AP Psychology - Unit 2: Biological Basis of Behavior
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/94
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
1
New cards
nature-nurture issue
nurture works on what nature bestows
2
New cards
genes
biochemical units of heredity that make up chromosomes
3
New cards
environment
surrounds/influences your behavior
4
New cards
behavior genetics
study of relative power and limits of genetics on behavior
5
New cards
genome
biological blueprints in cell nucleus to build biological structures/processes
6
New cards
chromosomes
specific DNA structures containing genes
7
New cards
DNA
double helix molecule of genes
8
New cards
Nucleotides
A, T, C, G nucleotide structures that make up DNA
9
New cards
identical twins
monozygotic; from single fertilized egg; genetically identical
10
New cards
fraternal twins
dizygotic; different fertilized eggs; genetically different
11
New cards
molecular genetics
the study of the molecular structures and functions of genes and how they play a role on our behavior
12
New cards
heritability
how much does variance between individuals come from genetic differences
13
New cards
epigenetics
study of how the surroundings express/unexpress genes without changing DNA
14
New cards
evolutionary psychology
study of evolution of behavior of mind under the lens of natural selection
introverts are quiet and do not draw attention -> lions do not eat people they do not know exist -> introverts survive to modern day
introverts are quiet and do not draw attention -> lions do not eat people they do not know exist -> introverts survive to modern day
15
New cards
charles darwin
"on the origin of species"
16
New cards
natural selection
evolutionary process; genes passed on by those who survive to reproduce
17
New cards
mutation
random errors in gene replication that change genetic code; source of diversity
18
New cards
nucleus
contains chromosomes -> DNA -> genes -> nucleotides
19
New cards
twin studies
compare fraternal (shared womb space and living environment) and identical (share DNA) twins to study nature v nurture
20
New cards
genetically influenced traits
extro/introversion
temperament
neuroticism
divorce rate
abilities
fears
temperament
neuroticism
divorce rate
abilities
fears
21
New cards
environmentally influenced traits
values
beliefs
manners
beliefs
manners
22
New cards
predisposition
unexpressed genes with possibility of expression
23
New cards
What is the endocrine system
slower to act than the nervous system; produces hormones via glands that circulate bloodstream
