22 Enthalpy and entropy
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
used knowt to generate flashcards based on notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What is lattice enthalpy (ΔLEH)?
Lattice enthalpy is a measure of the strength of ionic bonding in a giant ionic lattice, defined as the enthalpy change that accompanies the formation of one mole of an ionic compound from its gaseous ions under standard conditions.
Why are solid ionic compounds considered stable?
Solid ionic compounds are stable due to the strength of the ionic bonds that arise from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in the ionic lattice structure.
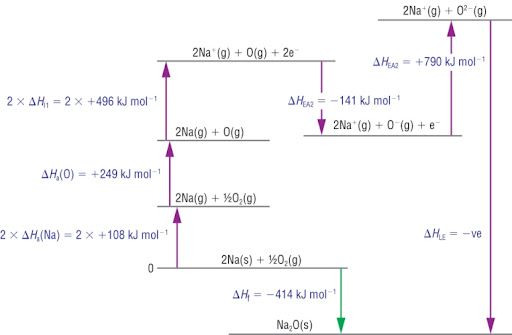
What is the Born-Haber cycle?
The Born-Haber cycle is a thermodynamic cycle used to calculate lattice enthalpy indirectly using known energy changes.
What is the standard enthalpy change of formation (ΔfH)?
The standard enthalpy change of formation is the enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions.
What is the standard enthalpy change of atomisation (ΔatH)?
The standard enthalpy change of atomisation is the enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of gaseous atoms from the element in its standard state, and it is always an endothermic process.
What is the first ionisation energy (ΔIEH)?
The first ionisation energy is the enthalpy change required to remove one electron from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions, and it is endothermic.
What is the first electron affinity (ΔEAH)?
The first electron affinity is the enthalpy change that occurs when one electron is added to each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1- ions, and it is exothermic.
Why is the second electron affinity endothermic?
The second electron affinity is endothermic because energy must be input to force a negatively charged electron onto a negative ion, due to the repulsion between the two negative charges.
What is ionic bonding?
Ionic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between positively and negatively charged ions in a compound.
What factors affect lattice enthalpy?
Lattice enthalpy is affected by the size of the ions and the charge on the ions; smaller ions and ions with higher charges result in stronger ionic bonds.
How is lattice enthalpy calculated?
Lattice enthalpy can be calculated using the Born-Haber cycle, which utilizes known enthalpy changes to find the lattice enthalpy indirectly.
What is the relationship between lattice enthalpy and solubility?
Generally, compounds with lower lattice enthalpy are more soluble in water, as less energy is required to separate the ions.
What does a high lattice enthalpy indicate about an ionic compound?
A high lattice enthalpy indicates strong ionic bonds, resulting in a more stable ionic compound.
What happens when an ionic compound dissolves in water?
Water molecules break up the giant ionic lattice and overcome the strong electrostatic attractions between oppositely-charged ions.
What is the enthalpy change of solution (ΔsolHθ)?
The enthalpy change of solution is the enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of a solute dissolves in a solvent, and can be exothermic or endothermic.
What is the enthalpy change of hydration (ΔhydHθ)?
The enthalpy change of hydration is the enthalpy change that accompanies the dissolving of gaseous ions in water to form one mole of aqueous ions.
What are the two types of energy changes involved in the dissolving process of ionic compounds?
Energy change for breaking up the ionic lattice into separate gaseous ions. 2. Energy change for the formation of hydrated aqueous ions from gaseous ions.
How do water molecules interact with ions in solution?
Water molecules, with partial charges, are attracted to the positive and negative ions, surrounding them as hydrated aqueous ions.
What are the properties of ionic compounds regarding melting and boiling points?
Ionic compounds generally have high melting points (mpt) and boiling points (bpt), though there is a wide range of variation.
What factors affect the solubility of ionic compounds in polar solvents?
Ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents like water because the energy released in hydration can overcome the lattice energy, but solubility varies depending on the specific ions involved.
What is entropy (S)?
Entropy is the dispersal of energy within the chemicals making up the chemical system.
What are the units of entropy?
The units of entropy are JK⁻¹mol⁻¹.
How does entropy relate to energy dispersion?
The greater the entropy value, the greater the energy is spread out per Kelvin per mole.
Which states of matter have the lowest to highest entropy?
Solids have the smallest entropies, liquids have greater entropies, and gases have the greatest entropies.
What happens to entropy at 0 K?
At 0 K, there would be no energy and all substances would have an entropy value of 0.
How does entropy behave above 0 K?
