Reading
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Accounting
preparing financial stateents showing income and expenditure, assets and liabilities. It is known as the language of business because it provides financial information to investors, creditors, and management.
Types of accounting
There are several branches of accouns including financial accounting, managerial accounting, tax accounting, and forensic accounting.
Financial statements
are formal records of the financial activities and position of a business. The three main types of financial statements are the cash flow statement, income statement, and balance sheet
Cash flow statement
a statement giving details of money coming into and leaving the business, divided into day-to-day operations, investing and financing. helping assess liquidity and solvency—how well the business generates and uses cash.
Components of cash flow statement
Operating activities- Cash from core operations (sales receipts, payments to suppliers) 2. Investing activities - Cash from buying or selling long-term assets (e.g. equipment). 3. Financing activities - Cash from owners and creditors (issuing shares, repaying loans).
Income statement
a statement showing the difference between the revenues and expenses of a period ts main purpose is to measure profitability and evaluate financial performance.
Components of income statement
Revenue - Income from selling goods or services 2. COGS- Direct costs of producing goods sold 3. Gross Profit- Revenue minus COGS/ 4. Operating Expenses - Costs of running the business (e.g. wages, rent)/// 5. Net Income - Final profit after all expenses are deducted from revenue
Balance sheet
a statement showing the value of a business's assets, its liabilities, and its capital or shareholders' equity. The balance sheet shows what a company owns, what it owes, and the shareholders’ investment at a specific point in time.
Main components of balance sheet
Assets- Resources owned by the company (e.g. cash, inventory, property)// 2. Liabilities - Amounts the company owes (e.g. loans, accounts payable)//// 3. Shareholders’ Equity- Owners’ claim after liabilities, including common stock and retained earnings
total equity
all the money belonging to the company's owners
intangibles, net
assets whose value can only be turned into cash with difficulty (e.g. reputation, patents, trademarks, etc.)
additional paid-in capital
capital that shareholders have contributed to the company above the nominal or par value of the stock
Accrued expenses
expenses such as wages, taxes and interest that have not yet been paid at the date of the balance sheet
Total, receivables, net
money owed by Customers for goods or services purchased on credit
accounts payable
money owed to suppliers for purchases made on credit
Prepared Expenses
money paid in advance for goods and services
Retained earnings
profits that have not been distributed to shareholders
Property/ Plant/ Equipment/ Total – gross
tangible assets such as offices, machines, etc.
Good well, net
the difference between the purchase price of acquired companies and their net tangible assets
Total liabilities
the total amount of money owed that the company will have to pay out
A clearing system
A clearing system is an arrangement where banks settle debts by netting all transactions over a period and paying only the final balances between accounts.
comperative parity method
choosing to spend the same amount on advertising as one's competitors
word of mouth advertising
free advertising, when satisfied customers recommend products to their friends
viral marketing
trying to get consumers to forward an online marketing message to other people
market differentiate
making a product (appear to be) different from similar products offered by other sellers, by product differences, advertising, packaging, etc.
market skimming
setting a high price for a new product, to make maximum revenue before competing products appear on the market
market penetration
the strategy of setting a low price to try to sell a large volume and increase market share
A market leader
aims to maintain its dominant position by protecting or increasing market share through innovation, cost efficiency, and strong marketing.
A market challenger
tries to gain market share by aggressively competing with leaders or followers using lower prices, better products, or improved services.
A market follower
avoids direct competition and instead imitates or adapts successful products while keeping costs low.
A market nicher
focuses on a small, specialized segment with a clear unique selling proposition to achieve profitability.
Introduction stage
The product is newly launched, so sales grow slowly and profits are low or negative due to high advertising and promotion costs. Companies may use high prices (market skimming) or low prices (market penetration) to enter the market.
growth stage
Sales increase rapidly as more customers accept the product. Profits rise, economies of scale are achieved, and competitors enter, often leading to price reductions.
Maturity stage
The market becomes saturated, sales stabilize, and competition is intense. Companies focus on brand loyalty, product improvements, promotion, or price cuts to maintain market share, often with lower profits.
Decline stage
Sales and profits fall due to new technologies or changing consumer tastes. Firms may withdraw the product or reduce investment and focus on more profitable products.
Push strategy
Goods are produced and distributed based on demand forecasts. Products are pushed through the supply chain in advance, often leading to higher inventory levels.
Pull strategy
Production and distribution are driven by actual customer orders. Products are made as needed, which reduces inventory and waste
Kaizen
A Japanese management approach meaning continuous improvement, which focuses on reducing waste through small, ongoing changes suggested by workers themselves rather than expensive new technology.
Cell production
A production method where work is organized into small, self-contained units (cells), each responsible for part of the product, improving efficiency, teamwork, and employee motivation.
The quaternary sector
includes information and knowledge-based services such as computing, ICT, consultancy, research and development, and more broadly education, media, libraries, and cultural activities.
