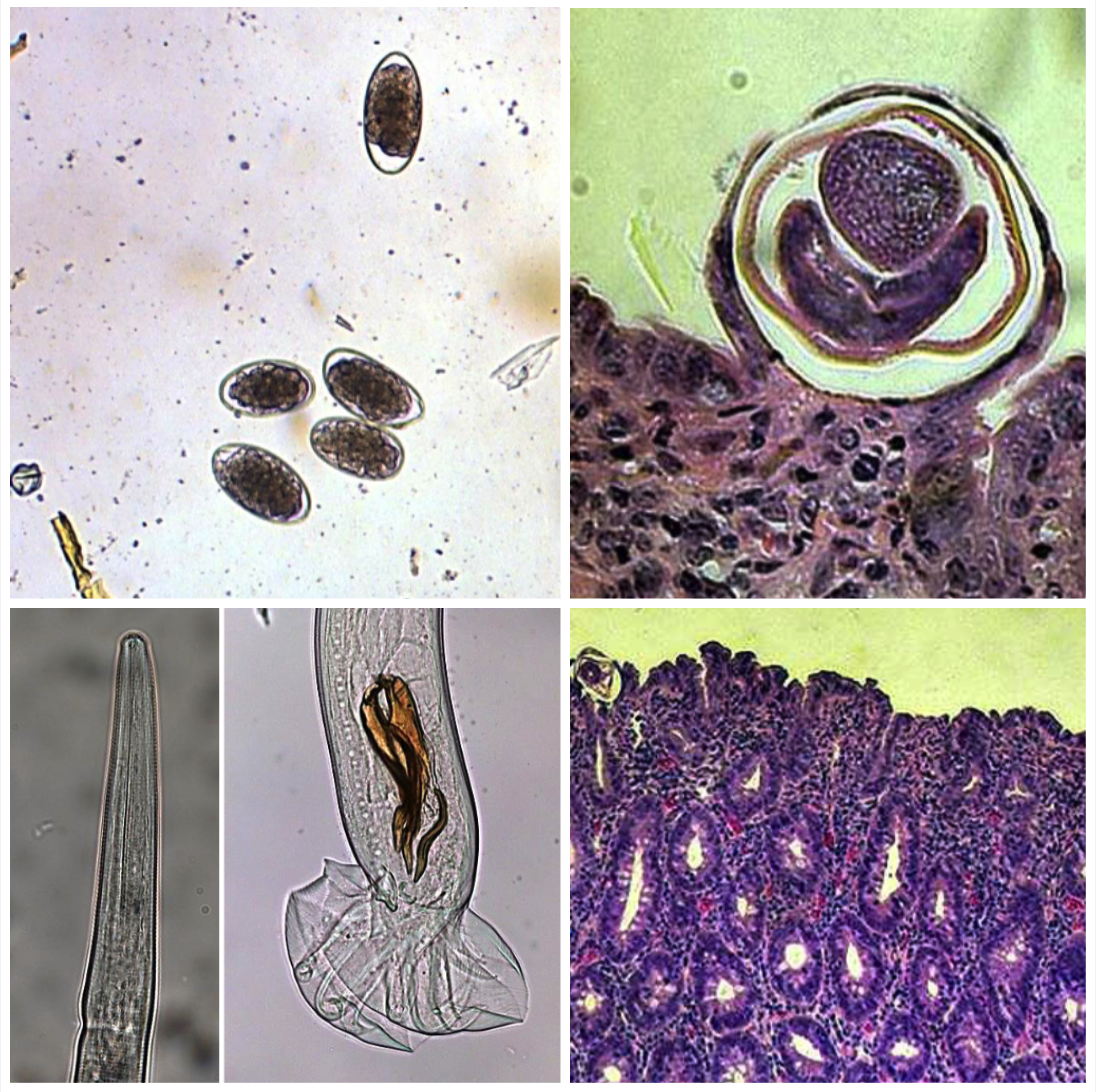
Haemonchus contortus
ABOMASUM
You have anaemic, weak and lethargic sheep. There is no weight loss or diarrhoea but some have bottle jaw. The abomasum has dark red-brown fluid and edmatous abomasal fold which focal areas of haemorrhage.
- Found in tropical climates
- Ingestion of L3 with pasture
- Lays 10,000 eggs/day
- PPR when ewes are pregant, shed more eggs
- Use FAMACHA and dipstix test
You have anaemic, weak and lethargic sheep. There is no weight loss or diarrhoea but some have bottle jaw. The abomasum has dark red-brown fluid and edmatous abomasal fold which focal areas of haemorrhage.
- Found in tropical climates
- Ingestion of L3 with pasture
- Lays 10,000 eggs/day
- PPR when ewes are pregant, shed more eggs
- Use FAMACHA and dipstix test
2
New cards
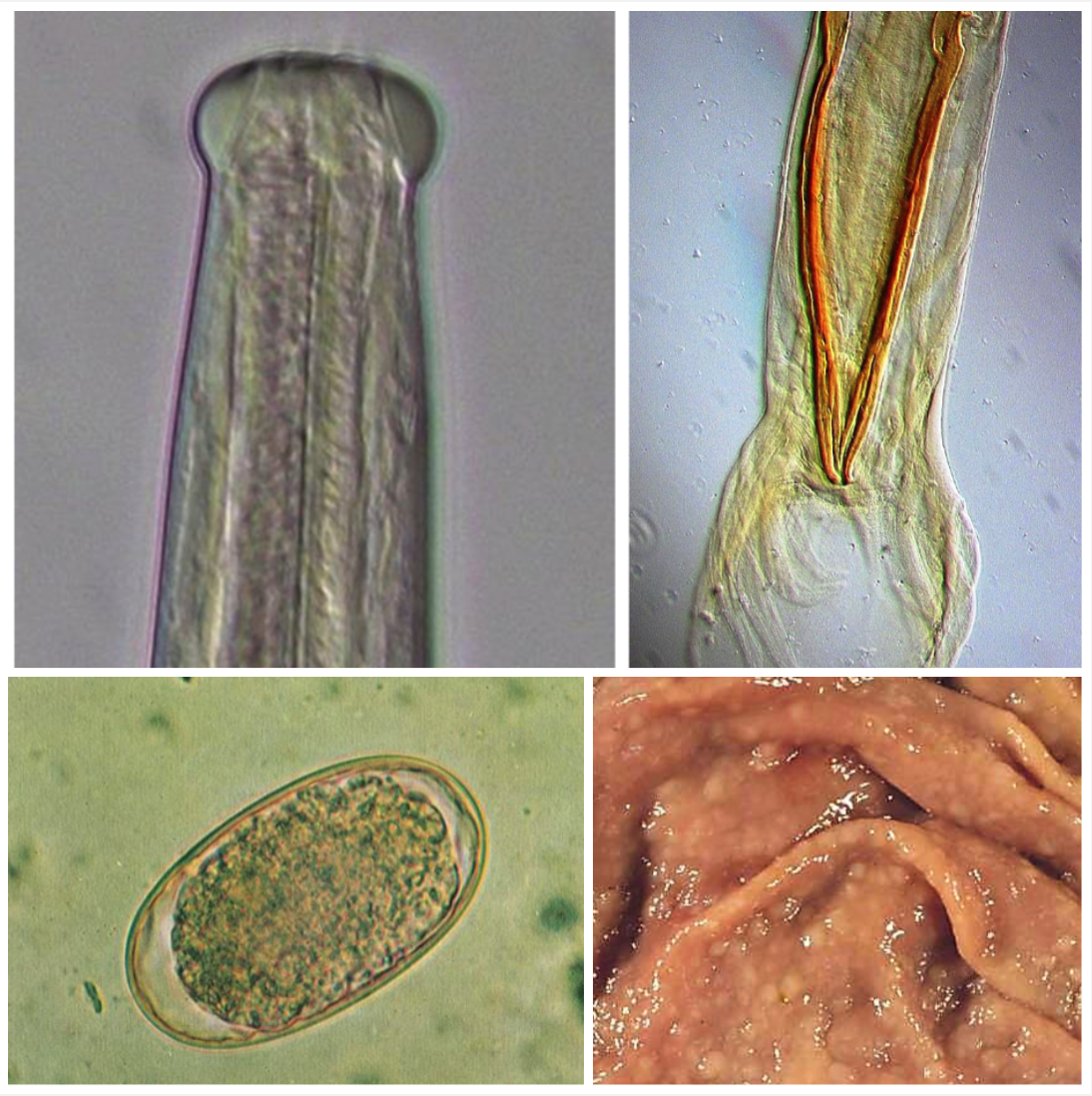
Trichostrongylus colubriformis
SMALL INTESTINE
Your sheep had villous atrophy and erosions of mucosa in the small intestine. They had soft faeces, anemia, anorexia and weight loss.
- Found in a temperate climate
- Ingestion of L3 with pasture
- 100 eggs/day
Your sheep had villous atrophy and erosions of mucosa in the small intestine. They had soft faeces, anemia, anorexia and weight loss.
- Found in a temperate climate
- Ingestion of L3 with pasture
- 100 eggs/day
3
New cards
Ostertagia ostertagi
ABOMASUM
In April-May (Autumn) you find 18-month old beef cattle with nodules/coalesced nodules in the abomasum, anorexia, diarrhoea and weight loss. Very few eggs are found in a FEC.
- Ingestion of L3 with pasture
- Hypobiotic larvae, infected in earlier warmer months and reactivated
- Hyperplasia of mucous cells form nodules
- Use pepsinogen and gastrin levels to diagnose due to reduction in gastric acid and alkaline stomach pH meaning no pepsin being converted from pepsinogen
- Confirm diagnosis with larvae culture
In April-May (Autumn) you find 18-month old beef cattle with nodules/coalesced nodules in the abomasum, anorexia, diarrhoea and weight loss. Very few eggs are found in a FEC.
