GI E2- Diseases of the Liver Pt 1
1/124
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
What is the functional unit of the liver that consists plates of hepatocytes hexagonally arranged around a central vein?
Lobule
What are wide, leaky capillaries without a basement membrane that empty into the central vein?
Sinusoids
What is the breakdown of heme metabolism?
Bilirubin
What does jaundice result from?
Hyperbilirubinemia
Which type of bilirubin is water soluble?
Direct (conjugated)
Which type of bilirubin is lipid soluble (90% of the serum bilirubin in healthy adults)?
Indirect (unconjugated)
What facilitates digestion, emulsification, absorption of fat via micelles, and solubilizes cholesterol?
Bile
Describe the pathway of bile secretion
Hepatocytes produce bile → bile duct → R or L hepatic duct → common hepatic duct (joins cystic duct of GB) → common bile duct (joins pancreatic duct) → hepatopancreatic ampulla (ampulla of Vater)
What controls bile secretion?
Parasympathetic stimulation via vagus nerve & hormonal stimulation (CCK causes GB to empty, Secretin causes bile secretion)
What functions in the synthesis of serum proteins, hormonal and growth factors, regulates nutrients, produces bile & carriers, conjugates bilirubin, and detoxes drugs for excretion?
Hepatocytes
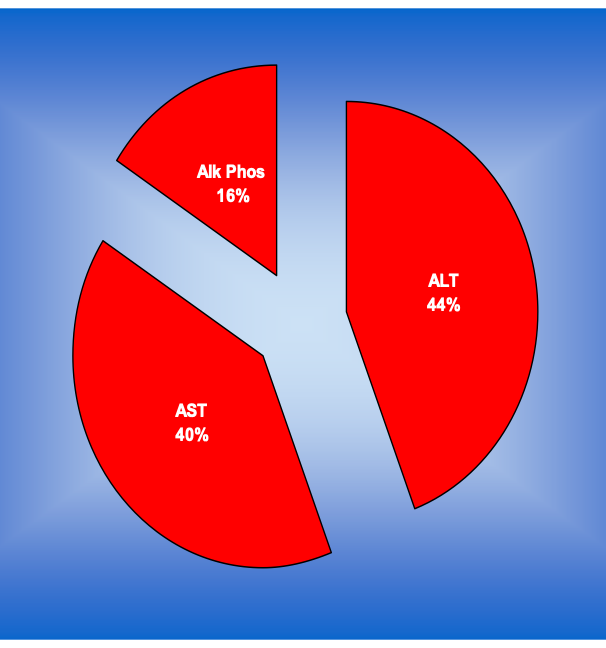
Hepatocellular or cholestatic disease?
increased AST, ALT predominately
Hepatocellular disease
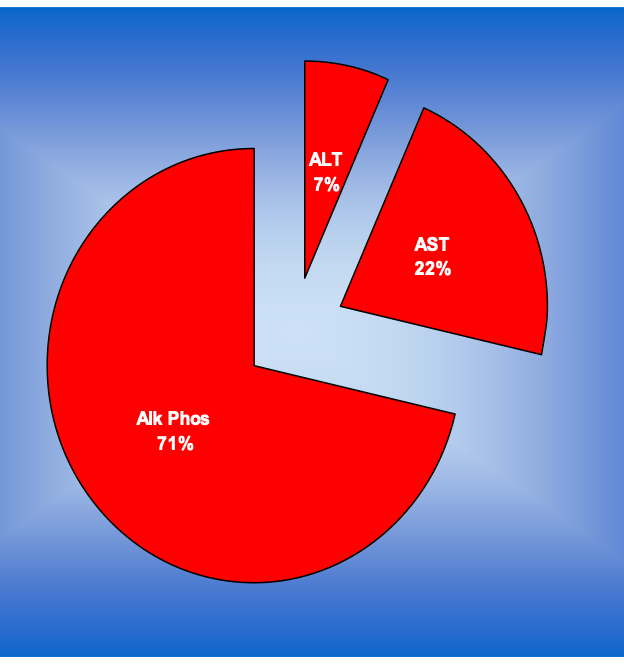
Hepatocellular or cholestatic disease?
retention of bile in the liver
increased ALP
Cholestatic disease
The aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) ratio can be a useful marker for what specific diseases?
Liver diseases
Which of the following conditions is most likely?
