Attention and information processing
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are the 4 types of attention?
Conscious = when someone is aware of what they are doing
Mental effort = anything that involves a mental effort (e.g. pupil dilation, change in heart rate)
A capacity = the idea that memory has a finite capacity
Selective = choosing what information is important to attend to
What is selective attention?
A performer focusing on relevant information while ignoring irrelevant stimuli
e.g. a footballer will process relevant stimuli such as calls from their teammates, but will disregard irrelevant information such as crowd noise
What are the stages of the bottleneck theory development?
Norman (1969) = information undergoes sensory detection and perceptual analysis, before we decide what to attend to and what to disregard
Keele (1973) = this attending or disregarding of information can happen as late as mid-way through the response selection stage
What is the bottleneck theory?
The brain can only process one piece of information at a time
What is inattentional blindness?
Focusing on one task and not noticing on other stimuli which may be relevant (e.g. not seeing the gorilla in the passing video)
What characteristics do automatic skills have?
Fast
Not attentionally demanding
Parallel (can occur at the same time as other processes)
Often not volitional (no conscious control)
What characteristics do controlled skills have?
Slow
Attentionally demanding
Serial (one step at a time)
Strongly volitional (requires conscious control)
What is the psychological refractory period?
The amount of time the response to the second stimulus is deteriorated due to the first stimulus
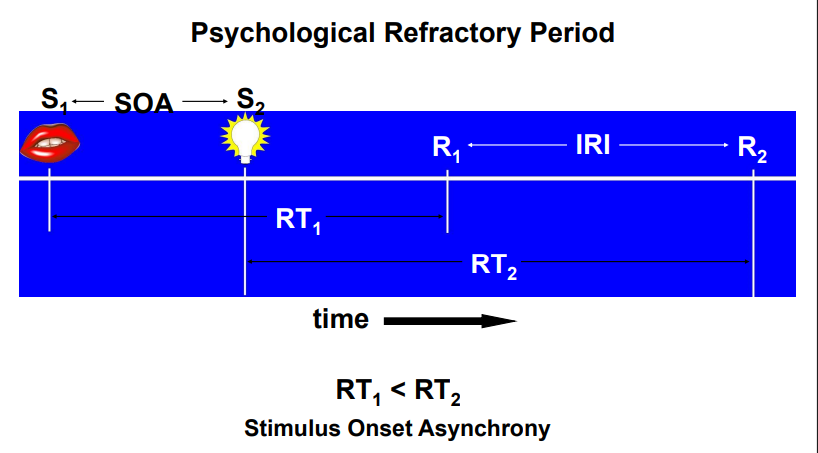
What is the stimulation-onset asynchrony
The time between the 1st and 2nd stimulus
What is the inter-response interval?
The difference in response time between the response 1 and response 2
What happens if the stimulus onset asynchrony is too long?
The 2 stimuli won’t interfere with each other, meaning no psychological refractory period
What is arousal?
Level of activation in the central nervous system
What is anxiety?
The interpretation of a situation and the resulting emotions
What is the Inverted-U principle?
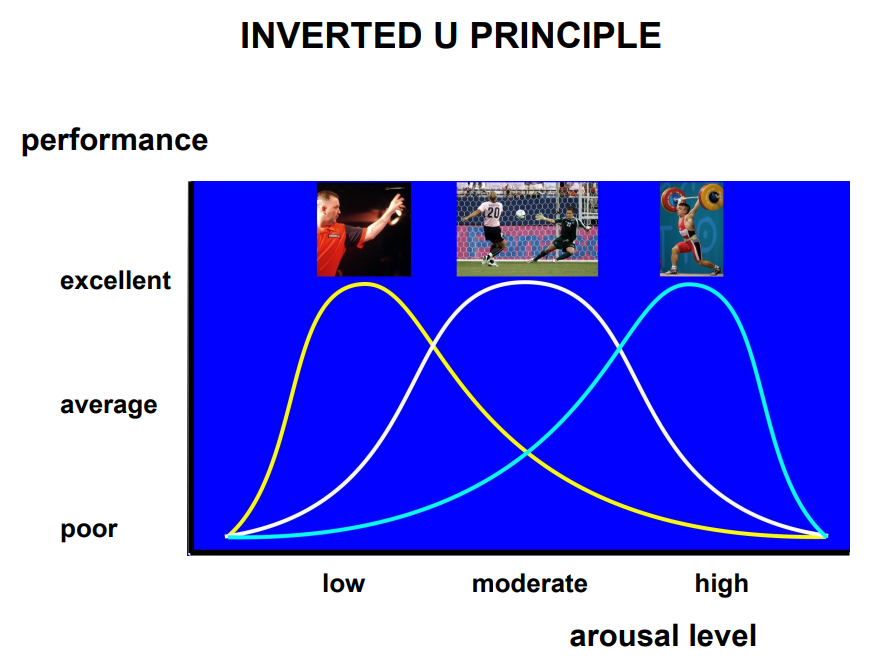
What effect does increased arousal have on attention?
Narrowing of attentional focus
Increase in attentional shifts
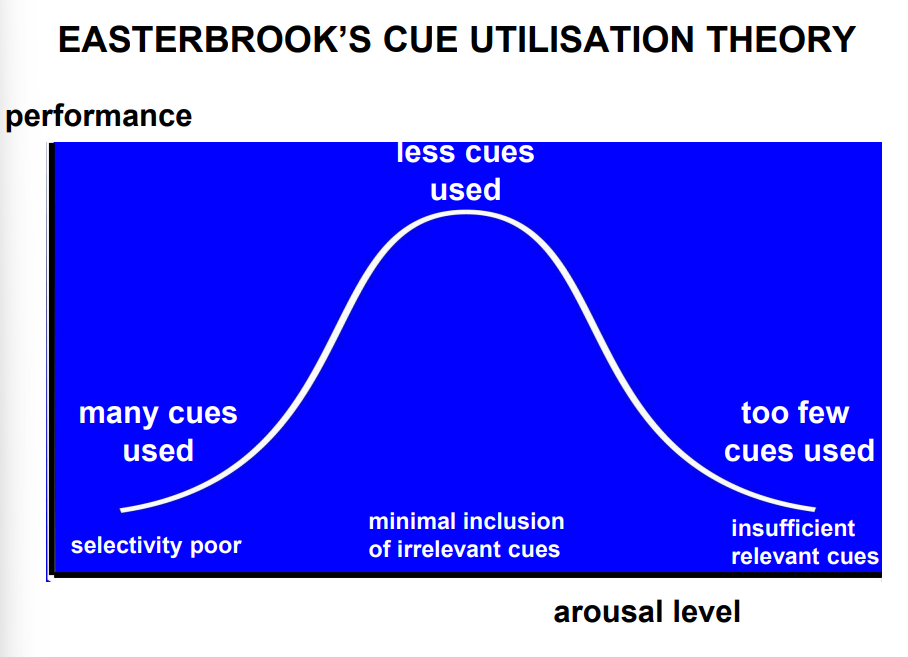
What is Easterbrook’s cue utilisation theory?
Low Arousal:
Attention is broad, but unfocused
Moderate Arousal (Optimal):
Attention narrows to task-relevant cues
High Arousal:
Attention becomes too narrow