- Ingestion of L3 with pasture
- Hypobiotic larvae, infected in earlier warmer months and reactivated
- Hyperplasia of mucous cells form nodules
- Use pepsinogen and gastrin levels to diagnose due to reduction in gastric acid and alkaline stomach pH meaning no pepsin being converted from pepsinogen
- Confirm diagnosis with larvae culture
4
New cards
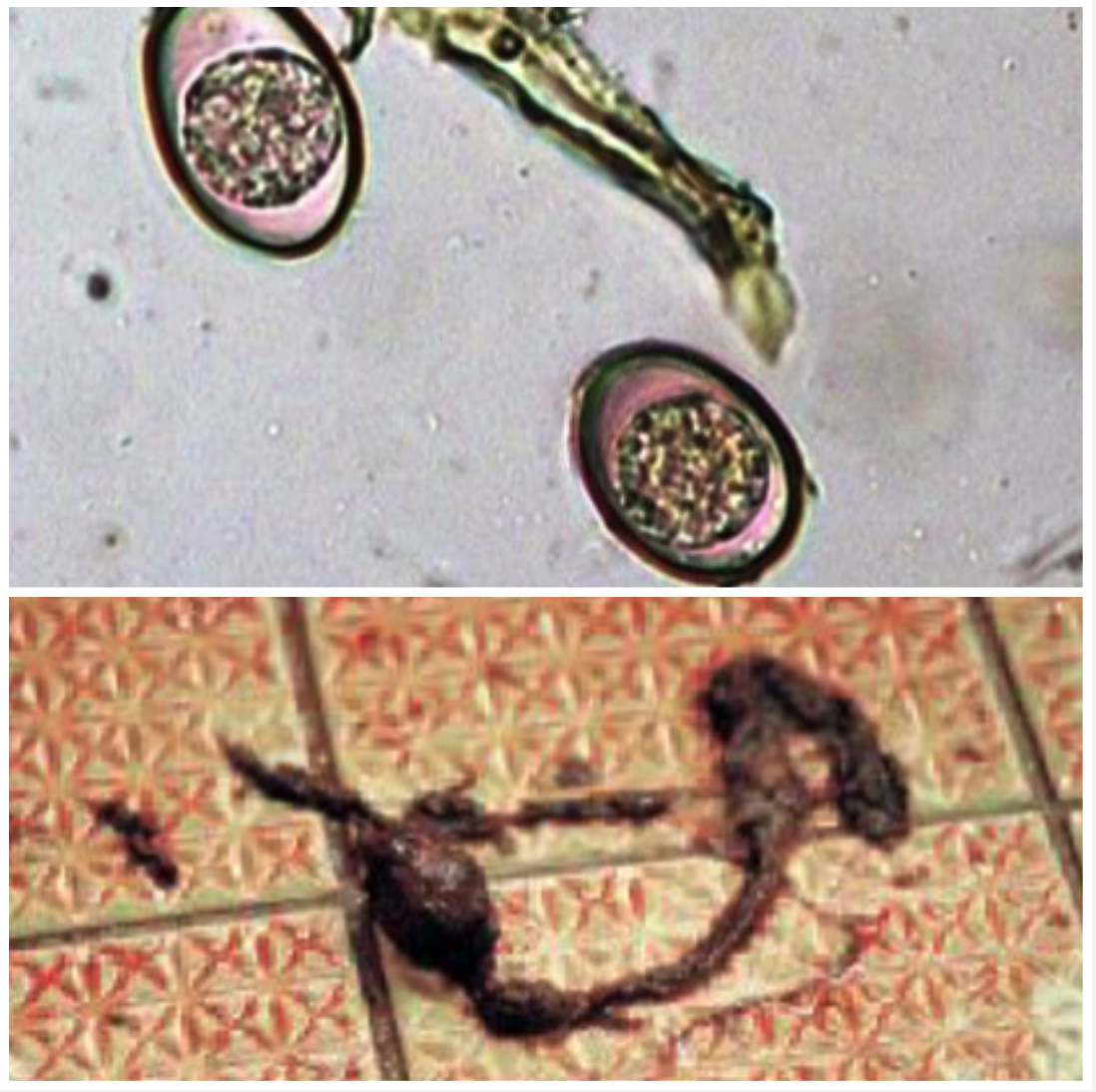
Eimeria spp.
SMALL & LARGE INTESTINE
You have 2 month old dairy calves that are anaemic, weak with profuse watery diarrhoea, sometimes with blood, tenesmus and rectal prolapse. The perineum and tail are stained with faeces
- Ingestion of sporulated oocysts
- Need to temp, humidity and vegetation state to sporulate
You have 2 month old dairy calves that are anaemic, weak with profuse watery diarrhoea, sometimes with blood, tenesmus and rectal prolapse. The perineum and tail are stained with faeces
- Ingestion of sporulated oocysts
- Need to temp, humidity and vegetation state to sporulate
5
New cards
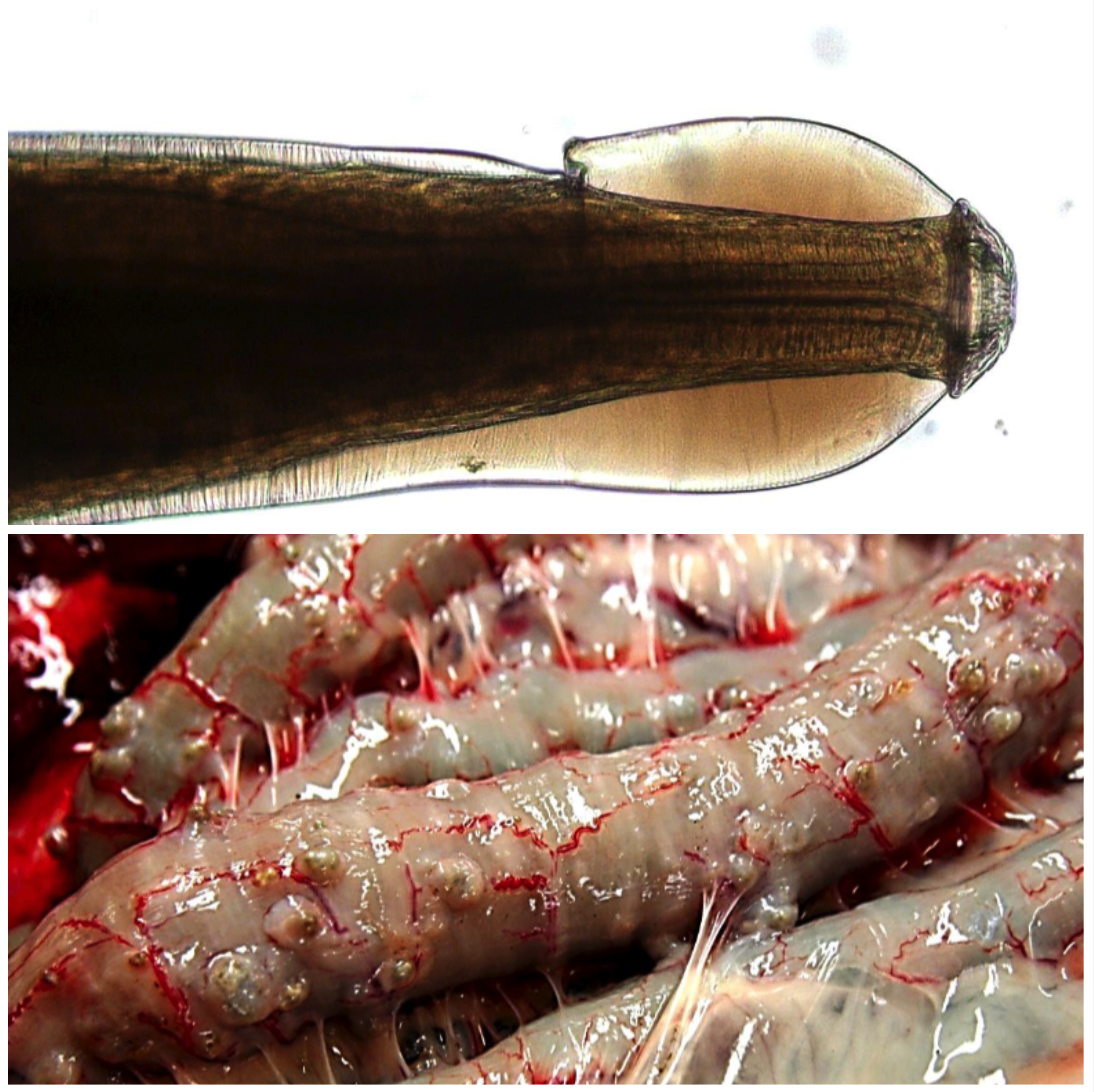
Oesophagostomum spp.
LARGE INTESTINE
You see 0.5-1cm nodules in the small and large intestine.
- Ingestion of L3 with pasture
- Cephalic vesicle
- Thin shell egg with many cells
- Pathogenic L4
You see 0.5-1cm nodules in the small and large intestine.
- Ingestion of L3 with pasture
- Cephalic vesicle
- Thin shell egg with many cells
- Pathogenic L4
6
New cards
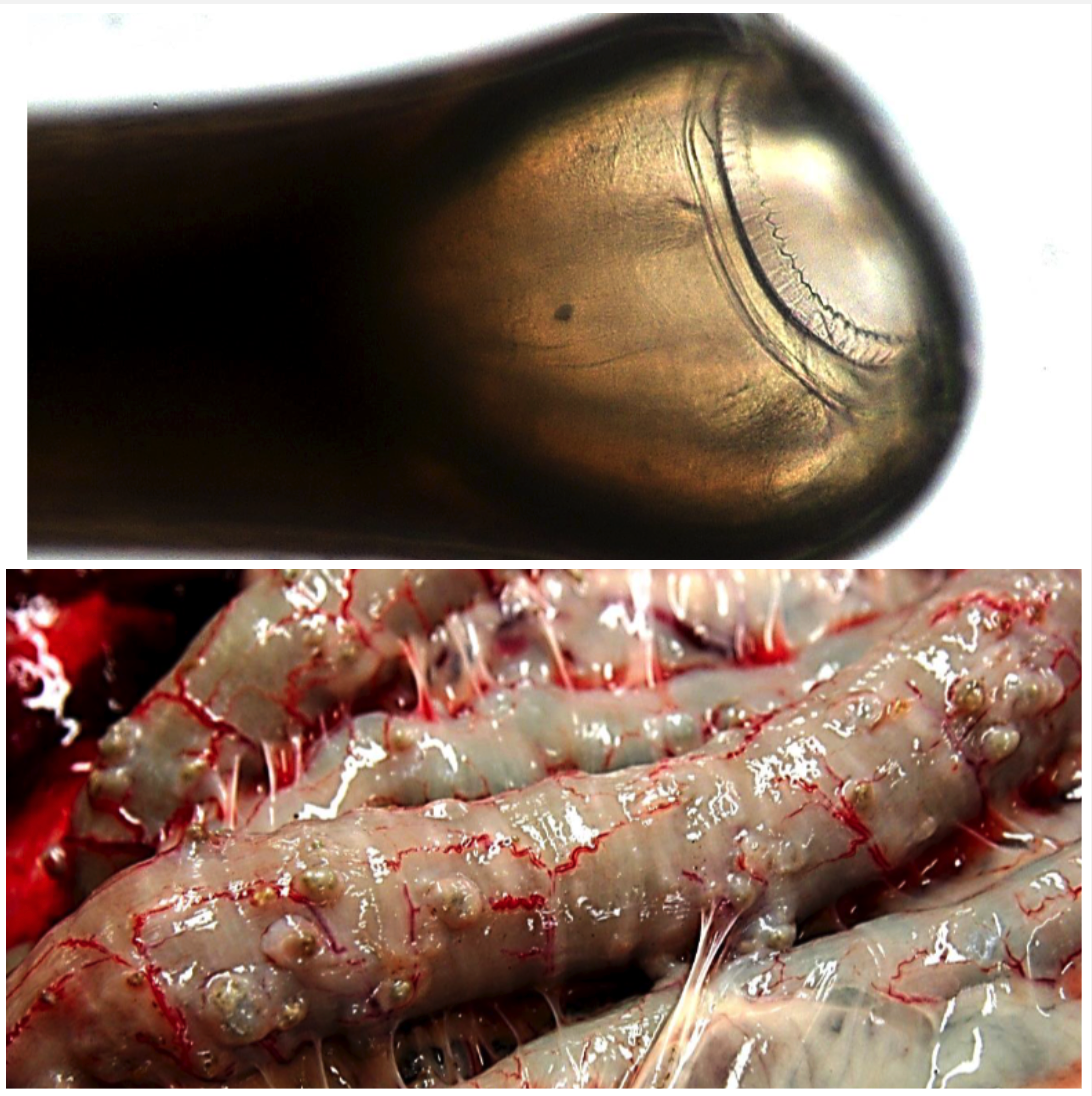
Chabertia ovina
LARGE INTESTINE
You see 0.5-1cm nodules in the small and large intestine.
