histology exam 1
1/199
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
200 Terms
What is the first step in preparation of a tissue or organ sample?
Fixation
____ usually by a chemical or mixture of chemicals permanently preserves the tissue structure for subsequent treatments.
Fixation
____ is used for terminating cell metabolism; preventing enzymatic degradation of cells and tissues by autolysis (self-digestion); killing pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses and harden the tissue as a result of either cross-linking or denaturing protein molecules.
Fixation
What is the most commonly used fixative for light microscopy?
Formalin
Does formalin react with lipids?
No
How long does formalin fix tissues?
15 mins - 2 hours
What is the 2nd step of tissue preparation?
DCE (Dehydrating, Clearing, Embedding)
____ dehydrates tissues while ____ clears tissues for wax impregnation.
Alcohol; xylene
____ infiltrates specimen to support tissues and allow for microsome slices.
Molten wax (paraffin)
what is the 3rd step in tissue preparation?
specimen is mounted and stained
true or false: paraffin sections are colorless
true
hematoxylin is more soluble in ____, while eosin is more soluble in ____.
water; alcohol
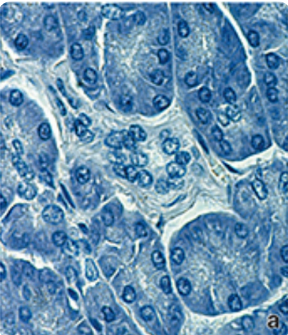
what stain is this? is it a basic or acidic dye?
hemotoxylin; basic
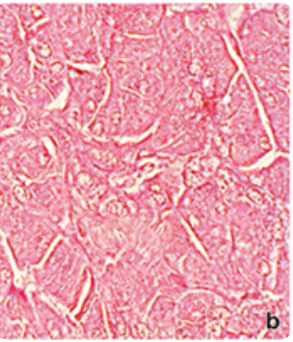
what stain is this? is it a basic or acidic dye?
eosin; acidic dye
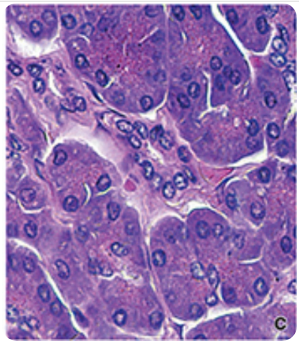
what stain is this?
hemotoxylin and eosin stain
tissues with hemotoxylin affinity stain ____ while tissues with eosin affinity stain ____.
blue; pink
what type of structures can you see with a hemotoxylin stain? what type of structures can you see with a eosin stain?
basophilic; eosinophilic
the ____ stains carbohydrates and carbohydrate-rich macromolecules.
Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) reaction
PAS stains are used to view ____, ____, ____, and ____.
1) glycogen in cells
2) mucus membrane in cells/tissues
3) basement membrane
4) reticular fibers in connective tissue
which stain is most commonly used for light microscopy?
h&e stain
____ are formed when the periodic acid cleaves the bond between adjacent carbon atoms.
aldehyde groups
aldehyde groups react with ____ in the PAS stain to give a characteristic ____ color.
Schiff reagent; magenta
what stain is this?
periodic acid schiff (PAS) stain
____ microscopy is a digital procedure that is an alternative to the examination of glass slides using a light microscope.
virtual
____ is the scientific study of microscopic structures of tissues and organs of the body.
histology
cells can be divided into two major components, what are they?
nucleus and cytoplasm
the ____ stores genetic code
nucleus
the ____ produces DNA and RNA
nucleus
true or false: the nucleus has unidirectional flow
false; it has bidirectional flow
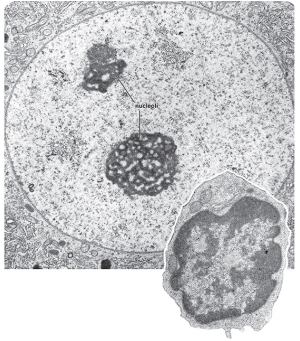
what is this?
