A&P 2 Lab Practical Studying
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ECG, Heart, & Respiratory System.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What is the heart muscle called?
Myocardium
What is the function of the SA (sinoatrial node)?
The SA node, also called the Pacemaker, generates an electrical signal that causes the atria to contract. This contraction pushes blood into the ventricles.
What is the function of the AV (atrioventricular) node?
The AV delays contraction of the ventricles until they have filled with blood completely.
What is the function of the Bundle of His?
The Bundle of His transmits the messages from the AV node to the ventricles.
What is the function of the Purkinje fibers?
The Purkinje fibers also aid in transmitting the message from the AV node.Upon this, the ventricles contract and blood exits the heart (either to the lungs or to the aorta and the body).
What are the four valves of the heart?
2 AV and 2 SL valves: Tricuspid Atrioventricular valve (right), bicuspid (or mitral) atrioventricular valve (left), pulmonary semilunar valve (right), and aortic semilunar valve (left)
What causes the “Lub-Dub” sound of the heart?
The Lub is the contraction of the ventricles and the AV valves closing, the Dub is the closing of the SL valves.
How do you estimate maximal heart rate?
220-age (in years)
How do you get lower level (60% of you maximum HR)?
Maximum (MHR) times .60
How do you get upper level (85% of you maximum HR)?
MHR times .85
How do you get your target HR when exercising?
Average of upper and lower HR
What is the function of the auricles?
blood reservoir
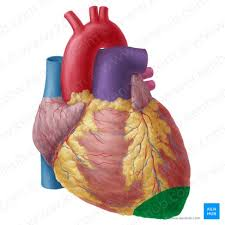
What is highlighted in green?
The apex of the heart
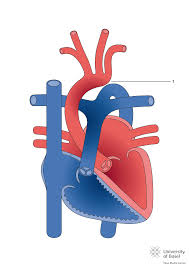
What is numbered?
The aortic trunk
What part is highlighted in green?
The aorta.
How do you get HR with ECG values
60 over R-R
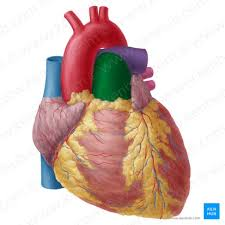
What is highlighted in green?
Pulmonary Trunk
What is the function of the pulmonary trunk?
Carry oxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
What is the function of the aorta?
Bring oxygenated blood from the left ventricle out to the body.
What is the function of the atria?
Pump blood into the ventricles
What is the function of the ventricles?
Pump blood out of the heart either to the lungs or to the body.
What is the function of the semilunar valves?
control blood flow from ventricles into the body, prevent backflow.
What is the function of the AV valves?
Control blood flow between atria and ventricles.
How much is lower level HR?
60% of maximum.
How much is upper level HR?
85% of maximum
What is the function of chordae tendineae?
Open and close the AV valves.
What is the function of the papillary muscles?
move and pull the chordiae tendinae.
What is the function of the septum?
Separate the right and left halves.
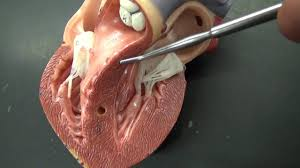
What are they pointing at?
