DNA, Protein, Mutations
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
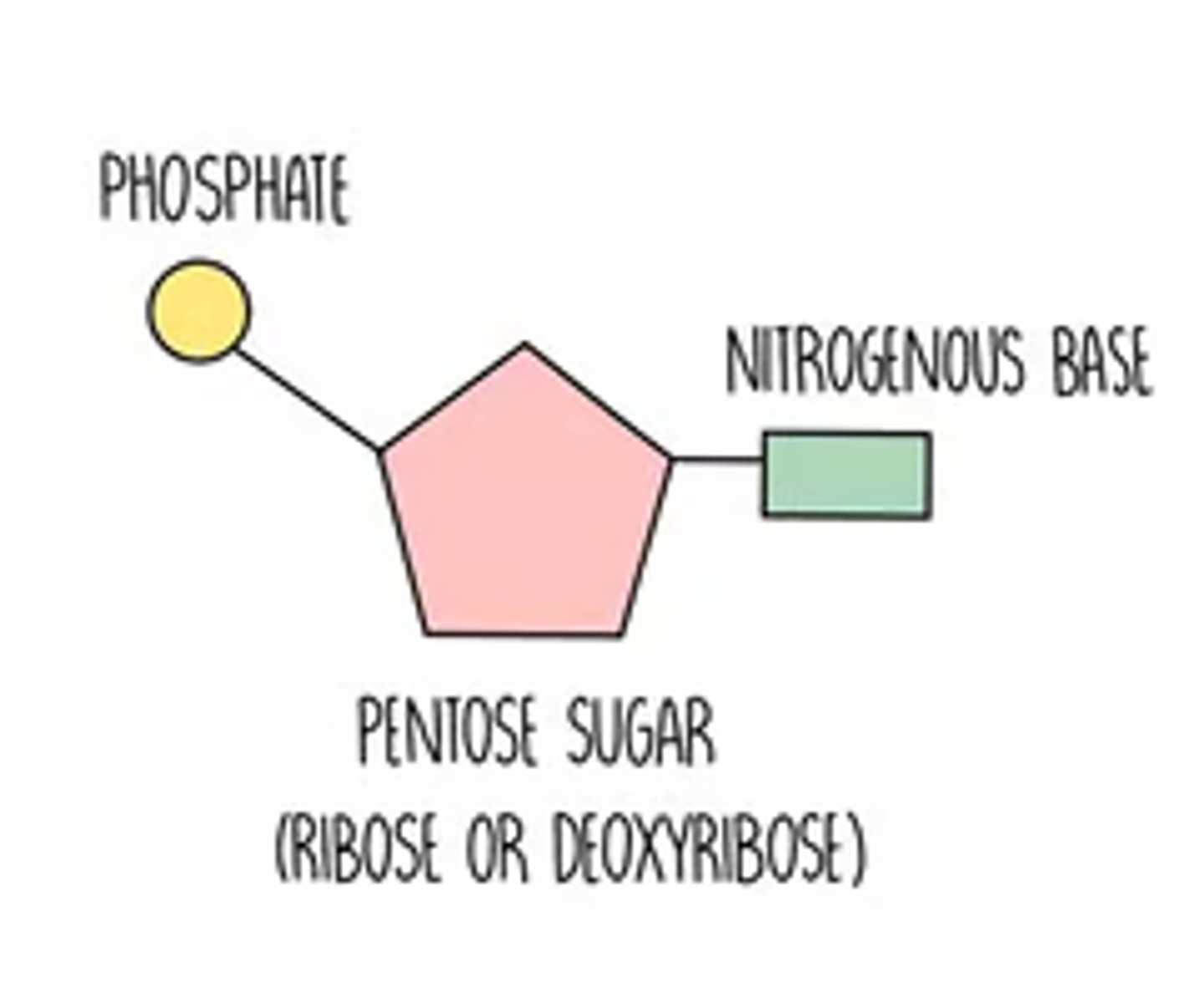
Nucleotides
the repeating subunit that makes up DNA
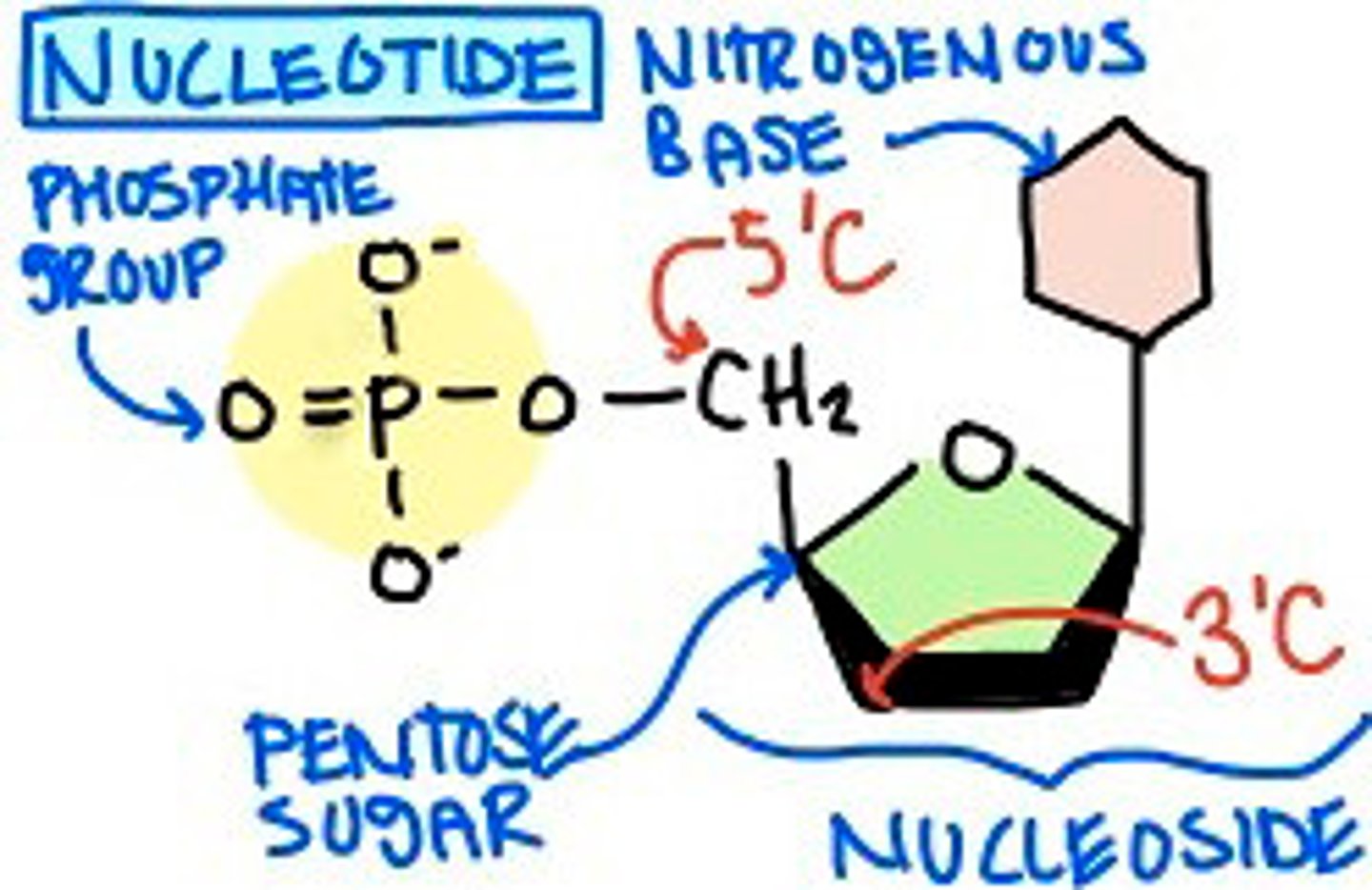
DNA Nucleotide 3 Parts
1. Deoxyribose sugar
2. phosphate
3. Nitrogenous base
4 DNA Nitrogenous bases
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
Who determined the relationship between nucleotides?
Erwin Chargaff (1950)

Chargaff's Rule
always same amount of Adenine as Thymine (same for C and G)
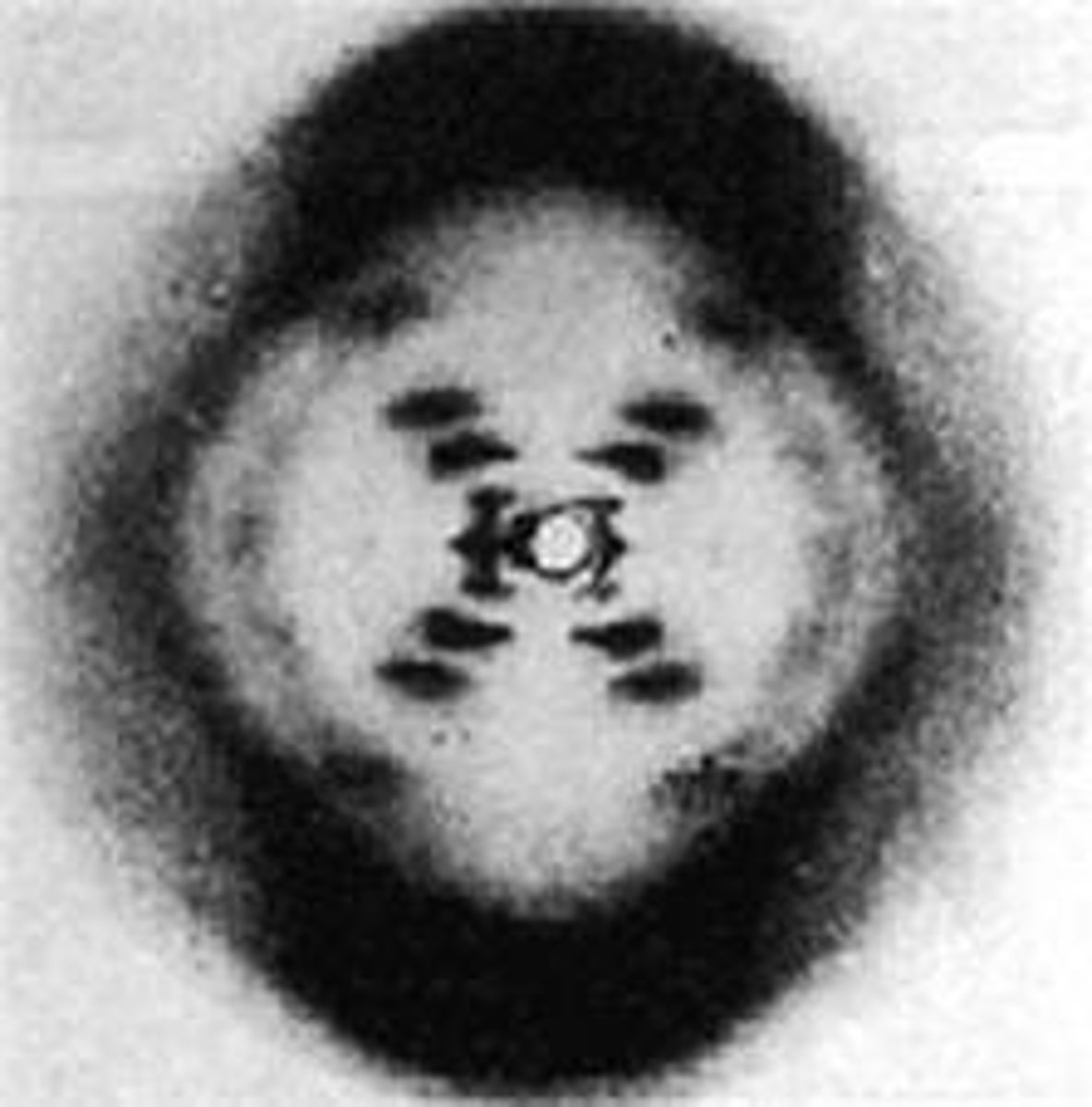
Who caught an X-ray Diffraction showing a DNA Double Helix?
Rosalind Franklin (1952)
Who discovered the DNA Double Helix model?
Watson and Crick (1953)

What forms the backbone of DNA?
