Chapter 10: Liquids, Solids, and Phase Changes in Chemistry
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What are dipole-dipole forces?
Attraction between molecules with dipole moments, maximizing (+) ----- (-) interactions and minimizing (+) ----- (+) and (-) ----- (-) interactions.
How strong are dipole-dipole forces compared to ionic bonds?
Dipole-dipole forces are about 1% of the strength of ionic bonds.
What is hydrogen bonding?
A special dipole-dipole attraction where hydrogen is covalently bonded to highly electronegative elements (N, O, F), resulting in a higher than normal δ+ charge.
Why are hydrogen bonds important?
They are crucial in the bonding of molecules such as water and DNA.
What are London dispersion forces?
Forces that arise from instantaneous dipoles created by random movement of electrons, existing between all molecules but are the weakest forces of attraction.
What factors influence polarizability in London dispersion forces?
Polarizability increases with the number of electrons in a molecule.
What is surface tension?
The resistance of a liquid to an increase in its surface area, which is higher with stronger intermolecular forces.
What is capillary action?
The ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces against gravity, influenced by cohesive and adhesive forces.
How does viscosity relate to intermolecular forces?
Viscosity is a measure of a liquid's resistance to flow and increases with stronger intermolecular forces and larger molecular size.
What distinguishes crystalline solids from amorphous solids?
Crystalline solids have a highly regular arrangement of components organized in a three-dimensional lattice, while amorphous solids lack orderly arrangement.
What is a unit cell in crystalline solids?
The smallest repeating unit of the lattice in crystalline solids.
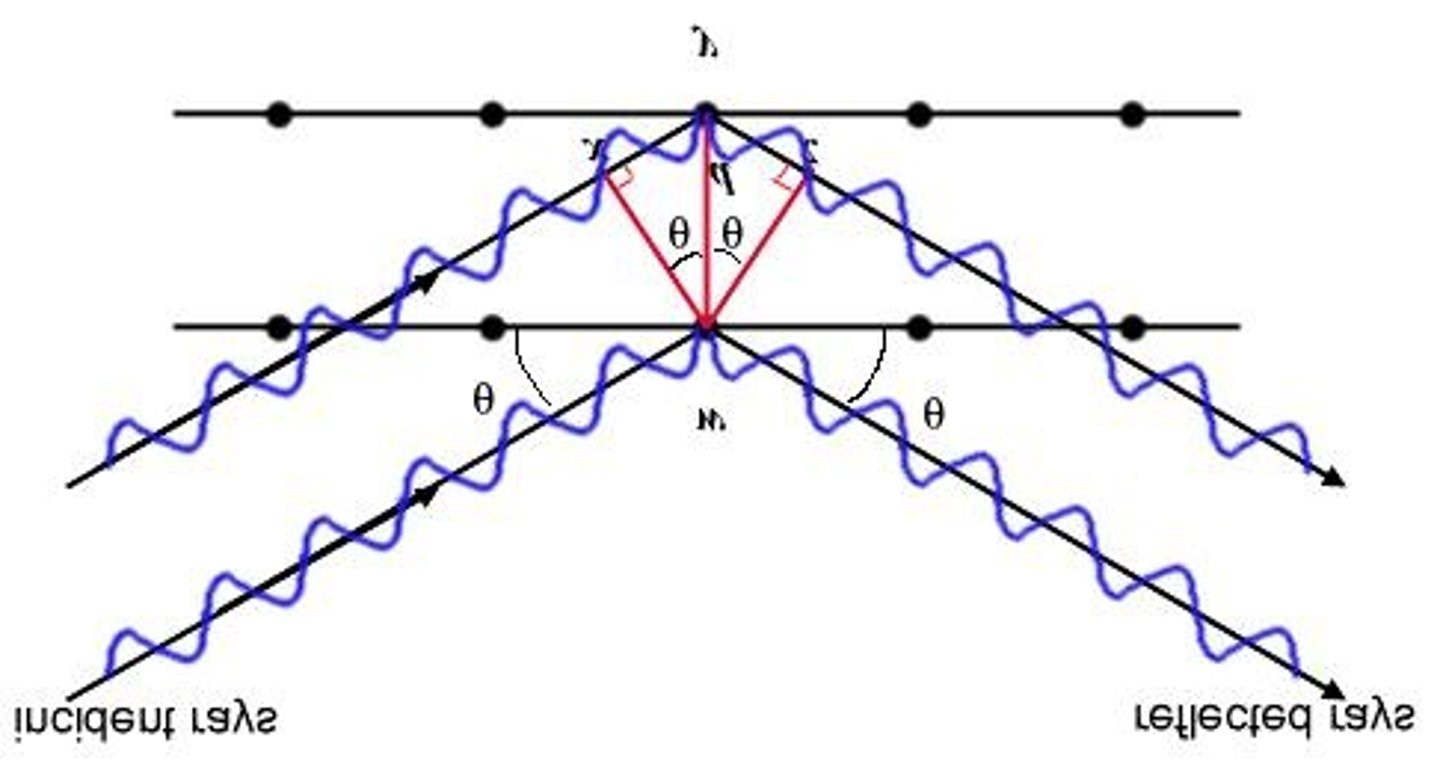
What technique is used to determine the structure of crystalline solids?
