Corso- quiz answers
1/43
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Match the structure to what kind of bonding they have:
______ holds secondary structure together
______ holds tertiary and quaternary structures together
______ holds primary structure together
options: hydrogen bonds, peptide bonds, hydrophobic forces+ionic forces+crosslinks+hydrogen bonding
hydrogen bonding holds secondary structure together
hydrophobic forces+ionic forces+crosslinks+hydrogen bonding holds tertiary and quaternary structures together
peptide bonds holds primary structure together
Which two functional groups form a peptide bond?
carboxylic acid (carboxylate) group of an AA
amine group of an AA
The alpha helix is what level of organization?
a. primary
b. secondary
c. tertiary
d. quaternary
b
Which bond has the least rotation in the protein (peptide) repeating sequence?
a. psy
b. peptide bond
c. phi
b
What is the primary structure?
a. Alpha helix and beta sheet
b. Amino Acid Sequence
c. Protein Assembly
d. Protein folding
b
What is the secondary structure?
a. Alpha helix and beta sheet
b. Amino Acid Sequence
c. Protein Assembly
d. Protein folding
a
For each of the following match the description to their protein organization:
The sequence of Amino Acids
alpha helix, beta sheet, beta bend, random coil
Folding
Assembly of multiple subunits
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
A peptide bond is which type of bond?
a. ionic
b. covalent
c. hydrogen
b
Which binds to hemoglobin stronger?
a. oxygen
b. carbon monoxide
b
Match the description with the type of subunit of hemoglobin:
found in both fetal and adult hemoglobin
found in embryonic hemoglobin E in place of beta’s found in adult
found in adult HbA1
found in embroyonic hemoglobin E in place of alpha’s found in adult
found in fetal HbF
found in adult HbA2
answer options: alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon, zeta
alpha
epsilon
beta
zeta
gamma
delta
What is cooperativity?
a. For proteins with multiple subunits, this is the in between conformations when there are more than one conformation found at the same time.
b. For proteins with multiple subunits, the subunits need to be in the same conformation as the ones next to them.
b
Which conformation of hemoglobin binds oxygen?
a. R
b. T
a
How many subunits are in hemoglobin?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
d
Match the subunits of hemoglobin to their type:
___________ zeta-2, epsilon-2
___________ alpha-2, gamma-2
___________ alpha-2, beta-2
___________alpha-2, delta-2
embryonic hemoglobin
fetal hemoglobin
adult hemoglobin/ HbA1
HbA2
What is the function of the heme group?
a. To hold on to the iron atom.
b. To hold the hemoglobin tetramer together.
c. To crosslink hemoglobin subunits to each other.
a
What is the Bohr effect?
a. As pH increases, oxygen binding increases
b. As pH increases, oxygen binding decreases
c. As pH decreases, oxygen binding increases
a
As the concentration of BPG increases:
a. hemoglobin releases oxygen.
b. hemoglobin binds oxygen tighter.
a
BPG stabilizes which form of hemoglobin?
a. The deoxygenated state
b. The oxygenated state
a
Describe the correlation between Sickle Cell & other hemoglobinopathies, and Malaria.
a. Resistance to malaria is common for other hemoglobinopathies as well.
b. Only sickle cell disease give resistance to malaria.
a
A patient is diagnosed with liver failure and has yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes. There are many biochemical pathways in the liver that are now impaired, but which specific biochemical pathway impairment brings this specific symptom?
a. A defect in heme synthesis
b. Failure to convert bilirubin to urobilinogen
c. A defect in the conversion of biliverdin to bilirubin
d. A defect in the glucuronidation of bilirubin
e. Failure to convert urobilinogen to stercobilin
d
What changes occur in the solubility of Hemoglobin in sickle cell anemia?
a. The hemoglobin S has an increased solubility compared to hemoglobin A.
b. The hemoglobin S precipitates inside the cell.
b
Which hemogobin elevates the most for a patient with (homozygous) Sickle Cell Disease?
a. HbC
b. HbA1
c. HbF
d. HbA2
c
Rank the following hemoglobins with highest affinity first and the lowest affinity last:
HbS, HbA2, HbA1, HbF, Myoglobin
myoglobin
HbF
HbA2
HbA1
HbS
What changes occur in the physical shape of Hemoglobin in sickle cell anemia?
a. The RBC inflates to a ball shape.
b. The RBC elongates in to a sickle shape.
b
What is the molecular cause of sickle cell disease?
a. Alpha 92 Arg --> Leu
b. Beta 6 Glu-->Val
c. Beta 6 Glu-->Lys
d. Beta 143 His --> Pro
b
A patient is diagnosed with acute intermittent porphyria. This defect would cause which of the following?
