IB SL Physics Semester One
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
distance: symbol, units, s/v
d, meters (m), scalar
displacement: symbol, units, s/v
s, m @ theta, vector
time: symbol, units, s/v
t, seconds (s), scalar
speed: symbol, units, s/v, equation
v, m/s, scalar, v=d/t
velocity: symbol, units, s/v, equation
v, m/s @ theta, vector, v=s/t
acceleration: symbol, units, s/v, equation
a, m/s^2 @ theta, vector, a=(v-u)/t
jerk: symbol, units, s/v, equation
j, m/s^3 @ theta, vector, j=(af-ai)/t
initial velocity: symbol, units, s/v
u, m/s @ theta, vector
final velocity: symbol, units, s/v
v, m/s @ theta, vector
velocity over the total time
average velocity
velocity at a specific time
instantaneous velocity
unchanging velocity
uniform velocity
an object influenced by gravity only
projectile
Newton’s First Law: the law of ______
inertia
(Newton’s First Law) _______ is dependant on ___
inertia mass
Newton’s Second Law: the law of
acceleration
(Newton’s Second Law) equation:
F=ma
Newton’s Third Law: the law of
force pair
(Newton’s Third Law): statement
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
two types of friction: _____ ______, ______
kinetic (dynamic) static
FN = _______ Force
normal
force 90° to the surface an object is on
normal force
Fg = _
R (reactionary force)
how to find reactionary force (R)
mass * gravity
FNET = ____ force
net
the sum of all forces is ____ force
net
translational equilibrium: what is equal to zero?
net force
study the equations for inclined planes!!
okay
for a ________ use the equation
a=(fg2-fg1)/(m1+m2)
or a=f__/__
pulley net a
energy
the ability to do work or cause change
work
force * displacement, measured in Joules
Joules
N*m = kgm²/s²
Kinetic
energy of motion (.5mu²)
potential
energy due to position or composition (chemical, gravitational, elastic, electric, nuclear, magnetic)
both
internal or mechanical energy
power
energy/time = J/s = Watt (W)
Hooke’s Law
F=-kx
Energy final
energy initial is always equal to
efficiency
useful energy/total energy = useful power/total power = 34% KE
combustion engine
CPE; KEf +TEf + sound
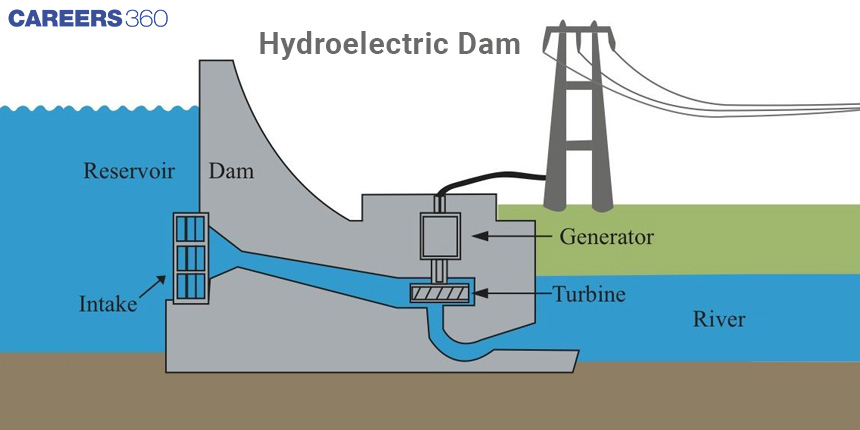
dam energy conversions
GPEw →KEw→KEt→EE (electrical energy)
momentum
mass in motion
m*v
p (momentum) =
impulse
an object’s change in momentum
Ft
J (impulse) =
conserved
momentum is __________ in every collision
inelastic collision
KE is not conserved (real life collisions)
elastic collision
KE is conserved
temperature
a measure related to average kinetic energy
kelvin fahrenheit celsius
the three measures of temperature
heat
the transfer of energy from high temperature to low temperature
interal energy
total potential energy + random kinetic energy
mole
quantity = 6.02 × 10²³
Avogadro’s constant
the number of particle in a mole (6.02 × 10²³)
molar mass
the grams in a mole of particles
fusion
Latent heat of __________ : solid to liquid
vaporization
latent heat of ___________: liquid to gas
latent heat (J/Kg)
change in Potential energy (change in state)
specific heat (J/(kg * °C))
change in temperature
Q=mL
latent heat uses which equation
Q=mc△t
specific heat uses which equation
greater than
latent heat of vaporization is [greater than/less than] latent heat of fusion
less than less than
specific heat of a liquid is [greater than/less than] specific heat of a solid is [greater than/less than] specific heat of gas
pressure (P)
Force (N)/Area (m²) = pascal (pa)
pascal (pa)
pressure is measured in a
Volume (V)
space it takes up (m³)
moles (n)
amount of gas
pressure temperature volume moles
the four gas laws are
a constant
in the ideal gas law equation (PV=nRT), R is
direct
Temperature (T) and Pressure (P) have a _________ relationship
direct
Temperature (T) and Volume (V) have a _________ relationship
inverse
Volume (V) and Pressure (P) have a _________ relationship
waves
a propagation of energy from one position to another
mechanical
_________ waves: need a medium
electromagnetic
_________ waves: don’t need a medium
gamma xray ultraviolet visible infared micro radio
order the types of electromagnetic waves from high energy to low energy
gamma xray ultraviolet visible infared micro radio
order the types of electromagnetic waves from high frequency to low frequency
gamma xray ultraviolet visible infared micro radio
order the types of electromagnetic waves from low wavelength to high wavelength
high low high
gamma has [high/low] energy, [high/low] wavelength, and [high/low] frequency
low high low
radio has [high/low] energy, [high/low] wavelength, and [high/low] frequency
transverse compressional
the two types of mechanical waves are _________ and __________
period (T)
time it takes for the wave to repeat (seconds/wave)
seconds/wave
period (T) is measured in
Frequency (f)
waves per unit time (waves/second = Hertz (Hz))
waves/second = Hertz (Hz)
Frequency (f)is measured in
meters/second
Speed (v) is measured in
Speed (v)
wavelength x frequency = wavelength/period
c
speed of light in a vacuum (3.0×10^8 m/s)
refraction
when light (or any wave) bends due to a change in media
n
index of refraction
Snell’s law
sinθ1/sinθ2 = n2/n1 = v1/v2
critical angle
angle at which 0 refraction occurs
diffraction
waves spread as they pass through an aperture or around objects
s
in the s = wavelength x D/d equation, the fringe width
d
in the s = wavelength x D/d equation, the slit distance
D
in the s = wavelength x D/d equation, the distance from slit to screen
standing
a ___________ wave has nodes and antinodes; two waves that are exactly the same travel in opposite directions
travelling
a ___________ wave has a consistent amplitude and goes to infinity
antiphase
exact opposite wave = π
π
quantity of antiphase