Quantum Physics: Blackbody Radiation, Photoelectric Effect, and Historical Developments
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is a black body in the context of quantum physics?
A black body is an object that completely absorbs all incident radiations of all wavelengths.
What is the significance of black body radiation?
The energy emitted from a black body depends on its frequency and temperature, and the intensity of radiation is maximum at a particular wavelength.
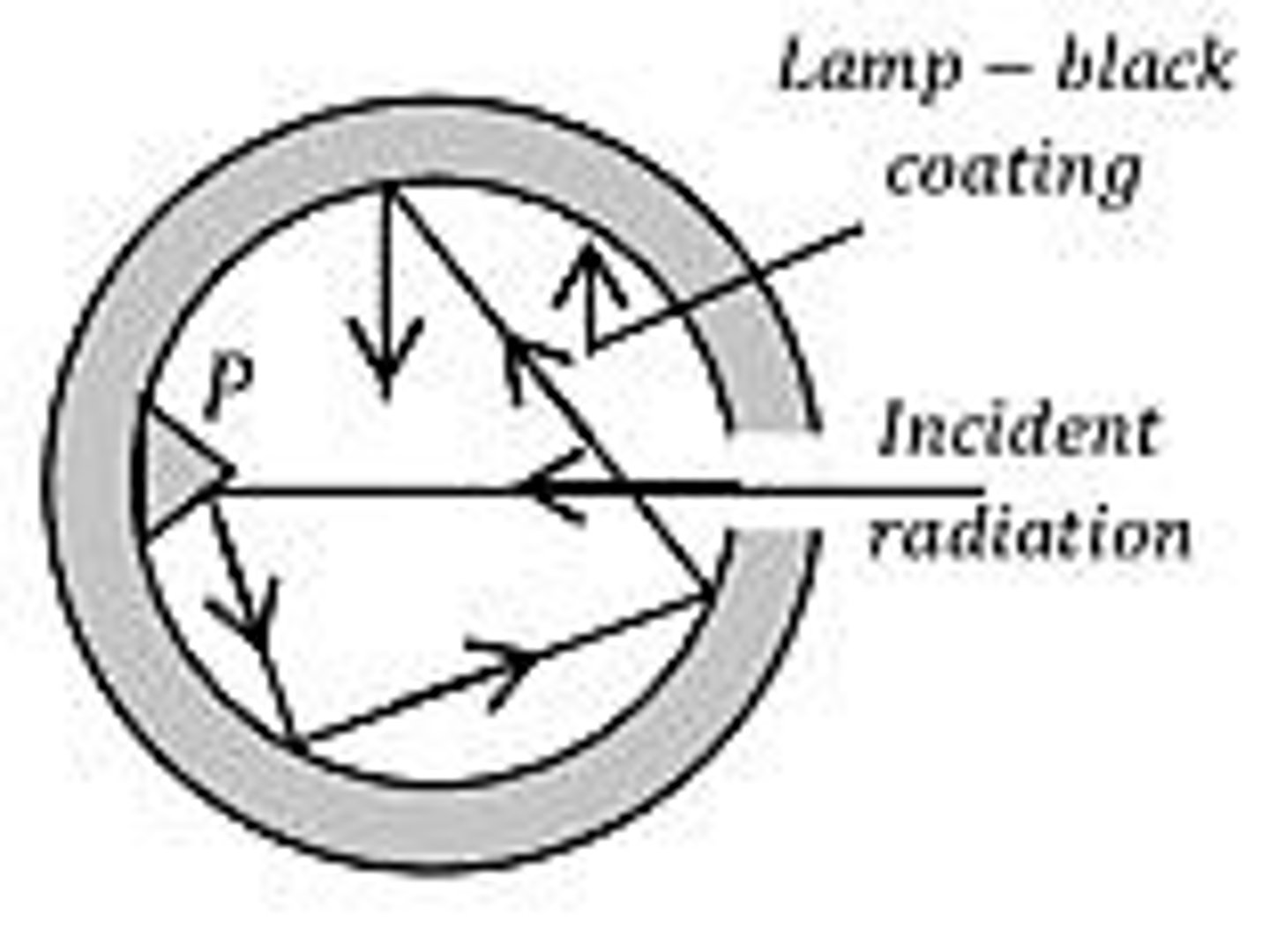
How is a black body constructed?
A black body is constructed using a hollow cavity with a small hole, coated with lamp-black, allowing incoming radiations to reflect in different directions.