Sugar and Phosphate
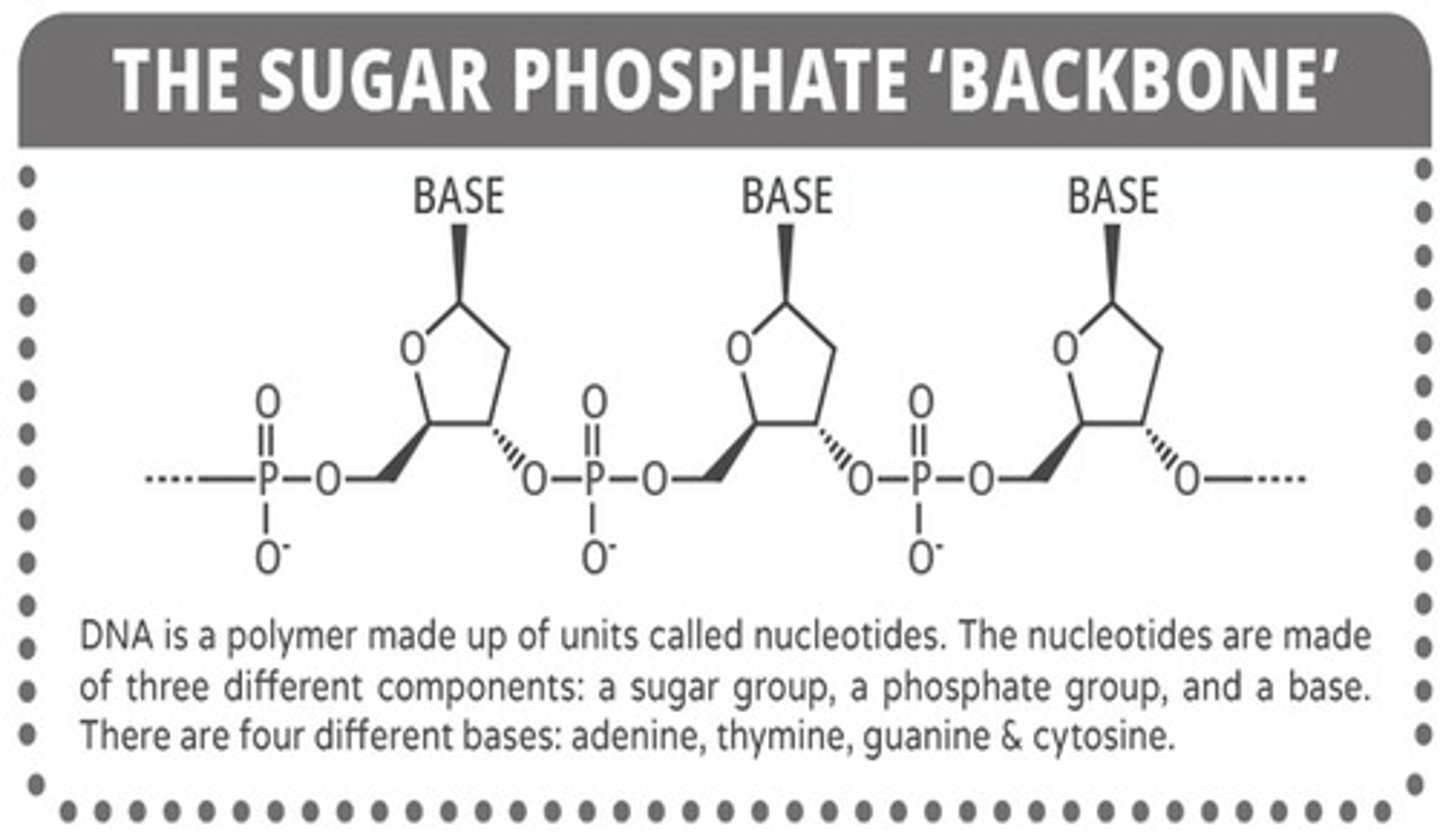
Nitrogen bases bond in the middle with weak _________ ____
Hydrogen bonds
All other bonds (Including the sugar-phosphate backbone) is made of what type of bond?
Covalent bonds
Nitrogen bases bond only to their __________
Complementary base pair
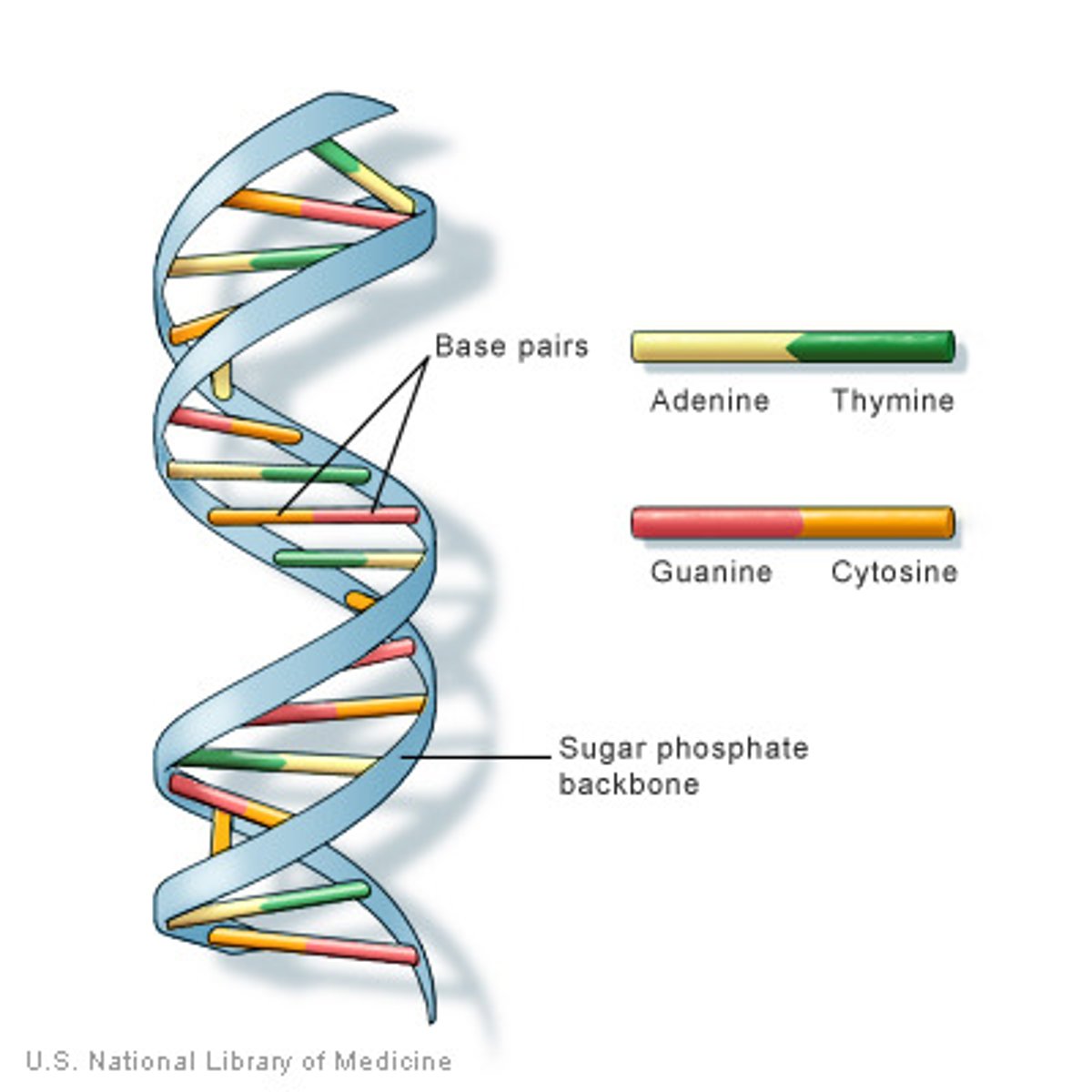
Complementary base pairing rules (DNA)
A bonds to T
G bonds to C
A _____ bonds to T
double
C _____ bonds to G
triple
Antiparallel
the strands run in opposite or antiparallel directions
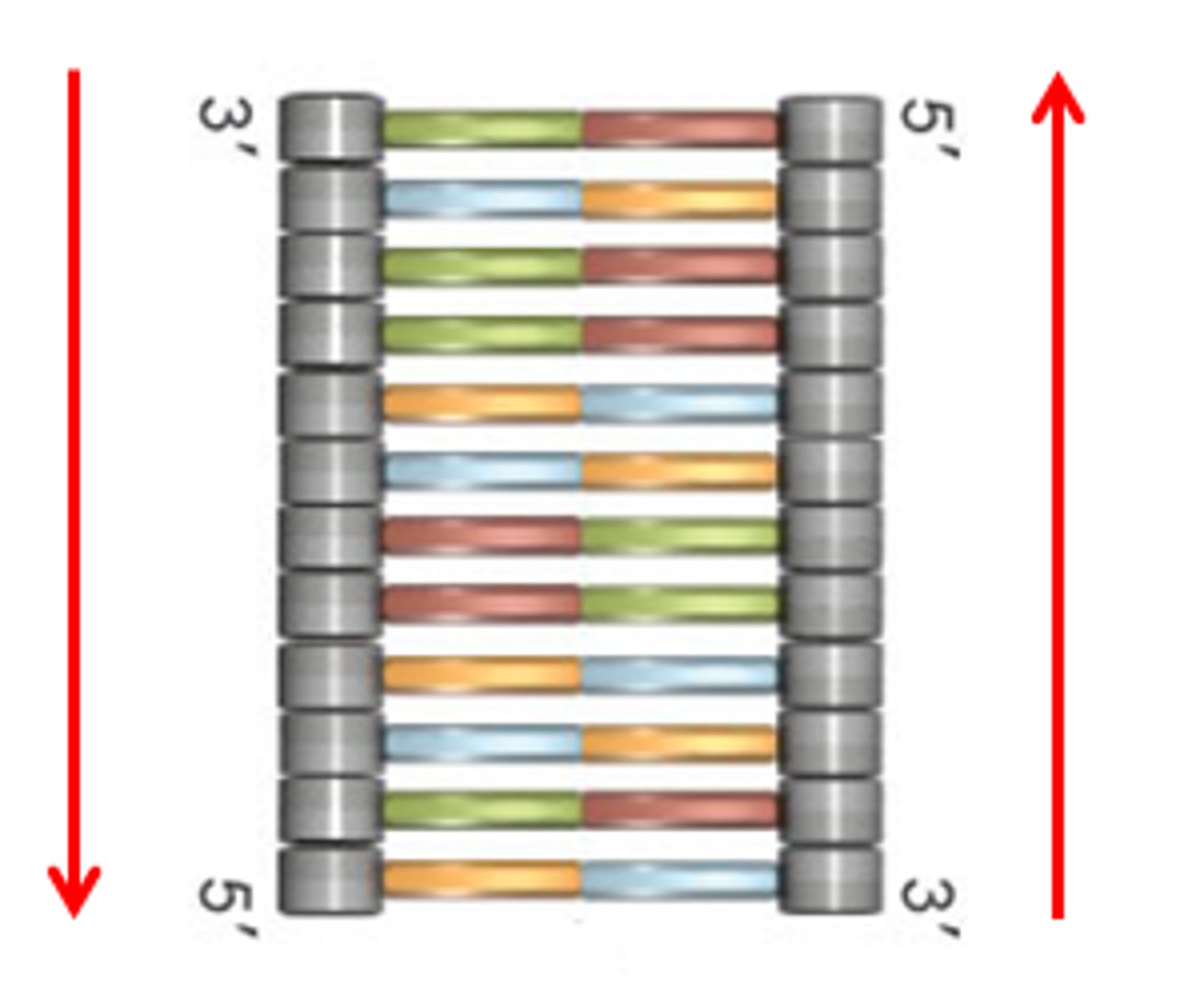
1sd strand runs in a __' to __' direction
5' to 3'
2nd strand runs in a __' to __' direction
3' to 5'
Phosphate end is ALWAYS the __' end
5'
Deoxyribose sugar is always the __' end
3'
RNA structure
Single strand of RNA nucleotides with exposed bases
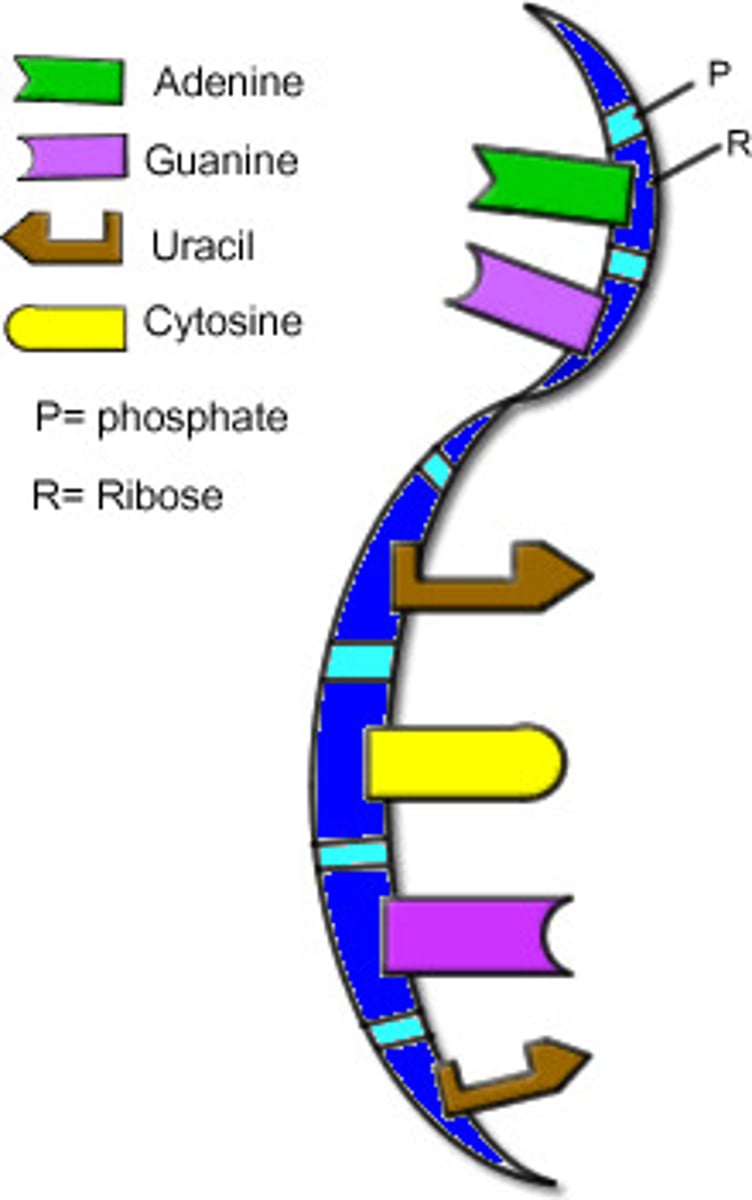
What type of sugar makes up RNA Nucleotides?
