a&p lab 3
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
epithelial & connective tissues, integumentary system
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
epithelial tissue types
simple: squamos, cuboidal, coloumnar
stratified: squamos
pseudostratified coloumnar
transitional epithelium
connective tissue types
CT proper loose : areolar, adipose, reticular
CT proper dense : regular, irregular, elastic
cartilage : hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
bone
blood
exocrine glands
have ducts
secrete onto epithelial surfaces
secretions are non hormonal (mostly h2o or proteins)
ex : salivary, eccrine, lacrimal, pancreas
endocrine glands
NO ducts
secrete into extracellular space ; bloodstream
secretions: hormones
ex : adrenal, thyroid, ovaries, testes, pancreas
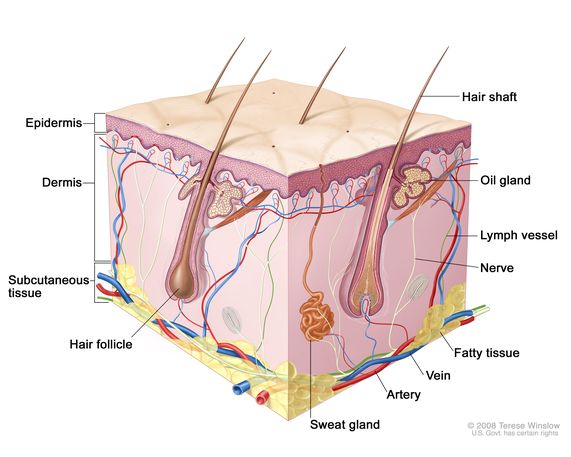
epidermis