- Ingestion of L3 with pasture
- Large buccal capsule
- Two small corona radiata with no teeth
- Thin shell egg with many cells
You see 0.5-1cm nodules in the small and large intestine.
- Ingestion of L3 with pasture
- Large buccal capsule
- Two small corona radiata with no teeth
- Thin shell egg with many cells
7
New cards
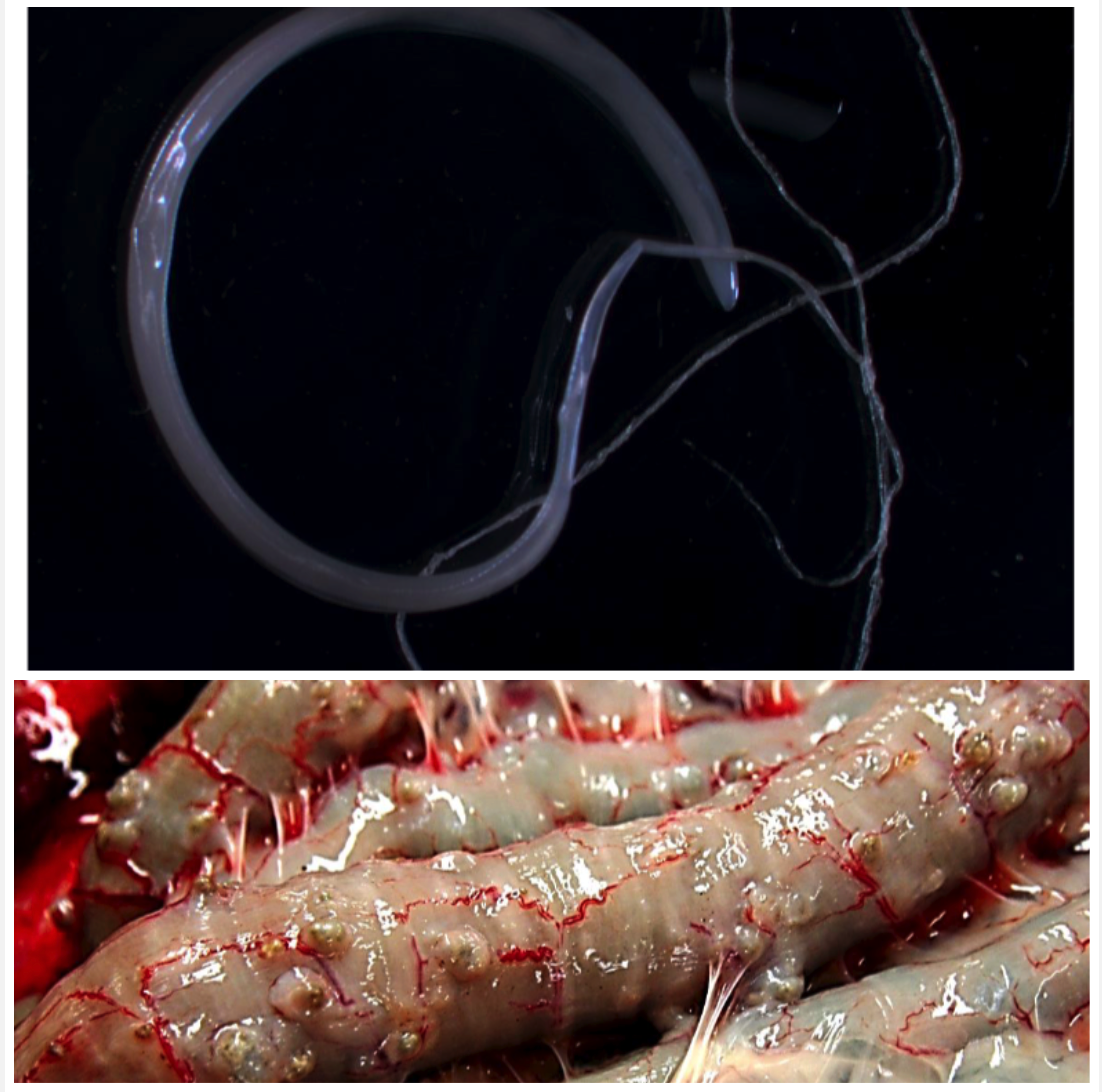
Trichuris spp.
LARGE INTESTINE
You see 0.5-1cm nodules in the small and large intestine.
- Ingestion of embryonated egg
- Brown/yellow egg, two polar plugs, one cell inside
You see 0.5-1cm nodules in the small and large intestine.
- Ingestion of embryonated egg
- Brown/yellow egg, two polar plugs, one cell inside
8
New cards
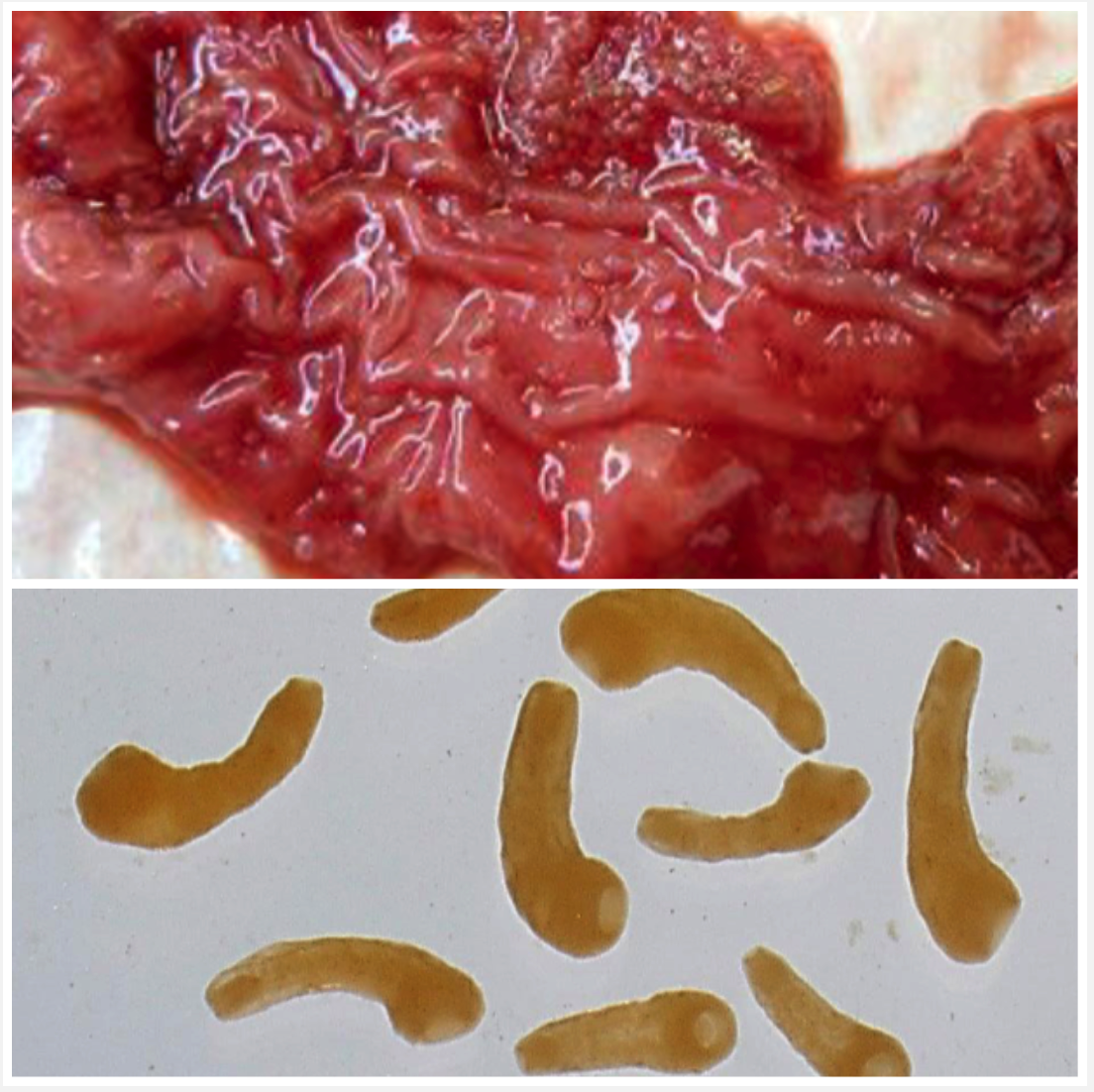
Paramphistoma spp. Calicophoron calicophorum
RUMEN/RETICULUM (adults) & ABOMASUM/DUODENUM (immature)
Your calves in Victoria have been in a swampy pasture for 4 weeks, they display anorexia, polydipsia, weight loss and fluid, foul-smelling diarrhoea. The duodenum was congested and oedomatous with erosions and petechiae.
- Ingestion of metacercaria with water and grass
- Pathogenic juveniles causes mechanical damage
Your calves in Victoria have been in a swampy pasture for 4 weeks, they display anorexia, polydipsia, weight loss and fluid, foul-smelling diarrhoea. The duodenum was congested and oedomatous with erosions and petechiae.
