Intelligence Theories
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/31
Last updated 11:42 PM on 4/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
Psychometric Theories
type of personality theory
= based on a model that portrays intelligence as a composite of abilities measured by mental tests. This model can be quantified.
\
ex. performance on a number-series test might represent a weighted composite of number, reasoning, and memory abilities for a complex series
= based on a model that portrays intelligence as a composite of abilities measured by mental tests. This model can be quantified.
\
ex. performance on a number-series test might represent a weighted composite of number, reasoning, and memory abilities for a complex series
2
New cards
Cognitive Theories
type of personality theory
= characterized by their focus on the idea that:
how and what people think leads to → the arousal of emotions
and
certain thoughts and beliefs lead to → disturbed emotions and behaviors
while other thoughts lead to → healthy emotions and adaptive behavior
= characterized by their focus on the idea that:
how and what people think leads to → the arousal of emotions
and
certain thoughts and beliefs lead to → disturbed emotions and behaviors
while other thoughts lead to → healthy emotions and adaptive behavior
3
New cards
Intelligence
the capacity to understand the world, think rationally, and use resources effectively
1. ability to learn from experience
2. ability to adapt to environment by reasoning, solving problems, and planning ahead
3. ability to evaluate your thinking (metacognitive skills)
1. ability to learn from experience
2. ability to adapt to environment by reasoning, solving problems, and planning ahead
3. ability to evaluate your thinking (metacognitive skills)
4
New cards
Individualistic Culture
a type of culture
= focus on gathering resources for yourself
\
ex. “I took the exam, I earned the grade”
= focus on gathering resources for yourself
\
ex. “I took the exam, I earned the grade”
5
New cards
Collectivist Culture
a type of culture
= focus on working well within a group
\
ex. my family helped me get here, so WE earned the grade together
= focus on working well within a group
\
ex. my family helped me get here, so WE earned the grade together
6
New cards
g
symbol for general intelligence
7
New cards
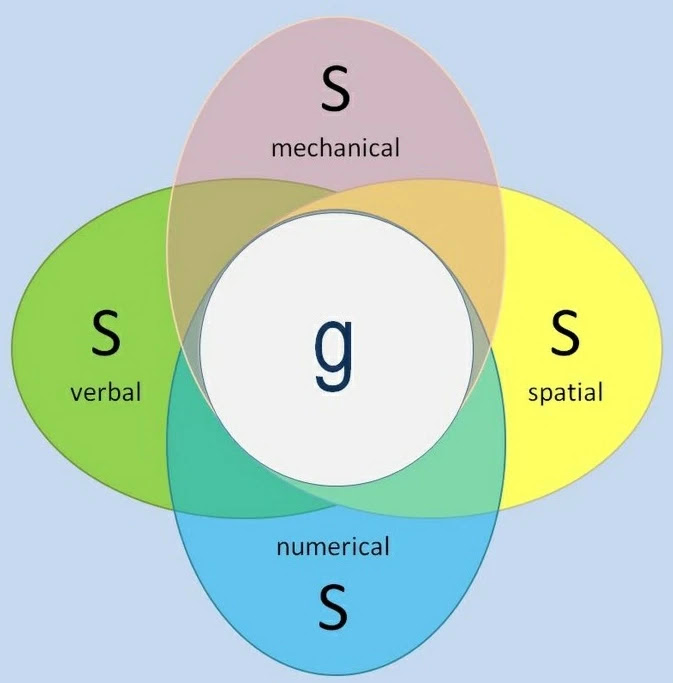
factor analysis
a statistical technique that finds relationships between items
\
* used to analyze g (general intelligence) into groups
* ex. people who do well on vocabulary do well on paragraph comprehension (so these two are clustered in the verbal intelligence group)
\
* used to analyze g (general intelligence) into groups
* ex. people who do well on vocabulary do well on paragraph comprehension (so these two are clustered in the verbal intelligence group)
8
New cards
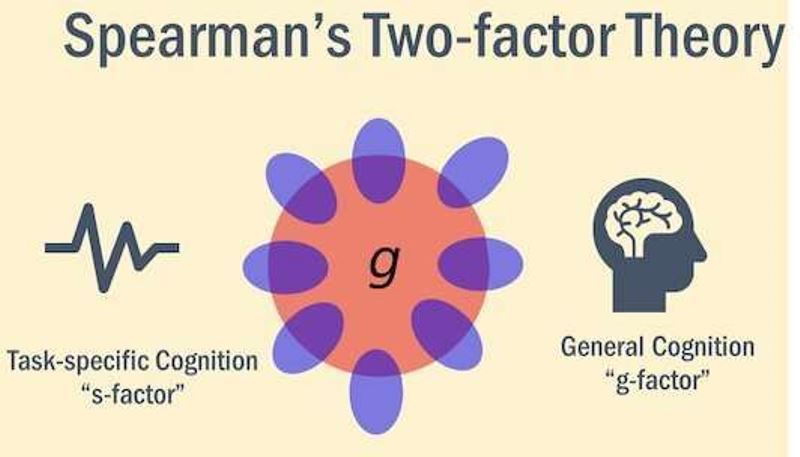
g-factor theory
a type of psychometric theory
= Spearman thought that if you’re good in 1 type of intelligence, then you’re probably good in other, related types of intelligence
