UNIT 3 EXAM - BIOMECHANICS
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Force
Push or pull that produces or changes motion of an object
External forces that affect motion
Gravity, air and water resistance, friction, reaction forces
Friction
Force that occurs when two surfaces are in contact with each other, opposes motion of an object
Torque
The turning effect of the force that has been applied
Angular Velocity
How fast an object or body is spinning
Increases when radius of rotation decreases (tuck v layout)
Stays constant unless acted upon by an external torque
Decrease moment of inertia = greater angular velocity and vise versa
Mass
Amount of matter an object is made up of
Weight
Force exerted on body by gravity
Momentum
Quantity of motion an object has
Is conserved when objects collide
Mass x velocity - greater mass = greater momentum
Summation of momentum
Sequential and coordinated movement of each body segment to produce maximum velocity
Angular momentum
Amount of angular motion a body has
Impulse
Change in momentum of an object
Force x Time
Velocity
Describes rate (speed) and direction of motion
Displacement/Time
Projectile Motion
How fast an object is travelling
Distance/Time
Newtons first law
A body will remain at rest or continue in a state of motion unless acted upon by an external force
Newtons Second law - Acceleration
A force applied to an object will produce a change in motion (acceleration) in the direction of the applied force that is directly proportional to the size of the force
Newtons third law
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
Newtons first angular law
Newtons second angular law
Newtons third angular law
Projectile
Any airborne object that is only affected by the forces of gravity an air resistance
Follows curved path
Vertical impacted by: Gravity (90m/s)
Horizontal impacted by: air resistance
Projectile path impacted by:
Speed of release
Angle of release
Height of release
Height of release greater than 0
Inertia
Tendency of a body to resist a change in motion
Greater the mass, the greater the inertia
Equilibrium
State of motion at rest or constant velocity, where all forces and torques are balanced
Stability
The body’s ability to resist a change in its current state
Base of support
Centre of gravity (higher = less stable)
Line of gravity
Mass
Friction between body and surface contacted
Balance
The ability to maintain and control the equilibrium of the body in different situations
Levers
Axis, resistance, force
Longer levers have higher inertia
Anatomical
Axis (joint)
Resistance (body part of weight being moved)
Force (applied by a muscle)
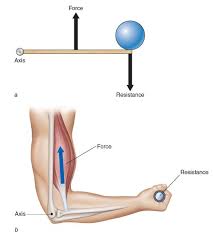
Mechanical advantage
Measure of efficiency of lever system
3rd class <1 - Large force is required to move small resistance