nucleus
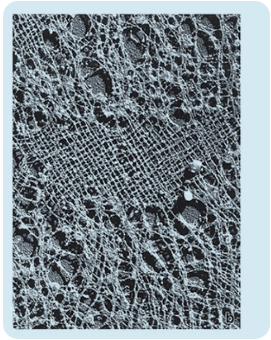
what is this?
nuclear lamina
where are organelles located
cytoplasm
where is the cytoskeleton located?
cytoplasm
where are inclusions (non-living accumulations in a cell like nutrients/pigments) located?
cytoplasm
true or false: the cytoplasm is a protoplasm that surrounds the nucleus and contains structures to provide absorption
true
____ contain products of metabolic activity of the cell and consist largely of lipofuscin (wear-tear pigment) granules, lipid droplets, and glycogen
inclusions
true or false: the plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer
true
true or false: the plasma membrane is a selective barrier for the transport of material in and out
true
the ____ is an amphipathic lipid bilayered structure visible with the transmission electron microscope
plasma membrane
what type of microscopy is used to view the plasma membrane?
transmission electron microscopy
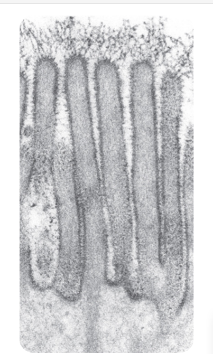
what is this? what are the dark edges supposed to depict
apical microvili; plasma membrane
____ represent microdomains in the plasma membrane that contain high concentrations of cholesterol and glycosphingolipids
lipid rafts
____ surround cells found between or among cells of any structure
intercellular materials
the function of intercellular materials include ____ and ____.
form nutrients; take up waste
the 3 types of intercellular materials are ____, ____, and ____.
1) soft
2) hard
3) intermediary
what type of intercellular material are cartilage, adipose, and teeth respectively?
cartilage - intermediary
adipose - soft
teeth - hard
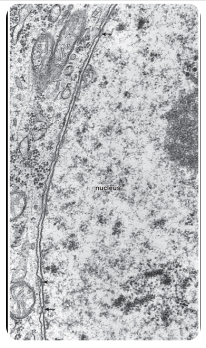
what do the arrows represent in this image?
nuclear pore complex
where is the site of ribosomal RNA synthesis
nucleolus
true or false: the nucleolus is involved with regulation of the cell cycle
true
true or false: the nucleolus contains nuclear RNA
true
ribosomal assembly starts in the ____ of the ____.
granular material; nucleolus
true or false: the nucleoli direct protein synthesis via rRNA
true
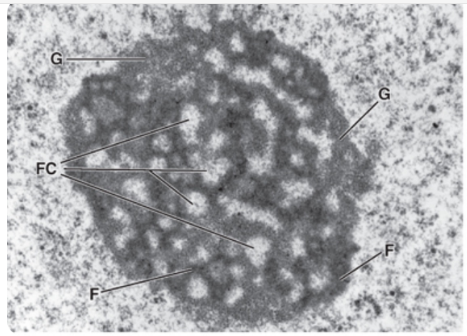
what is this?
nucleolus
About how many nucleoli are there in an nucleus?
1-4
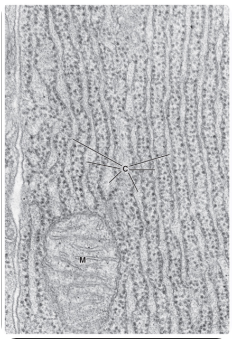
what is this?
rough endoplasmic reticulum
where is the site of production of protein?