- Ingestion of metacercaria with water and grass
- Pathogenic juveniles causes mechanical damage
9
New cards
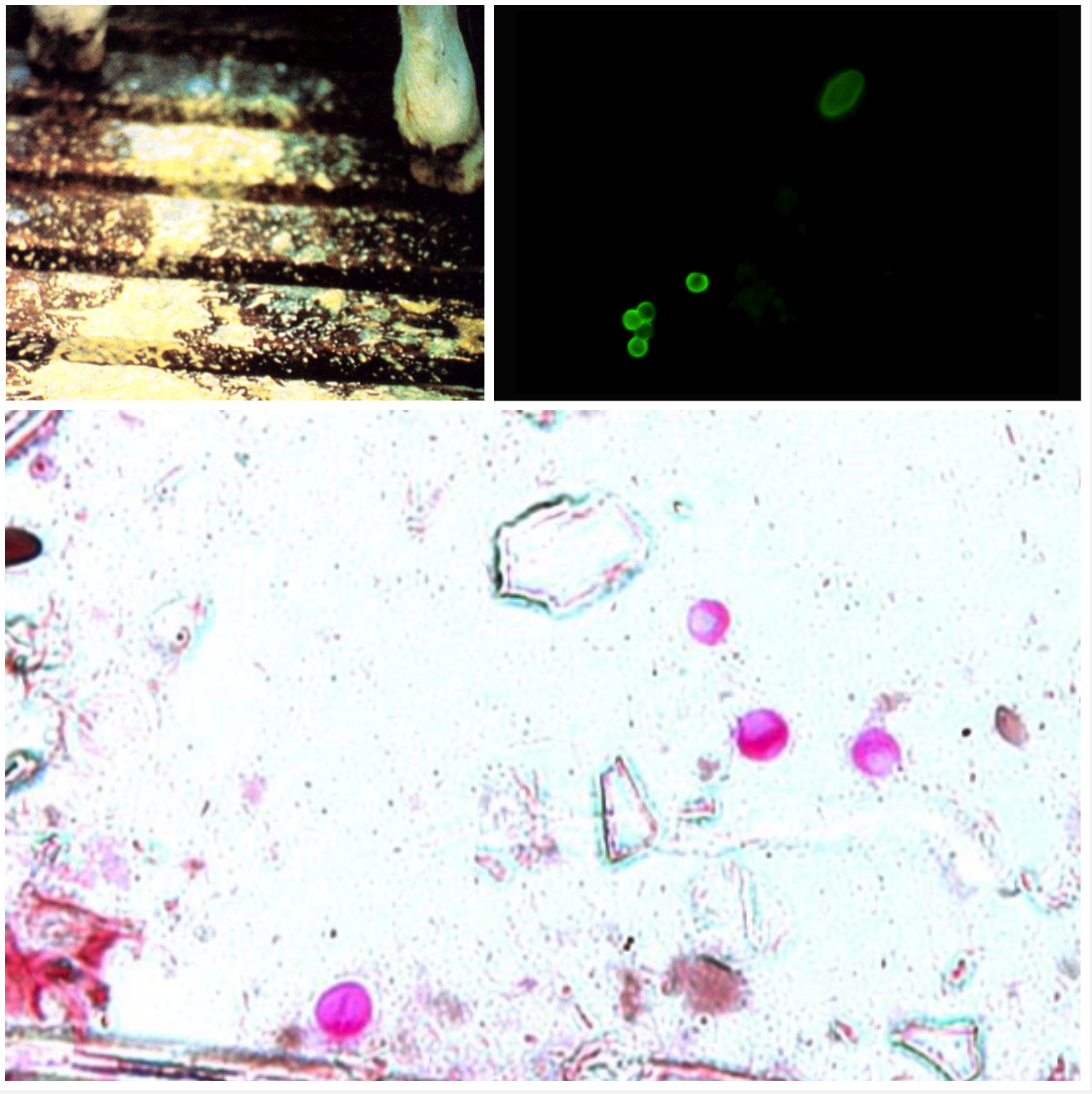
Cryptosporidium parvum
SMALL INTESTINE
You have 2 week old dairy calves with acute diarrhoea and yellowish faeces, anorexia, lethargic ad dehydrated.
- Ingestion of sporulated oocysts (sporulated and infective)
- Brush border of epithelia
- Four sporozoites and no sporocysts
- Need to do acid stain on faecal smear or immunofluorescence to see
You have 2 week old dairy calves with acute diarrhoea and yellowish faeces, anorexia, lethargic ad dehydrated.
- Ingestion of sporulated oocysts (sporulated and infective)
- Brush border of epithelia
- Four sporozoites and no sporocysts
- Need to do acid stain on faecal smear or immunofluorescence to see
10
New cards
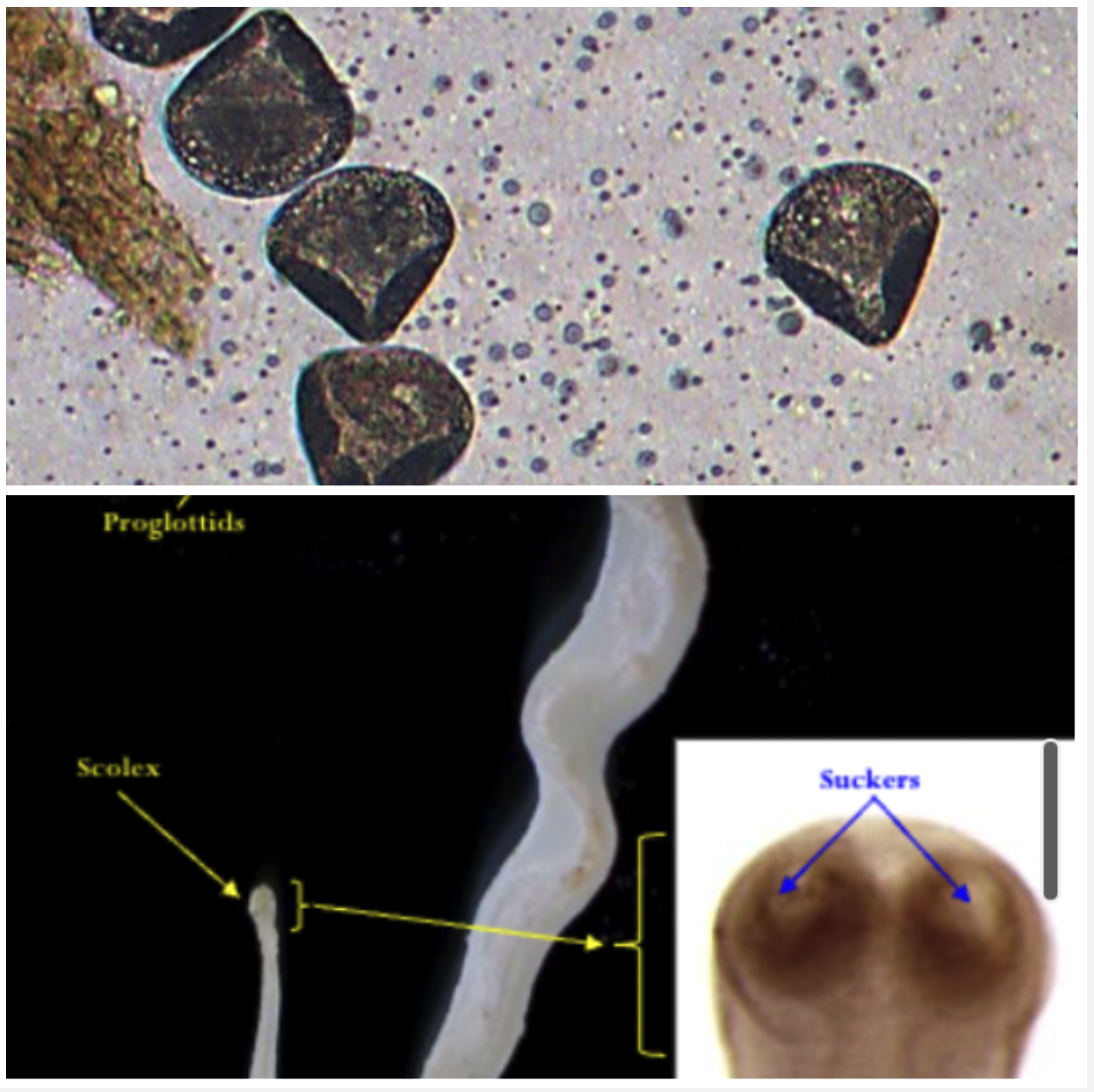
Moniezia expansa
SMALL INTESTINE
Your lambs have diarrhoea , anaemia and weight loss after 6-8 weeks of being on a pasture used by adult sheep.
- Ingestion of cysticercoid larvae in orbatid mites (IH)
- 2 sets of reproductive organs, 2 genital pores
- Triangular eggs with pyriform apparatus
Your lambs have diarrhoea , anaemia and weight loss after 6-8 weeks of being on a pasture used by adult sheep.