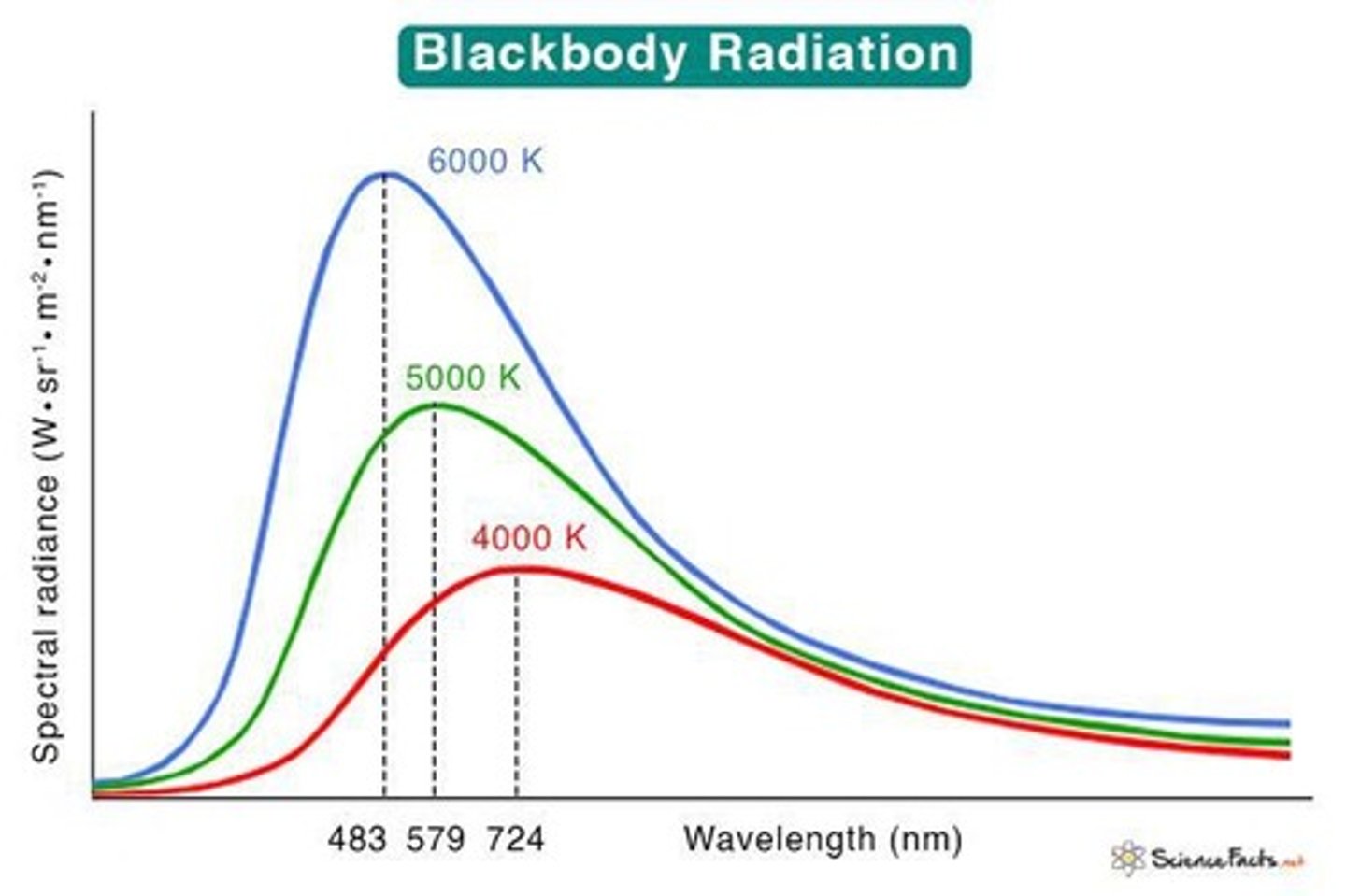
What does Wien's displacement law state?
Wien's displacement law states that the peak wavelength of black body radiation is inversely proportional to the temperature.
What are the key assumptions of Planck's theory of black body radiation?
1. A body containing black body radiation has simple harmonic oscillators that can vibrate at all frequencies. 2. The frequency of emitted radiation equals the frequency of vibration. 3. Radiation is emitted in discrete units called quanta.
What is the inadequacy of classical physics regarding small scales?
Classical physics fails to accurately describe phenomena at atomic and subatomic scales.
How does quantum mechanics differ from classical mechanics in terms of energy levels?
Quantum mechanics introduces the concept of quantized energy levels, while classical mechanics allows for continuous energy levels.
What phenomenon could classical physics not explain that quantum mechanics addressed?
