Language Disorders Across the Lifespan Exam 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Communication definition
an exchange of ideas between senders and receivers that involves transmission and response/feedback
Variables that affect communication:
1. Cultural identity
2. Setting
3. Participants
Sociolinguistics definition
the study of such influences on communication
language community
everyone belongs to one
Successful communication is influenced by:
Age
Socioeconomic status (SES)
Geographic background
Ethnicity
Gender
Ability
Etc.
The percentage of White non-Hispanic students in the public schools is…
below 50%
Cultural competence
Understanding, appreciating, and responding appropriately to a full range of diversity dimensions
Cultural humility
Recognize that learning and self-reflection are lifelong, that power imbalances exist and must be addressed, and that institutions must be accountable
Even when people share the same language…
perfect communication is rare
T/F: there is not a single “correct” way to communicate
True
Communication happens within…
environment/context
Context includes:
Location (where you are)
People involved
Event taking place
Communication reflects culture and the situation
—> communication only makes sense within context
Examples:
Someone asks, “Can you take the garbage out?” while you’re getting a haircut
Someone says, “You are hilarious!” at a funeral
Communication happens in many forms and can use multiple senses like…
Sight, hearing, smell, touch
Communication can be verbal or nonverbal:
Verbal: spoken or written words
Nonverbal: gestures, facial expressions, signs
T/F: Variations in communication are NOT impairments
True
Dialects definition
differences that reflect a particular regional, social, cultural, or ethnic identity and are NOT disorders of speech or language
legitimate, rule governed varieties of English.
Ex) African American Vernacular English (AAVE)
“ain’t” instead of “am not”/”have not”
What is the “primary vehicle” (primary means of language expression for most individuals) in human communication?
language and speech
Clinical practice requires an awareness of…
each person’s customs, beliefs, and ethical manner
Characteristics of the culturally competent/sensitive SLPs
Simultaneous appreciation of cultural patterns and individual variation
Engagement in cultural self-scrutiny
Embracing principles of evidence-based practice
Seeking to understand language disorders within the client’s social context
What is Language?
socially shared code used to represent concepts.
The code uses symbols to represent concepts in rule-governed ways.
NOT STEADY → constantly changes
Characteristics
Social-shared
Rule-governed
Arbitrary (but agreed upon)
Generative
Dynamic (NOT STATIC)
3 Components of Langauge
Form
Content
Use
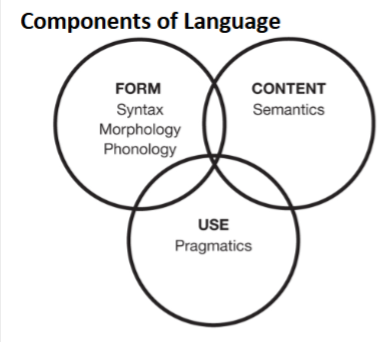
Form
Syntax
Morphology
Phonology
Syntax
how words are arranged into sentences
Sentence level structure of language that marks relationships between rules and ideas.
“Feed the dog!”
“Did you make your bed?”
“How are you feeling today?”
“I did not read my chapter yet”
“I will read my chapter and then I will write my notes”
Syntax: Sentence Types
Declarative – My sister walks the dog
Interrogative – Who is walking the dog?
Imperative – Walk the dog!
Negative – My brother didn’t walk the dog.
“never” also = negative
Passive – The dog was fed by my brother.
Conjoined – My brother and sister take turns walking the dog.
Clausal embedding – My sister walks the dog that lives next door.
Morphology
how words are formed from smaller parts (prefixes, suffixes, endings)
E.g., dog vs. dogs / pass vs passed
Prefixes and suffixes (pretest, softly)
Free morphemes: May stand alone as a word
“Cat”
Bound morphemes: Must be attached to free morphemes; change meaning of words
the “-s” in “cats”
Morphemes: How many morphemes are in these words?