4-5 layers of eithelium
body’s protective outer layer
surface epithelum of skin
- above the dermis
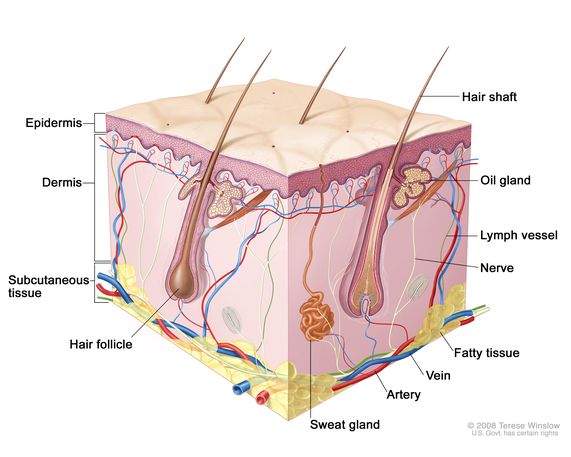
dermis (contains papillary and reticular layer)
meaty layer of skin, supports epidermis, contains nerve endings, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, hair follicles, and blood vessels
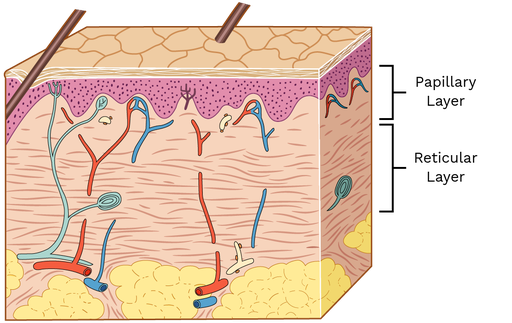
papillary layer (dermis)
top dermis layer
wavy bottom
made of areolar C.T proper
functions in temp regulation, sensory, provides nutrients to epidermis, increases surface layer
contains collagen, fibers, and blood vessels
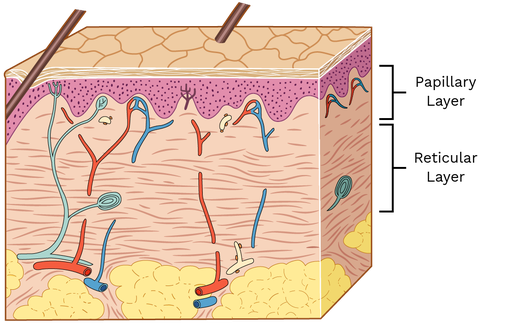
reticular layer (dermis)
bottom dermis layer
made of dense irregular connective tissue proper
functions in providing structure & elasticity to skin
