Materials
1/34
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What is plastic deformation?
An irreversible change in the shape of an object due to a compressive or tensile force - removal of the stress or force produces permanent deformation
What is elastic deformation?
A reversible change in the shape of an object due to a compressive or tensile force
If you remove the stress or force the object will return the to its original dimensions (there is no permanent strain)
What does elastic mean?
When a material will return to it's original length when the load is removed
Describe plastic behaviour
The material has a permanent change of shape when load is removed.
What is elastic behaviour?
When a material returns to original dimensions when the load is removed.
What is the elastic limit?
The value of stress or force beyond which elastic deformation becomes plastic deformation, and the material / object will no longer return to its original dimensions when the stress or force is removed
State Hooke’s law
The force applied is directly proportional to the extension of the spring given the limit of proportionality is not exceeded.
What is the force constant?
Force diveded by extension
Unit is Nm-1
It is called the constant of proportionality (k) in Hooke's law
What is the the limit of proportionality?
The value of stress or force beyond which stress is no longer directly proportional to strain or force is no longer directly proportional to extension
What is a yield point?
A point on a stress-strain graph at which the material starts to extend rapidly as stress increases.
Define ultimate tensile strength (UTS)
The maximum tensile stress that an object can withstand before it breaks
Define stiffness
The ability of an object to resist deformation
What is a polymeric material?
A material comprising of long-chain moleules (polymers) that does not obey Hooke’s law
May show large strains
Polyethene and Rubber are examples.
What does brittle mean?
When a material shows no plastic deformation before it brakes
What does ductile mean?
When the material undergoes a large plastic deformation before it breaks, so can be drawn into wires. This means the material has a large plastic region in a stress-strain graph.
Define stress
The force per unit cross sectional area, measured in pascals (Pa)
Define strain
The ratio of extension to original length.
What is the unit of strain?
Strain does not have a unit as it is a ratio.
Define young’s modulus
The ratio of tensile stress to tensile strain when these quantities are directly proportional to each other
What is the unit of young’s modulus?
Pa or Nm-2
What is the equation for young’s modulus?
E = σ/ε
Young’s modulus = tensile stress / tensile strain
What is the eqaution for tensile stress?
σ = F/A
Tensile stress = force / cross-sectional area
What is the equation for tensile strain?
ε = x/L
Tensile strain = extension / original length
What are compressive forces?
Two or more forces that act together to reduce the length or volume of an object
What is compressive deformation?
A change in the shape of an object due to compressive forces
What is compression?
The decrease in length of an object when a compressive force is exerted on it
What are tensile forces?
Equal and opposite forces acting on an object to stretch it
What is tensile deformation?
A change in the shape of an obiect due to tensile forces.
What is a hysteresis loop?
A loop-shaped plot on a stress-strain or force-extension graph.
Obtained when loading and unloading a material produce different deformations
What does the area of a hysteris loop represent on a force-extension graph?
The energy absorbed or released by the material when loaded and then unloaded
What does the area of a hysteris loop represent on a stress-strain graph?
The energy absorbed or released per unit volume
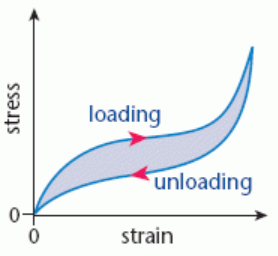
What does the area under a loading curve on a force-extension graph represent?
The energy absorbed by the object during loading
What does the area under a unloading curve on a force-extension graph represent?
The energy released by the object during unloading
What does the area under a loading curve on a stress-strain graph represent?
The energy absorbed per unit volume by the object during loading
What does the area under a unloading curve on a stress-strain graph represent?
The energy released per unit volume by the object during unloading