IB Business Management I
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/212
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Business Organization and Environment & Human Resources Management
Last updated 2:09 AM on 1/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
213 Terms
1
New cards
Leadership
The art of motivating a group of people towards achieving a common objective.
2
New cards
Management
A set of processes that keep an organization functioning.
3
New cards
Managers Responsabilities
Setting objectives, organizing resources and motivating staff to meet the organizations goals.
4
New cards
Leadership Characteristics
- Motivativating and inspiring.
- Innovators that promote change.
- Stems from personal traits.
- Natural abilities and instincts.
- Believes in doing the right thing.
- Respected and trusted by its followers.
- Creates and develops a culture of change.
- Innovators that promote change.
- Stems from personal traits.
- Natural abilities and instincts.
- Believes in doing the right thing.
- Respected and trusted by its followers.
- Creates and develops a culture of change.
5
New cards
Management Characteristics
- Directs and monitors others.
- Problem-sovers.
- Official position of responsability in the organization.
- Skilled and qualified for role.
- Listened to by others.
- Conforms to the norms of the organization.
- Problem-sovers.
- Official position of responsability in the organization.
- Skilled and qualified for role.
- Listened to by others.
- Conforms to the norms of the organization.
6
New cards
Trait Theory
Believes that you are born a leader and can't become one.
7
New cards
Leaders Characteristics
- Desire to succeed and self-confidence.
- Thinks outside the box and encourages other to do the same.
- Multi-talented.
- Easily identifies the heart of the problem at hand.
- Thinks outside the box and encourages other to do the same.
- Multi-talented.
- Easily identifies the heart of the problem at hand.
8
New cards
Autocratic Leaders
- All decision-making at the center of the organization.
- They make decions without discussing them with others.
- They set the organizations objectives, issue instructions and ensure they are being carried out.
- Workers can be dependant of their they won't show initiative.
- Motivation is likely to be low making supervisng the staff essential.
- Usually rely on one-way communication disencouraging feedback from employees.
- Ex. Police, army, hospitals.
- They make decions without discussing them with others.
- They set the organizations objectives, issue instructions and ensure they are being carried out.
- Workers can be dependant of their they won't show initiative.
- Motivation is likely to be low making supervisng the staff essential.
- Usually rely on one-way communication disencouraging feedback from employees.
- Ex. Police, army, hospitals.
9
New cards
Paternalistic Leaders
- Fatherly style typically used by dominant males.
- Their power is used to control and protect employees.
- Employees are expected to be loyal and obedient.
- Managers pay more attention to the social aspects.
- Decisions are made with the workers interests at heart.
- Feedback is encouraged this improves moreale.
- Decisions are still made by the senior manager.
- No true participation of employees leading to a sense of frustration.
- Usually in very patriarch societies.
- Their power is used to control and protect employees.
- Employees are expected to be loyal and obedient.
- Managers pay more attention to the social aspects.
- Decisions are made with the workers interests at heart.
- Feedback is encouraged this improves moreale.
- Decisions are still made by the senior manager.
- No true participation of employees leading to a sense of frustration.
- Usually in very patriarch societies.
10
New cards
Democratic Leaders
- Promotes active participation of workers in decision making.
- They engage in discussions with employees before taking a decision.
- Communication is both ways enabling staff to initiate and respond to a discussion.
- They have good communication skills.
- Full participation in the decision making process.
- Improves workers motivation. (Herzberg)
- To implment it it's a slow process.
- They engage in discussions with employees before taking a decision.
- Communication is both ways enabling staff to initiate and respond to a discussion.
- They have good communication skills.
- Full participation in the decision making process.
- Improves workers motivation. (Herzberg)
- To implment it it's a slow process.
11
New cards
Laissez-faire Leaders
- Leaves the decison making to the staff.
- Hand off approach, opposite of autocratic.
- Extreme version of democratic management.
- Little input form management.