contains collagen, elastin fibers, blood vessels, nerve endings, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands
hypodermis
not part of skin
below dermis
made of adipose (fatty) tissue
functions in storing energy, cussioning and protecting, insulating body
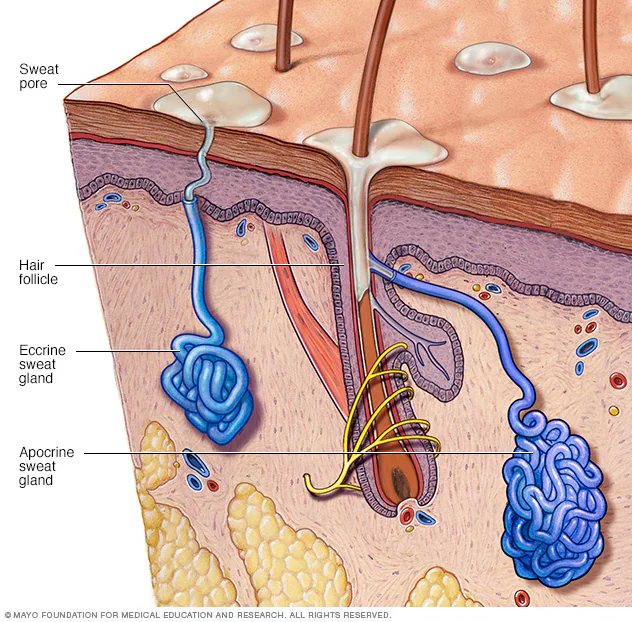
eccrine sweat gland
exocrine glands
secretes water based products
functions in temp regulation
structure: coiled ball with a pore on the
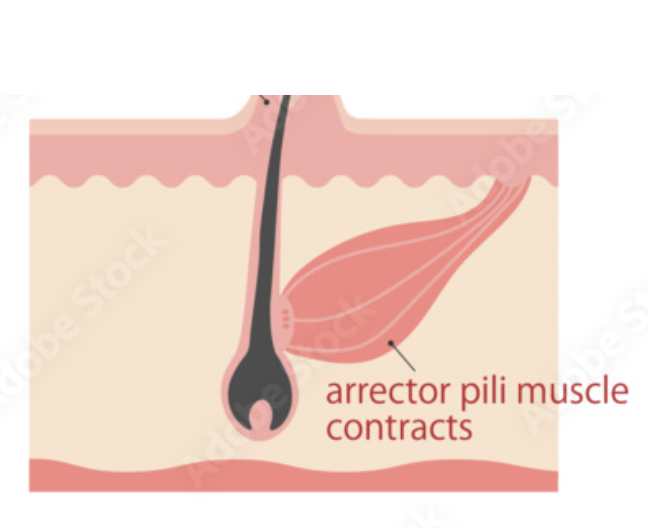
arrector pili muscle
connects hair follicle to dermis, making hair stand on end
functions in thermoregulation and sensory responses
structure: muscle attached to hair follicle
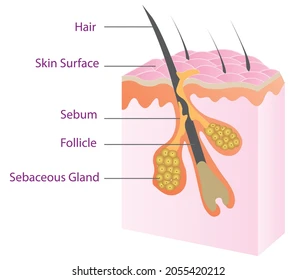
sebaceous (oil) glands
functions in secreting sebum onto skin
structure: wart looking thingies attached to hair follicles
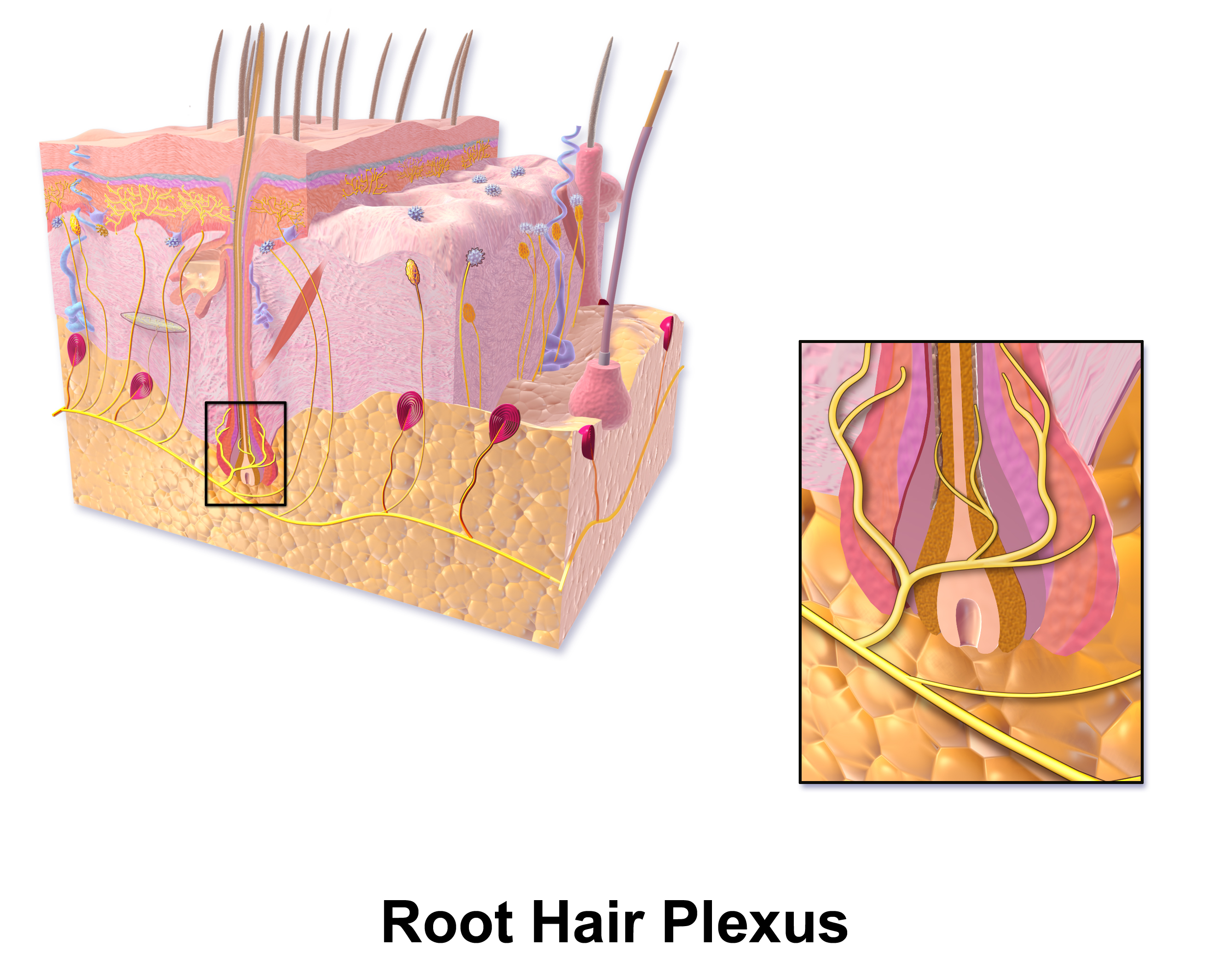
root hair plexus