Classical physics could not adequately explain black body radiation, which was addressed by Planck's theory.
What is wave-particle duality?
Wave-particle duality is the concept that particles, like electrons and photons, exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behaviors depending on the conditions.
What does Heisenberg's uncertainty principle state?
Heisenberg's uncertainty principle asserts that certain pairs of properties, such as position and momentum, cannot be precisely measured simultaneously.
What was Planck's Quantum Hypothesis?
Planck's Quantum Hypothesis proposed that energy is quantized and can only be emitted or absorbed in discrete units called 'quanta' or photons.
How did Einstein contribute to quantum mechanics in 1905?
Einstein explained the photoelectric effect by proposing that light consists of discrete particles (photons) that carry quantized energy.
What is Bohr's model of the atom?
Bohr's model describes the hydrogen atom with electrons occupying discrete energy levels and transitioning between these levels by emitting or absorbing energy.
What did de Broglie propose about particles?
De Broglie proposed that particles, such as electrons, exhibit wave-like properties and associated a wavelength with them.
What is matrix mechanics, and who developed it?
Matrix mechanics is a mathematical framework for quantum mechanics developed by Werner Heisenberg.
What is Schrödinger's contribution to quantum mechanics?
Schrödinger developed wave mechanics, describing how wavefunctions evolve over time and relate to particle behavior.
What is the Copenhagen interpretation?
The Copenhagen interpretation, developed by Bohr and Heisenberg, emphasizes the complementary nature of wave and particle descriptions in quantum mechanics.
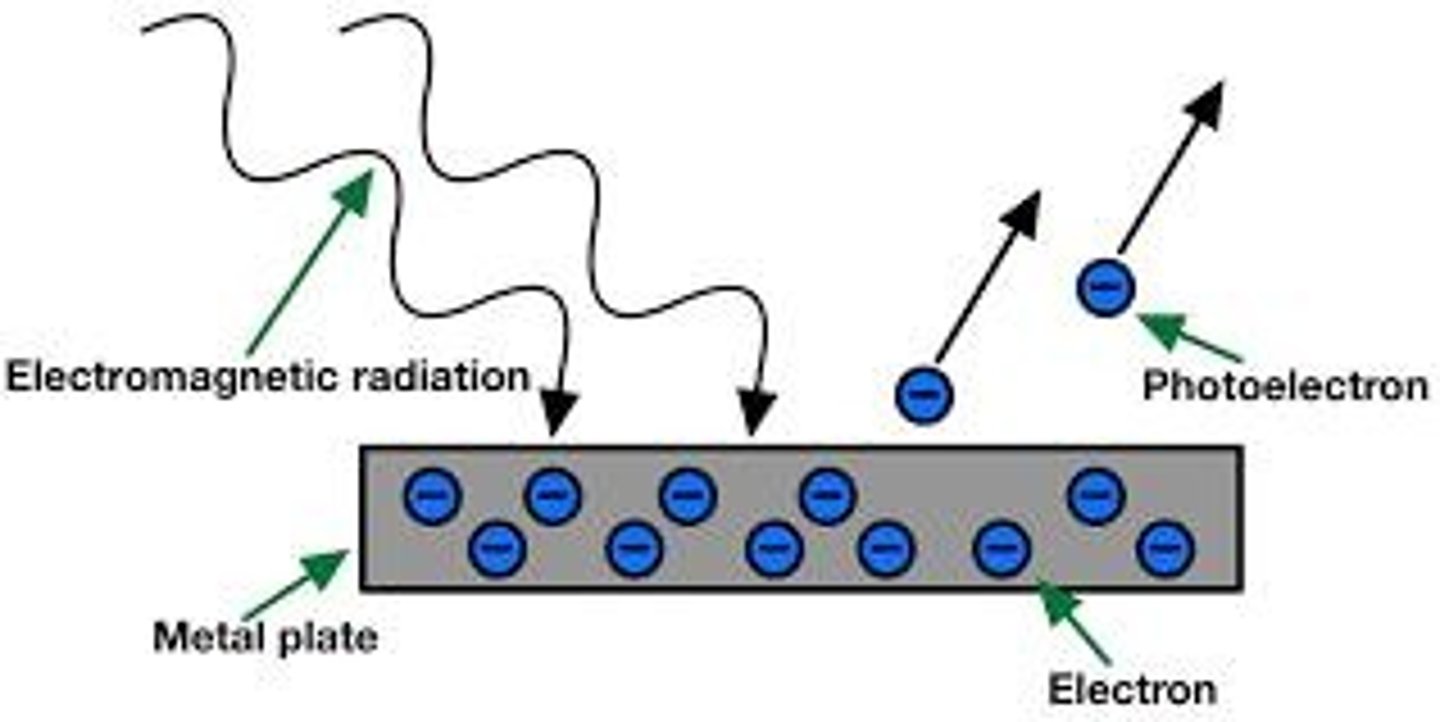
What is the photoelectric effect?