Ribose
RNA Bases
A with U
C with G
DNA Replication
the copying of DNA
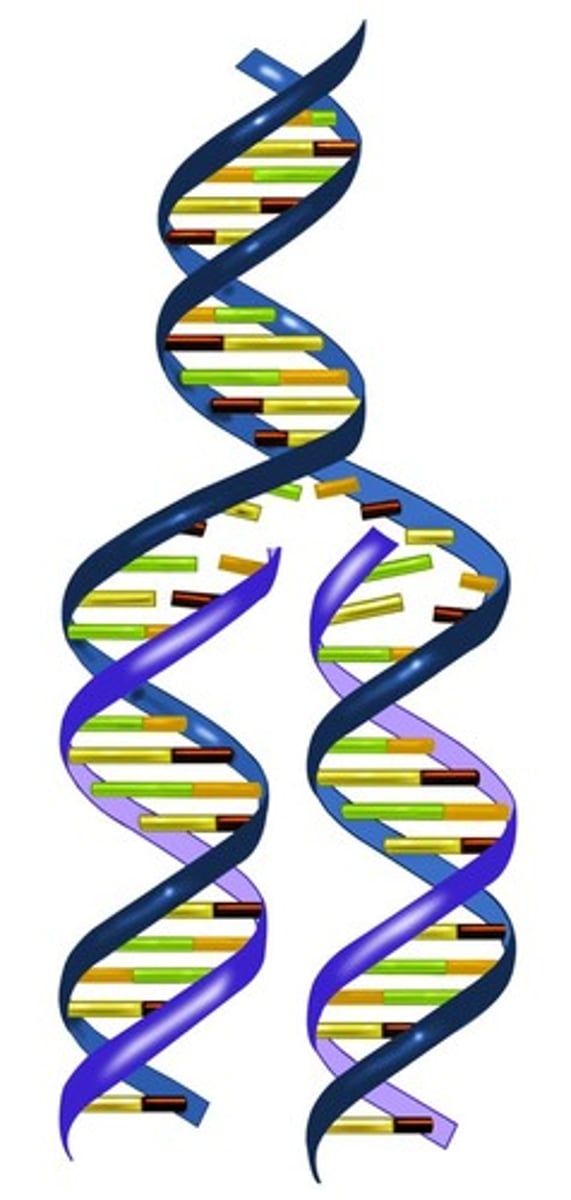

Why must DNA copy itself before cell division in mitosis?
To give each daughter cell an exact copy of the DNA
Why must DNA copy itself before cell division in meiosis?
so each daughter cell gets one of each chromosome
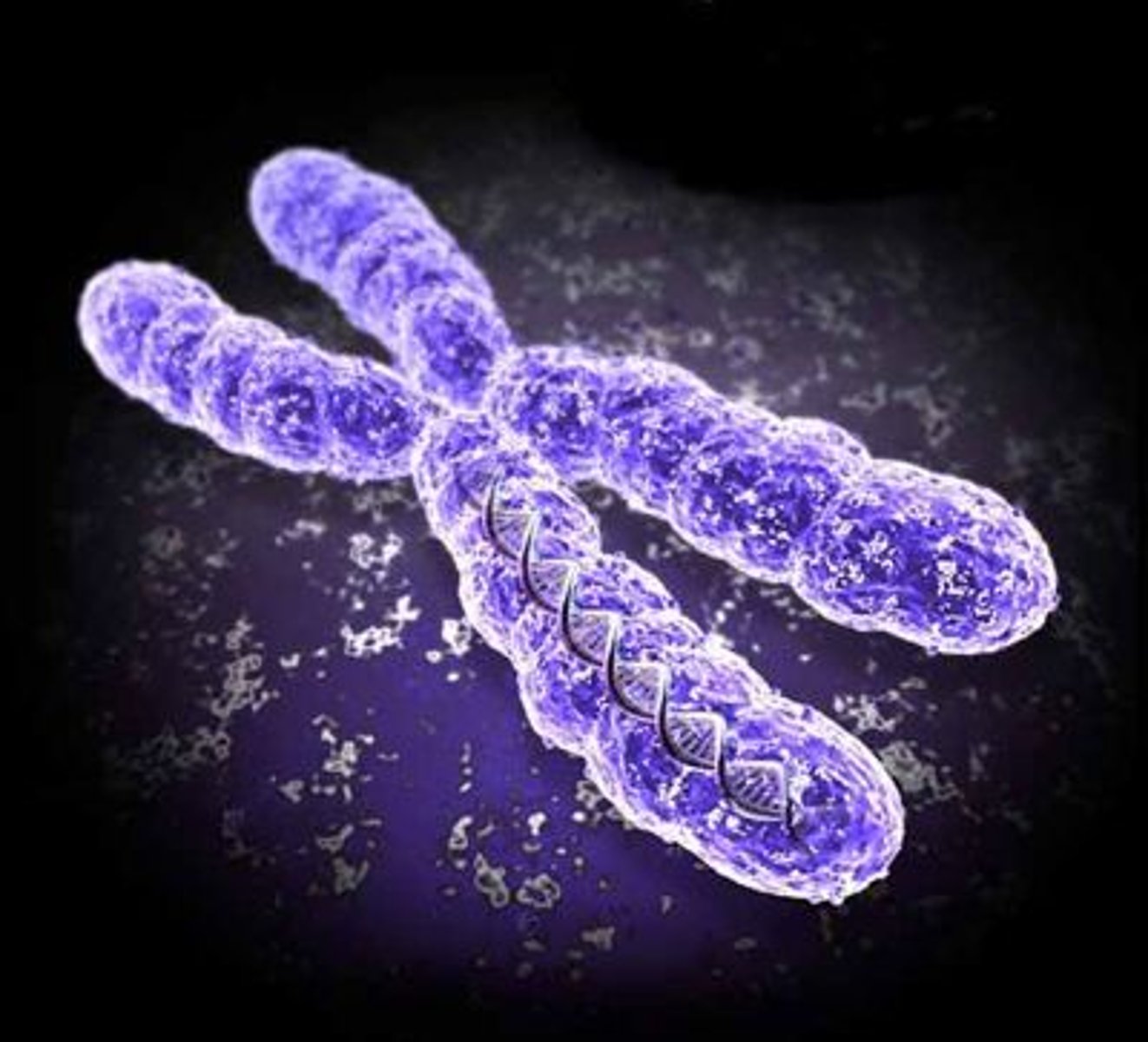
Chromosomes
tightly coiled strands of DNA
Gene
a piece of DNA that has instructions to code for ONE protein

One chromosome can contain _______ of genes
thousands
What phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur
S phase (of interphase)
Enzyme ______ unzips the DNA
helicase
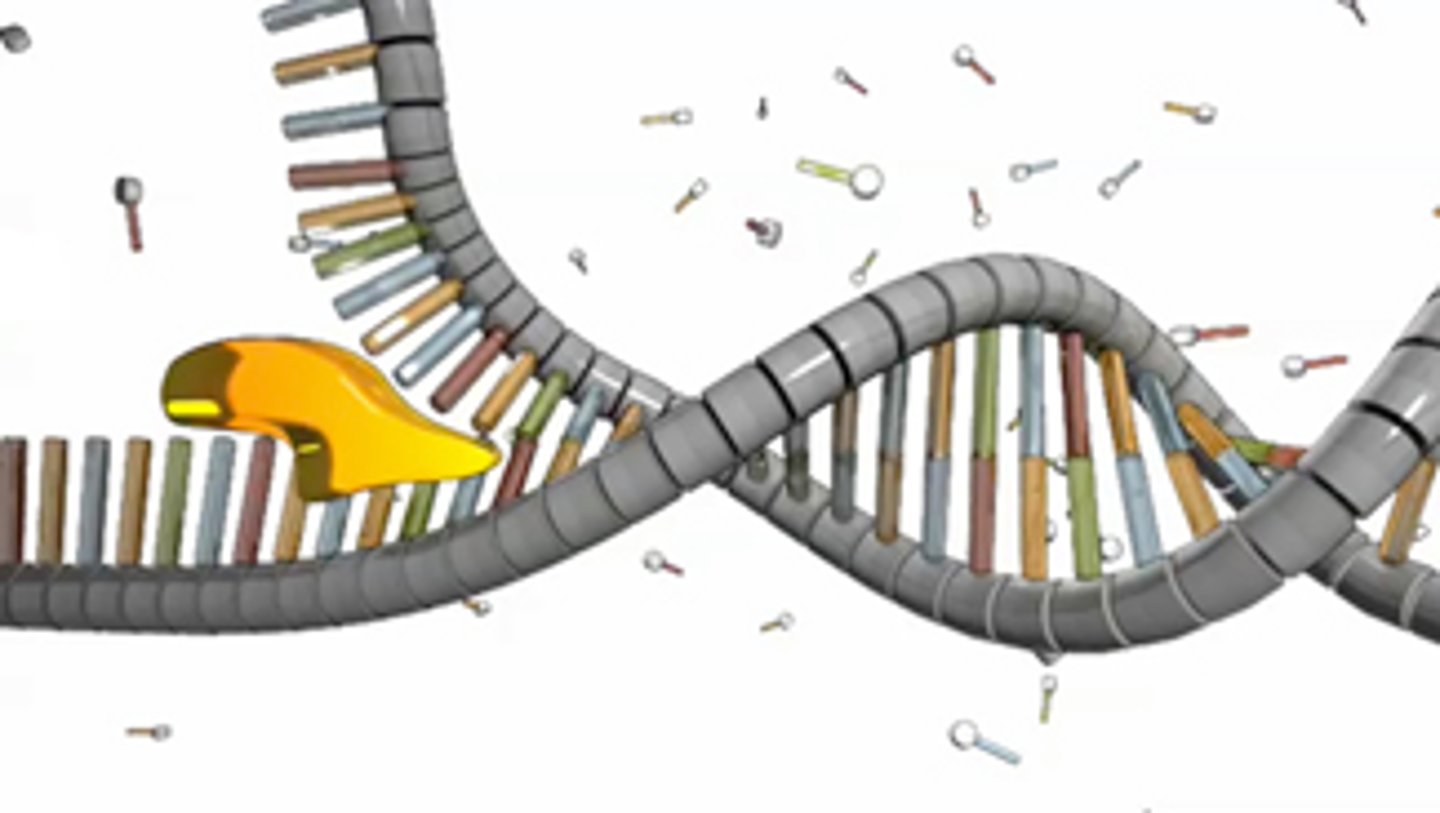
Openings in the DNA are called
origins of replication
Several places along the DNA will be unzipped at once. True or False?