attached to bottom of hair follicle
functions in sensory reception - determines if somethings touching hair
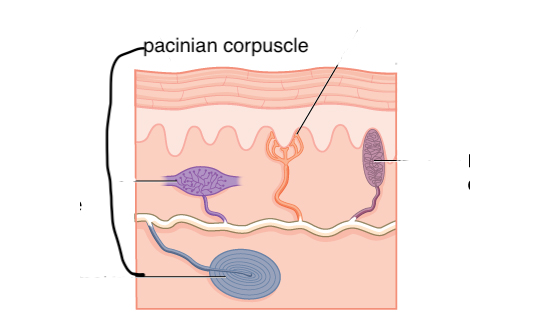
pacinian (laminar) corpuscle
functions in sensing deep pressure stimulus
structure - spiral shaped
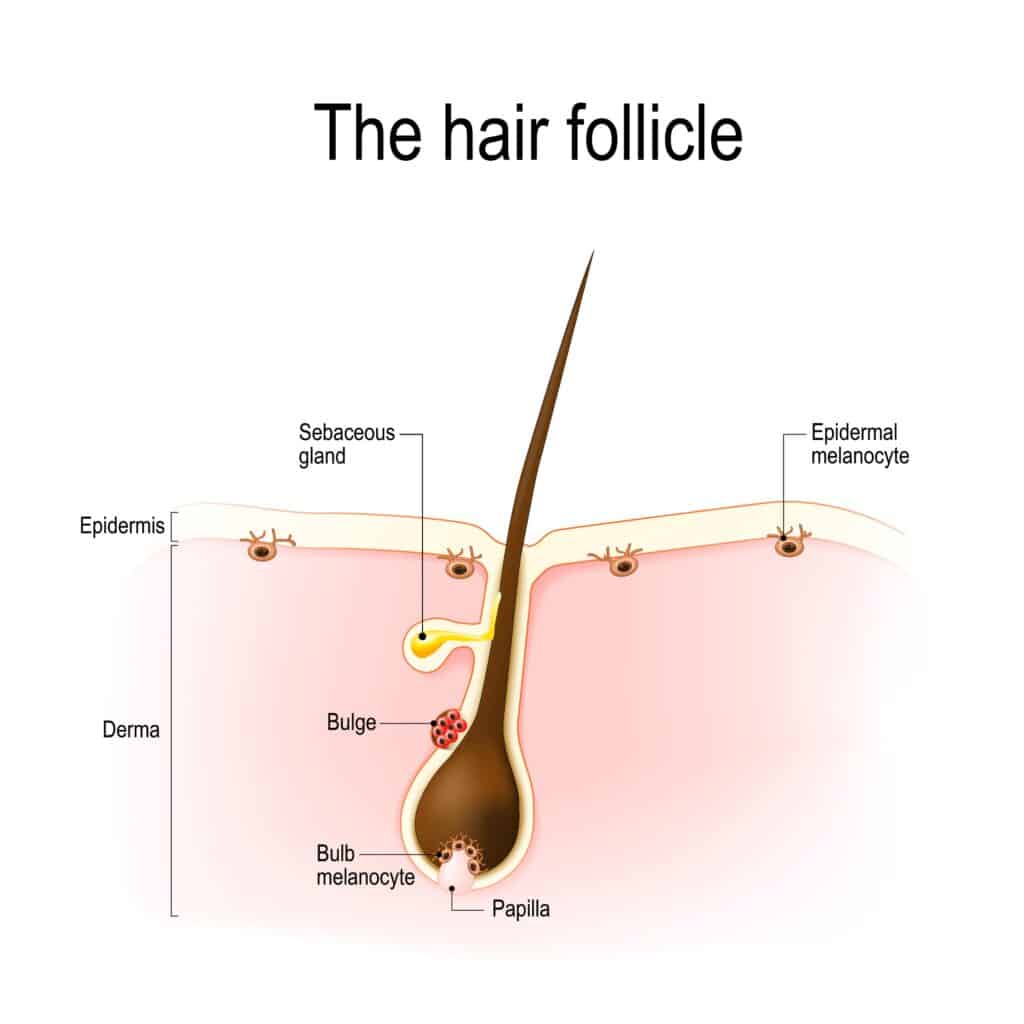
dermal papillae (papillary layer)
functions in increasing surface area between bottom of epidermis and top of dermis
more efficiently provides nutrients and oxygen and removes waste
structure - wavyness of the papillary layer
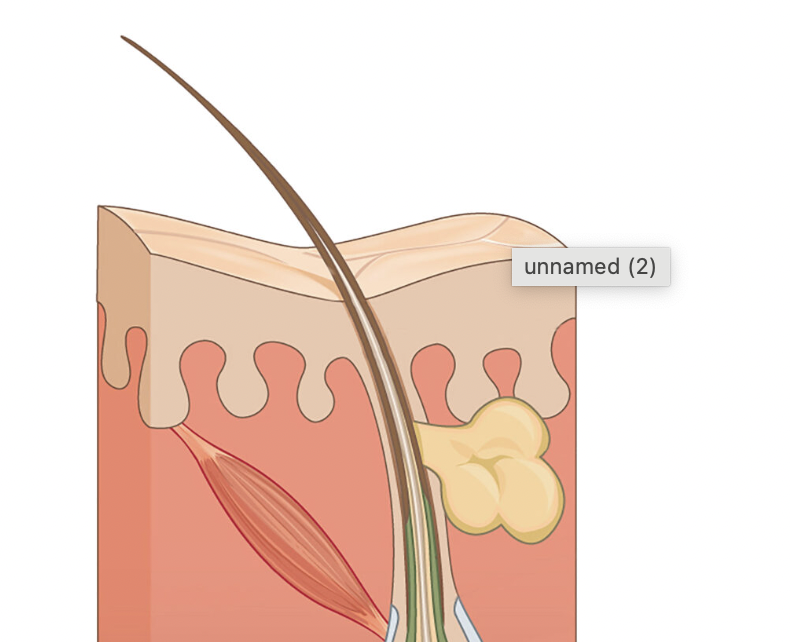
hair follicle
structure - hair strand lollll
function - grow hair and repair skin after wound
simple tissue
has one layer
stratified tissue
has multiple layers
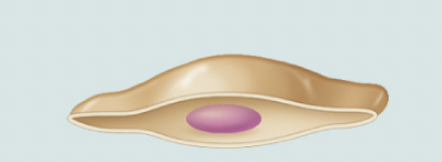
squamos
flat, oval shaped nucleus
cuboidal
cubeish shaped, round nucleus

columnar
tube shaped, oblong nucleus