- Ingestion of cysticercoid larvae in orbatid mites (IH)
- 2 sets of reproductive organs, 2 genital pores
- Triangular eggs with pyriform apparatus
11
New cards
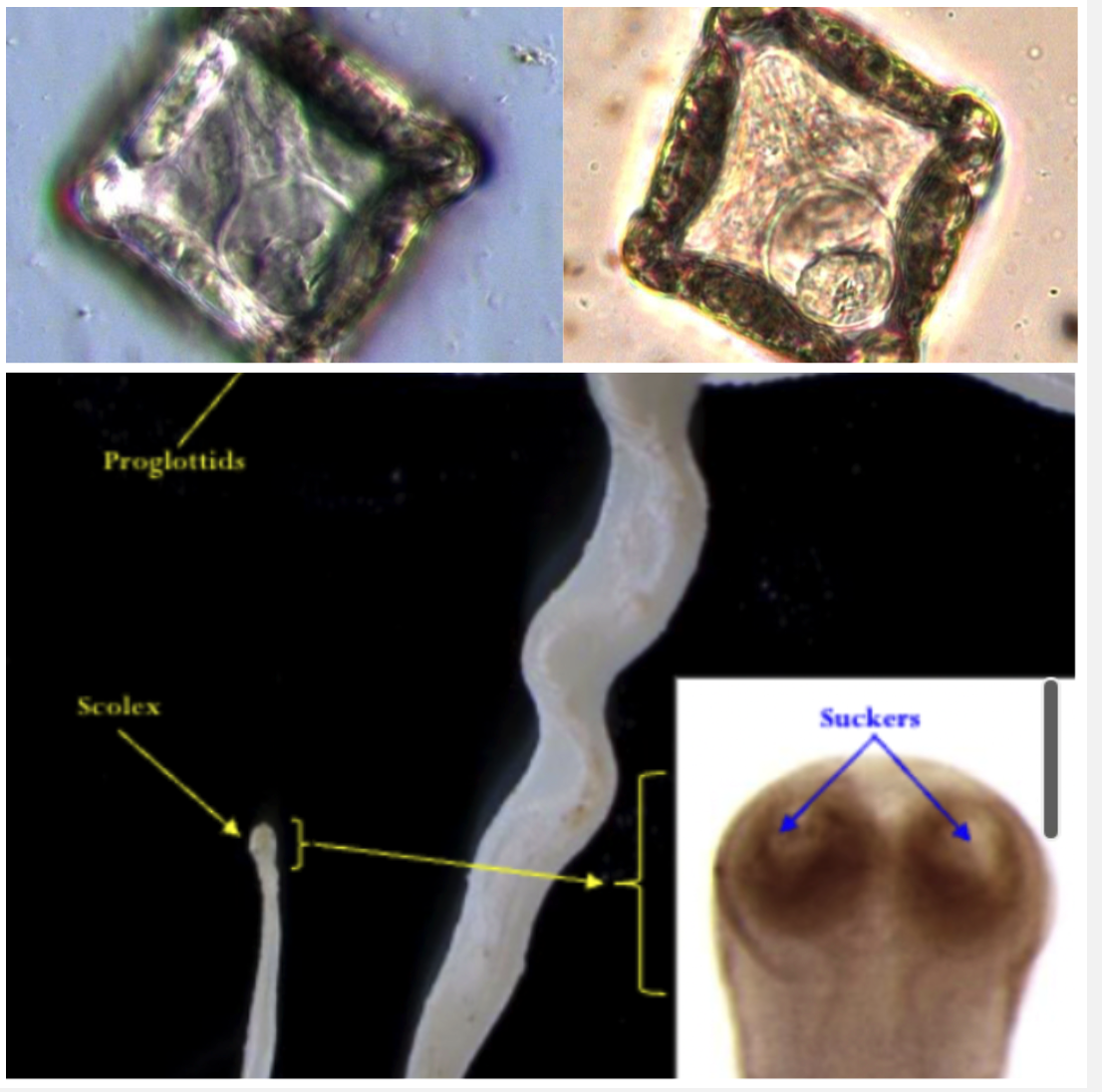
Moniezia benedeni
SMALL INTESTINE
Your lambs have diarrhoea , anaemia and weight loss after 6-8 weeks of being on a pasture used by adult sheep.
- Ingestion of cysticercoid larvae in orbatid mites (IH)
- 2 sets of reproductive organs, 2 genital pores
Square eggs with pyriform apparatus
Your lambs have diarrhoea , anaemia and weight loss after 6-8 weeks of being on a pasture used by adult sheep.
- Ingestion of cysticercoid larvae in orbatid mites (IH)
- 2 sets of reproductive organs, 2 genital pores
Square eggs with pyriform apparatus
12
New cards
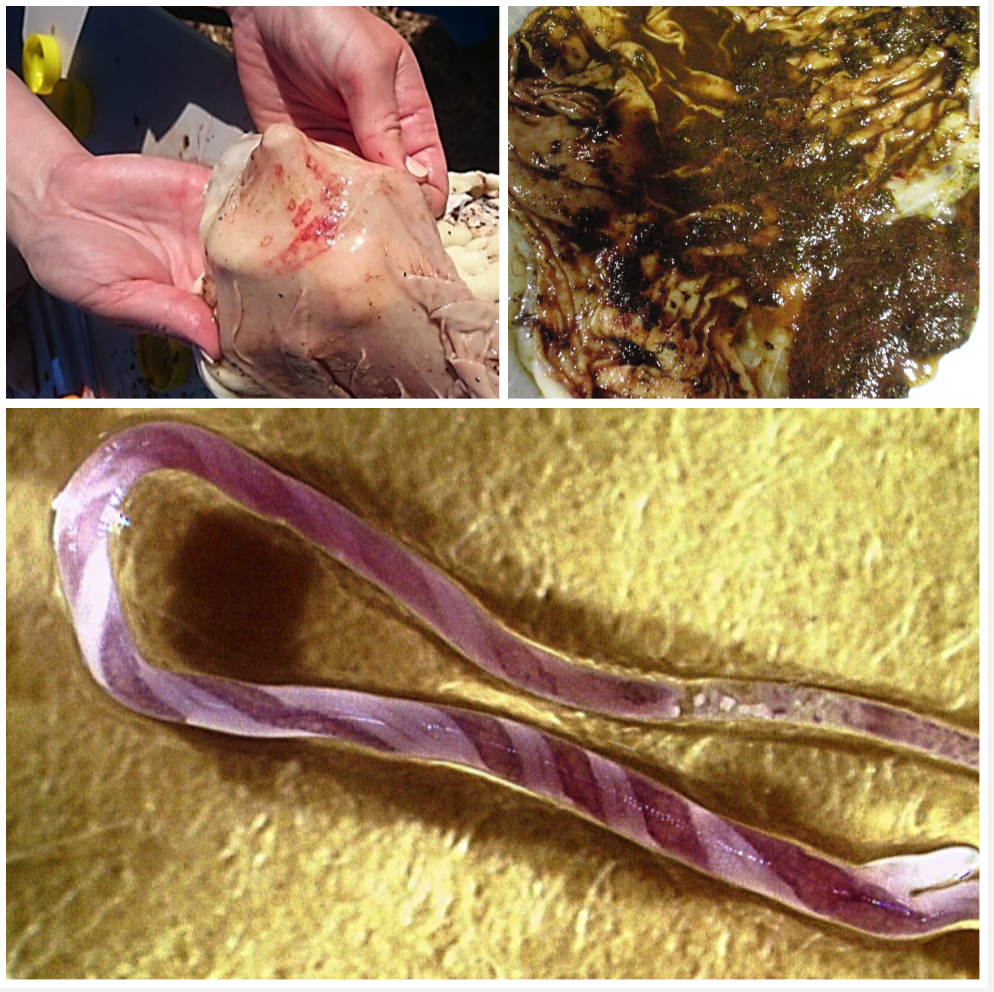
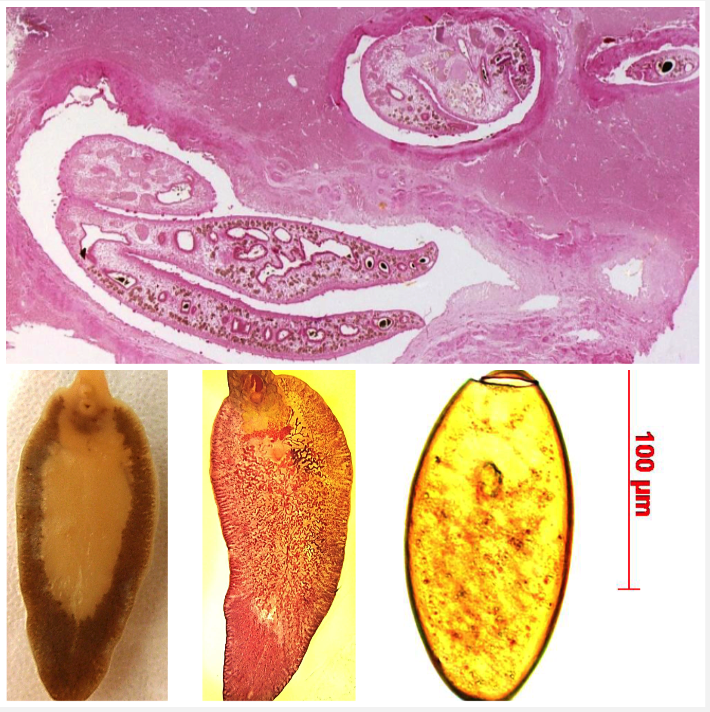
Fasciola hepatica
LIVER
Your sheep have weight loss, anaemia, jaundice, reduced appetite, weakness and ascites after 3-4 months on a pasture in a flooded area. They have hyperplastic cholangitis, fibrosis and cirrhosis in the liver.
- Ingestion of metacercaria with water or pasture
- Juveniles burrow through liver parenchyma
- Adults living in bile ducts
- Treat juveniles with triclabendazole
Your sheep have weight loss, anaemia, jaundice, reduced appetite, weakness and ascites after 3-4 months on a pasture in a flooded area. They have hyperplastic cholangitis, fibrosis and cirrhosis in the liver.
- Ingestion of metacercaria with water or pasture
- Juveniles burrow through liver parenchyma
- Adults living in bile ducts
- Treat juveniles with triclabendazole
13
New cards
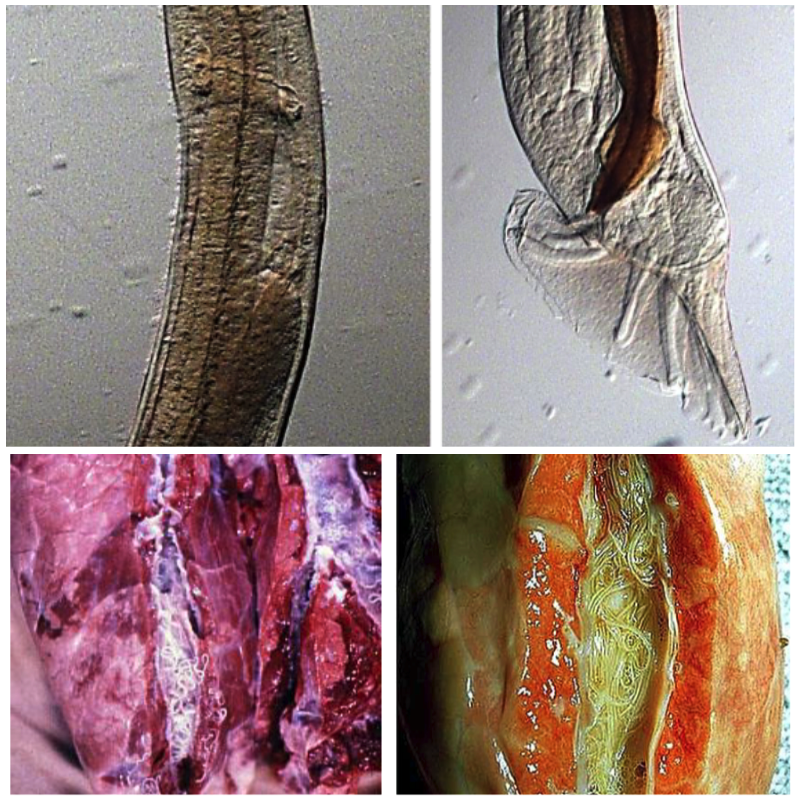
Dictyocaulus viviparus
BRONCHI & TRACHEA
Your calves are coughing and show dyspnoea, anorexia and weight loss. You find white mucous and whitish parasites in the bronchi and trachea.