True
Enzyme ______ _____ adds complementary nucleotides to template strands (DNA Replication)
DNA polymerase
DNA polymerase only adds nucleotides to the __' end of the template strand. This forms new DNA strands in the __' to ___' direction ONLY
3'
5' to 3'
Semi-Conservative Replication
in each new DNA double helix, one strand is from the original molecule, and one strand is new
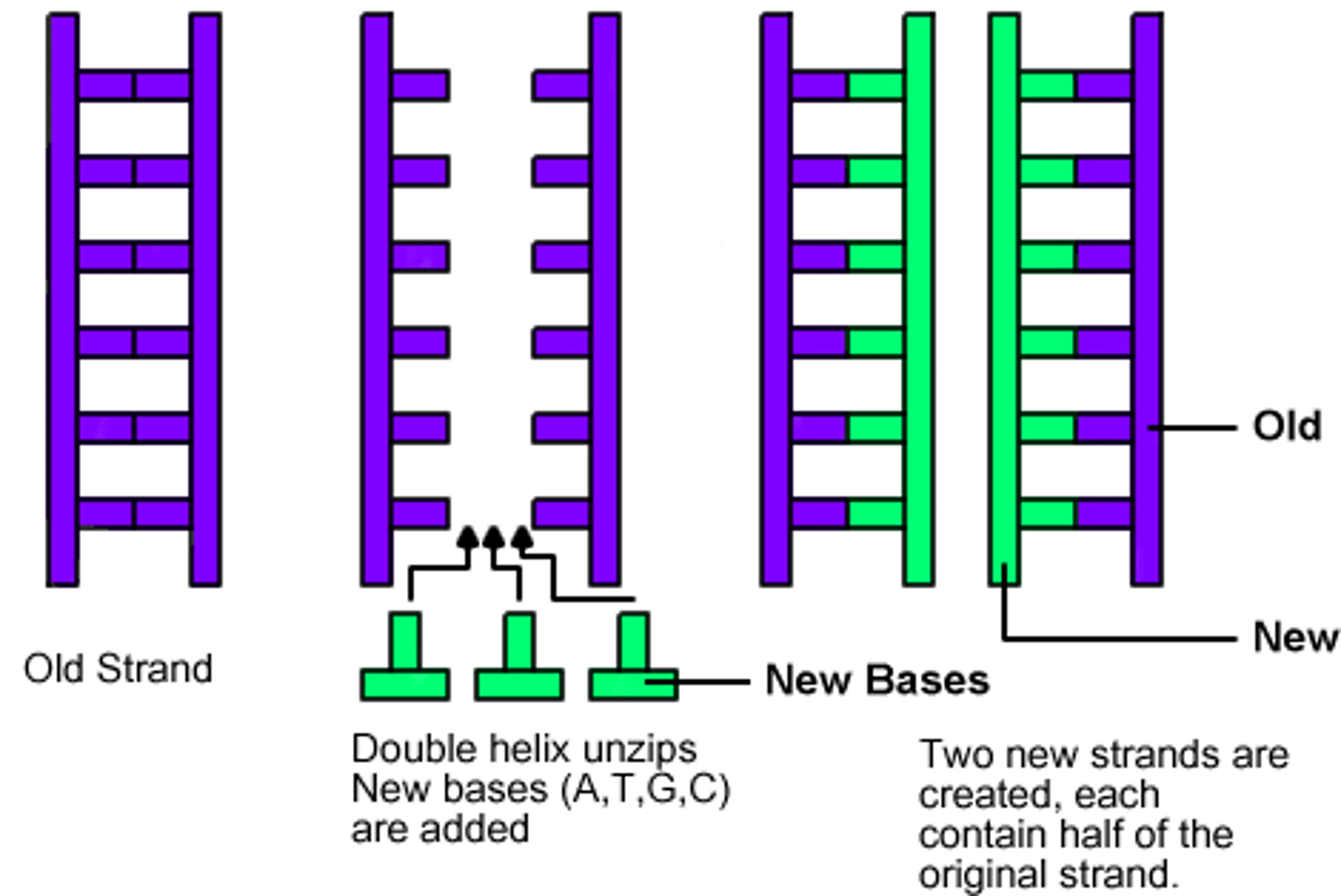
DNA Polymerase 2 roles
1. enzyme that matches up and join nucleotides to the template to produce new strands of DNA.
2. Also proofreads new DNA to make sure no errors
"Job" of DNA
code for proteins
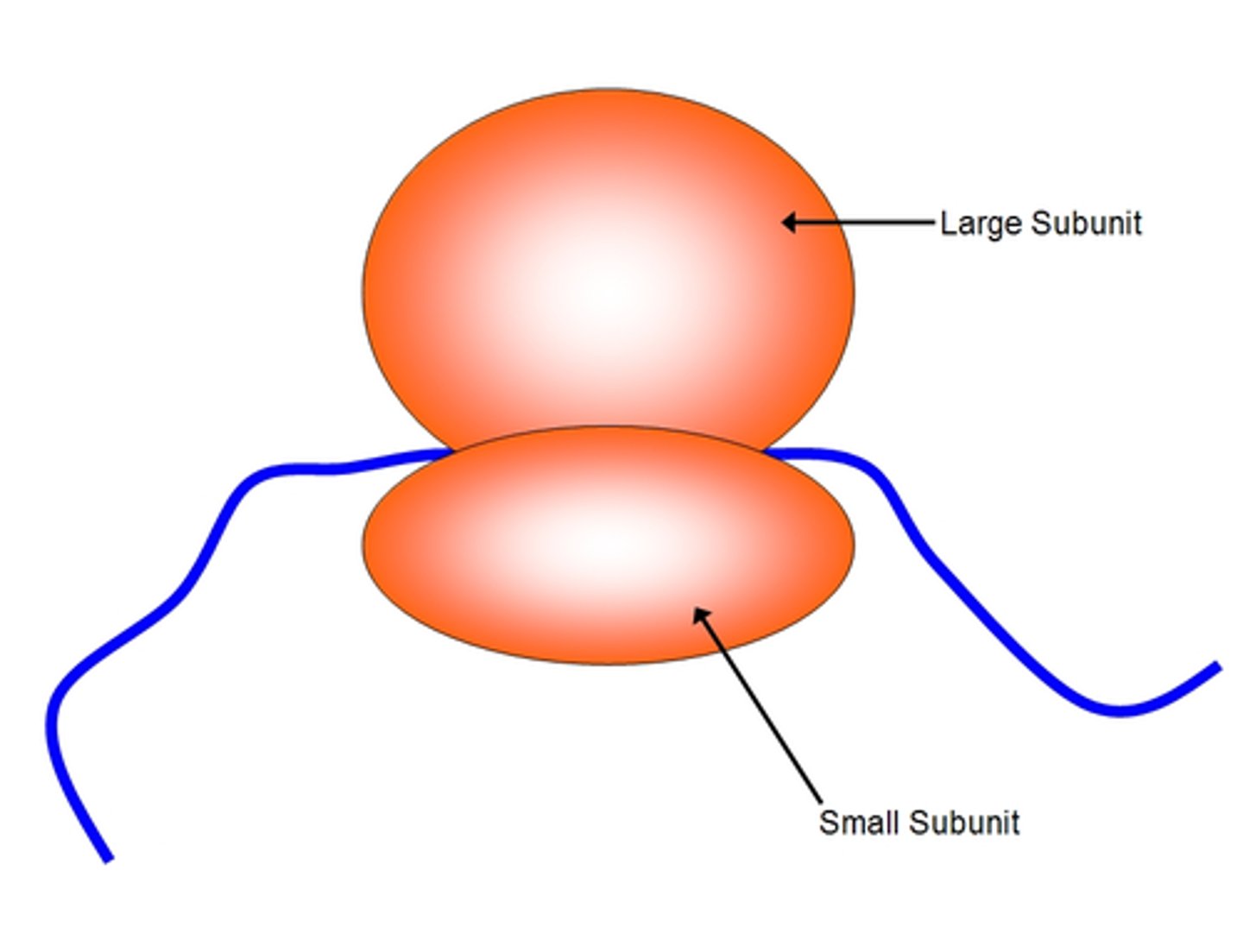
Which organelle makes proteins
Ribosomes
DNA can leave the nucleus. True or False
FALSE
How does mRNA exit the nucleus?