- Effective on research and design teams.
- This style could be a disaster in other areas.
- Hand off approach, opposite of autocratic.
- Extreme version of democratic management.
- Little input form management.
- Effective on research and design teams.
- This style could be a disaster in other areas.
12
New cards
Situational Leaders
- Adapt depending on the situation as well as skills and experience from the group being led.
- If the group is not receptive or lack specific skills then a high level of directive leadership is needed.
- If they are experienced and willing the a more participative or democratic leadearship is appropriate.
- If the group is not receptive or lack specific skills then a high level of directive leadership is needed.
- If they are experienced and willing the a more participative or democratic leadearship is appropriate.
13
New cards
Taylorism's Approach
- Created by Fredrick Winslow Taylor.
- Observed workers working slower than their capabilities.
- Studied each element of the job.
- Determined what each worker should be producing.
- Designed a plan for the most efficent way to carry out everything. (Time and motion studies).
- Implemented picework pay system. He increased their wages based on meeting targets.
- Observed workers working slower than their capabilities.
- Studied each element of the job.
- Determined what each worker should be producing.
- Designed a plan for the most efficent way to carry out everything. (Time and motion studies).
- Implemented picework pay system. He increased their wages based on meeting targets.
14
New cards
Scientific Management
- Develop a science for each elemnt of a job.
- Scientifacally select employees and train them to do the job.
- Supervise to make sure they are following the specific way to perform at their jobs.
- Continue to plan the work but workers get the job done.
- Scientifacally select employees and train them to do the job.
- Supervise to make sure they are following the specific way to perform at their jobs.
- Continue to plan the work but workers get the job done.
15
New cards
4 Principles of Scientific Management
1. Select methods based on science.
2. Assign workers based on aptitudes.
3. Monitor work performance.
4. Properly divide the workload.
2. Assign workers based on aptitudes.
3. Monitor work performance.
4. Properly divide the workload.
16
New cards
Intuitive Thinking
- Their strategy is more trial and error.
- They are more willing to try different methods and are observant to non-verbal cues.
- Reinvents strategies everytime he deals with a particular proble.
- They are better suited to approach problems that are more loosely structured or the nature of the problem doesn't allow for predetemined methods.
- They are more willing to try different methods and are observant to non-verbal cues.
- Reinvents strategies everytime he deals with a particular proble.
- They are better suited to approach problems that are more loosely structured or the nature of the problem doesn't allow for predetemined methods.
17
New cards
4 Functions of Management (FoM)
Planning, organizing, leading and controlling.
18
New cards
Planning (FoM)
- To establish organizational objectives and a course of action to achieve them.
- Management makes strategic decisions to set the direction of the organization.
- Brainstorming of alternatives to choose the best option.
- Management makes strategic decisions to set the direction of the organization.
- Brainstorming of alternatives to choose the best option.
19
New cards
Organizing (FoM)
- To distribute resources resources.
- Delegate tasks to achive goals.
- Delegate tasks to achive goals.
20
New cards
Leading (FoM)
- Motivating employees.
- Influencing their behavior to achive organizational objectives.
- Influencing their behavior to achive organizational objectives.
21
New cards
Controlling (FoM)
- Evaluating the plans execution.
- Adjusting the course of action to achive their objectives.
- Tasks manager can do in this phase could be training or managing deadlines.
- Adjusting the course of action to achive their objectives.
- Tasks manager can do in this phase could be training or managing deadlines.
22
New cards
Motivation
The intrinsinc and extrinsinc factors that stimulate people to take action that lead to achieving goals.
23
New cards
Intrinsinc Motivation
It comes from the satisfaction derived from working on and completing a task.
24
New cards
Extrinsinc Motivation
It comes from external rewards related to performing a task like salary, benefits or other compensations given by the company.
25
New cards
Indicators of Poor Staff Motivation
Absenteeism, lateness, poor performance, labor turnover, grievances and poor response rate.