AST- 160
ALT - 80
Alcoholic hepatitis
Which of the following conditions is most likely?
AST- 46
ALT- 78
Chronic hepatitis C
Which of the following conditions is most likely?
AST- 400
ALT- 800
Acute viral hepatitis
Which of the following conditions is most likely?
AST- > 1, 000
ALT- > 1,000
Acute Tylenol toxicity & ischemic hepatitis
What causes LFT elevations?
Toxins (new meds, Tylenol), viral, ischemia, passage of a gall stone
What is the gold standard to stage fibrosis?
Liver biopsy
What are disadvantages to liver biopsies?
Invasive, expensive, risk pain & bleeding
sample is small & sampling error can occur
What newer test is non invasive and measures the velocity of sound waves passing through the liver and gives a score that is converted into a liver stiffness measurement?
Fibroscan (liver ultrasonographic elastography)
What is a harmless, hereditary condition where the conjugation of bilirubin by glucuronide is impaired?
Gilbert’s syndrome
What causes the impairment of bilirubin conjugation by glucuronide seen in Gilbert’s syndrome?
Mild decrease in uridine phosphate (UDP) or glucuronyl transferase
** all other causes have been eliminated
What condition?
mildly persistently elevated unconjugated bilirubin
occurs w/ illness (flu), fasting, & some drugs
Asx & often found incidentally
Harmless & no treatment required
Gilbert’s syndrome
What is the loss of hepatocellular function or interrupted blood flow through?
Hepatocellular failure
Due to the livers large reserve capacity, significant injury can be masked in hepatocellular failure. How much of the liver must be destroyed before life is threatened?
80%
What are ssx of hepatocellular failure?
Jaundice, muscle wasting, ascites, excessive bleeding, vitamin or blood protein deficiencies, glucose imbalance, impaired hormone production
The following pathophysiology is seen in what condition?
Dec protein → dec production of clotting factors & hypoalbuminemia → generalized edema
Abnormal release/storage of glycogen → hyper/hypoglycemia
Dec bile salt production → impaired vitamin (ADEK) absorption
Dec lipoprotein processing → dyslipidemia
impaired processing or metabolism of:
endogenous steroid hormones
by products of protein metabolism (ammonia → urea)
drugs/toxins
bilirubin → jaundice
Hepatocellular failure
Due to the impaired processing of endogenous steroid hormones in hepatocellular failure (estrogen), what signs can be seen in men?
Gynecomastia, impotence, testicular atrophy
Due to the impaired processing of endogenous steroid hormones in hepatocellular failure, what signs can be seen in women?
Irregular menses, palmar erythema, spider telangiectasia
What is the yellowish coloration of sclera, skin, and mucous membranes due to hyperbilirubinemia (either conjugated or uncojugated bili accumulates)?
Jaundice
What category of jaundice?
due to increased bilirubin production
ex: hemolytic disease
Prehepatic
What category of jaundice?
deficient bile production or bilirubin metabolism due to liver disease
ex: hepatitis
Hepatic
What category of jaundice?
due to bile drainage blockage
ex: gallstones or pancreatic/bowel cancer
Posthepatic
What is the AC, 9H mnemonic for complications of liver failure?
Ascites, Coagulopathy
Hypoalbuminemia, portal HTN, Hyperammonemia, Hepatic encephalopathy, Hepatorenal syndrome, Hypoglycemia, Hyperbilirubinema (jaundice), Hyperestrinism, HCC
What is the irreversible end stage of hepatic injury characterized by diffuse hepatic fibrosis → permanent changes in hepatic blood flow/liver function?
Cirrhosis
What can cause cirrhosis?
Alc liver dz, chronic hepatitis, toxin induced, autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary sclerosis, non-alc fatty liver dz
What are the ensuing events of cirrhosis?
Portal HTN & impaired biochemical functions → dec albumin & clotting factor synthesis
What assesses the functional hepatic reserve of cirrhosis by measuring the disease severity and is also a predictor of morbidity and mortality?
Child-pugh classification
What assesses the functional hepatic reserve of cirrhosis by using bilirubin, creatinine & INR and also helps determine transplant status?
Model for end stage liver disease (MELD)
What condition?