through nuclear pores
RNA's sugar
ribose sugar
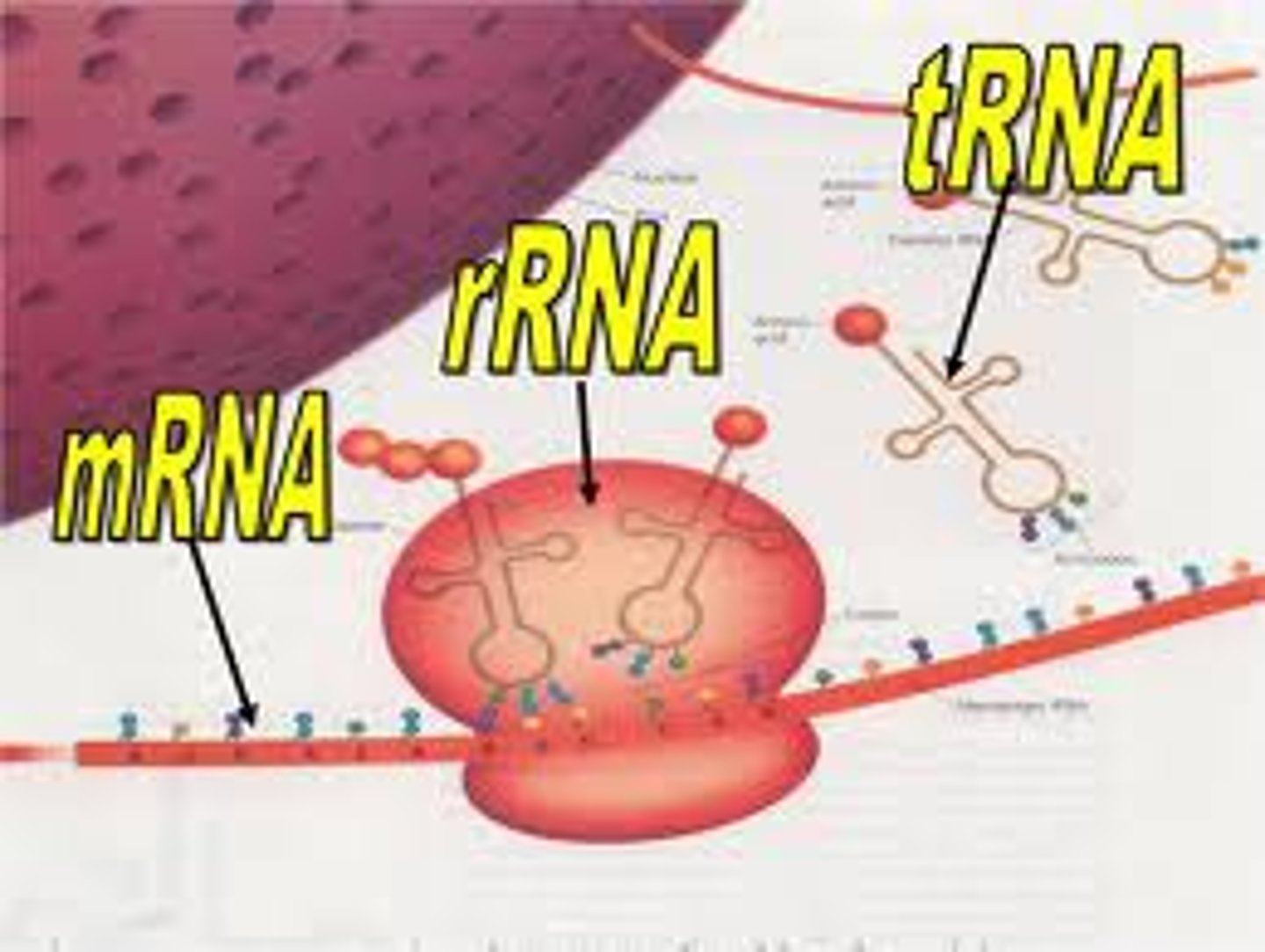
mRNA
messenger RNA
A copy of the DNA code for a gene, carries the gene code from the nucleus to the ribosome
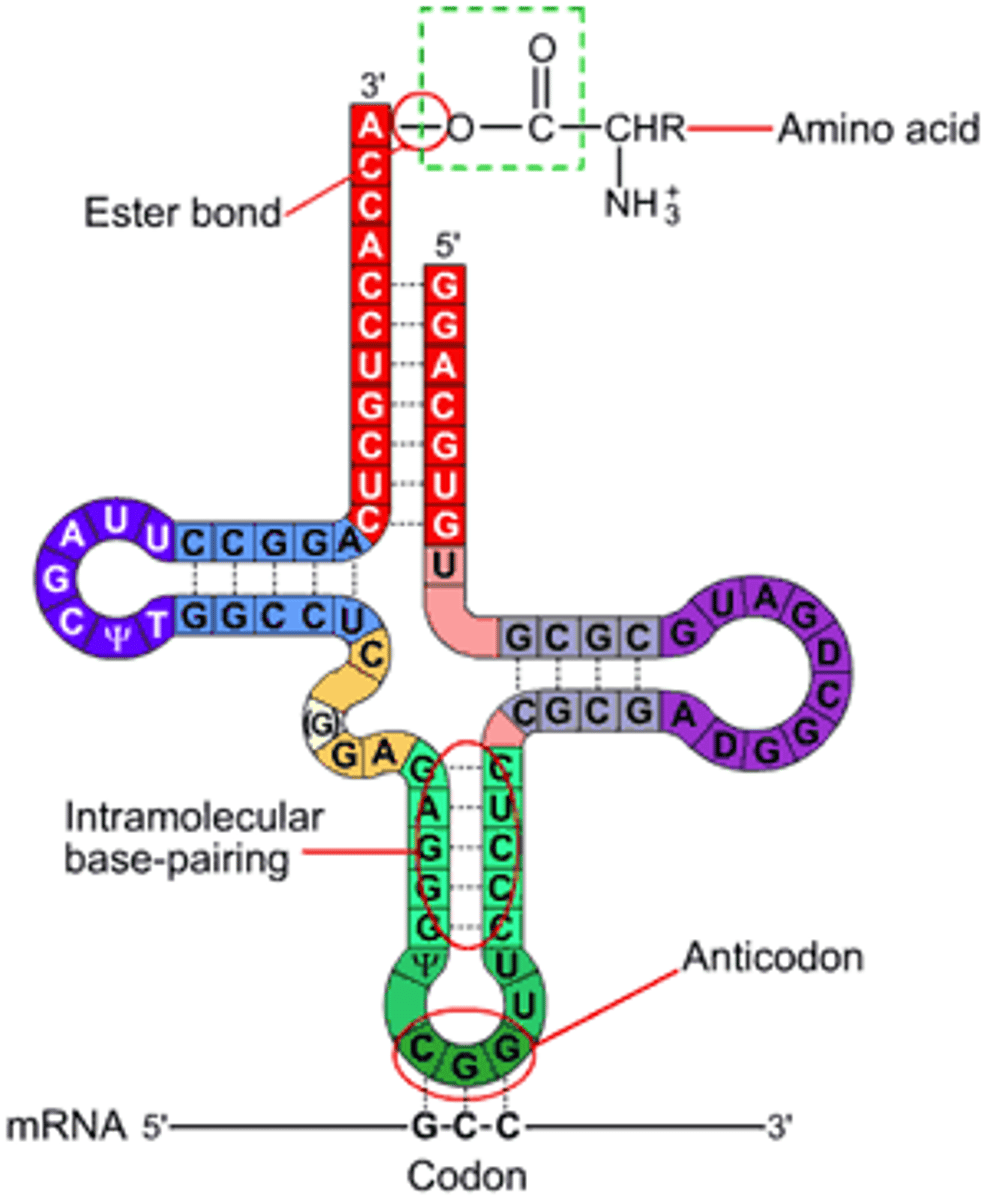
tRNA
transfer RNA
brings specific amino acids to ribosome
rRNA
ribosomal RNA
makes up structure of ribosome (along with protein)
Where does transcription occur?
in Nucleus
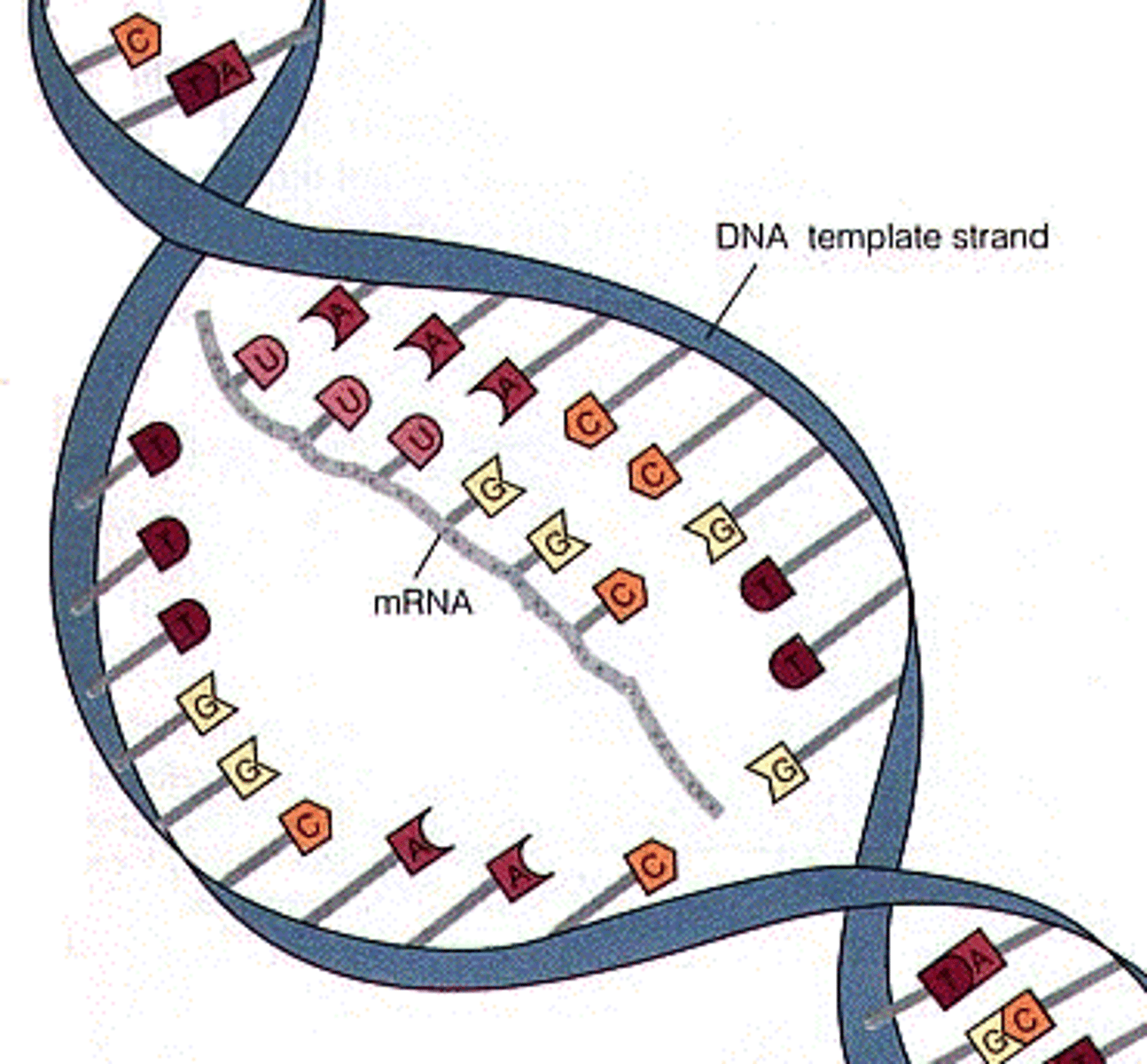
Transcription overview (3 step)
1. The DNA molecule unzips only in portion of the specific gene that will be copied.
2. A mRNA molecule created by the enzyme RNA polymerase makes a copy of the DNA's base sequence using RNA nucleotides.
3. the mRNA copy of the gene can leave the nucleus.
RNA Polymerase only binds to ______
Promoters
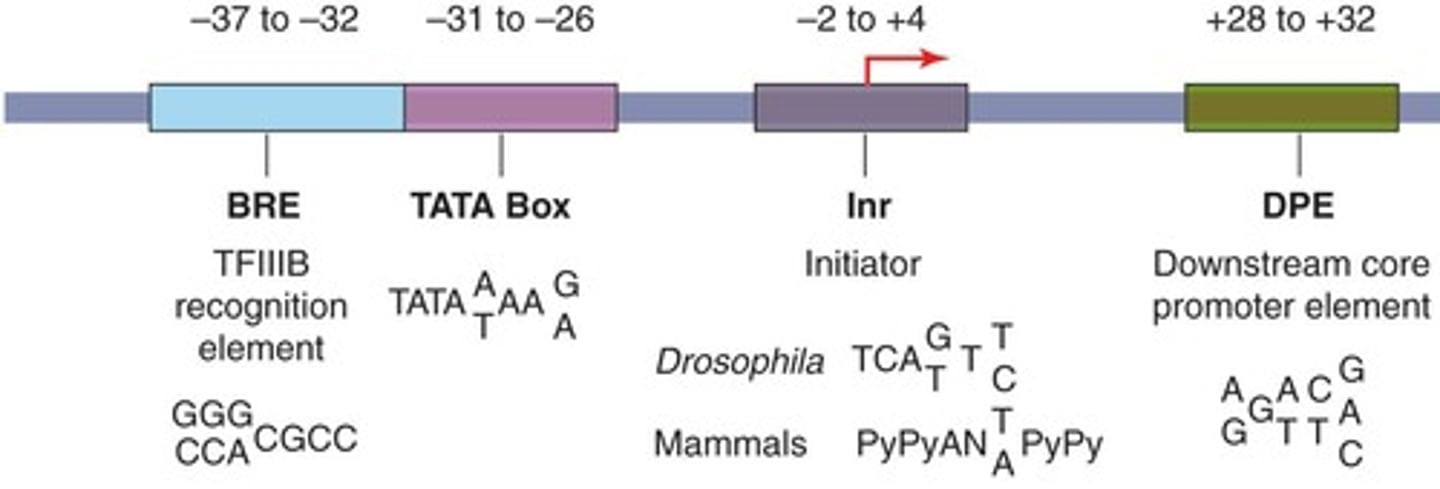
What tells RNA Polymerase to stop transcriping?