26
New cards
Absenteeism
Deliberate absence where ther is no reasonable explanation and usually follows a pattern.
27
New cards
Lateness
Usually habitual.
28
New cards
Poor Performance
Poor quality of work, low levels of work and/or wasting of materials.
29
New cards
Labor Turnover
People leave for negative reasons and even if they don't go to another job they are trying to get one.
30
New cards
Grievances
More complaints from the workforce and might increase the amount of union disputes.
31
New cards
Poor Response Rate
Workers don't respond or very little to orders or leadership.
32
New cards
Taylorism's Relevance to Modern Industry
- Some manager still belive money is the only motivation for staff.
- Intorduced the idea of carefully selecting staff.
- The time and motion studies technique but with the involvement of staff.
- Still important as effiiency is reliant on having the best woy to work.
- Limited relevance as it is difficult to identify the output of each worker.
- Intorduced the idea of carefully selecting staff.
- The time and motion studies technique but with the involvement of staff.
- Still important as effiiency is reliant on having the best woy to work.
- Limited relevance as it is difficult to identify the output of each worker.
33
New cards
Taylorism's Limitations
- Workers have more needs than just money.
- Requires an appropriate selcetion procedure.
- Autocratic approach makes workers suspicious of Taylor just makingt hem work harder.
- The no discussion or feedback to the approach makes it undesirable.
- Payment method is not widely used.
- Quantity over quality.
- Requires an appropriate selcetion procedure.
- Autocratic approach makes workers suspicious of Taylor just makingt hem work harder.
- The no discussion or feedback to the approach makes it undesirable.
- Payment method is not widely used.
- Quantity over quality.
34
New cards
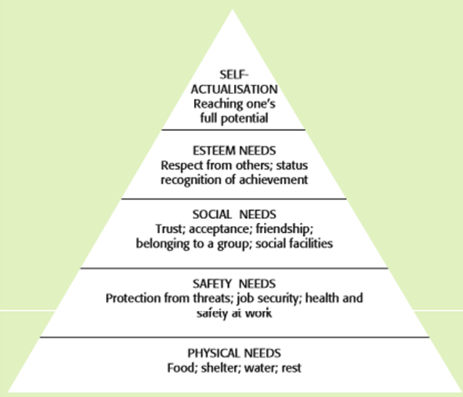
Maslow's Motivation Theory
Hierarchy of human needs:
1. Individuals need to start from the bottom.
2. Once a level has been satisfied they'll want to achive the next one.
3. Everyone is capable of reaching their potential but not all reach self-actualization.
4. Going back is possible as the satisfaction from one level can be taken back.
1. Individuals need to start from the bottom.
2. Once a level has been satisfied they'll want to achive the next one.
3. Everyone is capable of reaching their potential but not all reach self-actualization.
4. Going back is possible as the satisfaction from one level can be taken back.
35
New cards
Maslow's Limitations
- Not everyone has the same needs.
- In practice it is difficult to identify the level of satisfaction for each need and what level they're on.
- Money is needed to satisfy physical but also other needs.
- Self-actualization is never permanent.
- In practice it is difficult to identify the level of satisfaction for each need and what level they're on.
- Money is needed to satisfy physical but also other needs.
- Self-actualization is never permanent.
36
New cards
Self-Actualization
It's a sense of self-fulfillment reached by feeling enriched and developed by what thy have learned and achieved.
37
New cards
Maslow's Levels of Need: Physical
Income enough to meet essential needs.
38
New cards
Maslow's Levels of Need: Safety
A contract to ensure job security, structured organization with defined authorities, guaranteeing health and safety conditions.
39
New cards
Maslow's Level of Need: Social
Team work, good communication and a sense of involvement for workers.
40
New cards
Maslow's Level of Need: Esteem
Recongnition of their work, status, advancement and responsability to gain respect from others.