24
New cards
what are the components of the endocrine system and their functions
pineal gland: secretes melatonin/sleep patterns
hypothalamus: governs via pituitary gland
pituitary gland: master gland
thyroid gland: hormones to regulate metabolism
parathyroid gland: regulate blood calcium
thymus: immune system
adrenal gland: secretes (nor)epinephrine when stressed
pancreas: regulate blood sugar
ovary: secrete estrogen
testies: secrete testosterone
hypothalamus: governs via pituitary gland
pituitary gland: master gland
thyroid gland: hormones to regulate metabolism
parathyroid gland: regulate blood calcium
thymus: immune system
adrenal gland: secretes (nor)epinephrine when stressed
pancreas: regulate blood sugar
ovary: secrete estrogen
testies: secrete testosterone
25
New cards
hormones
chemical messengers
26
New cards
HPA Axis
Hypothalamus, Pituitary gland, Adrenal gland
bodily response to stress
bodily response to stress
27
New cards
nervous system
electrochemical communication system which receives, transfers, sends info
28
New cards
CNS components
brain, spinal cord
29
New cards
PNS definition and components
sensory/motor neurons connect CNS to body
somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
30
New cards
somatic nervous system
control/voluntary muscle movement
31
New cards
autonomic nervous system function and components
autonomous
controls glands/internal organ functions
sympathetic nervous system
parasympathetic nervous system
controls glands/internal organ functions
sympathetic nervous system
parasympathetic nervous system
32
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
mobilize body for fight/flight stress
heart beat
glucose rush
heart beat
glucose rush
33
New cards
parasympathetic nervous system
calm; conserve energy; rest/digest
34
New cards
neuron
building blocks of the nervous system
35
New cards
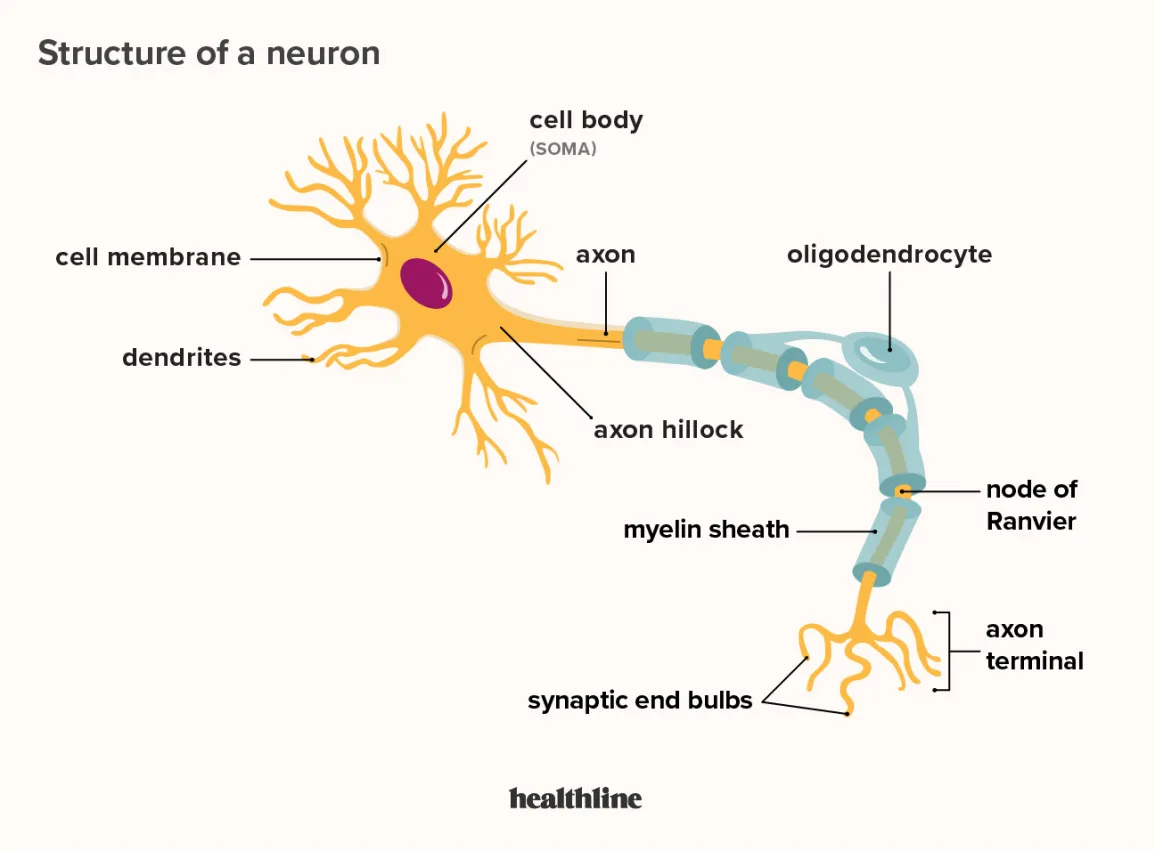
parts of the neuron
nucleus; soma; dendrites; myelin sheath; axon; axon terminal
36
New cards
function of dendrites
receives messages from other cells; covered in receptors
37
New cards
function of soma
messages build up, reach threshold, then release
38
New cards
function of axon
messages pass form soma to other neurons/muscle/glands
39
New cards
function of myelin sheath
fatty tissue insulates axon to speed up message transfer
40
New cards
function of axon terminal
forms junctions with other cells
contains vesicles to release neurotransmitters into synapse/dendrite receptors (converted from chemical to electrical signals)