Septum

What is #12
The left ventricle
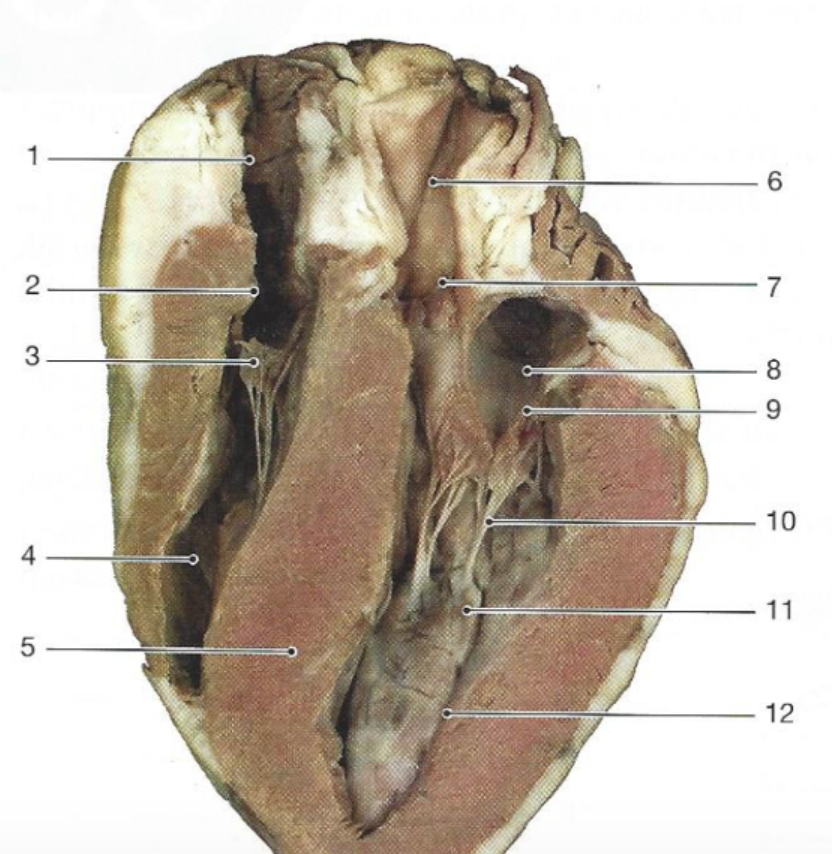
What is #8
The left atrium
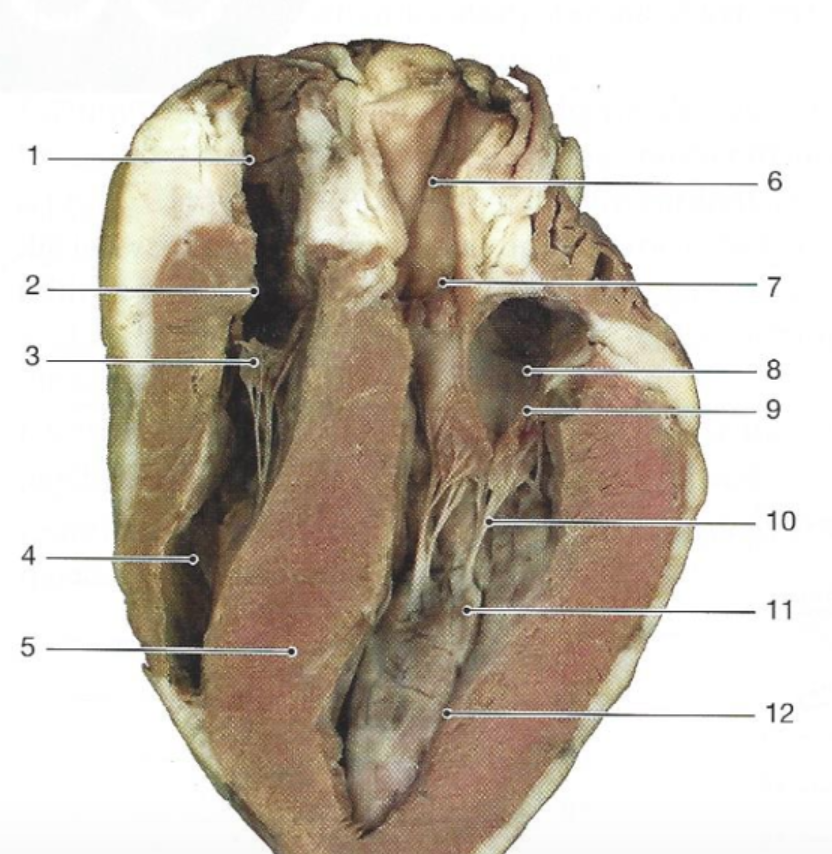
What is #4
The right ventricle
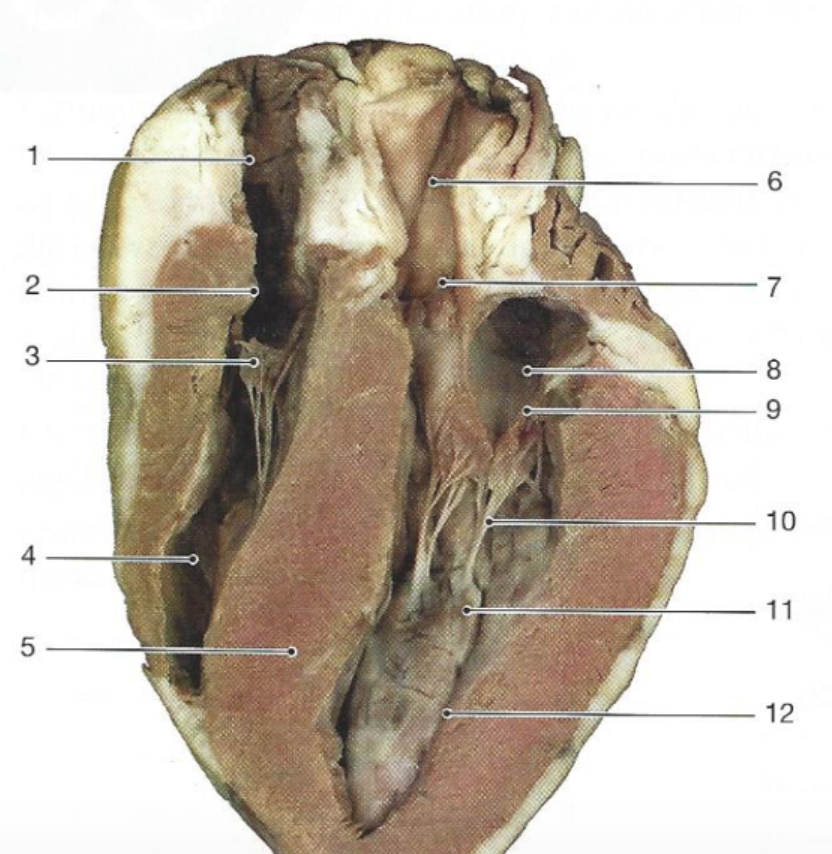
What is #2?
The right atrium

What is #10
Chordae tendonae
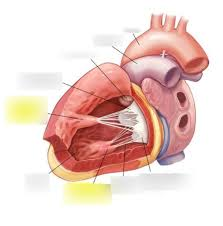
What is the highlighted pointing to?
The papillary muscles
What is produced in the liver?
Bile
Where is bile stored?
Gall Bladder
What is the function of bile
Emulsifies lipids (fats)
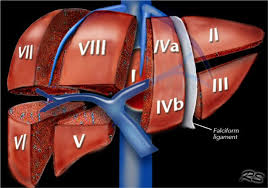
What organ is this? What blood vessel is shown?
Liver, with the SVC and renal veins visable

What organ is this?
The gallbladder
What kind of digestion occurs in the mouth?
Mechanical (teeth and tongue) and chemical (salivary amalyse)
What kind of digestion occurs in the stomach?
Mechanical (muscles) and chemical (HCl, gastrin, enzymes, intrinsic factor)
What does salivary amylase break down?
It breaks polysaccharides down into disaccharides (the beginning of carbohydrate digestion)
What are the three salivary glands?
The sublingual, parotid, and sub-mandibular glands
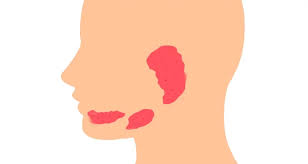
What is the largest posterior most gland?
Parotid
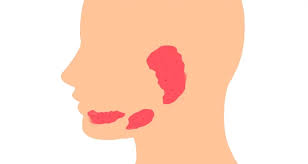
What is the inferior most gland?