41
New cards
Maslow's Level of Need: Self-Actualization and Fulfillment of Potential
Individuals are challenged by work sretches to give a sense of achievement. As well as opportunities to develop and apply skils to increase potential.
42
New cards
Herzberg's Motivation Theory
- Also known as two factor theory.
- A study that identofied what led workers to have very positive and very negative feelings about their jobs.
- A study that identofied what led workers to have very positive and very negative feelings about their jobs.
43
New cards
Herzberg's Factors for Job Satisfaction
The motivators:
1. Achievement.
2. Recognition of achievement.
3. The work itself. (Intrinsinc factor)
4. Responsability.
5. Advancement.
1. Achievement.
2. Recognition of achievement.
3. The work itself. (Intrinsinc factor)
4. Responsability.
5. Advancement.
44
New cards
Herzberg's Factors for Job Dissatisfaction
The hygiene factors:
1. Comapny policy and administration.
2. Supervision.
3. Salary.
4. Relationship with others.
5. Working conditions.
They are extrinsinc factors.
1. Comapny policy and administration.
2. Supervision.
3. Salary.
4. Relationship with others.
5. Working conditions.
They are extrinsinc factors.
45
New cards
Consequences of Herzberg's Theory
- Pay and working conditions can be improved but not directly relate to motivation levels.
- The motivators need to be in place for workers to be willing and eprform well.
- Higher pay can improve working conditions and heavy supervision.
- The motivators need to be in place for workers to be willing and eprform well.
- Higher pay can improve working conditions and heavy supervision.
46
New cards
McClelland's Motivation Theory
- States that all individuals are driven by achivement, affiliation and power.
- Identifying peoples drivers to be motivated makes it more likely for them to complete and perform well on a task.
- Inspired by Maslow but more in depth as to what motivations help reach self-actualization.
- Everyone has primary need hat drives their motivation for sel-actualization.
- Identifying peoples drivers to be motivated makes it more likely for them to complete and perform well on a task.
- Inspired by Maslow but more in depth as to what motivations help reach self-actualization.
- Everyone has primary need hat drives their motivation for sel-actualization.
47
New cards
McClelland's Accquired Need: Achievement
- Motivated from completing tasks.
- Look for projects and situations that highlight their skills and are not so challenging but also not so easy.
- Look for projects and situations that highlight their skills and are not so challenging but also not so easy.
48
New cards
McClelland's Accquired Need: Affiliation
- Motivated by connections with others.
- Motivates interpersonal relationsships and emotional connections.
- Motivates interpersonal relationsships and emotional connections.
49
New cards
McClelland's Accquired Need: Power
- Motivated by authority or control.
- Look for positions and relationships where they can demonstrate their leadership skills and be the main decision maker.
- Look for positions and relationships where they can demonstrate their leadership skills and be the main decision maker.
50
New cards
Implementing McClelland's Motivation Theory
1. Determine the driver.
- Overview of the person and what they do.
2. Establish the motivator.
- Achievement, affiliation or power.
3. Implement the process.
4. Refine as needed.
- Overview of the person and what they do.
2. Establish the motivator.
- Achievement, affiliation or power.
3. Implement the process.
4. Refine as needed.
51
New cards
Deci and Ryan's Motivation Theory
- Self-determination theory states that people becoem determined when their needs for competence, connection and autonomy are satisfied.
- It assumes the need for growth drives behavior.
- As well as that autonomous motivation is important. (Intrinsinc motivation)
- It assumes the need for growth drives behavior.
- As well as that autonomous motivation is important. (Intrinsinc motivation)
52
New cards
Components of Self-Determination
Autonomy, competence, connections.
53
New cards
Deci and Ryan's Self-Determination: Autonomy
- Feeling of control of their behavior and goals.
- Sense of ability to take direct action for change.
- Sense of ability to take direct action for change.
54
New cards
Deci and Ryan's Self-Determination: Competence
- Perfecting and learning different skills.