rough ER
the ____ modifies, stores, and transports proteins to the golgi
rough ER
the ____ is the site of protein synthesis and posttranslational modification of newly synthesized proteins
rough ER
the rough ER is visible in light microscopy as a ____ region
basophilic (ergastoplasm)
true or false: the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is not associated with ribosomes
true
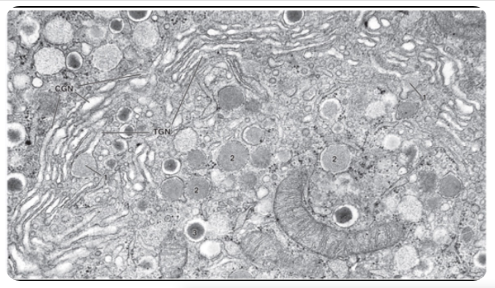
what is this?
golgi apparatus
what is this?
golgi cisternae
true or false: PTM of newly synthesized proteins occur in the rER and is continued in the golgi apparatus therefore PTMs occur in both rER and golgi
true
the ____ represent a series of stacked, flattened cisternae and functions in the posttranslational modificaiton, sorting, and packaging of proteins
golgi apparatus
the golgi apparatus sends proteins to four major destinations. what are they?
1) apical and basolateral plasma membrane
2) endosomes
3) lysosomes
4) apical cytoplasm
lysosomal production occurs in the ____.
golgi apparatus
lysosomes are protective structures prominent in ____ and ____.
macrophages; leukocytes
true or false: lysosomes are membrane bound
true
lysosomes are resistant to digestion
true
____ use digestive and hydrolytic enzymes like hyaluronidase.
lysosomes
what do lysosomes develop from?
endosomes
____ are digestive organelles containing hydrolytic enzymes that degrade substances derived from endocytosis and from the cell itself.
lysosomes
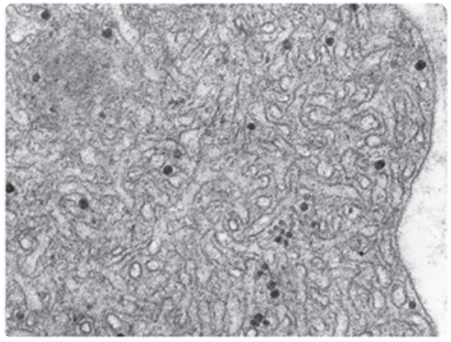
what is this? what do the dark circles represent?
smooth ER; glycogen particles
apoptosis is regulated by which organelle
mitochondria
____ are elongated, mobile organelles that contain the ETC.
mitochondria
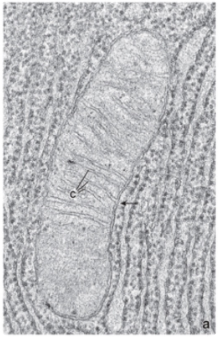
what is this?
mitochondria
what are the two types of cell death?
necrosis and apoptosis
____ is the result of acute cell injury while ____ is a programmed cell death.
necrosis; apoptosis
____ occurs under normal physiologic conditions to eliminate defective or senescent cells without inflammatory response by the tissue
apoptosis
true or false: apoptosis is a physiological process
true
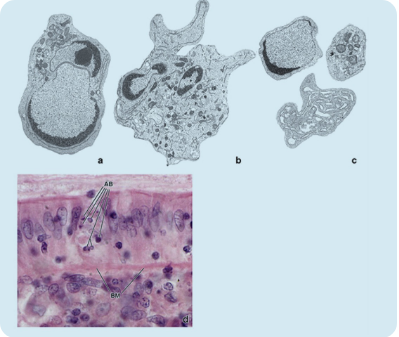
what type of cell death is this? what does AB stand for?
apoptosis; apoptotic bodies
list 5 examples where necrosis can occur
1) hypoxia
2) hypothermia
3) radiation
4) low pH
5) cell trauma
necrosis is a ____ process while apoptosis is ____ process.
pathologic; physiologic
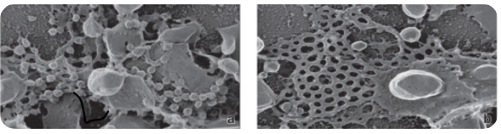
what type of technique is used to visualize membrane proteins?
free fracture techniques
what are four nonmembraneous organelles?