- Ingestion of L3 with pasture
- Mature to L4 and migrate to lungs as mature
- Lay eggs in lungs, cough up and swallowed
- Eggs hatch in intestines and L1 in faeces
- L1 to L3 in pasture
Your calves are coughing and show dyspnoea, anorexia and weight loss. You find white mucous and whitish parasites in the bronchi and trachea.
- Ingestion of L3 with pasture
- Mature to L4 and migrate to lungs as mature
- Lay eggs in lungs, cough up and swallowed
- Eggs hatch in intestines and L1 in faeces
- L1 to L3 in pasture
14
New cards
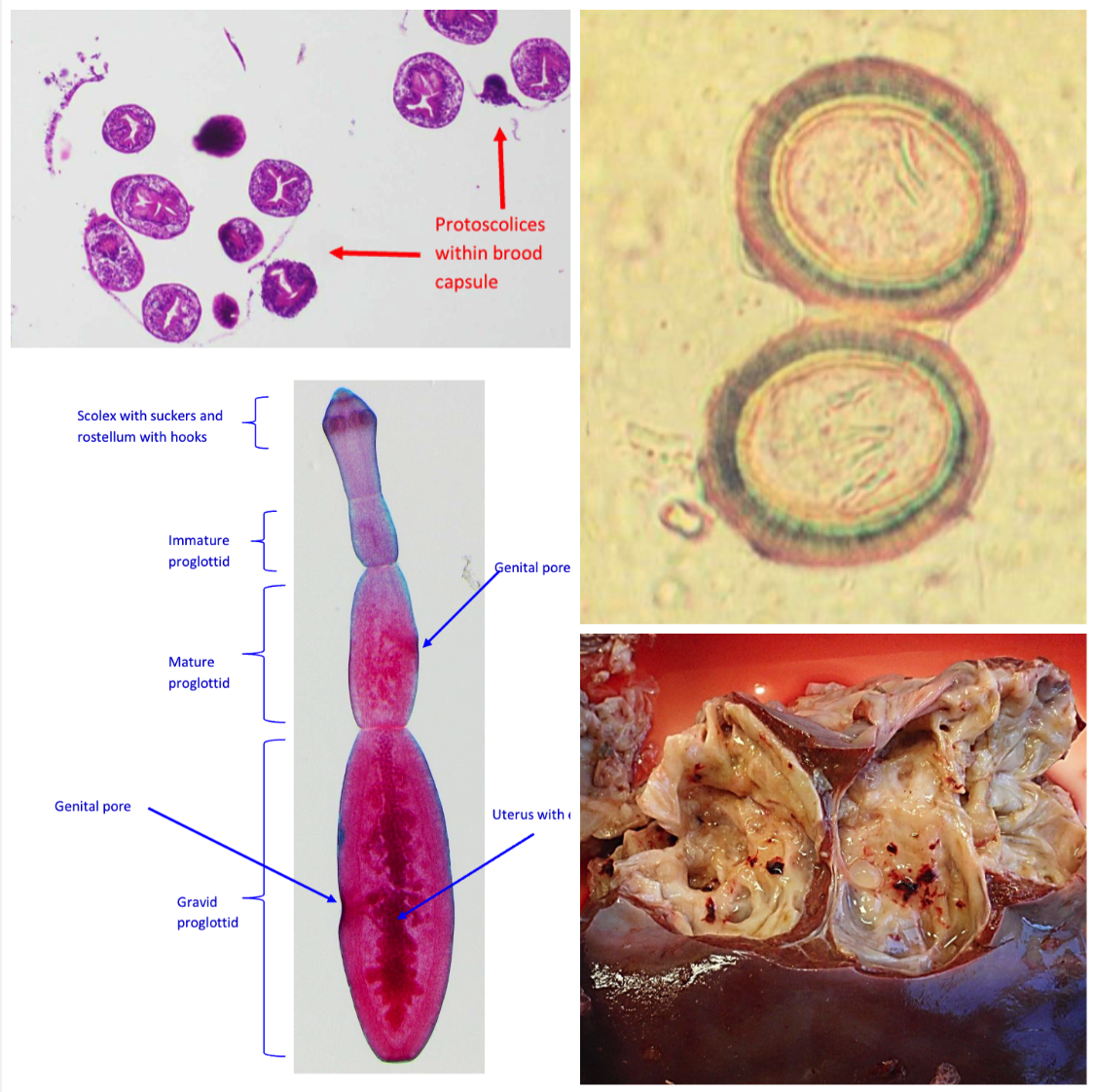
Echinococcus granulosus
LIVER & LUNGS
- Ingestion of eggs shed by dogs (IH)
- Hyatid cysts with brood capsule and invaginated/evaginated protoscolexes are pathogenic
- Laminated and germinal layer
- Egg is striated embryophore with hexacanth embryo within (oncosphere)
- Adult with 3-4 proglottids, scolex with 2 rows of hooks and cause no clinical signs, not pathogenic
- Develop in lung and livers of HUMANS
- Ingestion of eggs shed by dogs (IH)
- Hyatid cysts with brood capsule and invaginated/evaginated protoscolexes are pathogenic
- Laminated and germinal layer
- Egg is striated embryophore with hexacanth embryo within (oncosphere)
- Adult with 3-4 proglottids, scolex with 2 rows of hooks and cause no clinical signs, not pathogenic
- Develop in lung and livers of HUMANS
15
New cards
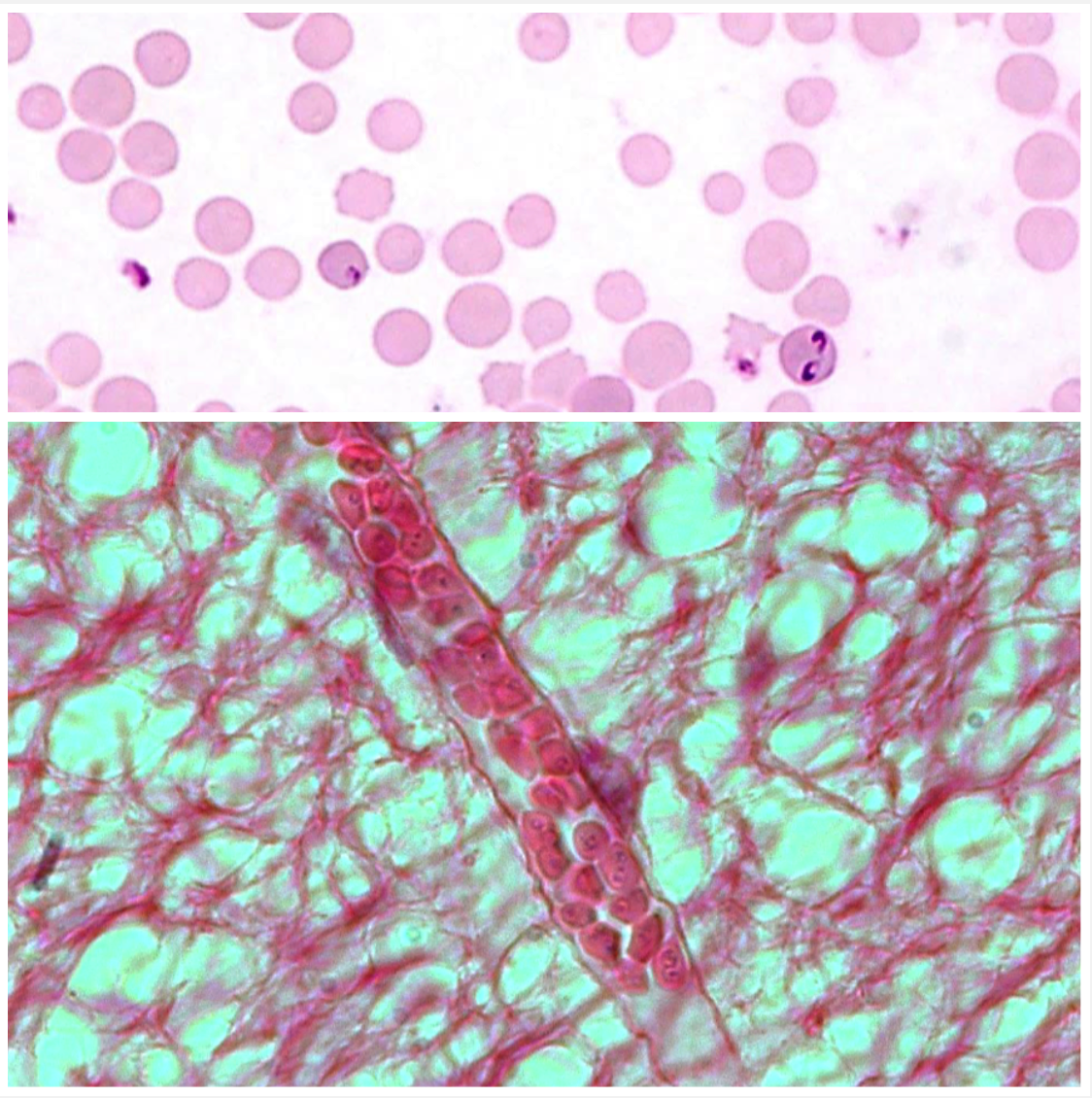
Babesia bovis
RED BLOOD CELLS
You have cows with inappetence, depression, convulsions, paralysis, aggression, ataxia, anemia, haemoglobinuria and jaundice.
- Ingestion of sporozoites from ticks with their saliva
- Clogs capillaries, ishcaemia in brain, neurological signs unlike babesia bigemina
You have cows with inappetence, depression, convulsions, paralysis, aggression, ataxia, anemia, haemoglobinuria and jaundice.
