22 Enthalpy and entropy
Lattice enthalpy
Solid ionic compounds tend to be v stable - arises from the strength of the ionic bonds.
Ionic bonding: the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in the ionic lattice structure
This creates a substantial energy barrier that must be overcome to break down the lattice, reflected in the high mpts of many ionic compounds.
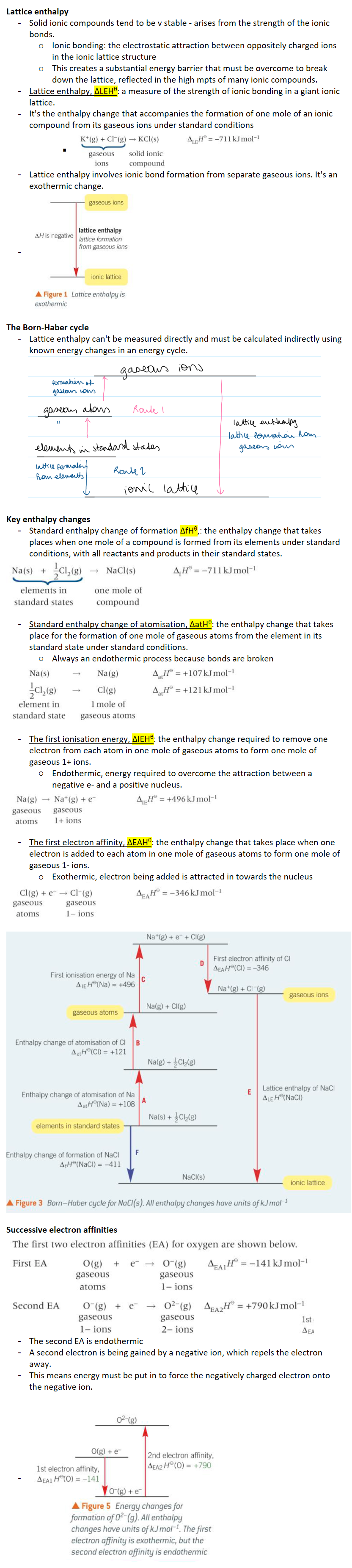
Lattice enthalpy, ΔLEHθ: a measure of the strength of ionic bonding in a giant ionic lattice.
It's the enthalpy change that accompanies the formation of one mole of an ionic compound from its gaseous ions under standard conditions
Lattice enthalpy involves ionic bond formation from separate gaseous ions. It's an exothermic change.
The Born-Haber cycle
Lattice enthalpy can't be measured directly and must be calculated indirectly using known energy changes in an energy cycle.
Key enthalpy changes
Standard enthalpy change of formation ΔfHθ,: the enthalpy change that takes places when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions, with all reactants and products in their standard states.
Standard enthalpy change of atomisation, ΔatHθ: the enthalpy change that takes place for the formation of one mole of gaseous atoms from the element in its standard state under standard conditions.
Always an endothermic process because bonds are broken
The first ionisation energy, ΔIEHθ: the enthalpy change required to remove one electron from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions.
Endothermic, energy required to overcome the attraction between a negative e- and a positive nucleus.
The first electron affinity, ΔEAHθ: the enthalpy change that takes place when one electron is added to each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous 1- ions.
Exothermic, electron being added is attracted in towards the nucleus
Successive electron affinities
The second EA is endothermic
A second electron is being gained by a negative ion, which repels the electron away.
This means energy must be put in to force the negatively charged electron onto the negative ion.