1) microtubules
2) filaments
3) centrioles
4) ribosomes
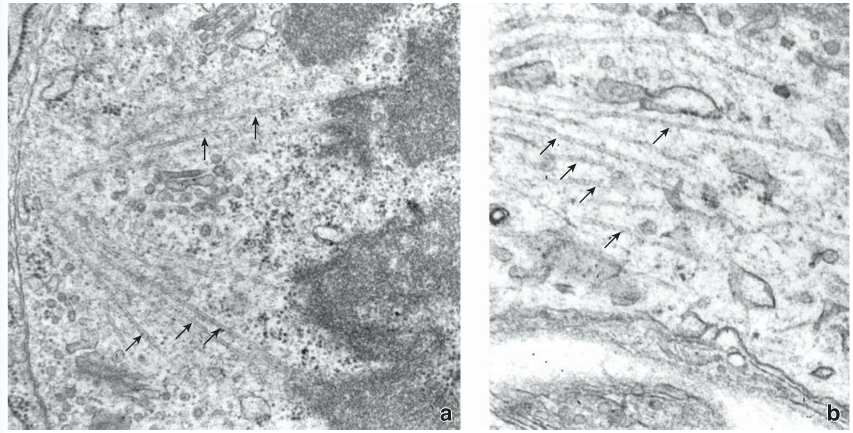
what is this?
microtubules
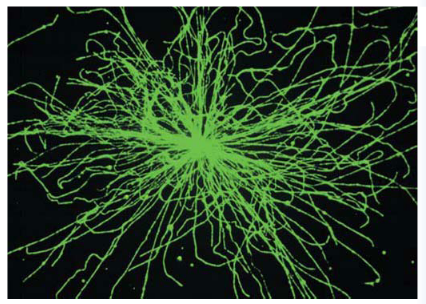
what is this?
microtubules
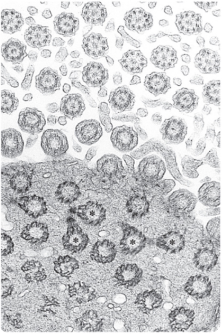
what is this?
centrioles
____ are responsible for forming/maintaining cytoskeleton and cell motility.
microtubules
____ form basal bodies of cilia.
centrioles
____ are paired, short rod-like cytoplasmic cylinders built from nine microtubule triplets | focal point for MTOC, basal bodies for cilia and flagella, align mitotic spindle
centrioles
____ form tracts for intercellular and extracellular transport.
microtubules
____ are responsible for cell strength and cell to extracellular matrix attachment (focal adhesions).
actin filaments
____ synthesize proteins that remain in the cell as cytoplasmic structures
free ribosomes
cells —> ____ —> organs —> organ systems
tissues
cells —> tissues —> ____ —> organ systems
organs
cells —> tissues —> organs —> ____
organ systems
____ —> tissues —> organs —> organ systems
cells
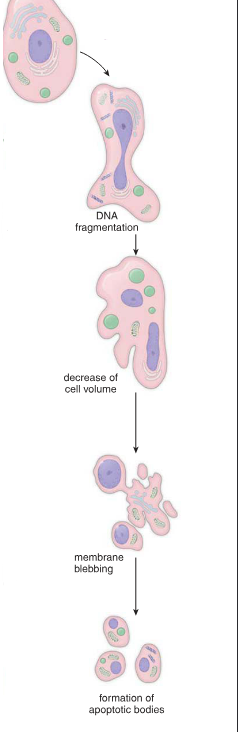
what is this?
apoptosis
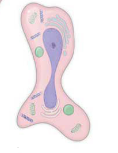
what is this?
DNA fragmentation