- Ingestion of sporozoites from ticks with their saliva
- Clogs capillaries, ishcaemia in brain, neurological signs unlike babesia bigemina
16
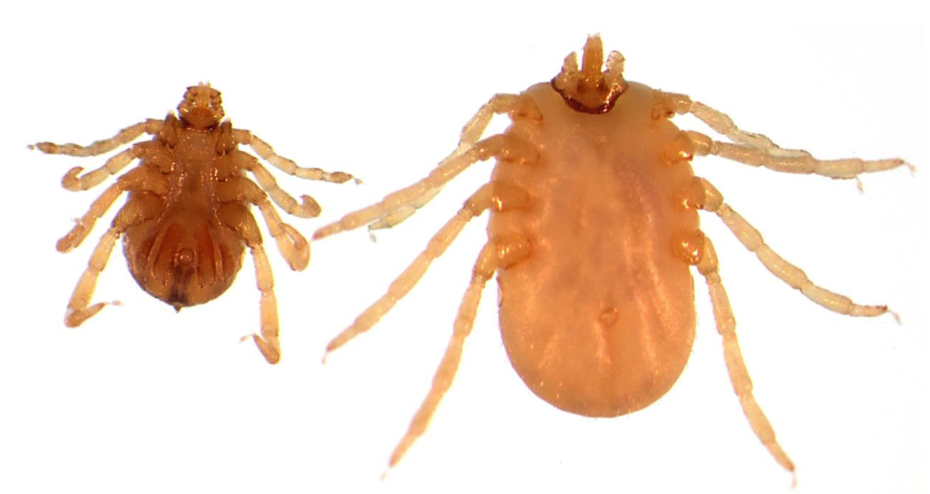
New cards
Rhipicephalus australis
ONE HOST TICK
Larvae - Babesia bovis
Nymph and adults - Babesia bigemina
Males - Anaplasma marginale
- Hexagonal basis captuli
- No festoons
- Pale whitish legs
- Wide distance between first legs and gnathostoma
- Coxa with two short spurs
Larvae - Babesia bovis
Nymph and adults - Babesia bigemina
Males - Anaplasma marginale
- Hexagonal basis captuli
- No festoons
- Pale whitish legs
- Wide distance between first legs and gnathostoma
- Coxa with two short spurs

17
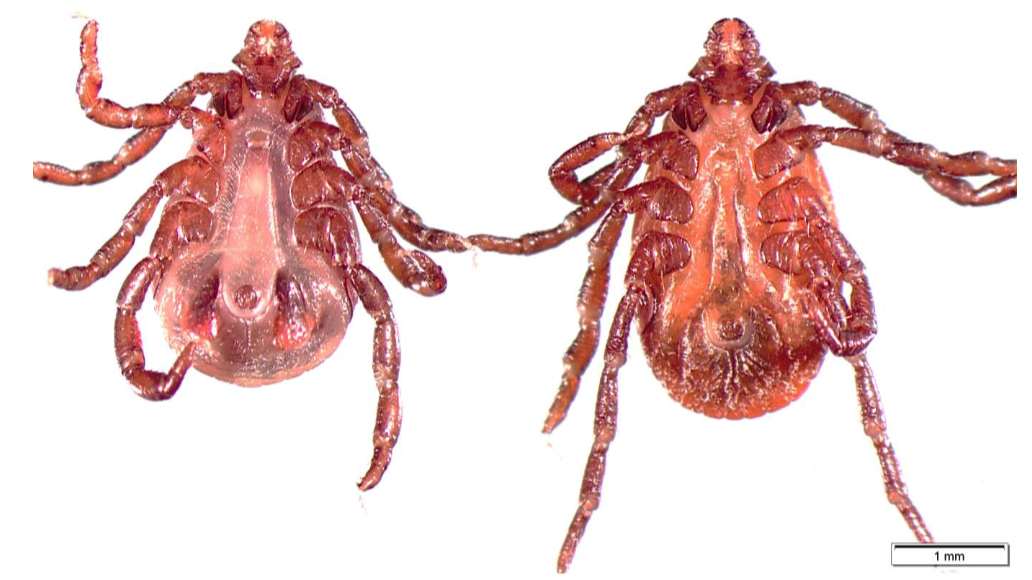
New cards
Rhipicephalus sanguineus
THREE HOST TICK
- Hexagonal basis captuli
- Festoons
- Coxa with two long spurs
- Hexagonal basis captuli
- Festoons
- Coxa with two long spurs

18
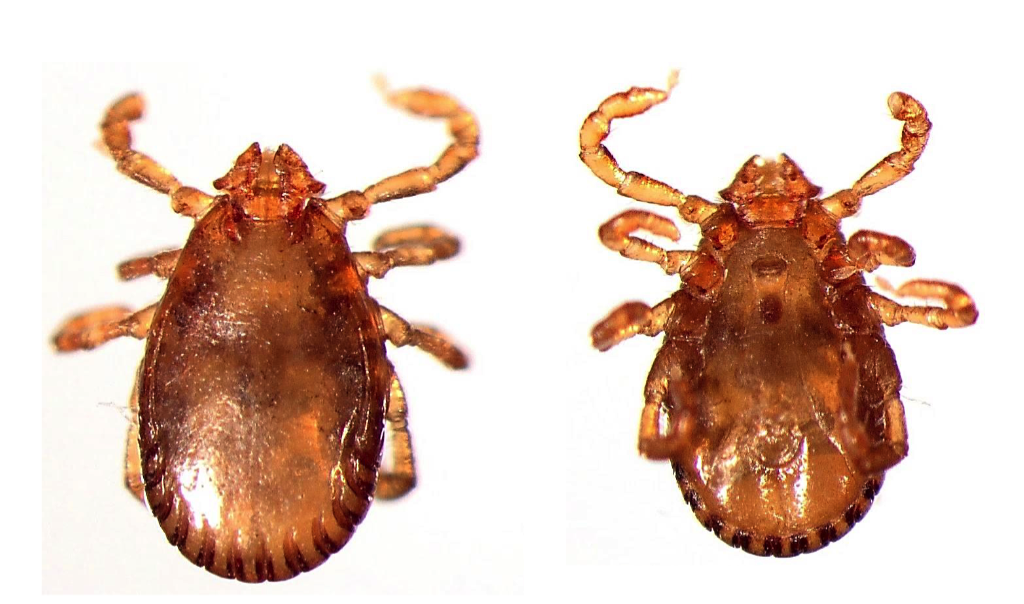
New cards
Haemaphysalis longicornis
THREE HOST TICK
- Rectangular basis captuli
- Dark brown legs
- Festoons
- Palps extend out laterally
- Rectangular basis captuli
- Dark brown legs
- Festoons
- Palps extend out laterally

19
New cards
Amblyomma triguttatum
THREE HOST TICKS
- Rectangular basis captuli
- Ornate scutum
- Festoons
- Second segment of mouthparts are almost 2x as long as third segment
- Rectangular basis captuli
- Ornate scutum
- Festoons
- Second segment of mouthparts are almost 2x as long as third segment
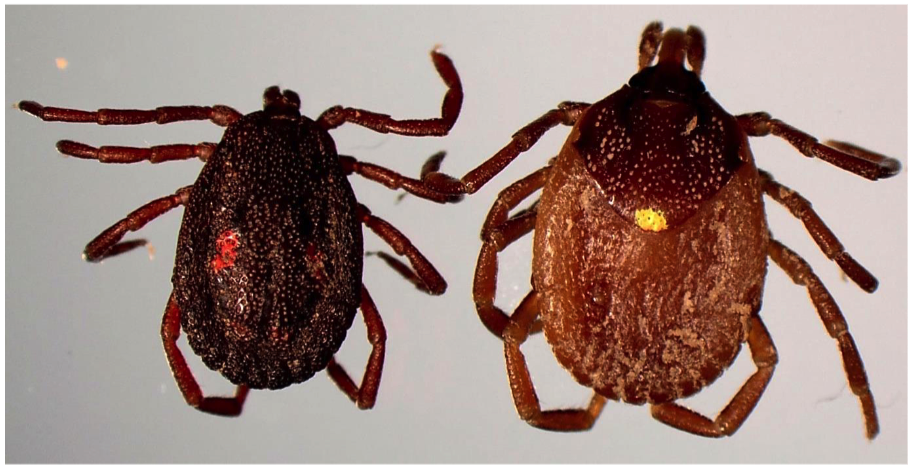

20
New cards
Bovicola ovis
SHORT WOOL: plunge, shower and cage dip, short wool backline
LONG WOOL: handjet and long wool backline
- Head wider than thorac (biting lice)
- Black transverse stripes on abdomen
- Feeds on skin debris, epidermal scales, scurf, suint, bacteria and dried serum
- Does not survive in high temperatures (
LONG WOOL: handjet and long wool backline
- Head wider than thorac (biting lice)
- Black transverse stripes on abdomen
- Feeds on skin debris, epidermal scales, scurf, suint, bacteria and dried serum
- Does not survive in high temperatures (
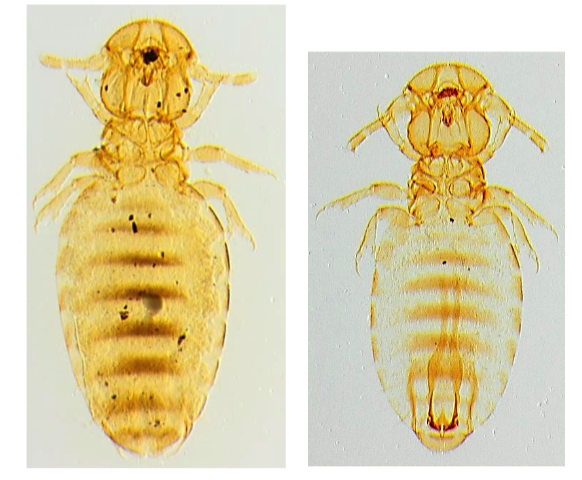

21
New cards
Linognathus africanus
- Head narrower than thorax (sucking lice)
- 1st pair of legs shorter and thinner than others
- No parategal plates
- Bulging post-antennal margins
- 1st pair of legs shorter and thinner than others
- No parategal plates
- Bulging post-antennal margins
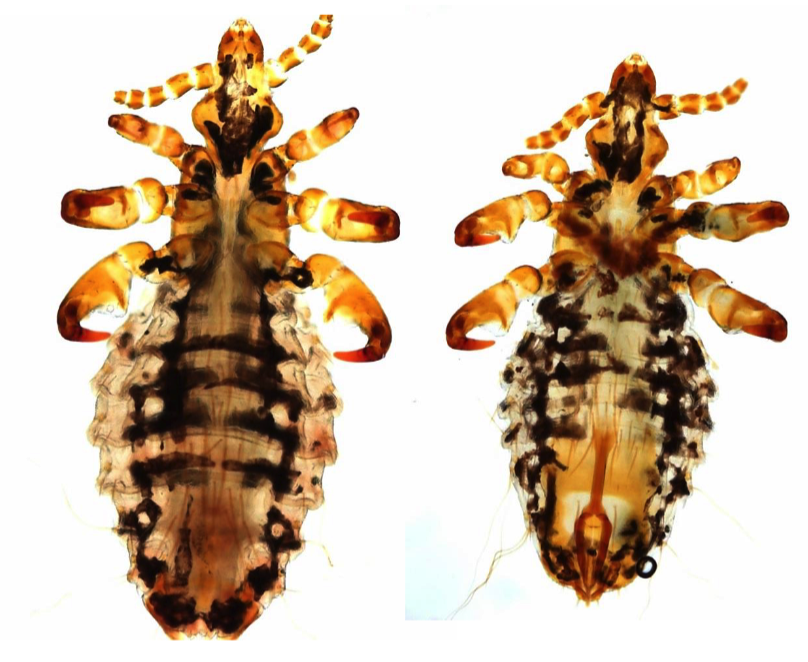

22
New cards
Haematopinus eurysternus
- Head narrower than thorax (sucking lice)
- All three pairs of legs are the same size
- Parategal plates
- Rectangular thorax
- Obvious ocular points
- All three pairs of legs are the same size
- Parategal plates
- Rectangular thorax
- Obvious ocular points
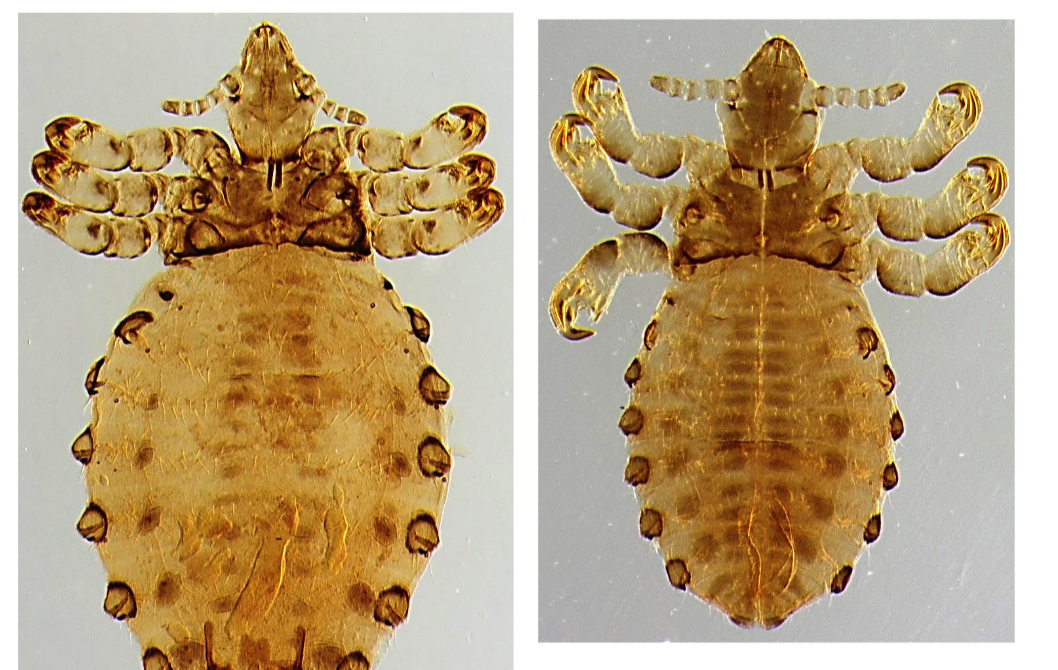
23
New cards
Haematobia irritans exigua
Blood pool feeders which cause bleeding under the skin which is painful
- Can transmit Stephanofilaria spp.