contains vesicles to release neurotransmitters into synapse/dendrite receptors (converted from chemical to electrical signals)
41
New cards
Afferent neurons
detect stimuli, carry info to CNS
42
New cards
Efferent neurons
carry info out of CNS to muscles
43
New cards
Interneurons
connect sensory/motor neurons in CNS
44
New cards
reflex neurons
skips CNS and directly connects efferent and afferent neurons
45
New cards
Describe the transmission of neural signals
resting potential: waiting, no incoming signal, - inside/ + outside
info build
reaching threshold: enough messages received
action potential: sends electrical charge along axon, depolarizes + inside/ - outside, neurotransmitters released into the synapse and bind to receptors of post-synaptic neuron
refractory period: brief period it can't fire impulse, reestablish resting potential conditions
info build
reaching threshold: enough messages received
action potential: sends electrical charge along axon, depolarizes + inside/ - outside, neurotransmitters released into the synapse and bind to receptors of post-synaptic neuron
refractory period: brief period it can't fire impulse, reestablish resting potential conditions
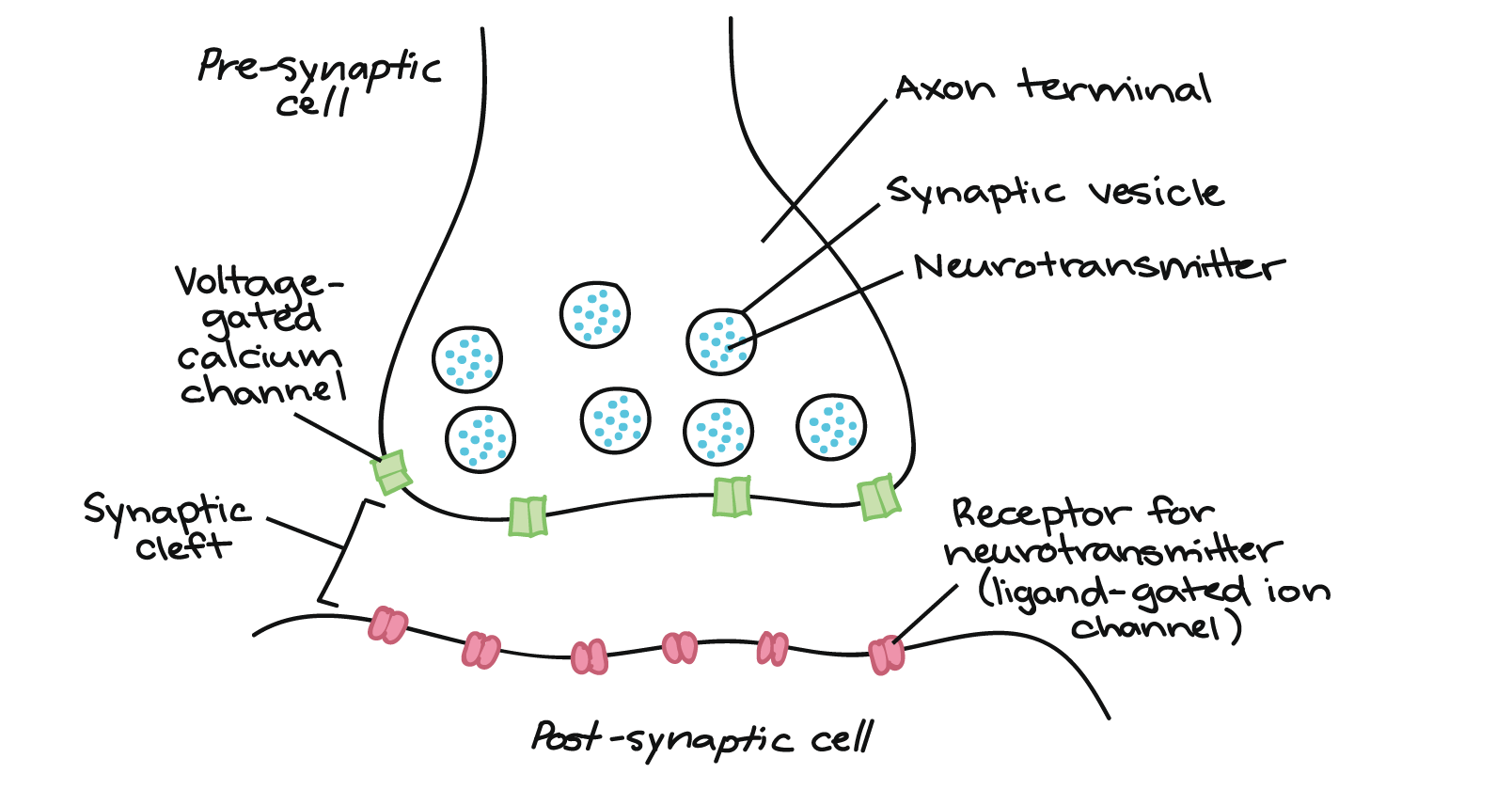
46
New cards
All or Nothing response
neuron either fires full force, or does not
47
New cards
reuptake
the reabsorption by a neuron of a neurotransmitter following the transmission of a nerve impulse across a synapse
eg: axon terminal releases dopamine, it binds to receptors, is released and returns to pre-synaptic axon terminal
eg: axon terminal releases dopamine, it binds to receptors, is released and returns to pre-synaptic axon terminal
48
New cards
acetylcholine ACh
In the somatic nervous system
muscle action
learning
memory
less ACh in those with alzheimer's
muscle action
learning
memory
less ACh in those with alzheimer's
49
New cards
Dopamine
learning
attention, emotion
excess associated with schizophrenia
attention, emotion
excess associated with schizophrenia
50
New cards
Serotonin
hunger
sleep
arousal
mood
low levels associated with depression
sleep
arousal
mood
low levels associated with depression
51
New cards
Norepinephrine
arousal and vigilance
52
New cards
GABA
inhibits action potential
anxiety
intoxication
anxiety
intoxication
53
New cards
Endorphins
pain reduction
reward
reward
54
New cards
Types of neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, BAGA, endorphins
55
New cards
agonist
mimic neurotransmitters, tricks synapse into thinking receptors are filled, boosts effects of neurotransmitters