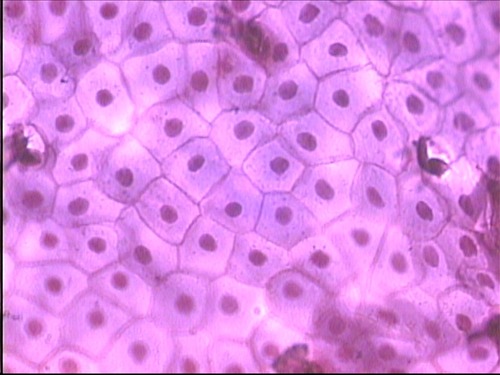
simple squamos epithelial tissue
function - allows diffusion, allows filtration, secretes lube into serosae (serous membranes)
location - lung air sacs, lining of heart, blood and lymphatic vessels, lining of ventral body cavity, kidney glomeruli
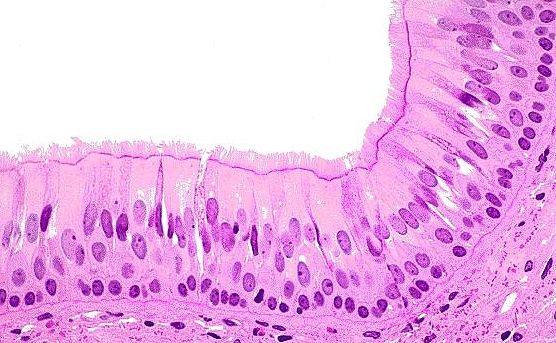
pseudostratisfied columnar epithelial tissue
looks like multiple layers of columnar but isn’t, hence “pseudo”
function - secretion and propulsion of mucus
location - nasal cavity, trachea, bronchi, parts of male reproductive system (epididymis, vas deferens, male urethra)
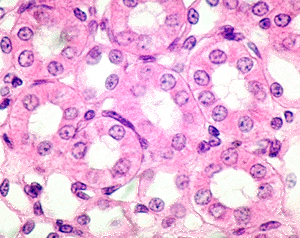
simple cuboidal epithelial tissue
function: secretion and absorption
location - kidney tubules, surface of ovaries, salivary gland ducts
simple columnar
function: absorption and secretion
location: