P3 : Particle model of matter
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What does the particle model of matter state?
Everything is made up of tiny particles
What are the 3 states of matter?
Solid, liquid, gas
Describe the properties of solids (3)
Strong forces of attraction hold particles together in a fixed regular arrangement
Particles don’t have much energy so they can only vibrate
Have high densities

Describe the properties of liquids (4)
Weaker forces of attraction between particles
Particles are close together but can move past each other and form irregular arrangements
Have more energy than solids + move in random directions at low speeds
Less dense than solids
Describe the properties of gases (4)
Basically no forces of attraction between particles
Particles have more energy than solids and liquids
Particles are free to move + travel in random directions at high speeds
Have low densities
What is density? (easy definition)
How ‘compact’ a substance is
What is density? (hard definition)
The mass for a given volume
What is the equation for density?
ρ = m/v
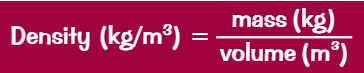
Explain how to find the density of a regular solid (cube) (3)
Use a top pan balance to measure the mass of the solid
Then measure the length, width and height of the solid and times them together to find the volume of the solid
Then use m/v to work out the density
Explain how to find the density of an irregular solid (6)
Use a top pan balance to measure the mass of the irregular solid
Get a displacement can and full it with water until it is level with the pipe
Place a measuring cylinder under the pipe
Place the object into the displacement can and wait until the displaced water has been transferred into the measuring cylinder
The displaced water is equal to the volume of the irregular object
Then use m/v to work out density
Explain how to find the density of a liquid (4)
Place a measuring cylinder onto a top pan balance and zero the balance (to reset it)
Then pour 10ml (10cm3) of liquid into the measuring cylinder
Then record the mass of 10ml of liquid
Then use m/v to find the density
What is internal energy?
The total kinetic and potential energy of all the particles that make up a system
Is the change of state a physical or chemical change?
Physical
Why do state changes happen?
Because particles gain or lose energy in their bonds
When a state changes what is conserved?
Mass
When a substance is heated what is increased? (2)
Temperature
Energy of particles
Solid → Liquid?
Melting
Solid → Gas?
Sublimation
Liquid → Gas?
Boiling or evaporating
Liquid → Solid?
Freezing
Gas → Liquid?
Condensing
What happens to the temperature when a substance changes state + why?
Stays constant because instead of energy being used for increasing temperature, it is now used to break forces of attraction between particles
What is specific latent heat?
The amount of energy needed to change the state of 1kg of substance with no change in temperature
What are the 2 types of specific latent heat?
Fusion
Vaporisation
What is the definition of specific latent heat of fusion?
The amount of energy needed to change of 1kg of substance from a solid to a liquid with no change in temperature
What is the definition of specific latent heat of vaporisation?
The amount of energy needed to change 1kg of substance from a liquid to a gas with no change in temperature
What is the equation for specific latent heat?
E = m x L
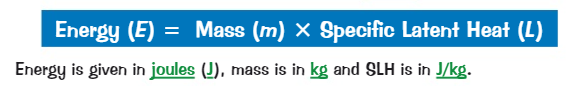
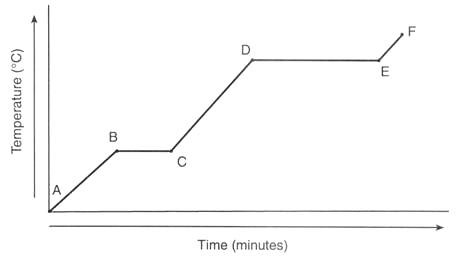
Explain what is happening at each stage (mention specific latent heat)
A → B = Temperature increase ∼ Solid
B → C = Temperature constant ∼ Solid → Liquid (specific latent heat of fusion)
C → D = Temperature increase ∼ Liquid
D → E = Temperature constant ∼ Liquid → Gas (specific latent heat of vaporisation
E → F = Temperature increase ∼ Gas
What is gas pressure caused by?
The particles colliding with the walls of the container (at right angles) apply a force to the walls of a container causing gas pressure
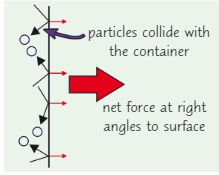
What do particles exert when they collide into something?
A force → pressure
How would an increase in pressure be achieved? (2)
Increase in number of collisions per second
Increased number of energy of each collision
At low temperatures what pressure does a gas have + why + what does this lead to?
Low because the particles have less kinetic energy which leads to fewer collisions per second which lowers pressure
At high temperatures what pressure does a gas have + why + what does this lead to?
High because the particles have more kinetic energy which leads to more collisions per second which increases pressure
What happens to pressure of a gas if the temperature increases but the volume is constant + why?
Pressure will increase because the particles will gain more energy which will lead to more successful collisions per second, leading to an increased in pressure
What will happen to the pressure of a gas if the temperature is constant but the volume increases + why?
The pressure will decrease because the volume will increase and the particles will be more spread out, leading to less collisions, and a decrease in pressure
What is the relationship between pressure and volume?
Inversely proportional
(volume increases, pressure decreases)
What is the equation for a fixed mass held at a constant temperature?
pV = constant
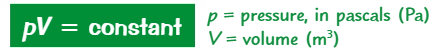
What happens when work is done on a gas?
Energy is transferred to the gas particles → increase in the internal energy (kinetic + potential energy) → increase in temperature