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons from the surface of metals when light of a suitable frequency falls on them.
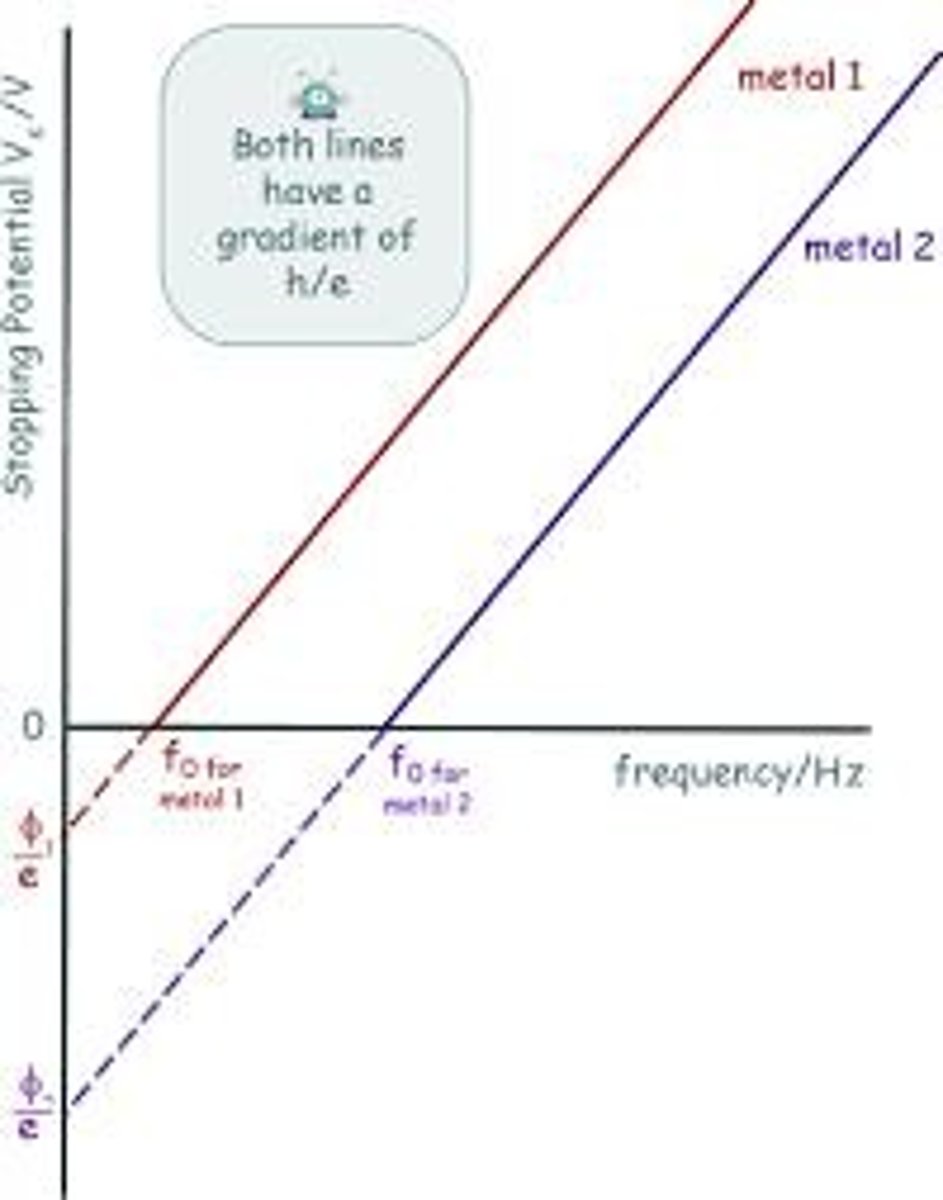
What is the threshold frequency in the context of the photoelectric effect?
The threshold frequency (νo) is the characteristic frequency for each metal below which no electrons are emitted.