Pts w/ liver failure experience occasional kidney failure- rising serum cr & oliguria
Kidney is fine but intrarenal blood flow is disturbed d/t imbalance bt vasoconstrictive & vasodilation mechanisms of liver dz
usually acute and progressive but can be chronic (poor prognosis)
Hepatorenal syndrome
What is the treatment for hepatorenal syndrome?
Preventative, supportive, hemodialysis, liver transplant if done early enough, r/o any reversible cause of renal failure
What condition is a chronic obstruction in blood flow through the liver & venous drainage is congested?
Portal HTN
What kind of blood supply does the liver have?
Dual - hepatic artery (20%) and portal vein (80%)
What does the congestion of venous drainage in portal HTN cause?
Abnormal venous patterns → varices, caput medusae, ascites
What is the superficial enlargement of umbilical veins and is pathognomonic for portal HTN?
Caput medusae
What is the accumulation of peritoneal fluid?
Ascites
Why do esophageal varices occur in portal HTN?
Collateral venous pathways (varices) dilate from inc portal vein pressure in an attempt to transport blood from the splanchnic bed around the cirrhotic liver to the heart
What can cause portal HTN?
Alcoholic cirrhosis, post hepatic cirrhosis, chronic infx
The following symptoms are seen with what condition?
Muscle wasting
spider angiomata
jaundice
caput medusae
splenomegaly
inc liver failure- ascites (transudate), AMS
Portal HTN
What is the pathologic accumulation of fluid w/in the peritoneal cavity (intra-abdominal collection of fluid) caused by decreased oncotic pressure?
Ascites
What is the treatment for ascites?
Abdominal paracentesis (analyze fluid, SAAG)
Na restriction 800 mg/day, fluid restriction 1 L/day
Diuretics: spironolactone, + loop (Lasix) to delay action
Tx fail/refractory: albumin infusion, abd shunts (peritovenous), TIPS
What is a complex neuropsychiatric syndrome that has distinctive EEG changes and symptoms ranging from mild confusion to lethargy, stupor and coma?
Hepatic encephalopathy
What ssx are associated with hepatic encephalopathy?
Reverse sleep cycle, dementia, psychotic sx, spastic myelopathy, asterixis “liver flap” (classic finding)
What is hepatic encephalopathy associated with?
Fulminant hepatic failure (onset w/in 8 wks of liver injury w coagulopathy) & severe chronic liver disease
What is the main cause of symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy and correlated with the severity of dysfunction?
Increased arterial ammonia level
What is the treatment for hepatic encephalopathy?
Correct cause, recommend AGAINST protein restriction, inc excretion of nitrogenous wastes
Osmotic diuresis or abx: lactulose, amoxicillin & rifampin, spironolactone
What often develops with grade 3 or 4 hepatic encephalopathy?
Cerebral edema → inc ICP → dec perfusion of brain → cerebral hypoxia (major cause of death)
What sx are associated with cerebral edema?
Deepening coma, systolic HTN, decerebrate posture, pupillary dilation, resp arrest w brain herniation
What is the treatment for cerebral edema?
1st line: IV mannitol infusion (pt in semi-fowler position)
2nd line: sodium pentothal
Other: moderate hypothermia
How does IV mannitol infusion work for cerebral edema?
Decreases edema via osmotic pull of water form brain while patient in semi fowler position
What is inflammation and necrosis of the liver cells resulting from different types of injury?
Hepatitis
What is the etiology of hepatitis?
Viral, alcoholic, drug induced, autoimmune, hereditary disease
What are 90% of cases of acute hepatitis?
Acute viral hepatitis (A, B, C, D, E)
What causes chronic viral hepatitis?
Hep B & C
Which type of viral hepatitis?
continued disease activity > 6 mos
inflammation is confined to portal triad w/o destruction of normal liver tissue
inc serum transaminases
Chronic viral hepatitis
Destruction of normal liver tissue occurs most frequently in what type of hepatitis?
Acute hep C
What condition has the following presentation?
prodrome of viral like sx
anorexia, N, V, malaise, aversion to smoking
low grade fever
hepatomegaly
± jaundice
normal-low WBC
marked transaminase elevations early in course
Hepatitis
The following symptoms are associated with what phase of acute viral hepatitis?
low grade fever
N, V, anorexia
RUQ or epigastric pain
Malaise, myalgia, arthralgia, fatigue
aversion to smoking
Prodromal phase
The following symptoms are associated with what phase of acute viral hepatitis?
jaundice in some
icteris of sclera
worsening of prodromal sx
Icteric phase
The following symptoms are associated with what phase of acute viral hepatitis?
increasing sense of well being
return of appetite
resolution of jaundice, abd pain, & fatigue
Convalescent phase
Describe the course of acute viral hepatitis
Acute illness lasts 2-3 wks (hep A complete recovery in 9 wks, hep B complete recovery in 16 wks)
Which hepatitis are more likely to be chronic?