a. Jaundice
b. Hemoglobin that binds oxygen too tightly
c. Acidosis
d. Decreased production of Hemoglobin
e. Black spots on the whites of the eyes
d
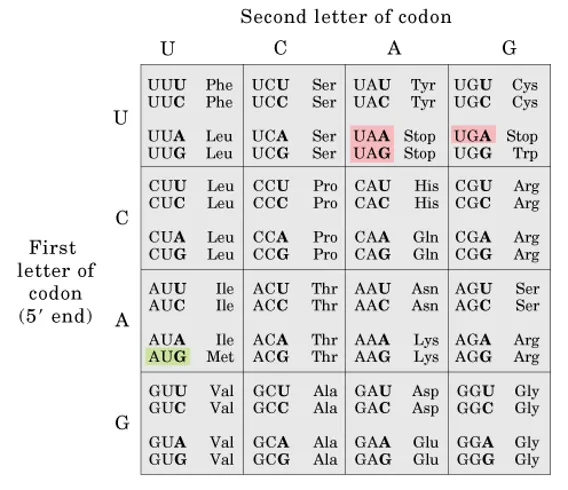
Match up each codon change to the type of mutation it would cause:
AAA to AAAA
UCU to UCC
UAG to UAC
GAG to GUG
insertion frameshift nonsense mutation
silent mutation
run-on nonsense mutation
non-conservative missense mutation
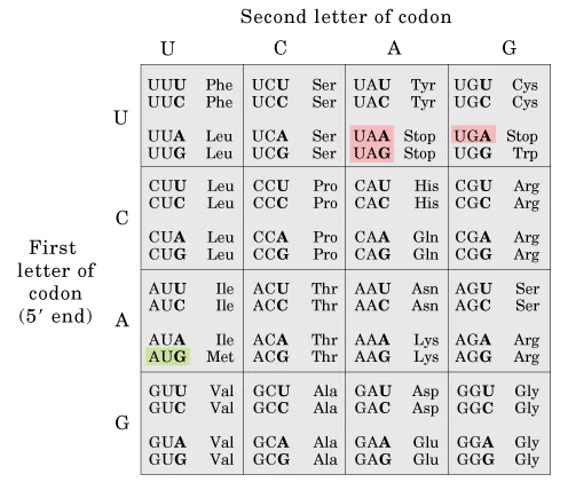
Match up each codon change to the type of mutation it would cause:
UGG to UGA
CCA to CA
CUC to AUC
early termination
deletion frameshift nonsense mutation
conservative missence mutation
A defect of the enzyme Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase most commonly causes
a. hyperglycemia
b. hemolytic anemia
c. enlarged liver
d. hypoglycemia
b
What is hemolytic anemia?
a. Red Blood Cells breaking open.
b. A substitution mutation in hemoglobin beta-chain
c. An early termination muation in the hemoglobin beta-chain
d. Not enough Red Blood Cells being made in the bone marrow.
a
What is the most concerning damage to the RBC, caused by hydroxyl radicals?
a. Lipid membrane damage
b. Mitochondrial damage
c. DNA damage
d. Damage to hemoglobin
a
If a patient has G6PDD, which of the following would be most helpful? Think about this, this is not a memorization question.
a. taking the drug primaquine
b. antioxidant vitamins
c. breathing 100% oxygen
d. fava beans
e. drinking alcohol
b
What medical conditions are associated with a folate deficiency? Select all that apply
a. night blindness
b. megaloblastic anemia
c. kidney stones
d. ketoacidosis
e. spina bifida
b, e
What are the products of the non-oxidative phase of PPP that return to glycolysis?
a. glucose-6-phosphate
b. glucose
c. fructose-6-phosphate
d. glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
e. dihydroxyacetone phosphate
f. Pyruvate
c. d
What is the most common genetic cause of hemolytic anemia?
a. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
b. The inability to absorb B-12
c. An early termination mutation at possition 17 of the beta-chain.
d. A Substitution of Valine for Glutamate in the 6th amino acid of the beta-chain.
a
Folate is used biochemically for which of the following functions?
a. phosphorylation reactions
b. carboxylation reactions
c. one-carbon transfers
d. dehydration reactions
c
What glycolysis intermediate is the starting point for the PPP?
a. glucose
b. glucose-6-phosphate
c. fructose-6-phosphate
d. glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
e. pyruvate
b
A well-nourished physician of Mediterranean heritage is suffering fatigue while doing missionary work in Africa. This physician doesn’t have a history of heavy alcohol consumption. Shortly after receiving an anti-malarial drug like Primaquine, symptoms started to appear. Lab tests indicate low RBC’s and a urine test indicates the presence of free hemoglobin. Which of the following conditions would best explain these symptoms?
a. Galactosemia
b. Beta-galactosidase deficiency
c. Aldolase B
d. Niacin deficiency
e. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
e
How do we neutralize hydrogen peroxide in red blood cells?
a. glutathione peroxidase
b. glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
c. reacting with super oxide ions
d. reacting with Fe+2
a
What is glutathoine needed for?
a. It is an oxidzing agent needed to make ATP.
b. It is a building block of a protein
c. It is needed as a component of hemoglobin
d. It is an antioxidant needed to neutralize peroxide.
d
Match the action of these drugs:
____________dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor
____________thymidylate synthase inhibitor
methotrexate, 5-Fu
When free radicals react with membrane lipids, what happens?
a. The membrane lipids are made more liquid.
b. Double bonds in the unsaturated lipids are broken, making the membrane less flexible.
c. The membranes lipids are turned into triglycerides
b
What are the most importnat Products of the pentose phosphate pathway? (pick all that apply)
a. ATP
b. NADH
c. ribose-5-phosphate
d. NADPH
e/ Glucose
c, d
A deficiency of which vitamin will inhibit the non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway?
a. Folate
b. B12
c. Riboflavin
d. B6
e. Niacin
f. Thiamine
g. Vitamin C
f