Electricity
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Hazards associated with electricity
Damaged insulation, cables overheating, damp conditions
Explain how damaged insulation is a hazard
Contact with the wire due to gaps in the insulation can cause an electric shock or pose a fire hazard by creating a short circuit
Explain how cables overheating is a hazard
Too high currents through too small wires cause wires to heat up to very high temperatures which could melt the insulation exposing live wires and cause a fire
Explain how damp conditions is a hazard
If moisture comes into contact with live wires, it could conduct electricity which could create a short circuit or electric shock
When is double insulation used
When there is no earth connection. The earth wire is not needed as you cannot get a shock from the plastic
What is double insulation
Plastic casing rather than metal case completely covering electrical components or designed so that live wire cannot touch metal casing
Why is an earth wire not needed for a double-insulated device
You can’t get a shock from the plastic
What is normal insulation
Cover wire w insulating material eg rubber
What colour is the earth wire
Green and yellow
What does the earth wire do when the appliance is working correctly
Doesn’t carry current
What happens to the earth wire when a wire touches the metal case
Current surges through low resistance path of earth wire + hence fuse
What happens when current flows through the earth wire
Surge of current also thru fuse; fuse melts; current flows to ground
What happens when the fuse breaks/melts
Cuts off electricity to appliance
Why is there a surge of current in the earth wire when a wire touches the metal casing
Earth wire has very low resistance
What is a fuse
Thin piece of wire which overheats and melts if current is too high
What are the most common current ratings
3, 5, 15A
What must you do when choosing current rating
Pick slightly higher than current used by device
What happens if the current rating is too low
Fuse will break circuit even when acceptable current flows thru
What happens if circuit rating is too high
Won’t break circuit in enough time before damage occurs
What is a circuit breaker
Automatic electromagnet switch
How does a circuit breaker protect circuit
Breaks circuit if current rises over certain value
Advantage of circuit breakers over fuses
Can be reset and reused; operate faster than fuses
Why does current in a resistor result in electrical transfer of energy
Work done when charge flows through a circuit; work done = e transferred => electrical transfer of energy
How does current passing through a resistor/wire result in an increase in temperature?
Collisions of free electrons within wire; transfer Ek to ions of resistor; some energy dissipated to surroundings by heating
Where can electrical transfer of energy + inc temperature be used in domestic contexts
Electric heaters, toasters, kettles
What happens when a current passes through a resistor / wire?
Electrical transfer of energy and increase in temperature
What is the relationship between power, current and voltage?
P = IV
Where might you rearrange equation to be I = P/V?
Selecting an appropriate fuse by calculating the current the device uses
What is the relationship between energy transferred, current, voltage and time?
E = VIt
What is the relationship between power, energy transferred and time
E = Pt
What kind of current is mains electricity?
A.c.
What kind of current is supplied by a cell or battery
D.c.
What is d.c. current
Current only flows in one direction
Which direction does current flow in a dc circuit
From positive to negative terminal
What is alternating current
Current continuously changes direction around circuit
How come alternating current still always flows from the positive to negative terminal
AC power supplies have 2 identical terminals which change between +ve and -ve
What is frequency of UK mains electricity
50Hz
What voltage/pd is uk mains electricity
230V
What is frequency of an a.c. Power supply
Number of times current changes direction back/forth each second
What is the relationship between voltage, current and resistance?
V = IR
What is current?
Rate of flow of charge (at a point in the circuit)
What is the relationship between charge, current and time?
Q = It
What is electric current in solid metallic conductors?
Flow of negatively charged electrons
Why is current conserved at a junction in a circuit?
Charge is always conserved; total number of e- must stay same; sum of current in branches = total before
What is conventional current
Rate of flow of positive charge
What direction is conventional current
Opposite direction to flow of electrons
Will current in each branch out of a junction always be identical?
No, only if resistance along each branch is identical
What is current measured with
Ammeter in series with component
What is voltage
Energy transferred per unit charge
What is the relationship between energy transferred, charge and voltage
E = QV
What is voltage measured with
Voltmeter in parallel across component
Why is a parallel circuit more appropriate for connecting lamps
If one breaks, current can still pass thru others
Why is a series circuit more appropriate for domestic lighting
Components all controlled by one switch; fewer wires required
Why might parallel circuits be a bad choice for some situations
More wires = more complicated; harder to control V across individual components
Why is it harder to control V across individual components in a parallel circuit?
All branches have same voltage as supply
Current in a series circuit
Same at all points + components
Current in parallel circuit
Shared between branches (sum in branches = supply)
Voltage in series circuit
Shared across each component (sum of pd = supply)
Which components in a series circuit might have greater pd across them
Components with higher resistance
Resistance in a series circuit
Sum of resistance of each component
Total resistance in parallel circuit
Total resistance < that of each component
What does current in a series circuit depend on
Applied voltage + number/nature of other components
If you have higher voltage in a series circuit what happens to current?
Current increases if number of components stays same
If you have more components in a series circuit what happens to current?