Cucumber = 1
Littering = 2
Monstrous / Mysterious = 2
Reappeared = 3
Farmer = 2
Finger = 1
Mother's = 2
Phonology
the sound system of a language and how sounds are used
Phonotactic rules: How sounds may be arranged
IPA e.g., /sup/ = “soup”
Context
Semantics
Semantics
the meaning of words and sentences
consists of 2 types of information: lexical and conceptual
Lexical: /d/ /o/ /g/
Concept: barks, wags tail, growls, soft, four legs
Use
Pragmatics
Pragmatics
how language is used in social situations (taking turns, staying on topic, using language appropriately)
Intent; request; quality of expression; topic initiation, maintenance, shifting, closure; eye contact; body gestures, intonation
Cultural pragmatics - Pragmatic rules vary with culture
Expressive Vs. Receptive Language
Expressive/Production
Speaking
Writing
Texting
Emails
Receptive Comprehension
Understanding
Reading
Reading text messages
Reading emails
Exercise Q1: smallest unit of language that expresses meaning
Answer: Morphology
Exercise Q2: sound system of language
Answer: phonology
Exercise Q3: meaning system of language
Answer: semantics
Exercise Q4: sentence lvl structure of language that marks relationships between words or ideas
Answer: syntax
Exercise Q5: how we use language in social interactions
Answer: pragmatics
Exercise Q6: way in which speech sounds are formed
Answer: articulation
Exercise Q7: smooth, forward flow of communication
Answer: fluency
Exercise Q8: includes vocal quality, loudness, and pitch
Answer: voice
Speech
Speech is the process of producing the acoustic representations or sounds of language
3 Parts:
Articulation
Fluency (smooth, forward flow of communication)
Voice
Nonverbal Communication
2/3 of our communication is nonverbal!
4 Parts:
Artifacts
Kinesics
Proxemics
Chronemics
Artifacts in nonverbal communication
The way you look, your clothes, your possessions
Kinesics in nonverbal communication
The way we move our bodies, “body language”
Proxemics in nonverbal communication
study of physical distance between people – reflects relationship and is influenced by age and culture
Chronemics in nonverbal communication
effect of time on communication. Linear
Cultural, status, work ethic, etc. – being late is disrespectful in US and Germany
Communication is considered impaired when it differs from community standards enough that it…
Interferes with sending or understanding messages
Sounds noticeably unusual or different
Causes negative feelings for the speaker (e.g., frustration, embarrassment)
ASHA (1997) defines communication disorders as disorders of:
Speech (articulation, voice, and fluency)
Oral neuromotor control and movement
Language and/or literacy
Hearing and balance
Feeding and swallowing (dysphagia)
Cognitive and social communication
Prevalence definition
the number or percentage of people in a population who have a disorder at a given time
About ___ of the U.S. population has a communication disorder
17%
About ___ have a hearing loss
11%
Percentage of people with hearing loss increases with age
About ___ of people have a speech, voice, or language disorder, including nearly ___ of children
6%; 8%
Q1: A person demonstrates abnormal movement patterns of the face and mouth
orofacial/myofunctional pattern disorders
Q2: A person demonstrates difficulty swallowing
Dysphagia
Q3: A person experiences deficits in one of the following areas: articulation, fluency, voice
Speech sound disorders
Q4: A person demonstrates deficits in one or more of the following areas: phonology, morphology, syntax, content, use
Language disorder
Language (verbal and nonverbal) = primary way humans communicate; What are the 3 types?
Spoken, written, and signed
Quiz Q1: Disorders with the rhythm of speech are known as _____ disorders
Fluency
Q2: Which of the following is NOT true regarding communication impairments
Interferes with the transmission of messages
it produces negative feelings within the communicator
Stands out as being unusually different
All of these are true
Q3: What percentage of people in the US have a communication disorder?
17%
Q4: Which of the following terms does NOT apply to language?
Static
Arbitrary
Social-shared
Rule-governed
Q5: As an SLP working with a client who is a speaker of a dialect other than your own you look up information on the linguistic features of your client's dialect. What characteristic of a culturally competent SLP have you demonstrated?
Simultaneous appreciation of cultural patterns and individual variation
Q6: Which of the following is an example of receptive language?
Reading
Q7: ____ of our messages are nonverbal
2/3
Q8: What sentence type has been demonstrated in the following sentence: "Make your bed!"
Imperative
Q9: _____ is the smallest unit of language that have some independent meaning/form/function.
Morphology
Q10: True or False: An individual can have both a language difference and a language disorder.
True
Language Impairments
Heterogeneous group of developmental and/or acquired disorders and/or delays
Languaage Impairments affect…
understanding and/or producing spoken or written language
They may involve:
Form
Content
Function (use) of language