redox
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
State the FOUR different ways that could describe oxidation
Loss of hydrogen
loss of electron
increase in oxidation state
gain of oxygen
State the FOUR different ways that could describe reduction
gain of electrons
gain of hydrogen
decrease in oxidation state
loss of oxygen
How are ions written
number first, then charge eg Mg 2+
How are oxidation states written
Charge first, then number eg the oxidation state of Mg ion is +2
What is the oxidation state of an element?
always zero
What is the oxidation state of the fluoride ion?
Always -1
What is the oxidation state(s) of oxygen in compounds
The oxidation state of oxygen in its compounds is usually –2 except if bonded to fluorine or in peroxides or superoxides
What is the oxidation state(s) of hydrogen in compounds
The oxidation state of hydrogen in its compounds is usually +1 except when bonded to a metal ion (metal hydride), when it is –1
What do half equation include?
Electrons (‘half equations have ‘h’electrons!)
What do overall equation NOT include
Electrons
what is a Disproportionation reaction
A reaction where the same element is simultaneously oxidised and reduced.
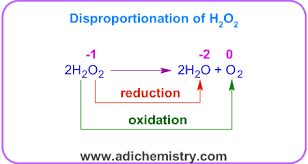
what are reducing agents
Electron Donors cause something else to be reduced by themselves getting oxidised
what are Oxidising agents
Electron acceptors, cause something else to be oxidised by themselves getting reduced
formula for a nitrate ion and systematic name
nitrate (V)

formula for a nitrite ion and systematic name
nitrate (III)
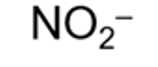
formula for sulphate ion and systematic name
sulfate (VI)
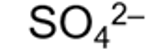
formula for sulphite ion and systematic name
sulfate (IV)
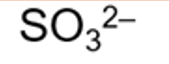
formula for chloride ion and systematic name
chloride
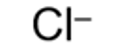
formula for chlorate ion and systematic name
chlorate(V)
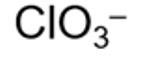
formula for chlorite ion and systematic name
chlorate(III)
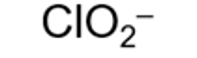
formula for hyppochlorite ion and systematic name
chlorate(I)

list the monatomic elements
(group 0 elements/ Nobel gases)
helium
argon
neon
krypton
enon
radon
list all the simple molecular elements
all of the diatomic elements plus sulphur and phosphorus as they form covalent bonds to their selfs just form several bonds
hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, iodine, chlorine, bromine, sulphur, phosphorus
name all the ionic elements
there are no ionic elements
example of three elements that form giant metallic lattices
magnesium
aluminium
iron
sodium
give two examples of giant molecular structures formed by carbon atoms
Dimond
graphite
what atom other than carbon can form a macromolecular lattice
silicone
define a compound
a substance formed by the chemical union of two or more different elements in a fixed ratio, where the elements are chemically bonded together and cannot be separated by physical means
define a mixture
two or more substances (elements or compounds) that are physically combined but not chemically bonded together.
list all of the monatomic compounds
there are no monatomic compounds
list 5 common molecular compounds
carbon dioxide
water
ammonia
silicon dioxide
methane
nitrogen monoxide
nitrogen dioxide
sulfur dioxide
sulfur trioxide
how can you calculate the formula of an ionic compound
using the charges on the ions
what are the 4 common acids that are ionic compounds and give their formula
hydrochloric acid - HCl
sulphuric acid- H2SO4
nitric acid- HNO3
phosphoric acid- H3PO4
name all the metallic compounds
there are no metallic compounds
name the giant covalent compound
silicone dioxide
formula for the following common ions
nitrate
sulfate
carbonate
hydroxide
hydride
phosphate
nitrate- NO3-
sulfate- SO42-
carbonate- CO32-
hydroxide-OH-
hydride- H-
phosphate- PO43-
how ro calculate the oxidation state of a compound
To find an element's oxidation state, assign known oxidation states to other atoms in the compound, set up an equation where the sum of all oxidation states equals the compound's total charge (zero for a neutral compound), and then solve for the unknown oxidation state

real the order of reactivity in the reactivity series