Submandibular gland
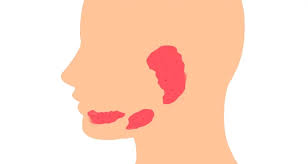
What is the anterior most gland?
Sublingual, below the tongue

What is #1
P wave
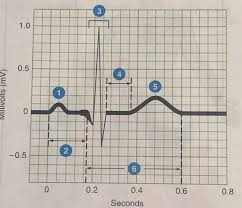
What is #6
The QRS complex
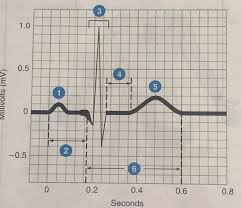
What is #5
T wave
What is the T to P wave?
The period of time the entire heart is in diastole- the heart cannot beat during this time.

What is highlighted in green
The superior vena cava
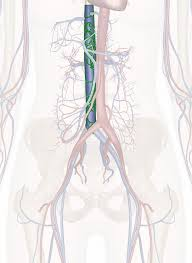
What vessel is highlighted here?
The IVC
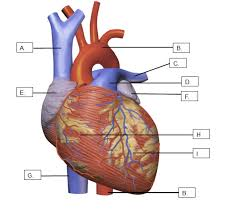
What is G?
The inferior Vena cava
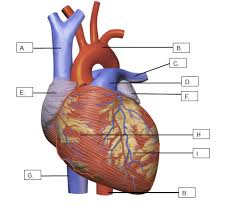
What is B?
The aorta
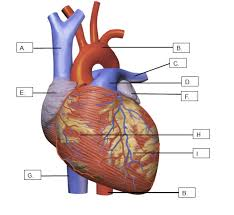
That are E and F?
The auricles
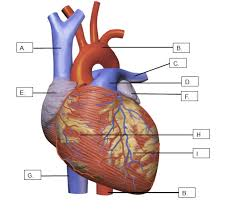
What is C?
The pulmonary artery
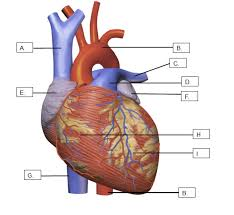
What is J
The descending aorta
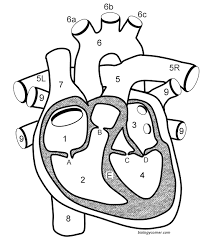
What is A?
The tricuspid valve
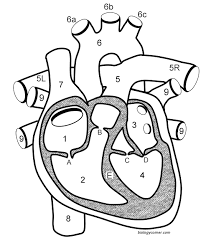
What is C?
The aortic semilunar valve
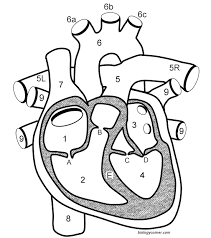
What is D?
The bicuspid/mitral valve
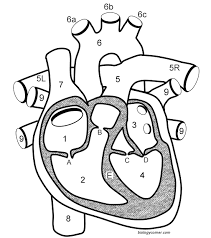
What is B?
The pulmonary semilunar valve
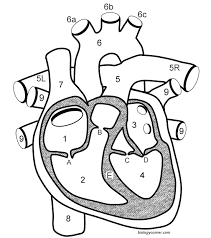
What are 9?
The pulmonary vein(s)
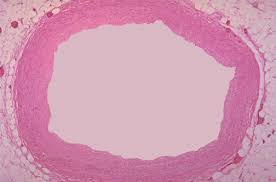
Is this a vein or an artery? Why?
An artery, it is thick walled and round around the lumen.
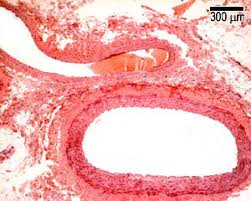
Is the superior a vein or an artery? Why?
A vein, it is thin walled and irregularly shaped.
What are the three arterial layers, in to out?
Tunica interna, tunica media, tunica externia/adventitia