56
New cards
antagonist
blocks neurotransmitters from binding with receptors
57
New cards
What is the function of the brainstem and what are its components?
automatic survival functions (breathing, swallowing, vomiting)
Medulla
Pons
Thalamus
Reticular Formation
Cerebellum
Medulla
Pons
Thalamus
Reticular Formation
Cerebellum
58
New cards
Medulla
survival functions, death if damaged, heartbeat
59
New cards
Pons
regulates wakefulness/sleep
60
New cards
reticular formation
arousal and nerve network, coma if damaged
61
New cards
Thalamus
sensory switchboard except smell
smell triggers memory
distributes sensory info
smell triggers memory
distributes sensory info
62
New cards
cerebellum
coordinates voluntary movement and balance, muscle memory
63
New cards
Limbic system function and components
emotions
Amygdala, Hypothalamus, Hippocampus
Amygdala, Hypothalamus, Hippocampus
64
New cards
Amygdala
processes emotions, anger, fear, aggression
65
New cards
Hippocampus
attach memories to emotions, processes memories
66
New cards
Hypothalamus
maintenance activity, governs endocrine system via pituitary gland
67
New cards
cerebral cortex and components
information processing, connected to limbic system to reason and emotions factor into decisions
frontal lobe
parietal lobe
motor cortex
somatosensory cortex
occipital lobe
temporal lobe
frontal lobe
parietal lobe
motor cortex
somatosensory cortex
occipital lobe
temporal lobe
68
New cards
Frontal Lobe
planning/judgement, includes motor cortex
69
New cards
Parietal Lobe
sensory information
70
New cards
Motor Cortex
voluntary movement and intricate movement
71
New cards
Somatosensory cortex
processing body sensations/touch
72
New cards
occipital lobe
primary visual processing center
73
New cards
temporal lobe
auditory processing lobe
74
New cards
Glial cells
guides neural connections, provides insulating myelin and cleans up ions/neurotransmitters
75
New cards
Association areas
integrate information for higher mental function;
associate senses with memories
associate senses with memories
76
New cards
Plasticity
ability to change/reorganize pathways after damage
77
New cards
Neurogenesis
formation of new neurons
78
New cards
Broca's area
left frontal lobe; directs muscle movement in speech and expressive language
79
New cards
Wernicke's area
left temporal lobe; language comprehension and receptive language
80
New cards
Lesion
brain tissue destruction to study animal behavior afterwards
81
New cards
What are structure scans? What are some examples?