- When they feel they are capacitated for performing a task they are more likely take actions to help achive their goals.
- When they feel they are capacitated for performing a task they are more likely take actions to help achive their goals.
55
New cards
Deci and Ryan's Self-Determination: Connections
- Experiencing a sense of beolongin and attachement to people.
56
New cards
Deci and Ryan's Motivation Theory in the Workplace
- Allowing staff to take active rolls.
- Not overusing on extrinsinc rewards.
- Offering greater responsabilities to employees.
- Offering support and encouragement.
- Providing meaningful feedback.
- Not overusing on extrinsinc rewards.
- Offering greater responsabilities to employees.
- Offering support and encouragement.
- Providing meaningful feedback.
57
New cards
Equity and Expectancy Motivation Theory
- Attempt to explain behavior influenced by the norm of equity.
- People who feel they are in inequitable relationships try to reduce their distress by restoring actual or perceived equity to their relationship.
- It consists of four interdependant positions.
- People who feel they are in inequitable relationships try to reduce their distress by restoring actual or perceived equity to their relationship.
- It consists of four interdependant positions.
58
New cards
Equity and Expectancy Propositions
- Maximizing outcomes.
- Maximixing rewards in groups.
- Distress proportional to inequitable situation.
- Elimination of distress.
- Maximixing rewards in groups.
- Distress proportional to inequitable situation.
- Elimination of distress.
59
New cards
Equity and Expectancy Propositions: Maximizing outcomes
People will try to maximize outcomes where an outcome is a reward minus punishment.
60
New cards
Equity and Expectancy Propositions: Maximizing Rewards in Groups.
People in groups maximize collective rewards by implementing systems to quitably dostribute resources. Rewarding people for their equitable treatment and punishment for inequitable treatment.
61
New cards
Equity and Expectancy Propositions: Distress Proportional to Inequitable Situation
People when they fond themselves in inequitable relationships become distressed in a level poportional to the level of distress presented.
62
New cards
Equity and Expectancy Propositions: Elimination of Distress
People will attemptto eliminate their distress and resolve inequity when in inequitable situations.
63
New cards
Expectancy Motivation Theory
- It studies the relationship between worker motivation and valence, instrumentality and expectancy.
- Great relationship between rewards and quantity of work to achive said reward.
- Employees is more likely to increase effort if it results in positive reward.
- If employees don't receive a reward they will be demotivated to perform better.
- Great relationship between rewards and quantity of work to achive said reward.
- Employees is more likely to increase effort if it results in positive reward.
- If employees don't receive a reward they will be demotivated to perform better.
64
New cards
Expectancy Theory: Valence
- The perceived value of an outcome like the value of the reward.
- If they don't value a particular reward they won't be as likely to better performance and obtain it.
- If they don't value a particular reward they won't be as likely to better performance and obtain it.
65
New cards
Expectancy Theory: Intrumentality
- Perceived probability that an outcome will lead to another.
- Ex. Greater rewards = greater job satisfaction.
- Ex. Greater rewards = greater job satisfaction.
66
New cards
Expectancy Theory: Expectancy
- Perceived probability that a behaviour will lead to an intrumental outcome.
- Ex. Working harder = greater reward.
- Ex. Working harder = greater reward.
67
New cards
Organizational Structure
The internal, formal framework of a business that explains the way management is organized and connected as well as how authority functions within the company.