Terminator
Transcription Factors
1. Control rate of transcription: which genes and how often transcribed
2. Turn genes on and off. Control gene expression.
3. Help coordinate cell cycle
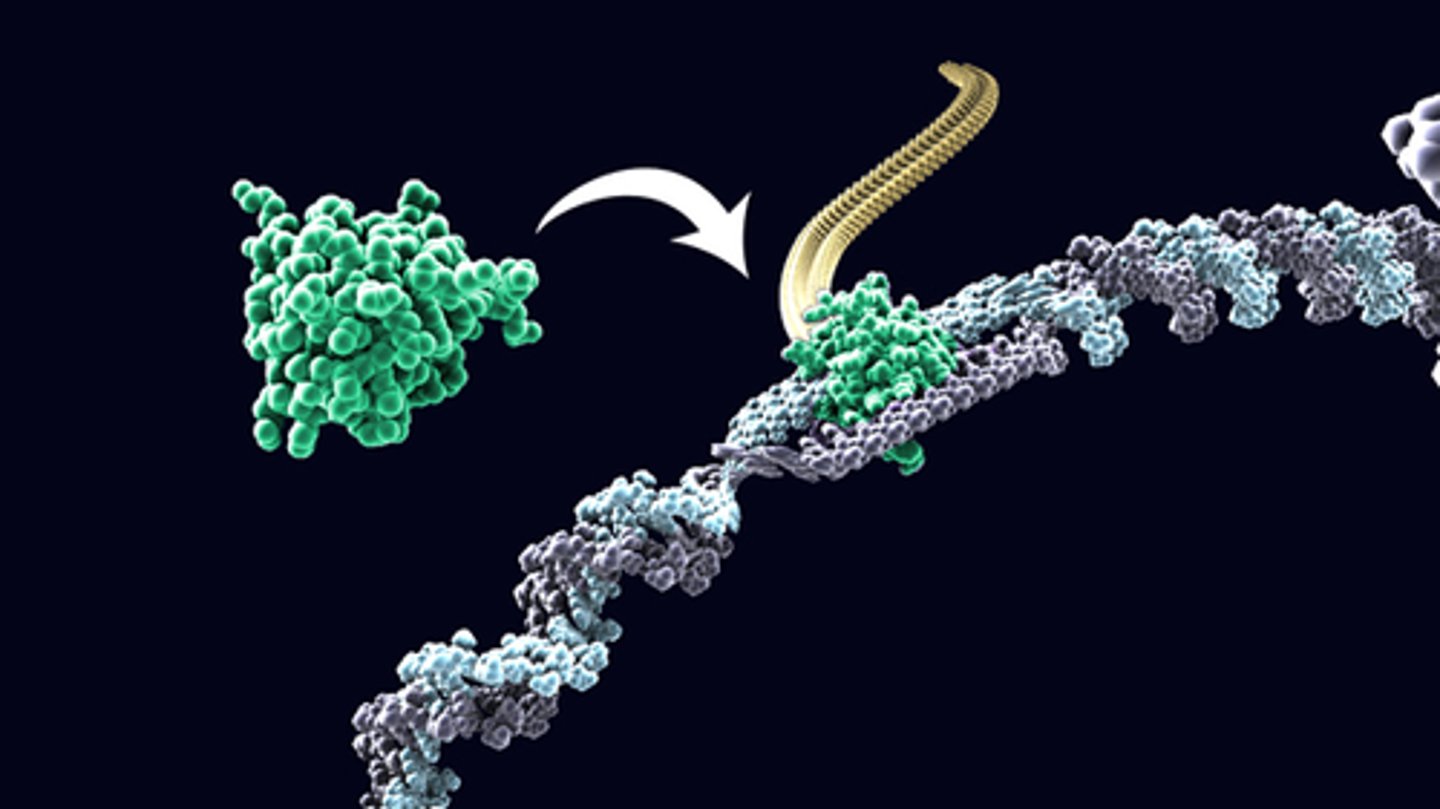
Where does translation occur?
Outside nucleus
Translation overview (4 steps)
1. mRNA attaches to a ribosome outside nucleus.
2. Ribosome reads the code 3 bases at a time (codon)
3. Codon on the mRNA matches the anticodon on the tRNA
4. A protein chain is formed.
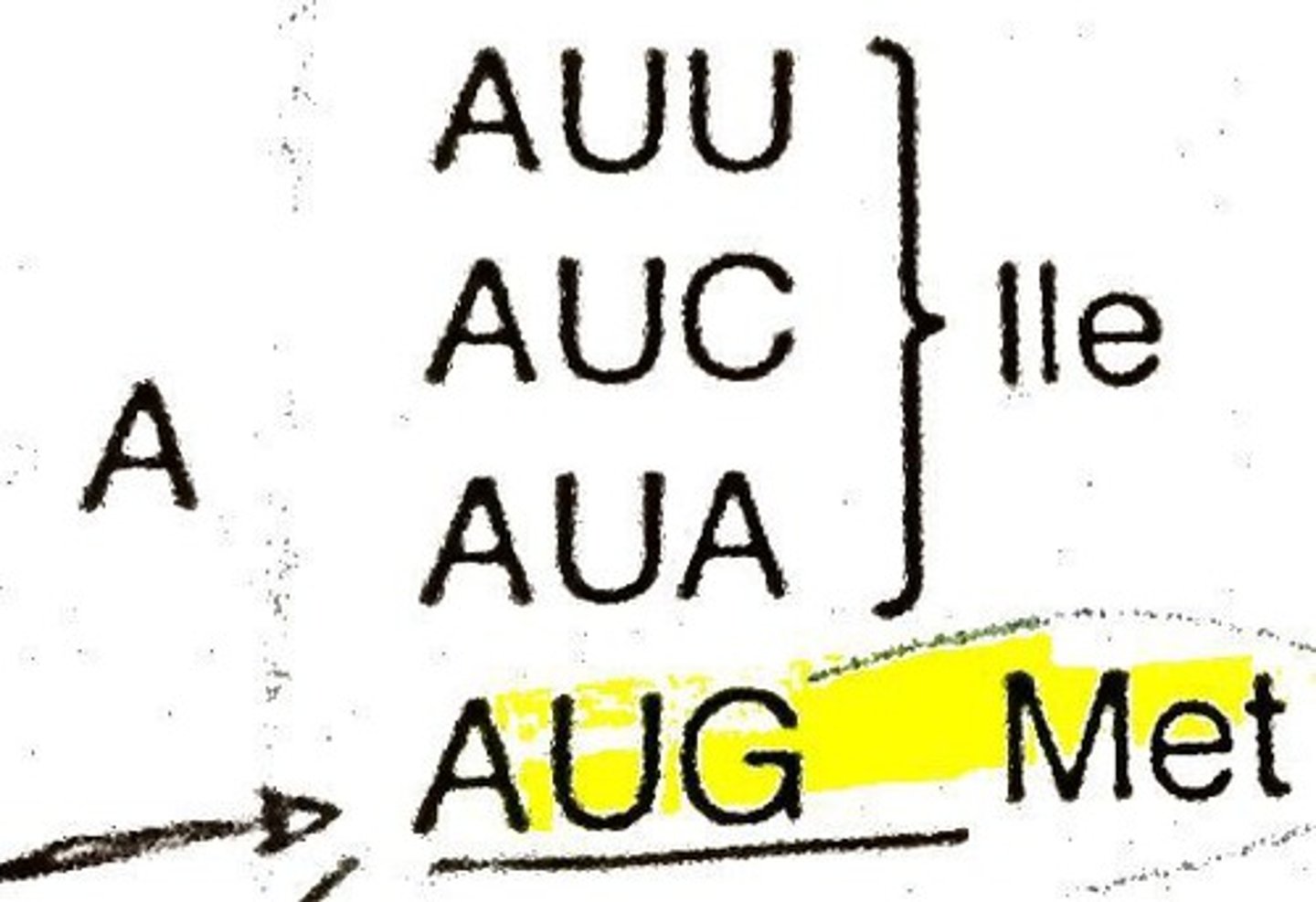
Start codon
AUG - methionine
How many amino acids are there?
20
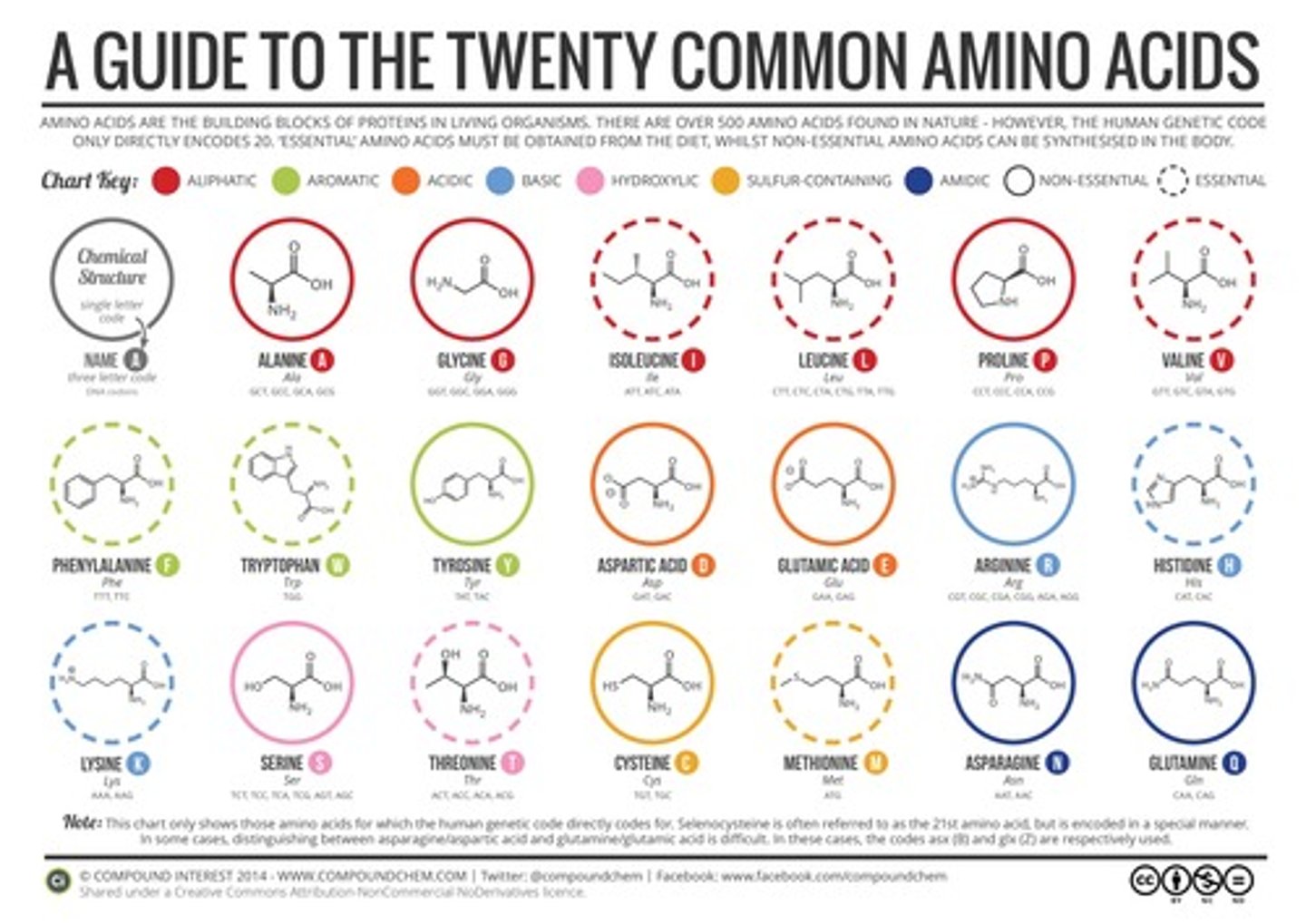
How many codons are there?