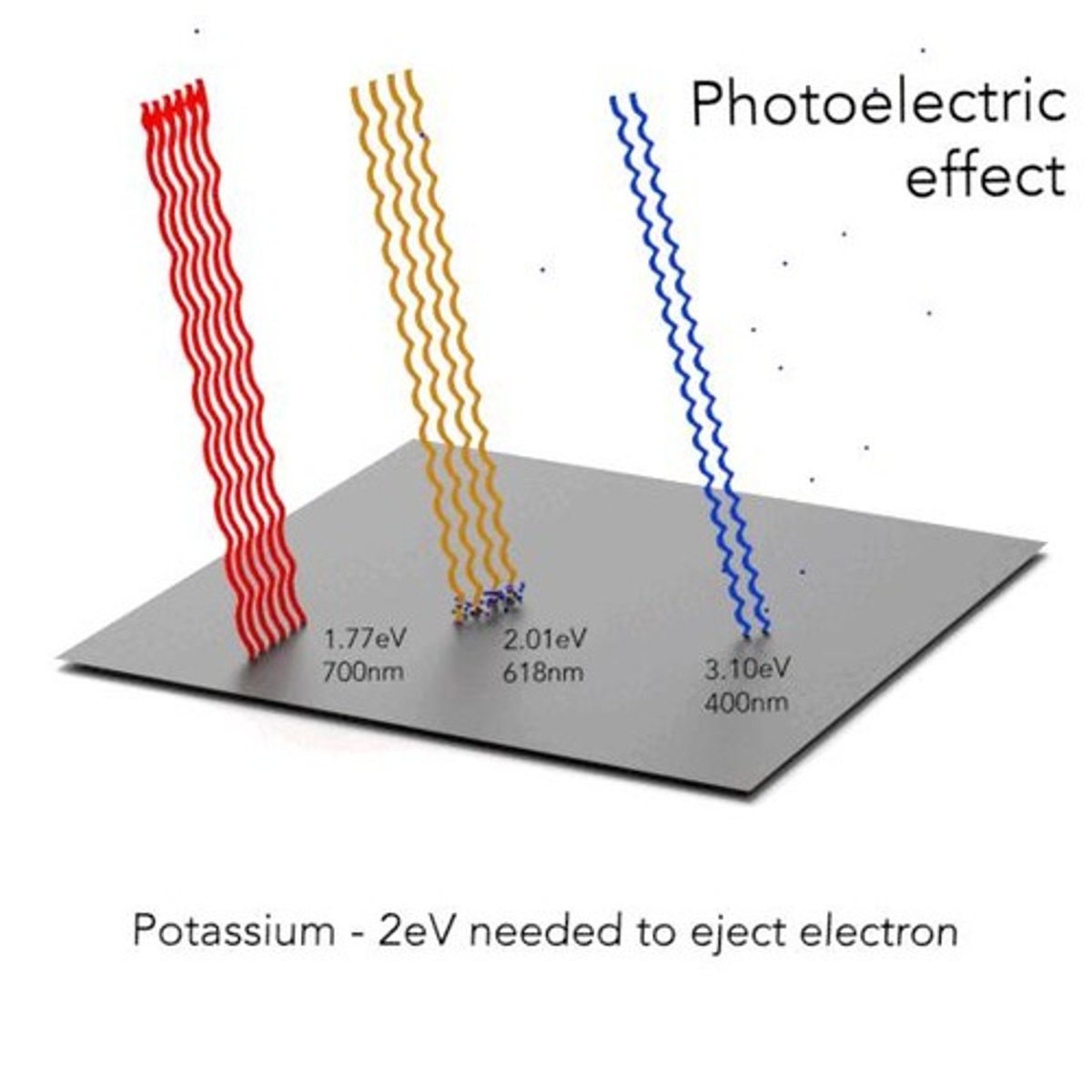
How does the velocity of photoelectrons relate to the intensity of incident light?
The velocity of photoelectrons is independent of the intensity of incident light but depends on its frequency.
What is the relationship between the rate of emission of photoelectrons and the intensity of light?
The rate of emission of photoelectrons is directly proportional to the intensity of incident light.
How did Einstein explain the photoelectric effect?
Einstein explained it by stating that electromagnetic radiation consists of photons, and energy is used to eject electrons from the surface.
What is the work function of a metal in relation to the photoelectric effect?
The work function is the minimum energy required to eject an electron from a metal's surface, related to the threshold frequency.
What happens if the frequency of photons is less than the threshold frequency?
If the frequency is less than the threshold frequency, the kinetic energy of the photoelectron is negative, preventing emission.
How does the number of ejected electrons relate to the number of photons?
The number of ejected electrons per unit time depends on the number of photons falling on the surface per unit area per second.
What is stopping potential in the context of the photoelectric effect?
Stopping potential refers to the minimum voltage needed to stop the emitted photoelectrons from reaching the anode in a photoelectric experiment.