68
New cards
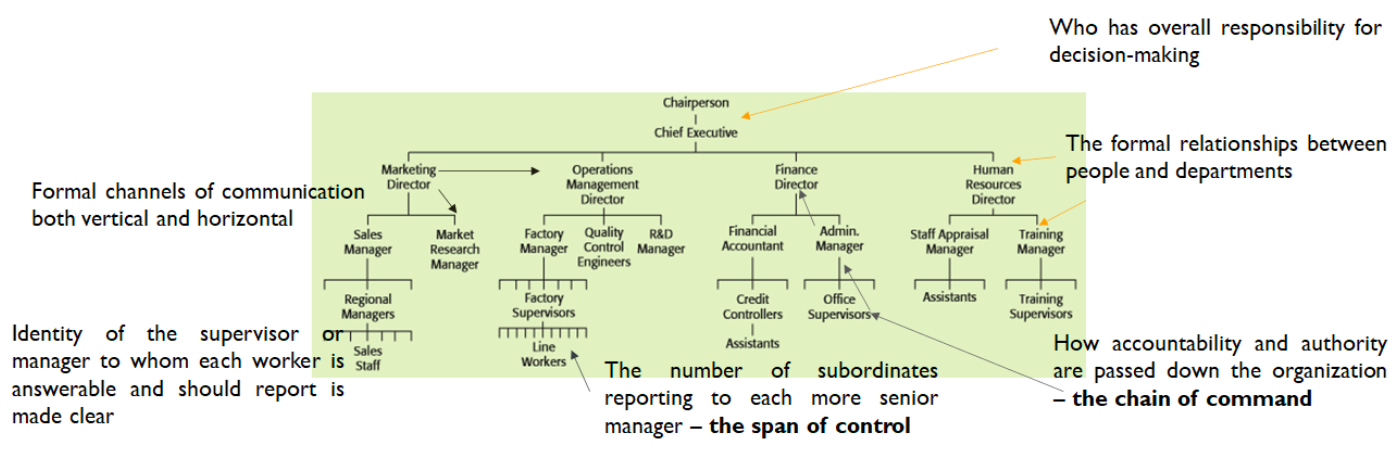
Organizational Structure by Function
- Overall responsability for decision making.
- Relationships between people and departments.
- Chain of command.
- Subordinates of each manager.
- Formal channels of communication.
- Relationships between people and departments.
- Chain of command.
- Subordinates of each manager.
- Formal channels of communication.
69
New cards
Key Principles of Organizational Structure
Level of hierachy, chain of command, span of control, delegation, accountability, delayering, bureaucracy
70
New cards
Principle of Organizational Structure: Level of Hierarchy
- Were personnel have equal satus and authority.
- Each level is a rank of the staff.
- Lower ranks are subordinates to the higher ranks.
- More levels more ranks in the organization.
- Each level is a rank of the staff.
- Lower ranks are subordinates to the higher ranks.
- More levels more ranks in the organization.
71
New cards
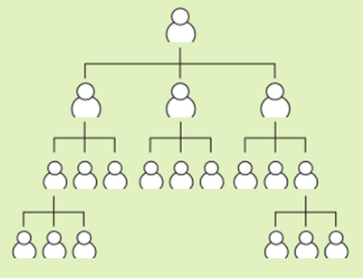
Level of Hierarchy: Tall Organizational Structure
- Large number of levels.
- Main problems are communication, distorted messages, narrow spans of control and greater sense of remoteness.
- Main problems are communication, distorted messages, narrow spans of control and greater sense of remoteness.
72
New cards
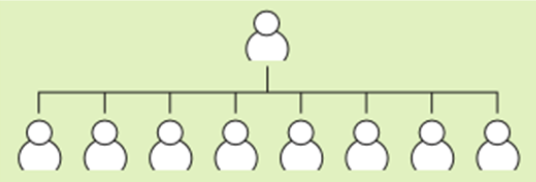
Level of Hierarchy: Flat Organizational Structure
- Few levels of hierarchy.
- More delgation as they can't control that much work efficiently.
- Beter communication between ranks.
- More delgation as they can't control that much work efficiently.
- Beter communication between ranks.
73
New cards
Principle of Organizational Structure: Chain of Command
- Route in which authority is passed dow.
- Instructions are passed down the hierarchy.
- The longer the chain of command the slower the communication.
- Instructions are passed down the hierarchy.
- The longer the chain of command the slower the communication.