64
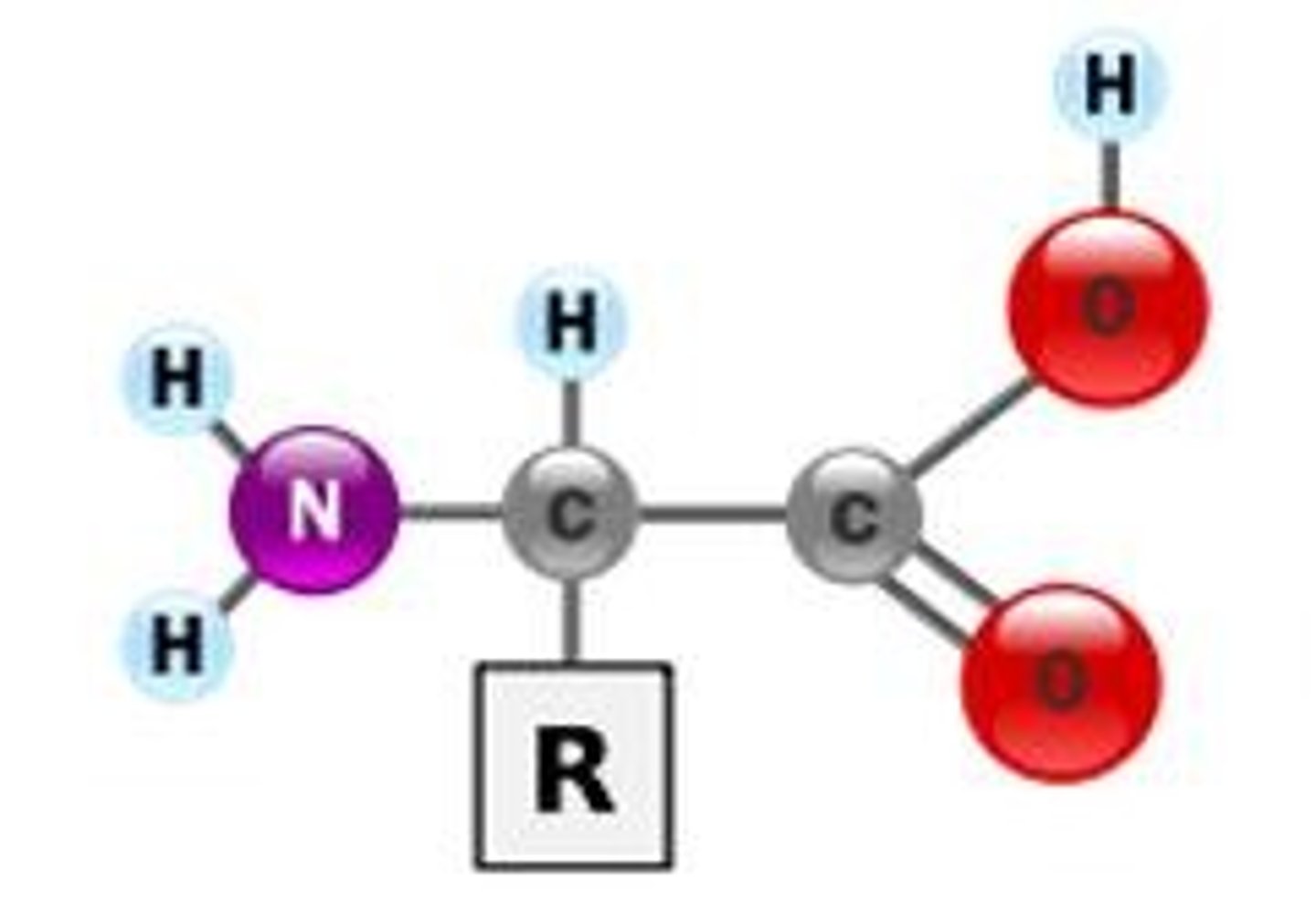
Proteins are made of??
Amino acids
Mutation
a change in DNA
Germ line or hereditary mutation
inherited from a parent and present in all the individuals cells
Somatic mutations
a mutation in somatic cells that can not be passed onto offspring. Caused by environmental factors.
Gene mutations / point mutations
changes in one or a few nucleotides that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence
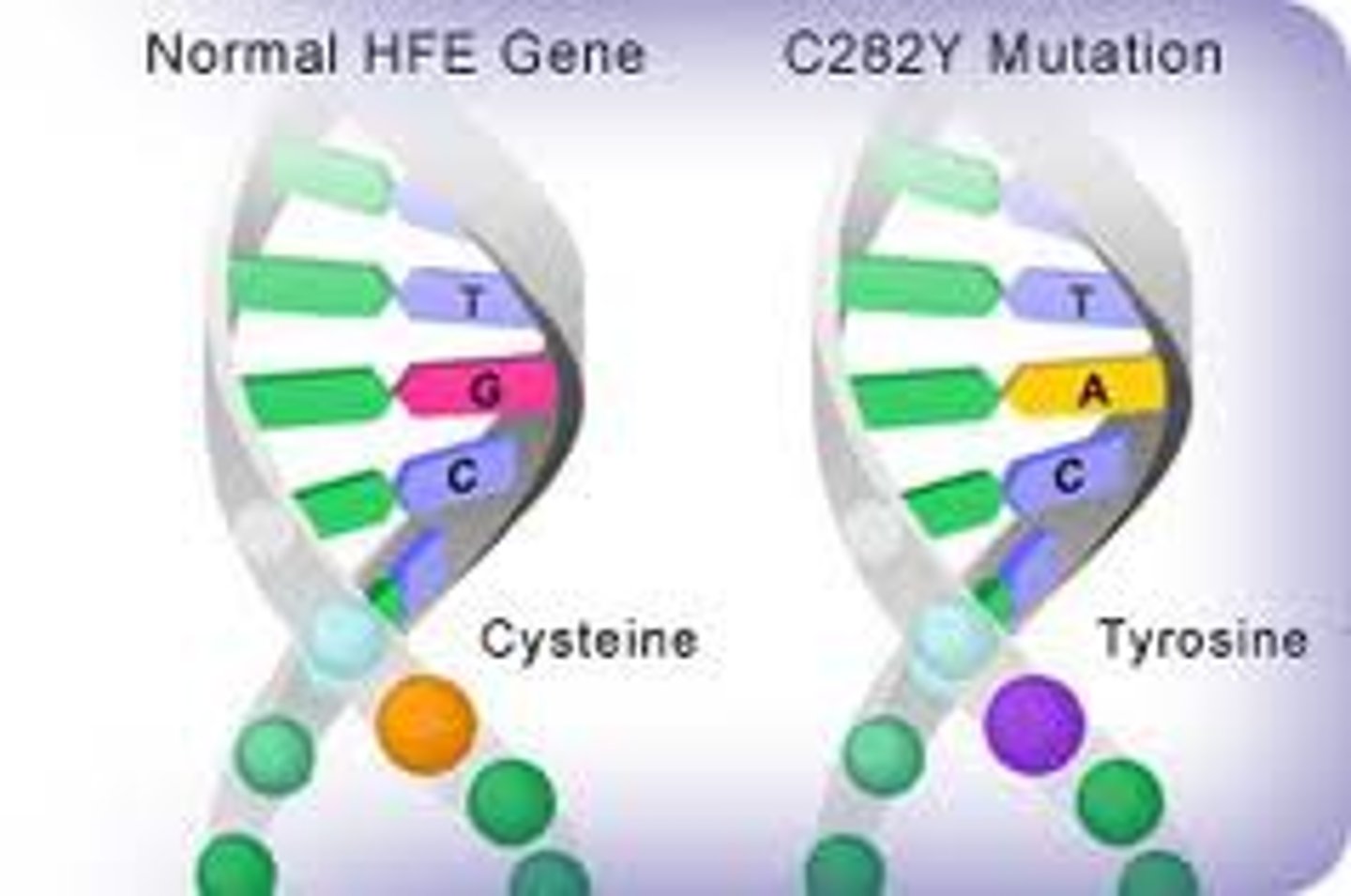
Germ mutations only affect a _____ gene
SINGLE
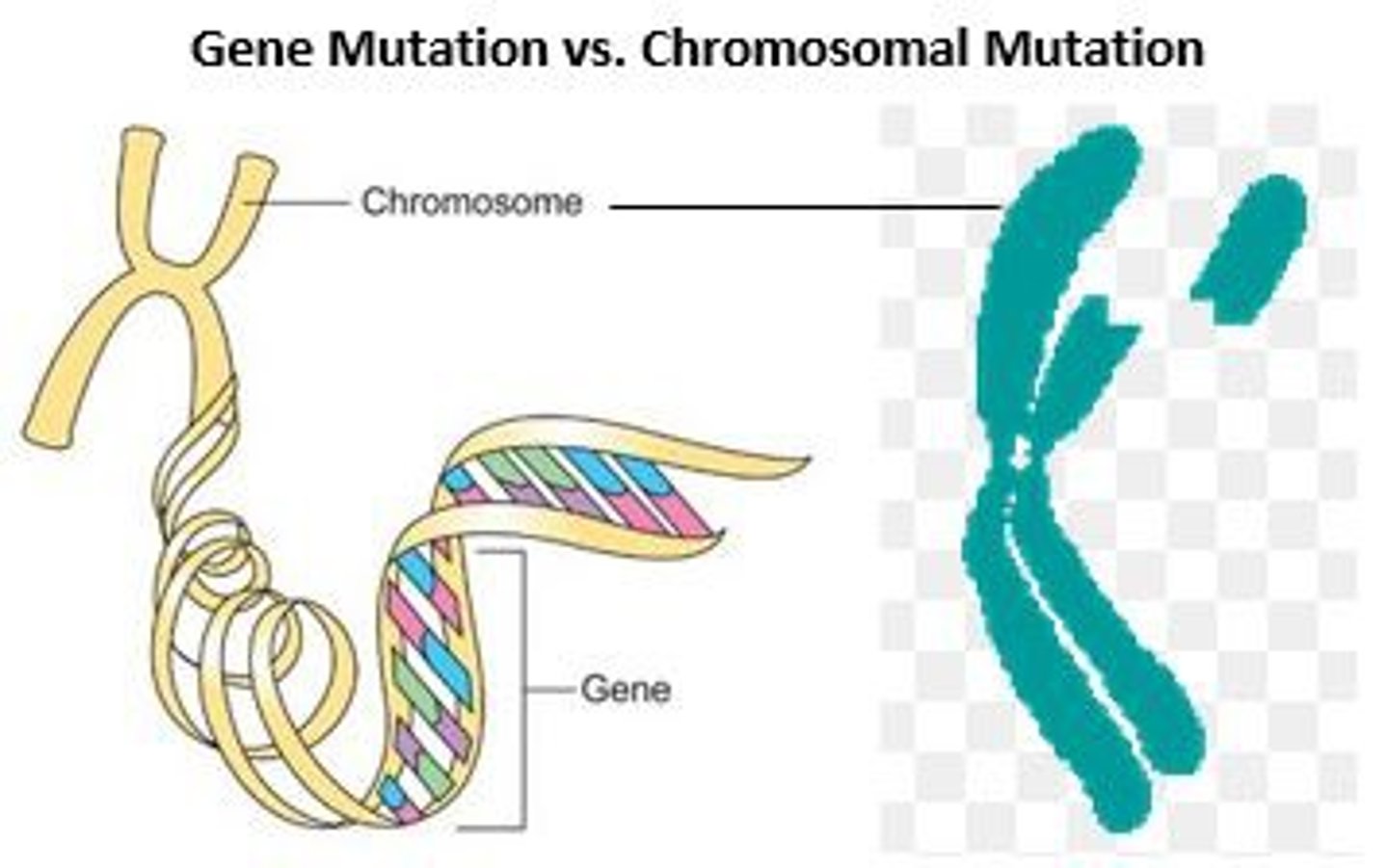
Chromosomal mutations
changes in the number or structure of chromosomes
Types of Point Mutations
substitutions, insertions, and deletions
Frameshift mutations
insertions and deletions
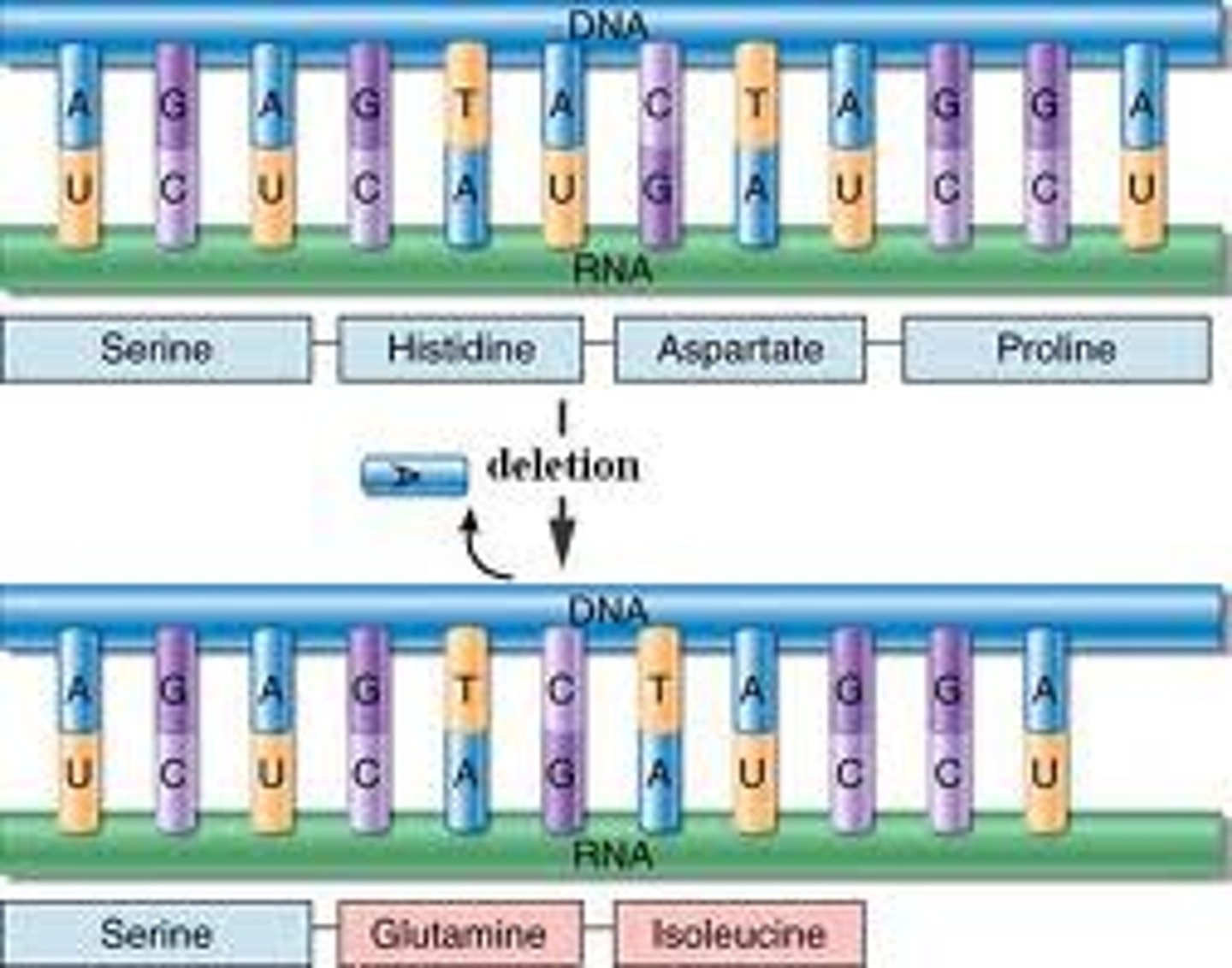
Substitution
One base is changed to a different base. Only affects a single amino acid and may have no effect at all
Types of Chromosomal Mutations
Deletion: loss of all or part of chromosome
Duplication: extra copy of all or part of chromosome
Inversion: reverse the direction of parts of a chromosome
Translocation: Part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another
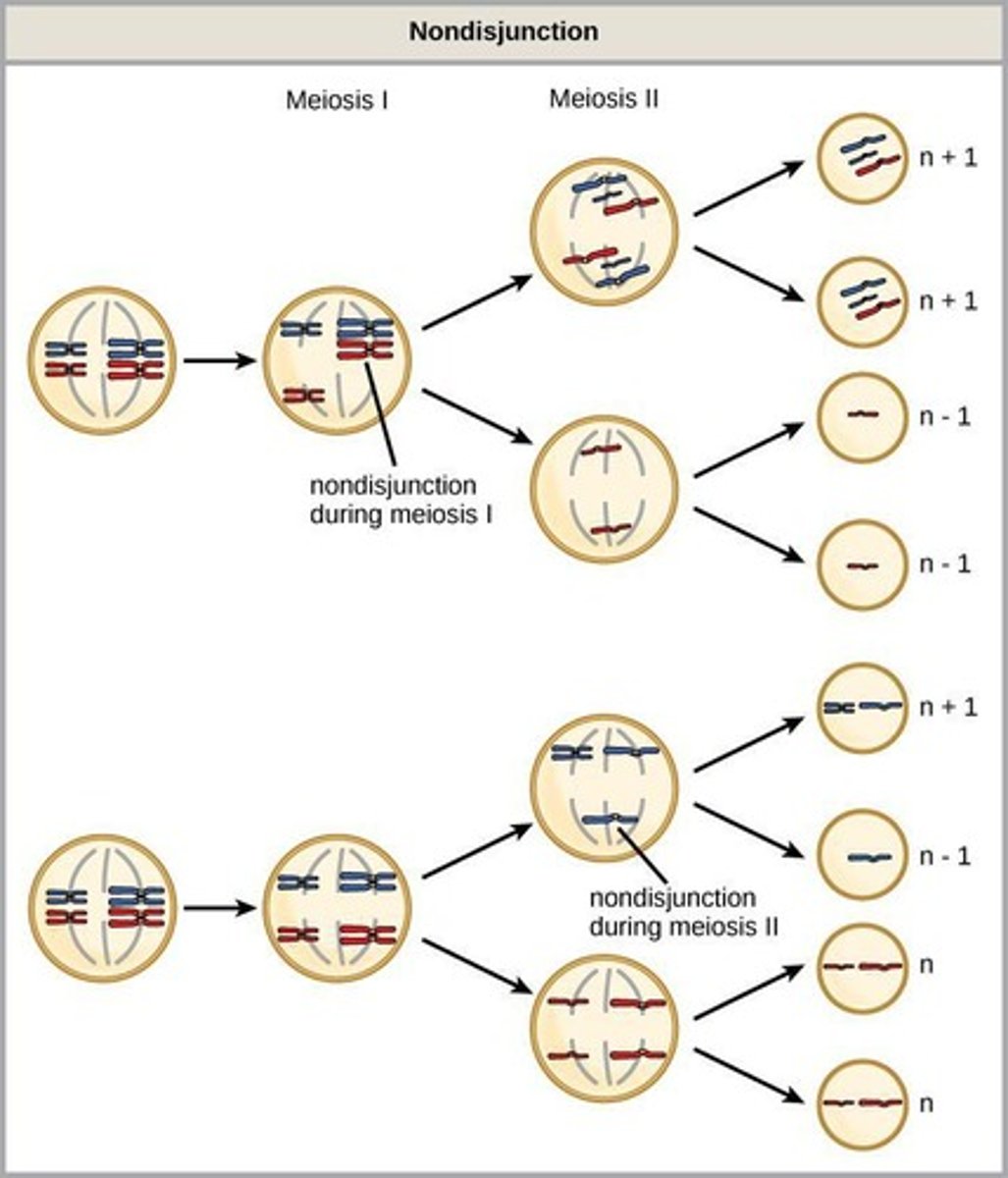
Nondisjunction
Failure of chromosomes to separate during cell division
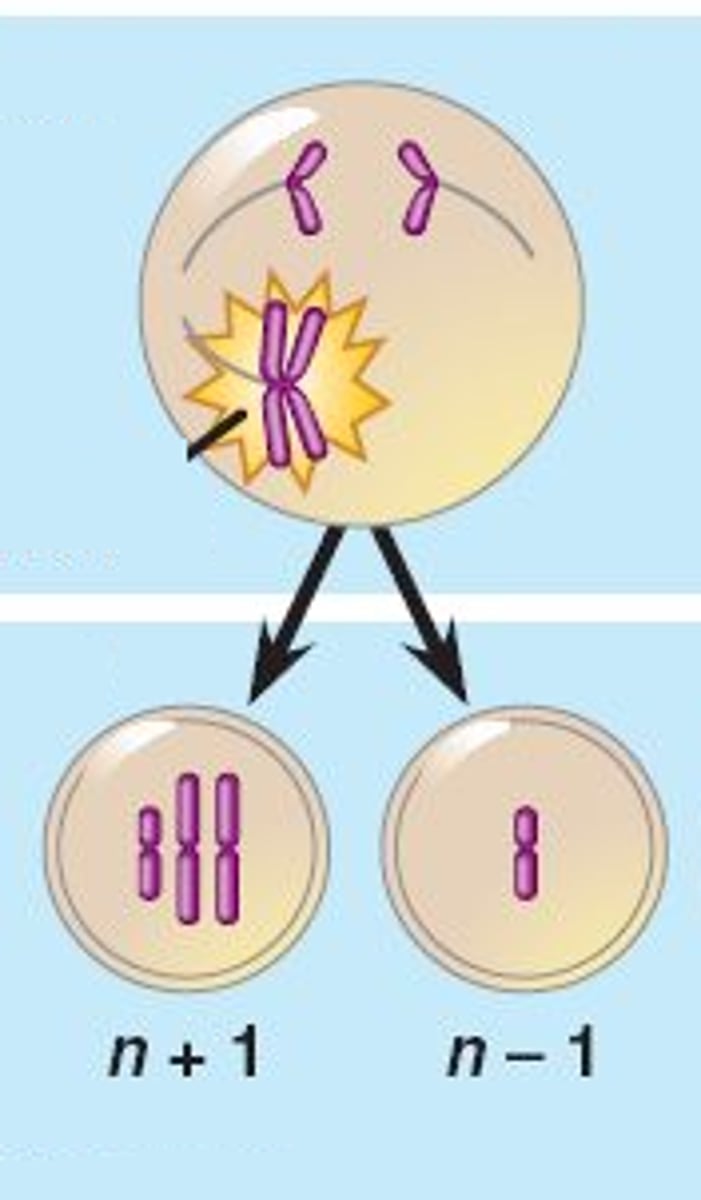