- Dung beetles can eat dung to prevent flies from laying eggs
- Large red eyes
- Wings resting in V shape
- Two black stripes on thorax
- Maxillary palps more than half as long as probiscus
- Can transmit Stephanofilaria spp.
- Dung beetles can eat dung to prevent flies from laying eggs
- Large red eyes
- Wings resting in V shape
- Two black stripes on thorax
- Maxillary palps more than half as long as probiscus
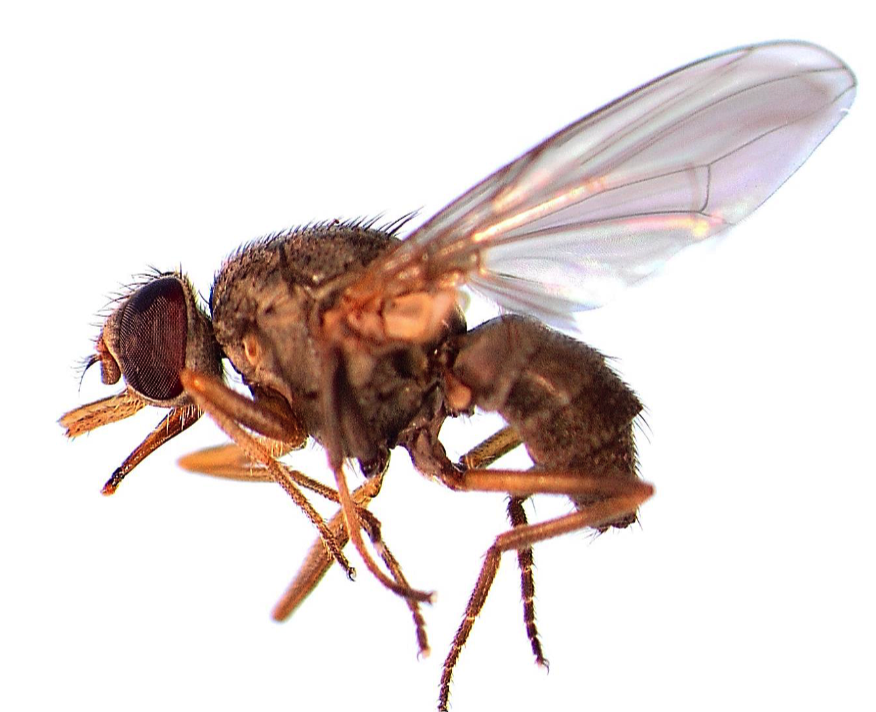

24
New cards
Chorioptes bovis
COWS: hindlegs, perineum, udder and base of tail
HORSES: hindlegs
SHEEP & GOATS: hindlegs and scrotum
- Feed on skin debris
- Must repeat treatments in 2-4 weeks as no chemicals treat eggs, let hatch and treat to kill larvae
HORSES: hindlegs
SHEEP & GOATS: hindlegs and scrotum
- Feed on skin debris
- Must repeat treatments in 2-4 weeks as no chemicals treat eggs, let hatch and treat to kill larvae
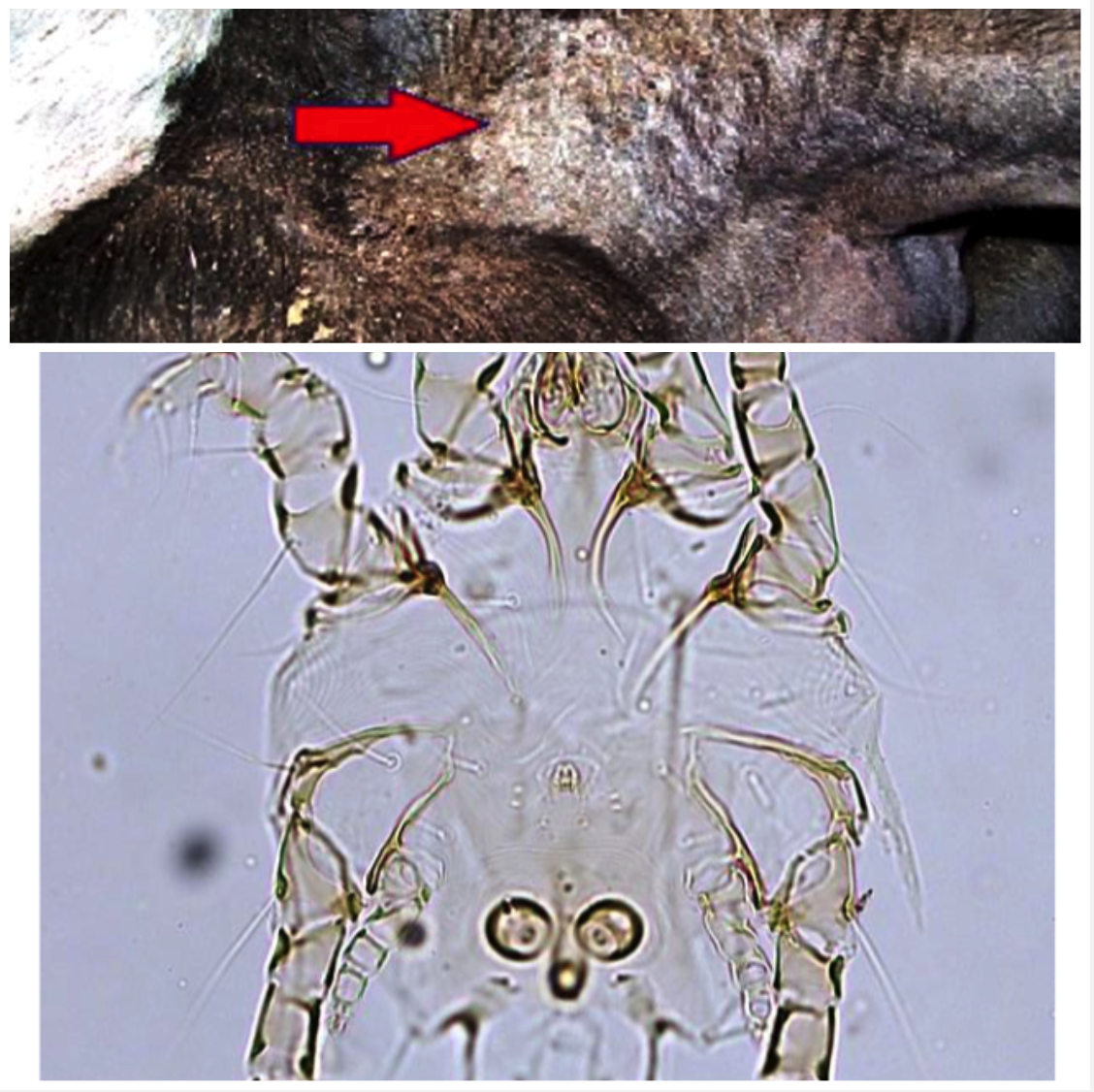
25
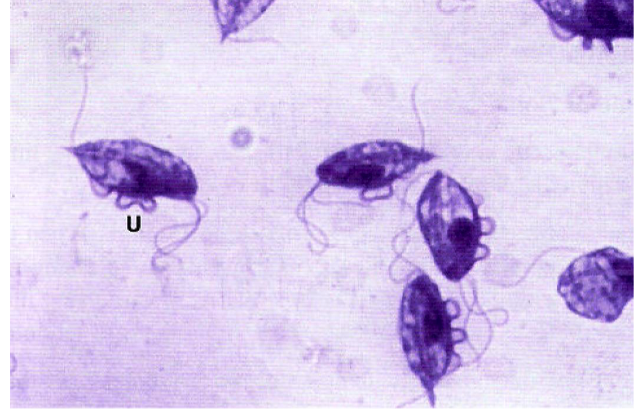
New cards
Tritrichomonas foetus
- Sexual transmission, use AI to prevent transmission
- Three anterior flagellum
- One posterior flagella
- Causes vaginitis, endometriosis, pyometra and abortion
- Three anterior flagellum
- One posterior flagella
- Causes vaginitis, endometriosis, pyometra and abortion