74
New cards
Principle of Organizational Structure: Span of Control
- Number of subordinates of a manager.
- Wide or narrow depending of the amount of epmloyees they are directly responsible of.
- Wide or narrow depending of the amount of epmloyees they are directly responsible of.
75
New cards
Principle of Organizational Structure: Delegation
- Passing authority down the hierarchy.
76
New cards
Principle of Organizational Structure: Accountability
- Obligation of an individual to be responsible of their activities and present results transparently.
77
New cards
Principle of Organizational Structure: Delayering
- The removing of one or several levels of the hierarchy.
78
New cards
Principle of Organizational Structure: Bureaucracy
- A system with standarized procedures and rules.
79
New cards
Delayering Advantages
- Reduction of costs.
- Shorter chain of command.
- Improved communication.
- Increased span of control and delgation.
- Increase in motivation due to less remoteness.
- Shorter chain of command.
- Improved communication.
- Increased span of control and delgation.
- Increase in motivation due to less remoteness.
80
New cards
Delayering Disadvantages
- Could be unique costs of making managers redundant.
- Increased workloads for managers.
- Sense of job insecurity.
- Increased workloads for managers.
- Sense of job insecurity.
81
New cards
Centralization
Keeping al decision making at the center of the organization.
82
New cards
Decentralization
When decision making powers are passed down the organization to empower subordinates and regional managers.
83
New cards
Centralization Advantages
- Bureaucracy should lead to quick decision making.
- Consistent policies prevent conflicts between divisions and confusions in consumers.
- Senior manager are experienced making decisions and make them in the interest of the whole business.
- Central buying allow for greater economies of scale.
- Consistent policies prevent conflicts between divisions and confusions in consumers.
- Senior manager are experienced making decisions and make them in the interest of the whole business.
- Central buying allow for greater economies of scale.
84
New cards
Decentralization Advantages
- Local decisions reflect different conditions as manager have closer contact with consumers.
- Junior managers can develop skills to prepare them for challenging roles.
- Delegation and empowerement impoving motivation.
- Decision making in response to changes are quicker and more flexible.
- Junior managers can develop skills to prepare them for challenging roles.
- Delegation and empowerement impoving motivation.
- Decision making in response to changes are quicker and more flexible.
85
New cards
Factors Influencing Organizational Structure
- Size of business.
- Style of leadearship and culture of management.
- Reduction of activities due to recession or competition leading to delayering to cut costs.
- Corporate objectives.
- New technologies.
- Style of leadearship and culture of management.
- Reduction of activities due to recession or competition leading to delayering to cut costs.
- Corporate objectives.
- New technologies.
86
New cards
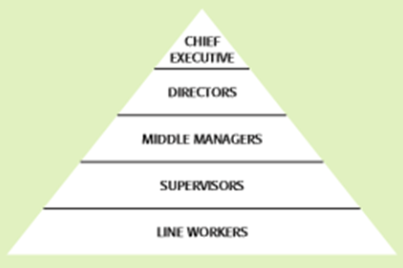
Hierarchal Structure
- Structure in which power and responsibility is clearly specified and assigned to individuals according to their position in the hierarchy.
- Can be organized by product, function or region.
- Can be organized by product, function or region.
87
New cards
Hierarchal Structure Advantages
- Very common.
- They don't have to be based on departments.
- The growth in the organization for an employee is defined in the levels of hierarchy.
- Roles and chain of commad is clear and well defined.
- Usually implemented in businesess were the importance of the role detrmines the position in the hierarchy.
- They don't have to be based on departments.
- The growth in the organization for an employee is defined in the levels of hierarchy.
- Roles and chain of commad is clear and well defined.
- Usually implemented in businesess were the importance of the role detrmines the position in the hierarchy.
88
New cards
Hierarchal Structure Disadvantages
- Suggest communication (going down) is the norm.
- Few horizontal links between departments leading to lack of coordination.