When can nondisjunction occur
Can occur during mitosis (not genetic), meiosis I, or meiosis II.
Nondisjunction effects
Causes errors in chromosome #
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) and monosomy X (Turners Syndrome
also common cause of early miscarriage
What Causes Mutations?
Errors in DNA replication, Cell division.
Mutagens: chemicals (ex. Pesticides, tobacco smoke) Physical agents (ex. radiation from x-rays or UV rays)
Mutations will only have effect if there is a change in the _________
phenotype
Eukaryotic Gene expression can be regulated at ___ stages
many
Eukaryotic Gene expression depends on _____ and ____ factors
internal, external
Main control point of eukaryotic gene regulation
transcription
TATA Box
part of a promoter sequence that binds a protein (transcription factor) that helps position RNA polymerase by marking a point just before beginning of a gene.
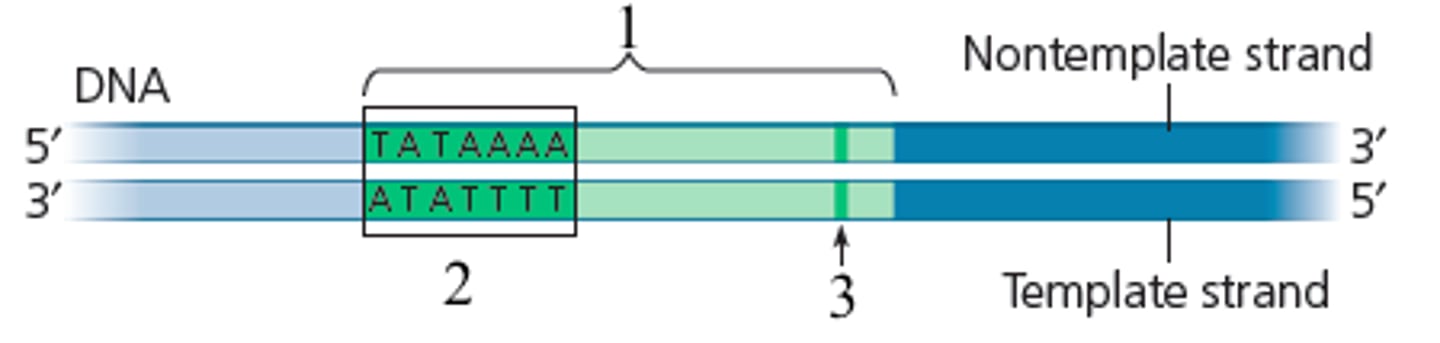
What do certain transcription factors do?
- open up tightly packed chromatin
- Attract RNA polymerase
- Block access to certain genes
________- transcription factors must bind before RNA polymerase is able to attach to the promoter and start transcription.
multiple
Homeotic/Hox Genes
master control genes that regulate body development during embryonic development