Franchising
A business model in which a company allows independent operators to sell its products or services using its brand and business system
Joint venture
A partnership where two or more companies create a new business together, sharing investment, risks, and profits.
High-context cultures
managers are perceived as authority figures, employees often show respect through deference and formal behavior. Team members are less likely to voice opinions, challenges decisions or take initiative without permission, as they wish to avoid losing face. This cultures allow fast decisions but limit the communication and innovation
Low-context culture
managers are approachable and employees are encouraged to take part in decision-making. Employees expect equality and feel comfortable when sharing ideas, asking questions or taking responsibility. This cultures promote openess and engagement but may delays urgent decisions or creates ambiguity in final responsibility
Linear-active cultures
are logical and task-focused. People plan carefully, do one thing at a time, follow rules, and value individual responsibility.
Multi-active cultures
are relationship-focused and emotional. People multitask, change plans easily, rely on relationships, and value hierarchy over rules.
Reactive cultures
focus on harmony. People listen more, avoid confrontation, communicate indirectly, and seek mutual solutions.
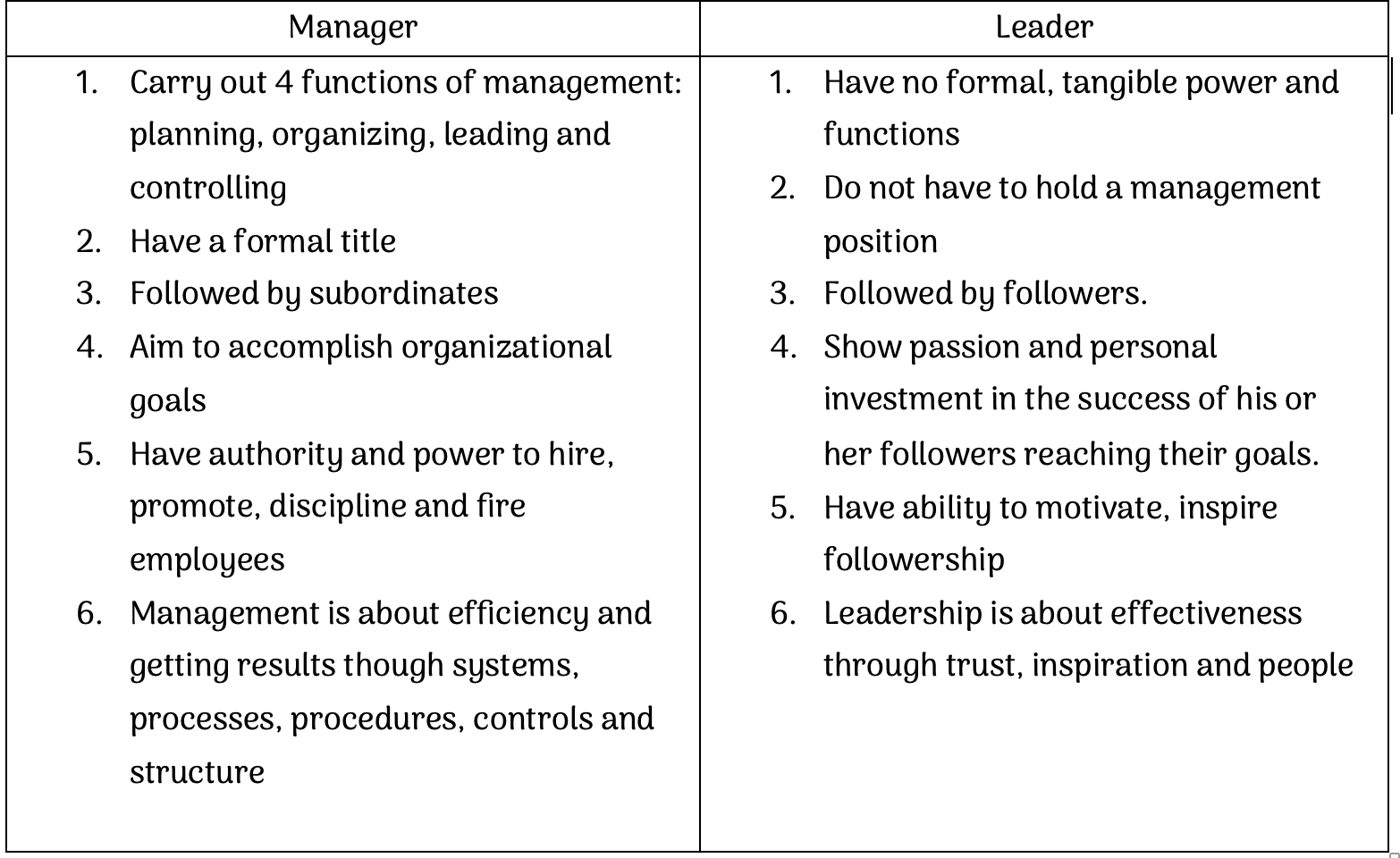
Manager and leader