Above 0 K, energy becomes dispersed among particles, and all substances have positive entropy.
What is the relationship between chaos and entropy?
Systems that are more chaotic have a higher entropy value.
What is the effect of producing gases on entropy?
Reactions that produce gases typically increase entropy, as they increase the disorder of particles.
What is the effect of a decrease in the number of gas molecules on entropy?
A decrease in the number of gas molecules results in lower randomness of particles, leading to a negative change in entropy (ΔS).
What is standard entropy (Sθ)?
Standard entropy is the entropy of one mole of a substance under standard conditions (100 kPa and 298 K).
What are the properties of standard entropy?
Standard entropy values are always positive and can be found in data books.
Why do reactions happen?
Reactions happen if the products have a lower overall energy than the reactants.
What is free energy change (ΔG)?
Free energy change (ΔG) is the overall change in energy during a chemical reaction, made up of enthalpy change (ΔH) and entropy change (TΔS).
What does ΔH represent?
ΔH represents the enthalpy change, which is the heat transfer between the chemical system and the surroundings.
What does TΔS represent?
TΔS represents the entropy change at the temperature of the reaction, indicating the dispersal of energy within the chemical system.
What is the condition for feasibility in reactions?
For a reaction to be feasible, there must be a decrease in free energy (ΔG < 0).
What do the following ΔG values indicate: ΔG < 0, ΔG = 0, ΔG > 0?
ΔG < 0: reaction is feasible; ΔG = 0: system is at equilibrium; ΔG > 0: reaction is not feasible.
How is the significance of ΔH and ΔS determined in the Gibbs' equation?
The value for ΔH is usually much larger than for ΔS and often dominates the Gibbs' equation.
What happens during an endothermic reaction like the dissolution of KCl in water?
Endothermic reactions like the dissolution of KCl can occur at room temperature, cooling down the water due to the energy required to separate ions.
Why do some reactions with a negative ΔG not occur?
Some reactions may have a negative ΔG but do not occur due to a large activation energy resulting in a very slow rate, e.g., hydrogen peroxide decomposition.
What does Gibbs' equation account for regarding reaction feasibility?
Gibbs' equation accounts for the balance between ΔH and TΔS to determine the thermodynamic feasibility of a reaction.
What is lattice enthalpy (ΔLEHθ)?
Lattice enthalpy is the enthalpy change that accompanies the formation of one mole of an ionic compound from its gaseous ions under standard conditions.
Born Haber cycle example
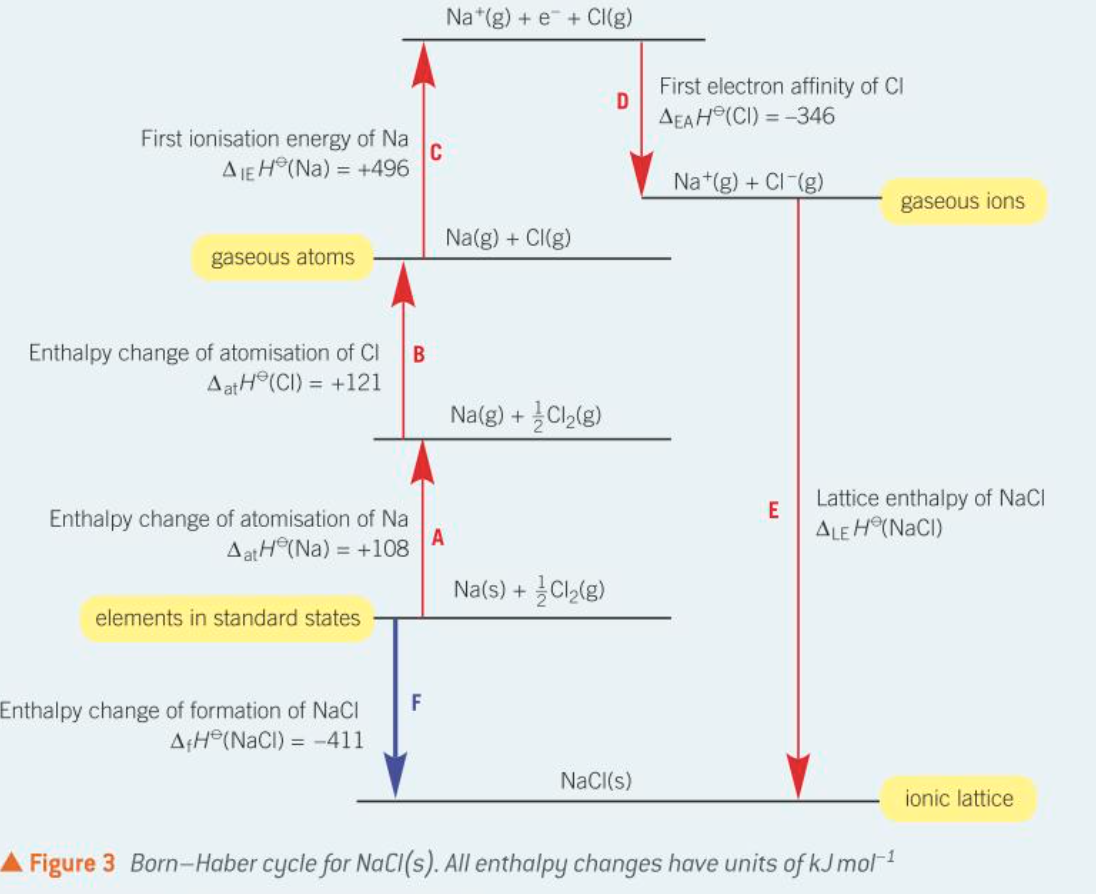
Born Haber cycle w hydration example
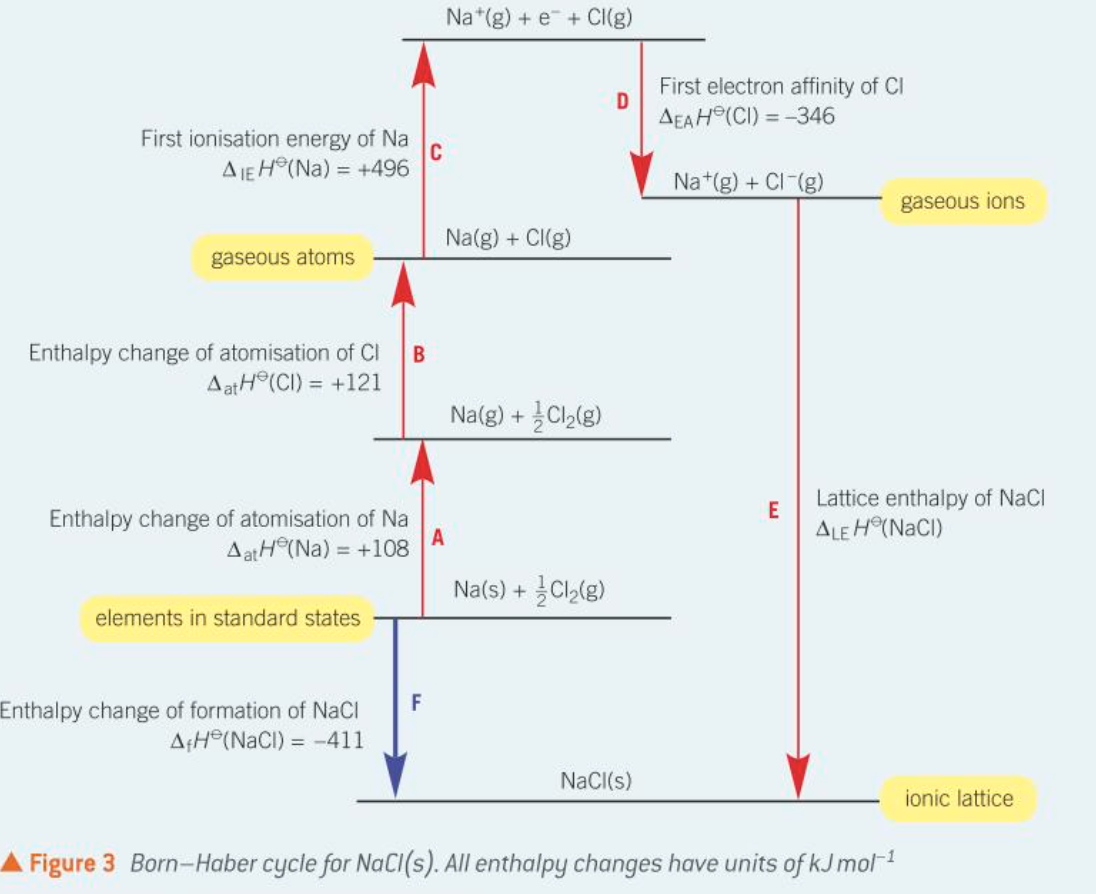
born haber cycle w 2nd electron affinity