B, C, and D
What can result in severe cases of acute viral hepatitis?
Liver failure & its complications (hepatic encephalopathy, hepatorenal syndrome, bleeding diathesis), fulminant hepatitis
Which type of hepatitis?
acute short lived illness with very low mortality and no long term sequala
fecal oral transmission - contaminated food/water
sx: malaise, anorexia, N, low grade fever, RUQ pain, jaundice ~ 2 wks
generally self limited lasting ~9 wks
Hepatitis A
In hepatitis A, when does virus excretion start and when does it clear from feces?
Starts 2 weeks before clinical illness & clears from feces after the first week of physical sx
When are blood and stools most infectious in hepatitis A?
During incubation period (2-7 weeks) & early illness
What is the diagnosis for hepatitis A?
Anti-HAV IgG (previous infx & immunity) & anti-HAV IgM (acute infx)
Which indicates a previous hep A infection and immunity?
Anti-HAV IgG
What is the treatment for hepatitis A?
Rest, nutritious diet, avoid hepatotoxins (alc, Tylenol), separate and clean items/laundry, active immunization (2 wks before travel, exposure, etc)
Which type of hepatitis?
longer and more insidious onset; slower recovery
can survive for atleast 7 days
longer course of dz → inc risk of HCC
transmission- parenteral, sexual contact, perinatal
present in- blood, saliva, semen, vaginal secretions
Hepatitis B
What route of of HBV transmission is associated with 90% risk of chronic infection?
Mother to neonate
What are RF for HBV?
Working in health care, transfusions, dialysis, acupuncture, tattooing, extended overseas travel to endemic area, residence in institution/correctional facility
What type of hepatitis?
insidious onset- can easily be missed
incubation 2-6 mos
sx: fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, N, V, abd pain, dark urine, clay colored BMs, arthralgia, pruritus jaundice
HBV
Who does the CDC recommend HBV testing for?
Anyone born between 1945-1965**, pts on immunosuppressive therapy
and a lot more like 2 slides on it idk just read it
What is the dx for HBV?
Hepatitis panel, LFTs, U/S guided laporoscopic bx
What 3 distinct antigen-antibody systems are useful markers for HBV diagnosis?
HBs, HBc, HBe
What indicates an acute HBV infection?
HBsAg
What indicates immunized or recovered from HBV?
Anti-HBs
What appears shortly after HBsAg is detected & fills the serological gap in pts who have cleared HBsAg and have not yet made anti-HBs?
IgM anti-HBc
What appears during acute hepatitis but persists indefinitely, no matter if pt recovers or becomes chronic?
IgG anti-HBc
What appears during the incubation period of HBV shortly after detection of HBsAg & indicates viral replication and infectivity?
HBeAg
What is there an increased risk of with chronic HBV cases?
Cirrhosis or HCC (esp in endemic areas, seen at younger age)
*prevent HCC w/ HBV vaccine
What is the treatment for acute cases of HBV?
Supportive, usually resolves spontaneously
What is the treatment for HBV fulminant disease?
Aggressive tx for coagulopathy, encephalopathy, cerebral edema, etc
What is the treatment for chronic HBV?
Antivirals → Tenofovir, Entecavir, Lamuvidine (has inc resistance)
What are recommendations for HBsAg positive patients?
Vaccinate sexual contacts, use barrier protection, dont share toothbrushes/razors, cover wounds, clean blood spills w/ detergent or bleach, don’t donate organs/blood/sperm
T/F: Pts who are HBsAg positive should -
should not participate in activities, including contact sports
be excluded from daycare or school participation and be isolated from other kdis
should not share food, utensils, kiss others
False
When should people receive HBV recombinant vaccine?
3 doses at birth, 1 and 6 mos, may need booster after 10 yrs (check titer)
What should HBV patients receive to decrease the risk for fulminant hepatitis with a superimposed hepatitis infection?
Hep A vaccine