\
divided intelligence into 2 categories:
1. general = average intelligence (IQ)
2. specific = a specific skill
= Spearman thought that if you’re good in 1 type of intelligence, then you’re probably good in other, related types of intelligence
\
divided intelligence into 2 categories:
1. general = average intelligence (IQ)
2. specific = a specific skill
9
New cards
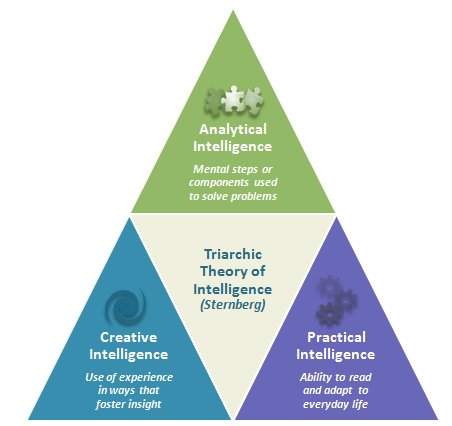
Triarchic Theory
a type of cognitive personality theory
= Sternberg divided intelligence into 3 categories arranged in a triangle
\
1. Analytical Intelligence
2. Creative Intelligence
3. Practical Intelligence
= Sternberg divided intelligence into 3 categories arranged in a triangle
\
1. Analytical Intelligence
2. Creative Intelligence
3. Practical Intelligence
10
New cards
Analytical Intelligence
one aspect of Sternberg’s triarchic theory
= abstract/deductive reasoning
= abstract/deductive reasoning
11
New cards
Creative Intelligence
one aspect of Sternberg’s triarchic theory
= ability to generate new ideas and solve new problems
= ability to generate new ideas and solve new problems
12
New cards
Practical Intelligence
one aspect of Sternberg’s triarchic theory
= ability to make quick decisions for navigating everyday life and solving real-world problems
* AKA “common sense” and “street smarts”
= ability to make quick decisions for navigating everyday life and solving real-world problems
* AKA “common sense” and “street smarts”
13
New cards
Multiple Intelligence Theory
a type of cognitive personality theory
= Gardner divided intelligence into 9 categories
\
1. Musical
2. Spatial
3. Verbal
4. Mathematical
5. Kinesthetic
6. Interpersonal
7. Intrapersonal
8. Naturalistic
9. Existential
= Gardner divided intelligence into 9 categories
\
1. Musical
2. Spatial
3. Verbal
4. Mathematical
5. Kinesthetic
6. Interpersonal
7. Intrapersonal
8. Naturalistic
9. Existential
14
New cards
Musical
one aspect of Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory
= sensitivity towards sounds, pitch, rhythm
= sensitivity towards sounds, pitch, rhythm
15
New cards
Spatial
one aspect of Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory
= ability to perceive, understand and reconstruct objects
ex. architects
= ability to perceive, understand and reconstruct objects
ex. architects
16
New cards
Verbal
one aspect of Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory
= ability to use words articulately
ex. journalists, poets, comics
= ability to use words articulately
ex. journalists, poets, comics
17
New cards
Mathematical-Logical
one aspect of Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory
= understand numbers to solve problems
= understand numbers to solve problems
18
New cards
Kinesthetic
one aspect of Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory
= move body and recognize other’s body positions in space
ex. dancers, athletes, etc.
= move body and recognize other’s body positions in space
ex. dancers, athletes, etc.