brain anatomy
CT: x-ray photographs at different angles integrated into single slice image
MRI: magnetic field and radio waves to create computer generated image to distinguish soft tissue AND anatomy
CT: x-ray photographs at different angles integrated into single slice image
MRI: magnetic field and radio waves to create computer generated image to distinguish soft tissue AND anatomy
82
New cards
What are function scans? What are some examples?
brain activity/functionality
PET: visual display of brain activity via radioactive glucose in bloodstream
EEG: recording of brain waves from eclectic activity (action potentials) that sweeps brain surface
fMRI: identifies brain region engaged during performance of specific activities
PET: visual display of brain activity via radioactive glucose in bloodstream
EEG: recording of brain waves from eclectic activity (action potentials) that sweeps brain surface
fMRI: identifies brain region engaged during performance of specific activities
83
New cards
Psychoactive Drug
chemical alters perception/mood via stimulating/mimicking/inhibiting neurotransmitters
84
New cards
Tolerance/ Neuroadaptation
reduced drug effect from regular use as brain produces less to compensate for artificially induced amount
85
New cards
addiction
compulsive craving despite consequences
86
New cards
withdrawal
discomfort following discont. of drug
87
New cards
physical vs psychological dependence
physical: physical withdrawal symptoms due to change in bodily functions
psych: dependence to relieve negative emotions
psych: dependence to relieve negative emotions
88
New cards
Define depressants and provide examples
slows neural activity and bodily functions
alcohol: lower self awareness and guilt; inhibitant agonist and glutamate antagonist
barbiturates: lower anxiety and slower CNS
Opiates/heroin: less endorphins; agonist for inhabitants and dopamine
alcohol: lower self awareness and guilt; inhibitant agonist and glutamate antagonist
barbiturates: lower anxiety and slower CNS
Opiates/heroin: less endorphins; agonist for inhabitants and dopamine
89
New cards
Define stimulants and provide examples
excites bodily functions
cocaine: blocks reuptake of dopamine; dopamine antagonist
ecstasy: triggers release of dopamine/serotonin, blocks reuptake; agonist for serotonin and dopamine
meth: more energy and neural activity; dopamine agonist
cocaine: blocks reuptake of dopamine; dopamine antagonist
ecstasy: triggers release of dopamine/serotonin, blocks reuptake; agonist for serotonin and dopamine
meth: more energy and neural activity; dopamine agonist
90
New cards
Define hallucinogens and provide examples
distort perception, evokes sensations in absence of stimuli
LSD: powerful hallucinations; serotonin agonist
Marijuana: mild hallucinogen, distortion of time; antagonist for inhibitants and dopamine
LSD: powerful hallucinations; serotonin agonist
Marijuana: mild hallucinogen, distortion of time; antagonist for inhibitants and dopamine
91
New cards
corpus callosum
large band of neural fibers connecting brain hemispheres
92
New cards
laterlization
specialization of right/left cerebral hemispheres
93
New cards
left hemisphere responsibilities
controls right hand/side
speech
writing
reading
math
logic
analysis
details
speech
writing
reading
math
logic
analysis
details
94
New cards
right hemisphere responsibilities
left side
non verbal
visual-spacial perception
music/art
emotional thought
big picture
facial recognition
non verbal
visual-spacial perception
music/art
emotional thought
big picture
facial recognition
95
New cards
Split Brain procedure
isolates hemispheres by cutting corpus callosum, done to those with severe epileptic seizures