- Managers are blind to other problems outside their own department.
- Inflexible structure leading to change and resistance.
- Due to managers defending their position and importance of their own department.
- Few horizontal links between departments leading to lack of coordination.
- Managers are blind to other problems outside their own department.
- Inflexible structure leading to change and resistance.
- Due to managers defending their position and importance of their own department.
89
New cards
Matrix Structure
- Cretaes project teams instead of traditional function departments.
- Task or project focused.
- Emphasis is places on an individual's ability to contribute to the team instead of their position in the hierarchy.
- Task or project focused.
- Emphasis is places on an individual's ability to contribute to the team instead of their position in the hierarchy.
90
New cards
Matrix Structure Advantages
- Total communication between team members.
- Less focused on what is good for their department.
- Crossover ideas tend to create more successful solutions.
- New teams can be created quickly.
- It responds quickly to changing markets or techonological conditions.
- Less focused on what is good for their department.
- Crossover ideas tend to create more successful solutions.
- New teams can be created quickly.
- It responds quickly to changing markets or techonological conditions.
91
New cards
Matrix Structure Disadvantages
- Less direct control.
- Reduced bureaucratic control.
- Teams could have several leaders if they keep a department structure but allow crossovers for teams leading to conflicts of interest.
- Reduced bureaucratic control.
- Teams could have several leaders if they keep a department structure but allow crossovers for teams leading to conflicts of interest.
92
New cards
Horizontally Linked Structure
- Usually IT or high-tech sectors.
- Grouped by function of planning, building and running.
- Allows to respond to quickly changing market conditions and technologies.
- May not be as effective in organizations that produce products with longer lifespasn or service industries.
- Grouped by function of planning, building and running.
- Allows to respond to quickly changing market conditions and technologies.
- May not be as effective in organizations that produce products with longer lifespasn or service industries.
93
New cards
Horizontally Linked Structure: Planning
It is responsible for developing new projects and can include employees from research, development or finance.
94
New cards
Horizontally Linked Structure: Building
In charge of constructing the projects.
95
New cards
Horizontally Linked Structure: Running
Includes sales, marketing and maintenance.
96
New cards
Handy's Shamrock Organization
- Focused on people as the most important resource of an orgaization.
- Divided into core workers, temporary workers and contract workers.
- Flexible structure
- Emphasizes the ability of lower levels to make decisions as much as possible and adapt quickly to allow for growth.
- Usually habide spanof control.
- Communication more common among workers than from management.
- Divided into core workers, temporary workers and contract workers.
- Flexible structure
- Emphasizes the ability of lower levels to make decisions as much as possible and adapt quickly to allow for growth.
- Usually habide spanof control.
- Communication more common among workers than from management.
97
New cards
Handy's Shamrock Organization: Core Workers
- Consists of technicians, senior managers and professionals.
- They ensure that the corporate aims and objectives are well established
- Their pay depend on the succes of the company and have set salaries.
- They ensure that the corporate aims and objectives are well established
- Their pay depend on the succes of the company and have set salaries.
98
New cards
Temporary workers
- The majority of the workforce, contingency employees that perform routine jobs.
- Flexible and many times part-time workers.
- They normally don't have a lot of development within the company.
- Paid on the periods of time they work.
- Flexible and many times part-time workers.
- They normally don't have a lot of development within the company.
- Paid on the periods of time they work.
99
New cards
Contract Workers
- Self-employed professionals and contractors on a project-reliant basis.
- Are pay-based on performance to ensure high contract output.
- These contract workers are not managed by the company directly, so they can be more flexible.
- These contract workers can also be formal employees who provide their external services.
- Are pay-based on performance to ensure high contract output.
- These contract workers are not managed by the company directly, so they can be more flexible.
- These contract workers can also be formal employees who provide their external services.
100
New cards
Flexible Structures
Flat organizational structure, team based structure and region-branch structure.