19
New cards
Interpersonal
one aspect of Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory
= understand/empathize with others
ex. politicians, marketers
= understand/empathize with others
ex. politicians, marketers
20
New cards
Intrapersonal
one aspect of Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory
= look inward, understand own feelings/motivations
ex. psychologists, philosophers
= look inward, understand own feelings/motivations
ex. psychologists, philosophers
21
New cards
Naturalistic
one aspect of Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory
= understand/categorize elements of natural world
ex. farmers, archeologists
= understand/categorize elements of natural world
ex. farmers, archeologists
22
New cards
Existential
one aspect of Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory
= tackle deeper questions of existence
ex. philosophers, religious leaders
= tackle deeper questions of existence
ex. philosophers, religious leaders
23
New cards
Emotional Intelligence
= Interpersonal + Intrapersonal skills
a type of intelligence characterized by 4 abilities:
1. Perceive Emotion
2. Understand Emotion
3. Manage Emotion
4. Use Emotion
a type of intelligence characterized by 4 abilities:
1. Perceive Emotion
2. Understand Emotion
3. Manage Emotion
4. Use Emotion
24
New cards
Perceive Emotion
one component of Emotional Intelligence
= ability to recognize emotions in faces, music, and stories
= ability to recognize emotions in faces, music, and stories
25
New cards
Understand Emotion
one component of Emotional Intelligence
= ability to predict emotions, how they change and blend
= ability to predict emotions, how they change and blend
26
New cards
Manage Emotion
one component of Emotional Intelligence
= ability to express emotions in different situations
= ability to express emotions in different situations
27
New cards
Use Emotion
one component of Emotional Intelligence
= ability to utilize emotions to adapt or be creative
= ability to utilize emotions to adapt or be creative
28
New cards
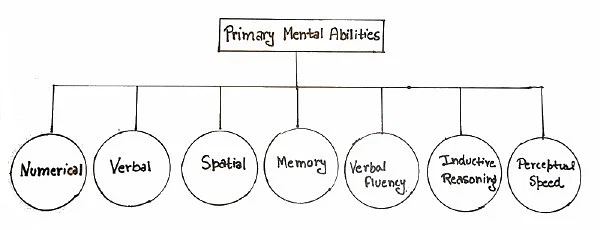
7 Primary Mental Abilities Theory
a type of psychometric personality theory
= Thurstone suggested that intelligence is a composite of seven distinct primary mental abilities (PMA):
* although he was a critic of %%spearman’s g-theory%% his work ended up supporting/being similar to it
\
1. verbal comprehension
2. word fluency
3. number facility
4. spatial visualization
5. associative memory
6. perceptual speed
7. reasoning
= Thurstone suggested that intelligence is a composite of seven distinct primary mental abilities (PMA):
* although he was a critic of %%spearman’s g-theory%% his work ended up supporting/being similar to it
\
1. verbal comprehension
2. word fluency
3. number facility
4. spatial visualization
5. associative memory
6. perceptual speed
7. reasoning
29
New cards
fluid and crystallized intelligence theory
a type of psychometric personality theory
= Cattell believed general intelligence (g) is subdivided into gf and gc and that there was a speed-accuracy trade-off
= Cattell believed general intelligence (g) is subdivided into gf and gc and that there was a speed-accuracy trade-off
30
New cards
Fluid Intelligence (gf)
a type of general intelligence (g)
= youth, speed, processing large amounts of into
* is biologically influenced; teen brain is great at flexibility and this type of intelligence
= youth, speed, processing large amounts of into
* is biologically influenced; teen brain is great at flexibility and this type of intelligence
31
New cards
Crystalized Intelligence (gc)
a type of general intelligence (g)
= experience, using heuristics (shortcuts)
* is use it or lose it (the more you use your brain, the more active it is)
* synaptic genesis = brain grows new neurons
* is learning-based intelligence (makes sense, because the older you get, the more life experience and time you have to develop heuristics in life)
* This combats the myth of ageism; although elders get older, they also get smarter!
= experience, using heuristics (shortcuts)
* is use it or lose it (the more you use your brain, the more active it is)
* synaptic genesis = brain grows new neurons
* is learning-based intelligence (makes sense, because the older you get, the more life experience and time you have to develop heuristics in life)
* This combats the myth of ageism; although elders get older, they also get smarter!
32
New cards
Speed-Accuracy Trade-off (SAT)
= refers to the finding that when people focus being fast, they tend to make more errors during a task; when they focus on being accurate, they tend to perform more slowly.