Current decreases if voltage stays same
The voltage across two components connected in parallel is
The same
How does current vary with voltage in a wire/fixed resistor
Straight line through origin
Relationship between i and V for a wire/fixed resistor is
Directly proportional
IV graph for a filament bulb
As current increases, resistance increases
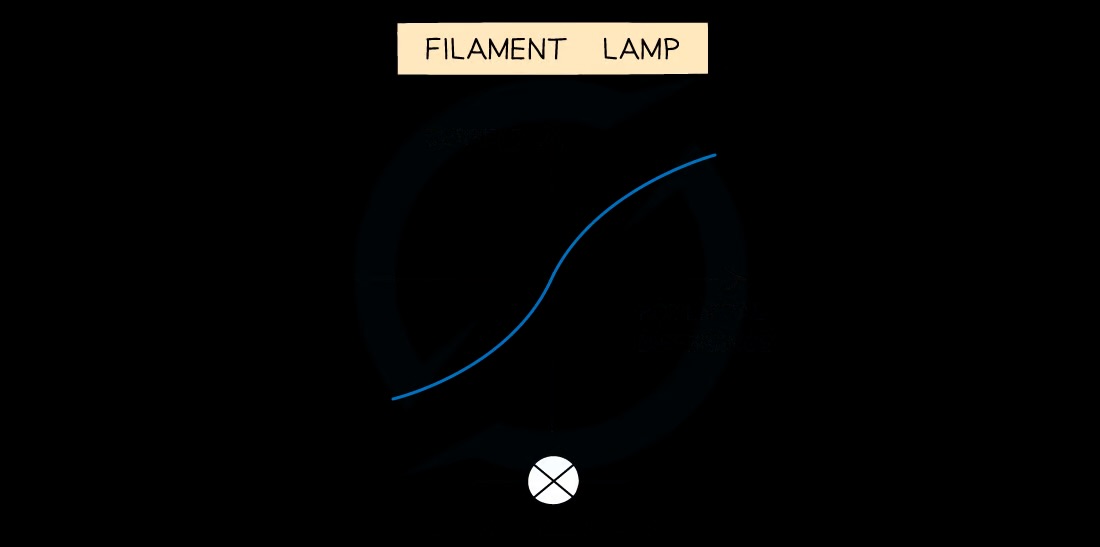
Why does resistance increase as current through a filament lamp increase
Higher current = hotter filament = ions vibrate more = more difficult for electrons to pass through = current increases at a slower rate
IV graph for a diode
Only allows current in one direction
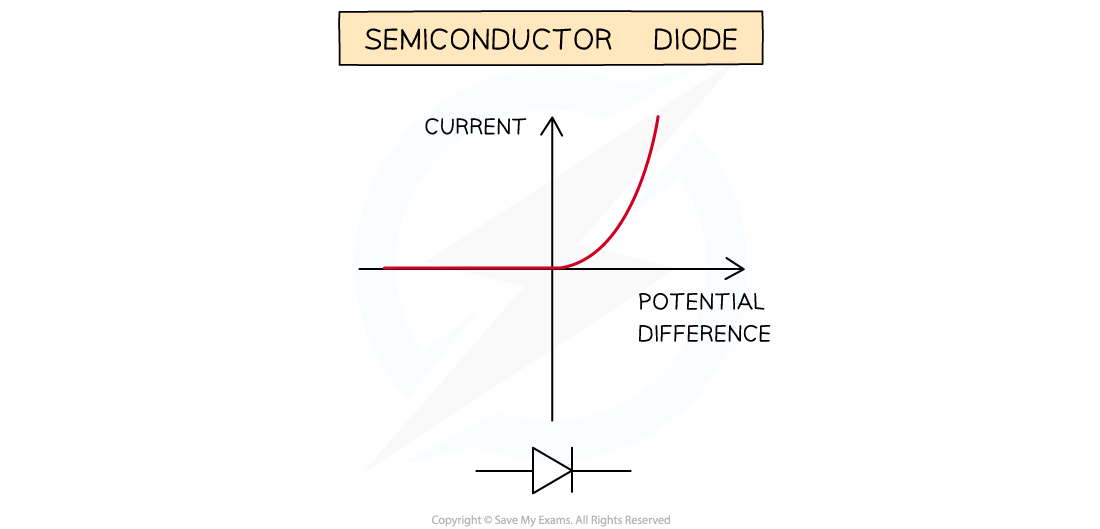
Why doesn’t diode let current flow in the other direction
Has very high resistance in the other direction
What do you need for an I-V graph practical
Ammeter, voltmeter, variable resistor, power source, wires, component
What is the independent variable in IV graph practical
Current - changed by variable resistor
What is the voltmeter for in the IV graph practical
Measure voltage (dependent variable)
What could you use to indicate the presence of current in a circuit
Lamps, LEDs
If you increased resistance what would happen to current in a circuit
I = V/R so current would decrease
How would you calculate the total resistance of resistors in a series circuit
Add up individual resistors
How would you calculate the total voltage across a series circuit of resistors
Add up voltages of individual resistors
How do thermistors work
Low temp = high resistance
Would a thermistor be high or low resistance when it’s hot?
Low
How does a light-dependent resistor work?
More light = less resistance
If it was dark, would there be high or low resistance through the LDR?
High