X-ray diffraction, which analyzes constructive and destructive interference of waves.
What is Bragg's Law?
A formula that relates the angle of incidence and reflection to the distance between atoms and wavelength in x-ray diffraction.
What are ionic solids?
Solids where ions occupy lattice points, such as sodium chloride.
What are molecular solids?
Solids where discrete covalent molecules occupy lattice points, examples include ice and sucrose.
What is the electron sea model?
A model describing metallic bonding where metal cations are surrounded by a mobile sea of valence electrons that conduct heat and electricity.
What are substitutional alloys?
Alloys where host metal atoms are replaced in the lattice by other atoms of similar size, such as brass and sterling silver.
What are interstitial alloys?
Alloys formed when small atoms fill the holes in the closest packed metallic structure, often seen in steel with carbon added to iron.
What characterizes network solids?
Atomic solids with strong directional covalent bonds.
Why is diamond a poor conductor of electricity?
It has a large gap in energy between occupied and unoccupied orbitals.
How does graphite conduct electricity?
Through delocalized electrons in π molecular orbitals between layers, despite strong σ bonds within fused rings.
What is silica based on?
Silica (SiO2) is based on interconnected SiO4 tetrahedra.
What is the basic structure of quartz?
Quartz (SiO2) is based on interconnected SiO4 tetrahedra.
How is glass produced?
Glass is produced by quickly cooling silica, resulting in an amorphous solid.
What are ceramics made from?
Ceramics are made from clays containing silicates (silicon-oxygen anions).
What is the structure of ceramics?
Ceramics are heterogeneous, consisting of crystals of silicates suspended in a glassy cement.
What is a key property of semiconductors like silicon?
Silicon has a smaller energy gap between occupied and unoccupied orbitals than diamond, allowing some electrons to be conducted.
What happens to the conductivity of silicon with temperature?
The conductivity of silicon increases with temperature.
What is an n-type semiconductor?
An n-type semiconductor is created by doping silicon with elements like arsenic, which adds extra valence electrons and increases conductivity.
What is a p-type semiconductor?
A p-type semiconductor is created by doping silicon with elements like boron, resulting in a shortage of valence electrons that creates 'holes' for electron movement.
What are examples of molecular solids?
Examples include water, dry ice, P4, and S8.
What types of forces are involved in bonding molecular solids?
Bonding in molecular solids involves London dispersion forces and dipole-dipole interactions, including hydrogen bonding in polar molecules.
What is the closest packing arrangement in ionic solids?
Large particles (usually anions) arrange in closest packing, while smaller particles (usually cations) fit into holes between anions.
What is vaporization?
Vaporization (evaporation) is the escape of molecules from a liquid's surface to form a gas and is always endothermic.
What is vapor pressure?
Vapor pressure is the pressure of the vapor present at equilibrium, also known as equilibrium vapor pressure.
How does intermolecular attraction affect vapor pressure?
Liquids with high intermolecular attraction have low vapor pressures, while those with low intermolecular attraction are more volatile and have high vapor pressures.
What is sublimation?
Sublimation is the process where a substance transitions directly from solid to gas.
What is the heat of fusion?
The heat of fusion (enthalpy of fusion, ∆Hfus) is the energy required to convert a mole of solid to a mole of liquid.
What is the normal boiling point?
The normal boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals 1 atmosphere.
What is supercooling?
Supercooling is the rapid cooling of a liquid that allows it to exist below its normal melting point without solidifying.
What is the critical point in a phase diagram?
