[13] CMSC 173 - Emotional Interaction
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Emotional Aspects
this of interaction design are concerned with how to facilitate certain states (e.g., pleasure) or avoid certain reactions (e.g., frustration) in user experiences
good feelings
Well-designed interfaces can elicit _____ in people.
Ortony et al.’s (2005) Emotional Design Model
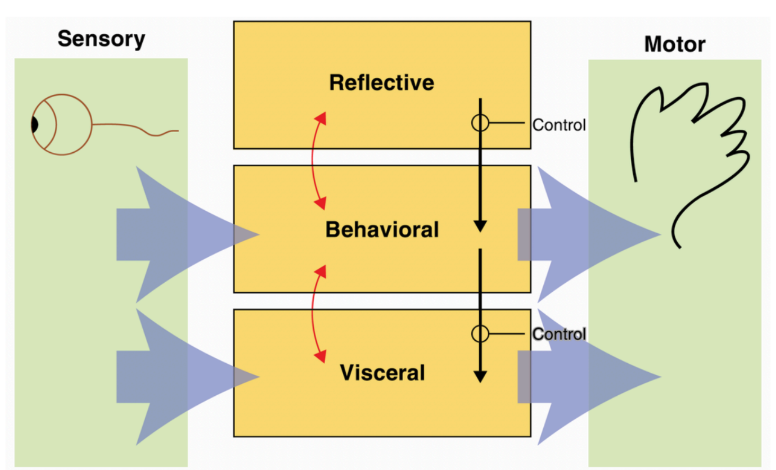
Three Levels of Ortony et al.’s (2005) Emotional Design Model
visceral
behavioral
reflective
Visceral Level
parts of the brain that are prewired to respond automatically to events happening in the physical world
Behavioral Level
the brain processes that control everyday behavior
Reflective Level
brain processes involved in contemplating
Visceral Design
refers to making products, look, feel, and sound good
Behavioral Design
about use and equates to the traditional values of usability
Reflective Design
about considering the meaning and personal value of a product in a particular culture
Plutchik’s Wheel of Emotions (1980)
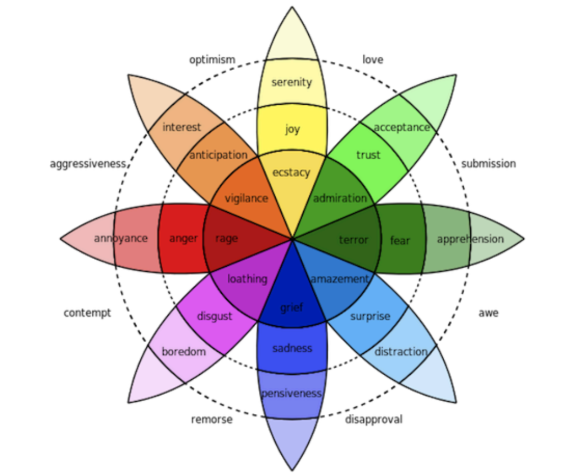
Seven Categories of Human Emotions
anger
disgust
fear
sadness
anticipation
joy
surprise + trust
intensity
Colors reflect the _____ of an emotion: the darker shade, the more intense emotion.
[Expressive Interfaces] Visual Techniques
use of emojis, sounds, colors, shapes, icons, animations, videos, photos, and virtual agents
[Expressive Interfaces] Sonifications
indicating actions and events
[Expressive Interfaces] Vibrotactile Feedback
refers to a type of haptic (touch-based) feedback where vibrations are used to communicate information or provide sensory responses to users
[Expressive Interfaces] Motivation
create an emotional connection or feeling with people
elicit certain kinds of emotional responses in people
aesthetically pleasing interfaces
_____ can be a pleasure to use.
expressive interfaces
_____ can provide reassuring feedback to users as well as be informative and fun.
badly designed interfaces
_____ often make people frustrated, annoyed, or angry.
Affective Computing
first coined by Rosalind Picard (1997)
refers to how computers can be used to recognize and express emotions in the same way as humans do
Affective Computing and Emotional AI Includes
techniques to evaluate frustration, stress, and moods by analyzing people’s expressions
designing wearable sensors to communicate emotional states
exploring how affect influences personal health
design computers and robots that responds appropriately to human emotions and exhibit empathy
AI and sensor technology
Emotional AI and affective computing use _____ for detecting people’s emotions by analyzing their facial expressions and conversations.
Persuasive Design
techniques used at the interface to draw people’s attention to certain kinds of information in an attempt to change what they do or think
Examples:
pop-up ads
warning messages
reminders
prompts
personalized messages
recommendations
Emotional Technologies
can be designed to persuade people to change their behaviors or attitudes
Anthropomorphism
the propensity people have to attribute human qualities to animals and objects
Examples:
people talk to their computers as if they were humans
treat robot cleaners as if they were pets
give cute names to their mobile devices, etc.