The critical point is defined by the critical temperature and critical pressure, beyond which a substance cannot exist as a liquid.
What is the Clausius-Clapeyron equation used for?
The Clausius-Clapeyron equation describes the relationship between vapor pressure and temperature.
What happens during a phase change in terms of temperature?
During a phase change, temperature remains constant as chemical bonds are not being broken.
What is the triple point in a phase diagram?
The triple point is where solid, liquid, and gas phases coexist in equilibrium.
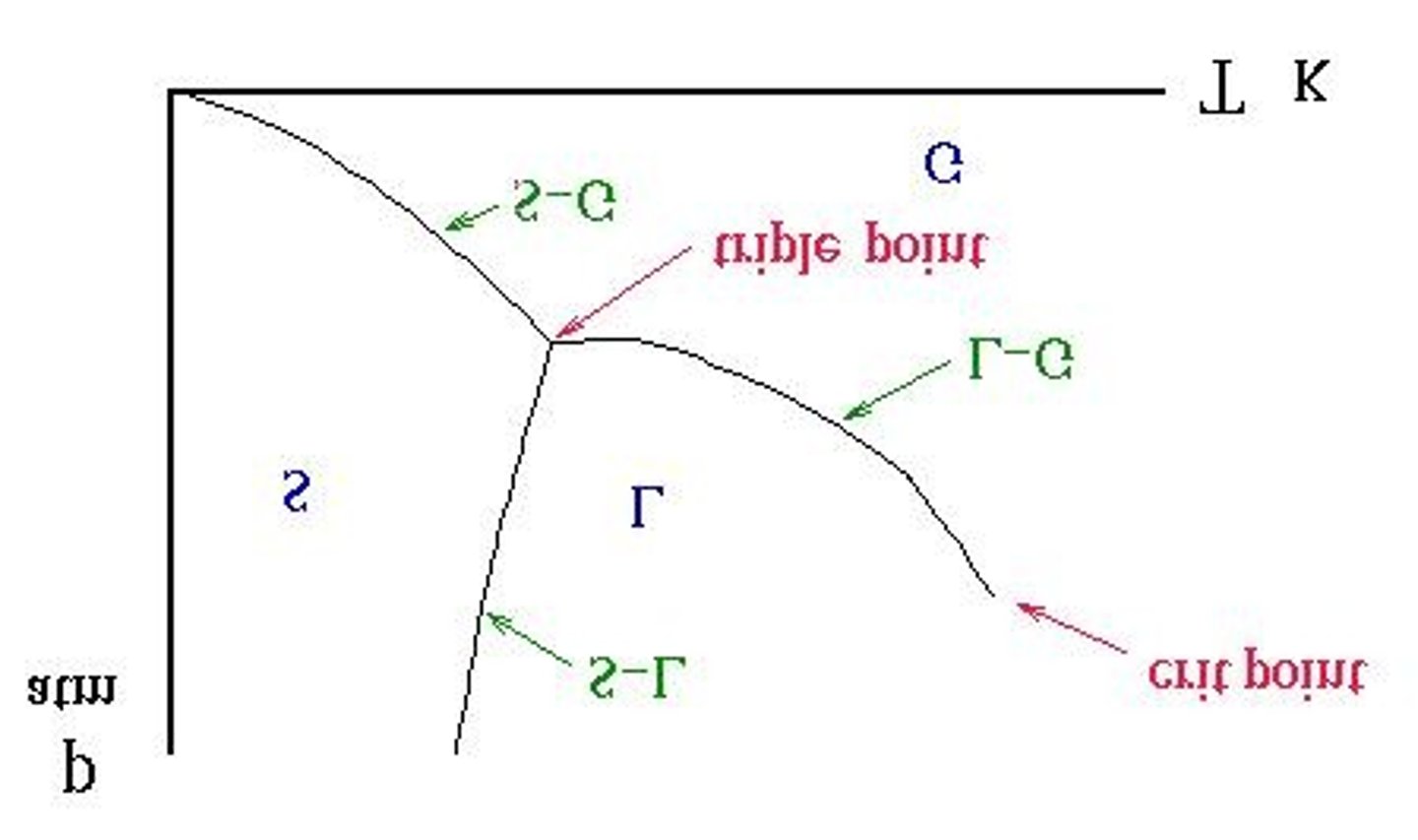
What is the significance of the normal melting point?
The normal melting point is the temperature at which solid and liquid states have the same vapor pressure at 1 atm.